IntersectionObserver API
背景
在网页开发的过程中,我们常常需要判断某个元素是否进入了"视口"(viewport),即用户能不能看到它。
一般采用这样的方法实现,兼容scroll事件,然后调用方法获取目标元素的坐标,判断是否在视口之内。代码不仅繁琐,而且由于scroll事件密集发生,计算量很大一不小心没有函数去抖就又可能导致严重的性能问题。
IntersectionObserver
现在我们有了更好的选择—— IntersectionObserver API ,IntersectionObserver 允许你配置一个回调函数,每当 target ,元素和设备视口或者其他指定元素发生交集的时候该回调函数将会被执行。这个 API 的设计是异步的,而且保证你的回调执行次数是非常有限的,而且回调是会在主线程空闲时才执行,在性能方面表现更优,使用起来也更简单。那么IntersectionObserver是如何实现的呢?
这里我们翻译一下Intersection就大概能明白其实现原理了。intersection 是交集的意思
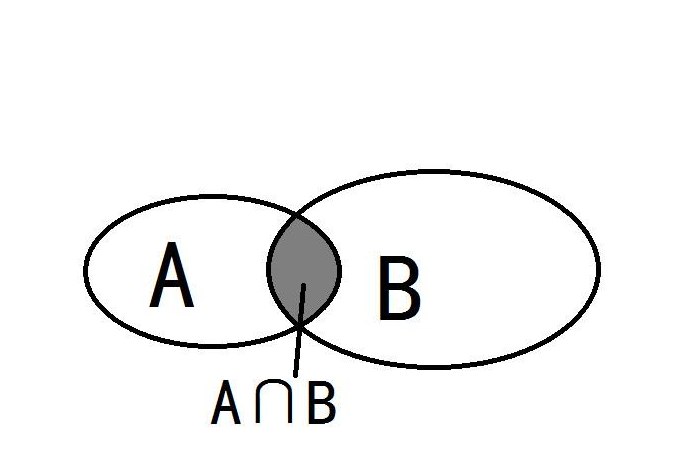
接口的原理就是通过观察两个元素之间是否是否有交集,然后对其进行监控操作。现在用一个简单的例子展示
<!DOCTYPE HTML> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <meta name="apple-mobile-web-app-capable" content="yes" /> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0, maximum-scale=1.0, user-scalable=0" /> <title></title> <style> #content { width: 100vw; height: 100vh; } #info{ position: fixed; top: 0; } #target { width: 100px; height: 100px; background: red; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="info">我藏在页面底部,请向下滚动</div> <div id="content"></div> <div id="target"></div> </body> <!-- --> <script type="text/javascript"> let observer = new IntersectionObserver(function(entries){ entries.forEach( function(element, index) { console.log(observer.takeRecords()); if (element.isIntersecting ) { info.textContent = "我出来了"; } else { info.textContent = "我藏在页面底部,请向下滚动" } }); }, { root: null, threshold:[0, 1] }) observer.observe(document.querySelectorAll('#target')[0]) </script> </html>
API的兼容情况
以下是api对于现代浏览器的支持情况
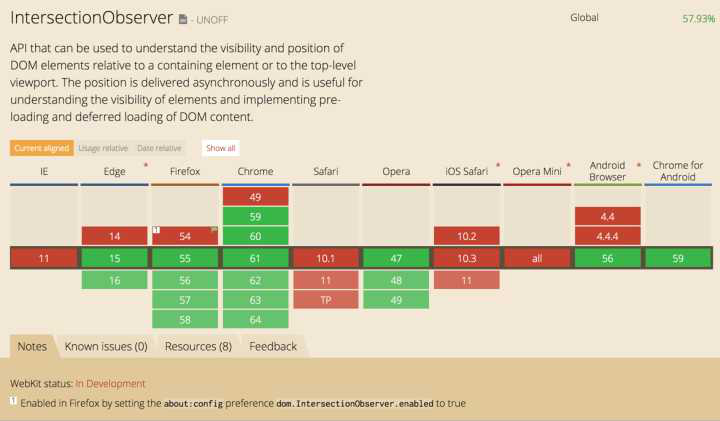
低版本浏览器可以通过 polyfill 兼容(https://github.com/w3c/IntersectionObserver/tree/master/polyfill)
API
构造函数
new IntersectionObserver(callback, options)
callback 是个必选参数,当有相交发生时,浏览器便会调用它,后面会详细介绍;options 整个参数对象以及它的三个属性都是可选的:
构造函数的返回值是一个观察器实例,提供了以下方法
io = new IntersectionObserver(callback, options); io.observe(document.getElementById('example')); //开始观察 io.unobserve(element); //停止观察 io.disconnect(); //关闭观察器 io.takeRecords(); //为所有监听目标返回一个IntersectionObserverEntry对象数组并且停止监听这些目标。
Callback
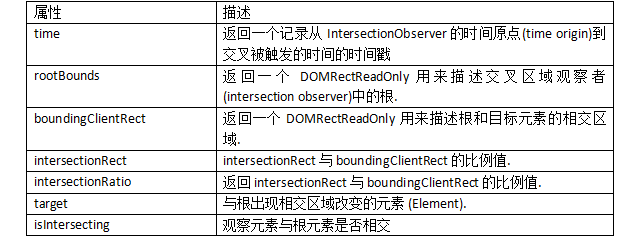
回调函数共有两个参数,第二个参数就是观察者实例本身,一般没用,因为实例通常我们已经赋值给一个变量了,而且回调函数里的 this 也是那个实例。第一个参数是个包含有若干个 IntersectionObserverEntry 对象的数组,每个 IntersectionObserverEntry 对象都代表一次相交,它的属性们就包含了那次相交的各种信息。
{ time: 3893.92, rootBounds: ClientRect { bottom: 920, height: 1024, left: 0, right: 1024, top: 0, width: 920 }, boundingClientRect: ClientRect { // ... }, intersectionRect: ClientRect { // ... }, intersectionRatio: 0.54, target: element, isIntersecting: true }
IntersectionObserverEntry
Options属性
root
所监听对象的具体祖先元素。如果未传入任何值或值为null,则默认使用viewport。
<!DOCTYPE HTML> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <meta name="apple-mobile-web-app-capable" content="yes" /> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0, maximum-scale=1.0, user-scalable=0" /> <title></title> <style> #root { position: relative; width: 200px; height: 100vh; margin: 0 auto; overflow: scroll; border: 1px solid #ccc; } #info { position: fixed; } #target { position: absolute; top: calc(100vh + 1px); width: 100px; height: 100px; background: red; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="root"> <div id="info">向下滚动就能看到我</div> <div id="target"></div> </div> </body> <!-- --> <script type="text/javascript"> let observer = new IntersectionObserver((entries) => { console.log(entries[0]) if (entries[0].isIntersecting) { info.textContent = "我出来了" } else { info.textContent = "向下滚动就能看到我" } }, { root: root }) observer.observe(target) </script> </html>
rootMargin
计算交叉时添加到根(root)边界盒的矩形偏移量, 可以有效的缩小或扩大根的判定范围从而满足计算需要。此属性返回的值可能与调用构造函数时指定的值不同,因此可能需要更改该值,以匹配内部要求。所有的偏移量均可用像素(pixel)(px)或百分比(percentage)(%)来表达, 默认值为"0px 0px 0px 0px",表达的位置与css margin属性一直, 上边距 右边距 下边距 左边距 ,为正值时表示区域扩大,负值时表示区域缩小
<!DOCTYPE HTML> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <meta name="apple-mobile-web-app-capable" content="yes" /> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0, maximum-scale=1.0, user-scalable=0" /> <title></title> <style> #content { width: 100vw; height: 100vh; } #info{ position: fixed; top: 0; } #target { width: 100px; height: 100px; background: red; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="info">我藏在页面底部,请向下滚动</div> <div id="content"></div> <div id="target"></div> </body> <!-- --> <script type="text/javascript"> let observer = new IntersectionObserver(function(entries){ entries.forEach( function(element, index) { console.log(observer.takeRecords()); if (element.isIntersecting ) { info.textContent = "我出来了"; } else { info.textContent = "我藏在页面底部,请向下滚动" } }); }, { root: null, rootMargin : '0px 0px -20px 0px', threshold:[0, 1] }) observer.observe(document.querySelectorAll('#target')[0]) </script> </html>
thresholds
一个包含阈值的list, 升序排列, list中的每个阈值都是监听对象的交叉区域与边界区域的比率。当监听对象的任何阈值被越过时,都会生成一个通知(Notification)。如果构造器未传入值, 则默认值为0.不仅当目标元素从视口外移动到视口内时会触发回调,从视口内移动到视口外也会。
<!DOCTYPE HTML> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <meta name="apple-mobile-web-app-capable" content="yes" /> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0, maximum-scale=1.0, user-scalable=0" /> <title></title> <style> #content { width: 100vw; height: 100vh; } #info{ position: fixed; top: 0; } #target { width: 100px; height: 100px; background: red; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="info"></div> <div id="content"></div> <div id="target"></div> </body> <!-- --> <script type="text/javascript"> let observer = new IntersectionObserver(function(entries){ entries.forEach( function(element, index) { info.textContent = '页面相交:' + element.intersectionRatio; }); }, { root: null, threshold:[0, 0.5,0.7,1] }) observer.observe(document.querySelectorAll('#target')[0]) </script> </html>
实例,图片懒加载(lazyload)
下面我们通过这个接口来实现内容的懒加载
<!DOCTYPE HTML> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <meta name="apple-mobile-web-app-capable" content="yes" /> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0, maximum-scale=1.0, user-scalable=0" /> <title>使用IntersectionObserver实现懒加载</title> <style type="text/css"> * { margin: 0; padding: 0; } ul,li { list-style: none; } .list { width: 800px; margin: 0 auto; } .list ul { width: 100%; overflow: hidden; } .list ul li { float: left; width: 185px; height: 400px; margin-bottom: 10px; margin-left: 10px; background-color: #ccc; overflow: hidden; text-align: center; line-height: 400px; color: red; font-size: 24px; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="list"> <ul> <li class="lazy-loaded"> <template> <img src="images/1.jpg" width="100%" height="100%" border="0"/> </template> <span class="loading">正在加载...</span> </li> <li class="lazy-loaded"> <template> <img src="images/1.jpg" width="100%" height="100%" border="0"/> </template> <span class="loading">正在加载...</span> </li> <li class="lazy-loaded"> <template> <img src="images/1.jpg" width="100%" height="100%" border="0"/> </template> <span class="loading">正在加载...</span> </li> <li class="lazy-loaded"> <template> <img src="images/1.jpg" width="100%" height="100%" border="0"/> </template> <span class="loading">正在加载...</span> </li> <li class="lazy-loaded"> <template> <img src="images/1.jpg" width="100%" height="100%" border="0"/> </template> <span class="loading">正在加载...</span> </li> <li class="lazy-loaded"> <template> <img src="images/1.jpg" width="100%" height="100%" border="0"/> </template> <span class="loading">正在加载...</span> </li> <li class="lazy-loaded"> <template> <img src="images/1.jpg" width="100%" height="100%" border="0"/> </template> <span class="loading">正在加载...</span> </li> <li class="lazy-loaded"> <template> <img src="images/1.jpg" width="100%" height="100%" border="0"/> </template> <span class="loading">正在加载...</span> </li> <li class="lazy-loaded"> <template> <img src="images/1.jpg" width="100%" height="100%" border="0"/> </template> <span class="loading">正在加载...</span> </li> <li class="lazy-loaded"> <template> <img src="images/1.jpg" width="100%" height="100%" border="0"/> </template> <span class="loading">正在加载...</span> </li> <li class="lazy-loaded"> <template> <img src="images/1.jpg" width="100%" height="100%" border="0"/> </template> <span class="loading">正在加载...</span> </li> <li class="lazy-loaded"> <template> <img src="images/1.jpg" width="100%" height="100%" border="0"/> </template> <span class="loading">正在加载...</span> </li> <li class="lazy-loaded"> <template> <img src="images/1.jpg" width="100%" height="100%" border="0"/> </template> <span class="loading">正在加载...</span> </li> <li class="lazy-loaded"> <template> <img src="images/1.jpg" width="100%" height="100%" border="0"/> </template> <span class="loading">正在加载...</span> </li> <li class="lazy-loaded"> <template> <img src="images/1.jpg" width="100%" height="100%" border="0"/> </template> <span class="loading">正在加载...</span> </li> <li class="lazy-loaded"> <template> <img src="images/1.jpg" width="100%" height="100%" border="0"/> </template> <span class="loading">正在加载...</span> </li> <li class="lazy-loaded"> <template> <img src="images/1.jpg" width="100%" height="100%" border="0"/> </template> <span class="loading">正在加载...</span> </li> <li class="lazy-loaded"> <template> <img src="images/1.jpg" width="100%" height="100%" border="0"/> </template> <span class="loading">正在加载...</span> </li> <li class="lazy-loaded"> <template> <img src="images/1.jpg" width="100%" height="100%" border="0"/> </template> <span class="loading">正在加载...</span> </li> <li class="lazy-loaded"> <template> <img src="images/1.jpg" width="100%" height="100%" border="0"/> </template> <span class="loading">正在加载...</span> </li> <li class="lazy-loaded"> <template> <img src="images/1.jpg" width="100%" height="100%" border="0"/> </template> <span class="loading">正在加载...</span> </li> <li class="lazy-loaded"> <template> <img src="images/1.jpg" width="100%" height="100%" border="0"/> </template> <span class="loading">正在加载...</span> </li> </ul> </div> </body> <!-- --> <script type="text/javascript"> //获取dom function filterDom(selector) { // return Array.from(document.querySelectorAll(selector)); } //事件观察者 var observer = new IntersectionObserver(observerCall); function observerCall(changes) { changes.forEach(function(change) { setTimeout(function(){ if(change.intersectionRatio > 0){ var container = change.target; var content = container.querySelector('template').content; container.appendChild(content); container.querySelector('.loading').style.display = 'none'; observer.unobserve(container); } }, 100); }); } //过滤元素 filterDom('.lazy-loaded').forEach(function (item) { observer.observe(item); }); </script> </html>
通过这个接口来实现更多的功能,比如无限滚动,页面对于广告的展示等。




