走迷宫(用栈模拟实现非递归,并输出路径)

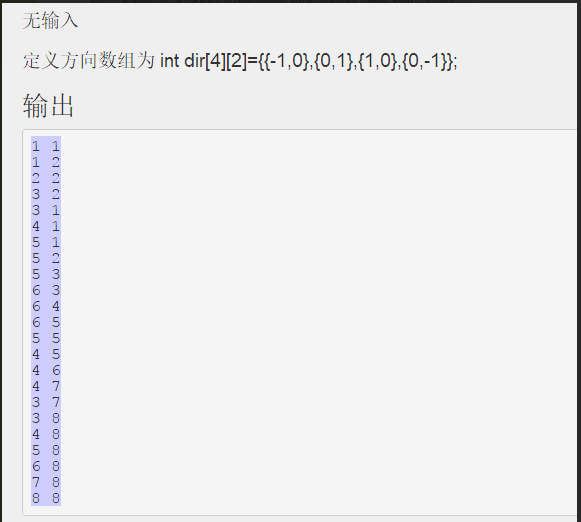
#include<iostream> #include<stack> using namespace std; int a[10][10]={ {1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1},{1,0,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,1}, {1,0,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,1},{1,0,0,0,0,1,1,0,0,1}, {1,0,1,1,1,0,0,0,0,1},{1,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,1}, {1,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,0,1},{1,0,1,1,1,0,1,1,0,1}, {1,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1},{1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1} }; int dir[4][2]={{-1,0},{0,1},{1,0},{0,-1}}; stack<int> s;//x坐标入栈 stack<int> t;//y坐标入栈 int di[10][10]; void search(int si,int sj) { int i1,j1,i,j; for(i=0;i<10;i++) for(j=0;j<10;j++) di[i][j]=-1;//记录是否4个方向已经走满 s.push(si);//入口方块进栈 t.push(sj); a[si][sj]=-1;//为避免来回找相邻方块,将进栈的方块置为-1 while(!s.empty()) { i=s.top(); j=t.top(); if(i==8&&j==8)//找到了出口 return; bool f=0; while (di[i][j]<4 && !f) //找下一个相邻可走方块 { di[i][j]++; switch(di[i][j]) { case 0: i1=i-1;j1=j;break; case 1: i1=i;j1=j+1;break; case 2: i1=i+1;j1=j;break; case 3: i1=i;j1=j-1;break; } if (a[i1][j1]==0) f=1;//找到下一个可走相邻方块(i1,j1) } if (f) //找到了下一个可走方块 { s.push(i1); //修改原栈顶元素的di值 t.push(j1); a[i1][j1]=-1; //为避免来回找相邻方块,将进栈的方块置为-1 } else //没有路径可走,则退栈 { a[i][j]=0; s.pop(); t.pop(); //将栈顶方块退栈 } } } int main() { search(1,1); stack<int>ss;//因为路径是从1到8,而栈s,t里的顶部是8,所以要再用一个栈倒回来 stack<int>tt; while(!t.empty()) { ss.push(s.top()); tt.push(t.top()); t.pop(),s.pop(); } while(!tt.empty()) { cout<<ss.top()<<" "<<tt.top()<<endl; tt.pop(),ss.pop(); } return 0; }

