网络安全技术与应用实验——SSL验证分析 & 基于DTLS的安全服务器设计
sudo add-apt-repository universe
sudo apt install wireshark安装 python3-dtls
pip install python3-dtls运行
sudo wireshark就会直接跳出
打开淘宝东点点西点点,然后 wireshark 里面我选择了有限,然后双击 any 那个,也可以选择 ens33

过滤器里填入ssl,Protocol 找到 TCP 就行了,抓包任务完成
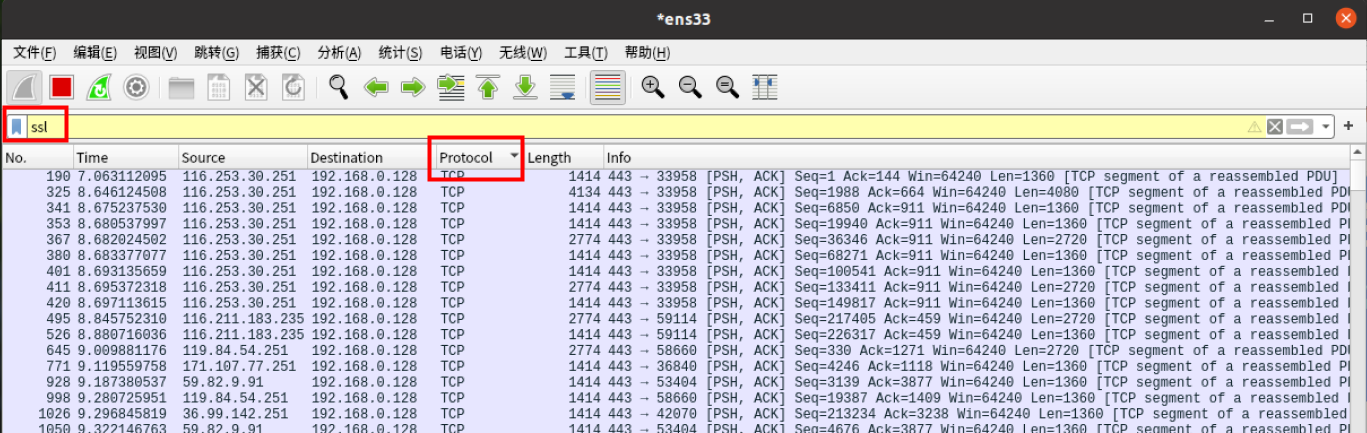
保存截图
2.基于DTLS的安全服务器设计传输层和应用层
实验目的:通过实验,掌握DTLS的基本原理,掌握python3-dtls库的基本使用。
实验内容:
(1)利用 DTLS 库编写客户端和服务器程序,服务端开启监听,提供数据传输、文件传输功能;
(2) 客户端对服务端进行证书认证(单向认证);
(3) 利用相关工具(如 Wireshark)验证 DTLS 通信结果;
首先方便编程,安装spyder
sudo apt install spyder出现如下错误,考虑换源
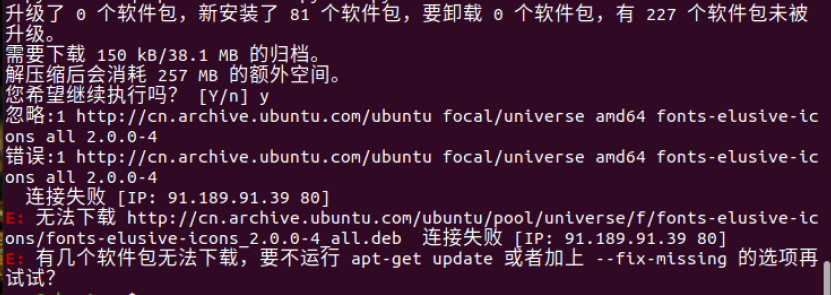
先备份源
sudo cp -a /etc/apt/sources.list /etc/apt/sources.list.bak更换源,自己编辑,编辑/etc/apt/sources.list文件, 在文件最前面添加以下条目(操作前请做好相应备份):
sudo gedit /etc/apt/sources.list链接:https://blog.csdn.net/xiangxianghehe/article/details/105688062
#阿里源
deb http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ focal main restricted universe multiverse
deb-src http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ focal main restricted universe multiverse
deb http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ focal-security main restricted universe multiverse
deb-src http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ focal-security main restricted universe multiverse
deb http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ focal-updates main restricted universe multiverse
deb-src http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ focal-updates main restricted universe multiverse
deb http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ focal-proposed main restricted universe multiverse
deb-src http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ focal-proposed main restricted universe multiverse
deb http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ focal-backports main restricted universe multiverse
deb-src http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ focal-backports main restricted universe multiverse然后执行命令:
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get upgrade然后再安装就成功了
在Ubuntu中 我们使用sudo ufw disable命令来关闭防火墙。执行该命令之后 我们使用sudo ufw status命令来查看当前防火墙的状态 如果是inactive 说明我们的防火墙已经关闭掉了。
密钥生成 https://blog.csdn.net/lwz15071387627/article/details/88103997
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_40909772/article/details/88901202
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/zhongbing1234/article/details/84797391
https://www.jianshu.com/p/1de38a3f50f3
查看代码
cys@ubuntu:~/NetworkSecurity/EXP1/miyao$ openssl genrsa -out server.key 2048
Generating RSA private key, 2048 bit long modulus (2 primes)
............................................+++++
.....................................................................................................................+++++
e is 65537 (0x010001)
cys@ubuntu:~/NetworkSecurity/EXP1/miyao$ openssl req -new -key server.key -out server.csr
You are about to be asked to enter information that will be incorporated
into your certificate request.
What you are about to enter is what is called a Distinguished Name or a DN.
There are quite a few fields but you can leave some blank
For some fields there will be a default value,
If you enter '.', the field will be left blank.
-----
Country Name (2 letter code) [AU]:CN
State or Province Name (full name) [Some-State]:hunan
Locality Name (eg, city) []:changsha
Organization Name (eg, company) [Internet Widgits Pty Ltd]:nudt
Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) []:
Common Name (e.g. server FQDN or YOUR name) []:127.0.0.1
Email Address []:cys@qq.com
Please enter the following 'extra' attributes
to be sent with your certificate request
A challenge password []:123456
An optional company name []:
cys@ubuntu:~/NetworkSecurity/EXP1/miyao$ openssl req -new -key server.key -out server.csr
You are about to be asked to enter information that will be incorporated
into your certificate request.
What you are about to enter is what is called a Distinguished Name or a DN.
There are quite a few fields but you can leave some blank
For some fields there will be a default value,
If you enter '.', the field will be left blank.
-----
Country Name (2 letter code) [AU]:CN
State or Province Name (full name) [Some-State]:hunan
Locality Name (eg, city) []:changsha
Organization Name (eg, company) [Internet Widgits Pty Ltd]:nudt
Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) []:cs
Common Name (e.g. server FQDN or YOUR name) []:127.0.0.1
Email Address []:myx@qq.com
Please enter the following 'extra' attributes
to be sent with your certificate request
A challenge password []:654321
An optional company name []:
cys@ubuntu:~/NetworkSecurity/EXP1/miyao$ openssl x509 -req -days 365 -in server.csr -signkey server.key -out server.crt
Signature ok
subject=C = CN, ST = hunan, L = changsha, O = nudt, OU = cs, CN = 127.0.0.1, emailAddress = myx@qq.com
Getting Private key
cys@ubuntu:~/NetworkSecurity/EXP1/miyao$ cat server.crt server.key > localhost.pem
cys@ubuntu:~/NetworkSecurity/EXP1/miyao$最终版本
查看代码
cys@ubuntu:~/NetworkSecurity/EXP1/certs$ openssl genrsa -out key.pem 2048
Generating RSA private key, 2048 bit long modulus (2 primes)
...............+++++
...................................+++++
e is 65537 (0x010001)
cys@ubuntu:~/NetworkSecurity/EXP1/certs$ openssl req -new -key key.pem -out cert.csr
You are about to be asked to enter information that will be incorporated
into your certificate request.
What you are about to enter is what is called a Distinguished Name or a DN.
There are quite a few fields but you can leave some blank
For some fields there will be a default value,
If you enter '.', the field will be left blank.
-----
Country Name (2 letter code) [AU]:ch
State or Province Name (full name) [Some-State]:
Locality Name (eg, city) []:
Organization Name (eg, company) [Internet Widgits Pty Ltd]:
Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) []:
Common Name (e.g. server FQDN or YOUR name) []:127.0.0.1
Email Address []:
Please enter the following 'extra' attributes
to be sent with your certificate request
A challenge password []:123456
An optional company name []:
cys@ubuntu:~/NetworkSecurity/EXP1/certs$ openssl x509 -req -days 365 -in cert.csr -signkey key.pem -out cert.pem
Signature ok
subject=C = ch, ST = Some-State, O = Internet Widgits Pty Ltd, CN = 127.0.0.1
Getting Private key
cys@ubuntu:~/NetworkSecurity/EXP1/certs$ cat cert.pem key.pem > keycert.pem服务器代码
scn = SSLConnection(
sck,
keyfile=path.join(cert_path,"keycert.pem"),
certfile=path.join(cert_path,"keycert.pem"),
server_side=True,
ca_certs=path.join(cert_path,"cert.pem"),
do_handshake_on_connect=False
)采用老师 3.31 上午的代码和文件
server.py的代码如下:
查看代码
import socket
import subprocess
from os import path
from logging import basicConfig, DEBUG
#basicConfig(level=DEBUG) # set now for dtls import code
from dtls.sslconnection import SSLConnection
from dtls.err import SSLError, SSL_ERROR_WANT_READ, SSL_ERROR_ZERO_RETURN
blocksize = 1024
#def main():
current_path = path.abspath(path.dirname(__file__))
cert_path = path.join(current_path, "certs")
sck = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_DGRAM)
sck.bind(("127.0.0.1", 28000))
sck.settimeout(30)
print("ok1")
scn = SSLConnection(
sck,
keyfile=path.join(cert_path, "keycert_ec.pem"),
certfile=path.join(cert_path, "keycert_ec.pem"),
server_side=True,
ca_certs=path.join(cert_path, "ca-cert_ec.pem"),
do_handshake_on_connect=False)
print("ok2")
cnt = 0
while True:
cnt += 1
print("Listen invocation: %d" % cnt)
peer_address = scn.listen()
if peer_address:
print("Completed listening for peer: %s" % str(peer_address))
break
print("Accepting...")
conn = scn.accept()[0]
sck.settimeout(5)
conn.get_socket(True).settimeout(5)
cnt = 0
while True:
cnt += 1
print("Listen invocation: %d" % cnt)
peer_address = scn.listen()
# assert not peer_address
print("Handshake invocation: %d" % cnt)
try:
conn.do_handshake()
except SSLError as err:
if err.errno == 504:
continue
raise
print("Completed handshaking with peer")
break
cnt = 0
while True:
cnt += 1
# print("Listen invocation: %d" % cnt)
peer_address = scn.listen()
# assert not peer_address
# print("Read invocation: %d" % cnt)
# print("Hi there")
try:
message = conn.read()
except SSLError as err:
if err.errno == 502:
continue
if err.args[0] == SSL_ERROR_ZERO_RETURN:
break
raise
data = message.decode()
print("from client:%s"%data)
cmd_filename = data.split(' ')
if cmd_filename[0] != "ls" and cmd_filename[0] != "get":
conn.write("please input True cmd")
continue
else:
if cmd_filename[0] == "ls":
obj = subprocess.Popen(data,shell=True,stdout=subprocess.PIPE)
cmd_result = obj.stdout.read()
conn.write(cmd_result)
else:
filename = cmd_filename[1]
if filename[0] == "/":
filedir = filename
else:
if filename[:2] == "./":
filename = filename[2:-1]
filedir = path.join(current_path,filename)
with open(filedir,"r") as fd:
while True:
byte = fd.read(blocksize)
if not byte:
conn.write("Already Send".encode())
break
conn.write(byte.encode())
cnt = 0
while True:
cnt += 1
# print("Listen invocation: %d" % cnt)
# peer_address = scn.listen()
# assert not peer_address
print("Shutdown invocation: %d" % cnt)
try:
s = conn.unwrap()
s.close()
except SSLError as err:
if err.errno == 502:
continue
raise
break
sck.close()
pass
#if __name__ == "__main__":
# main()client
查看代码
from os import path
import ssl
from socket import socket, AF_INET, SOCK_DGRAM
from logging import basicConfig, DEBUG
basicConfig(level=DEBUG) # set now for dtls import code
from dtls import do_patch
do_patch()
blocksize = 1024
#def main():
cert_path = path.join(path.abspath(path.dirname(__file__)), "certs")
s = ssl.wrap_socket(socket(AF_INET, SOCK_DGRAM), cert_reqs=ssl.CERT_NONE,
ca_certs=path.join(cert_path, "ca-cert_ec.pem"))
s.connect(('127.0.0.1', 28000))
try:
while True:
print("input ls <dir> to list files in dir.\n")
print("input get <filename> to get files from dir.\n")
send_msg = input(">")
cmd, filename = send_msg.split(" ")
try:
s.send(send_msg.encode())
except Exception as e:
print("[-]Can not send Data")
try:
if cmd == "ls":
data = s.recv(blocksize)
print(data.decode())
else:
filename = filename.split("/")[-1]
filedir = "./"+filename
with open(filedir,"wb") as fd :
while True:
data = s.recv(blocksize)
if data.decode() == "Already Send":
print("Already Reveive.")
break
fd.write(data)
except Exception as e:
print("[-]Can not receive Data")
except KeyboardInterrupt:
s.close()
sys.exit(0)
#if __name__ == "__main__":
# main()
1)启动客户端和服务端
python server/server.py
python client/client.py2)服务端接受客户端连接
并输出握手消息:
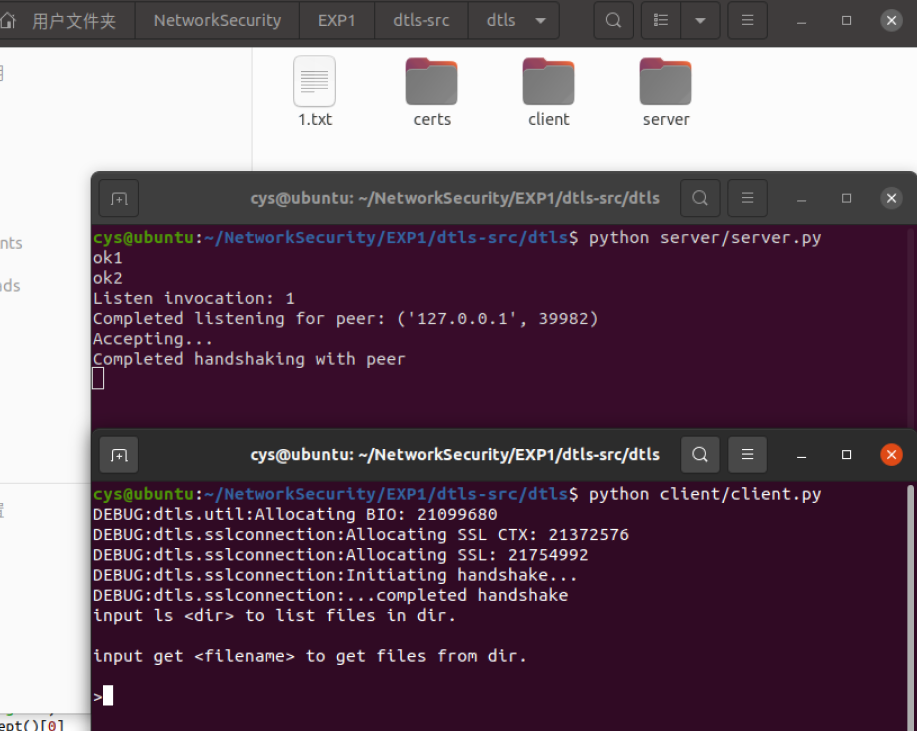
cys@ubuntu:~/NetworkSecurity/EXP1/dtls-src/dtls$ python server/server.py
ok1
ok2
Listen invocation: 1
Completed listening for peer: ('127.0.0.1', 42416)
Accepting...
Completed handshaking with peer
cys@ubuntu:~/NetworkSecurity/EXP1/dtls-src/dtls$ python client/client.py
DEBUG:dtls.util:Allocating BIO: 25437344
DEBUG:dtls.sslconnection:Allocating SSL CTX: 25710240
DEBUG:dtls.sslconnection:Allocating SSL: 26092656
DEBUG:dtls.sslconnection:Initiating handshake...
DEBUG:dtls.sslconnection:...completed handshake
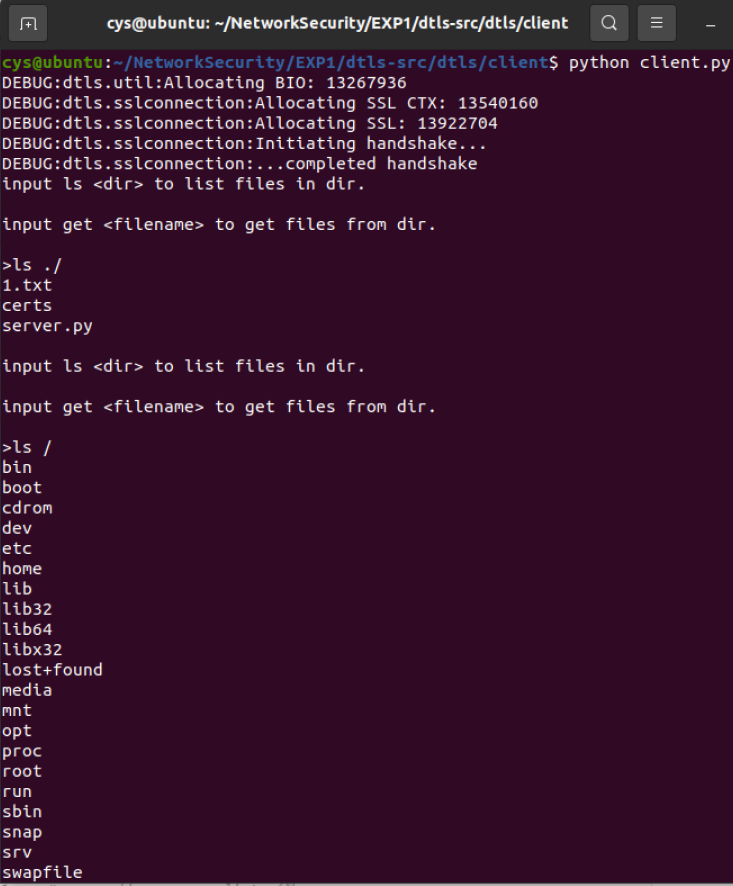
input ls <dir> to list files in dir.
input get <filename> to get files from dir.
>输入文件名
3)客户端从服务端下载文件
过程截图及代码:
client
ls ./
ls /
get 1.txt
get server.pyServe
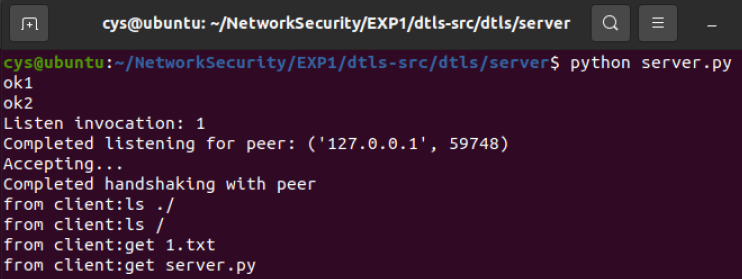
获取到了两个文件
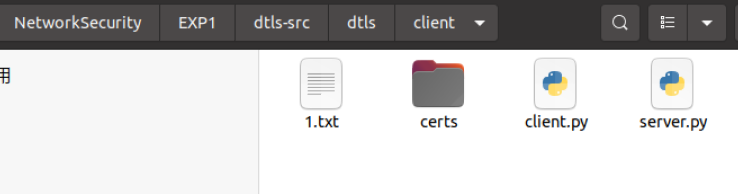
查看client文件下有该文件:
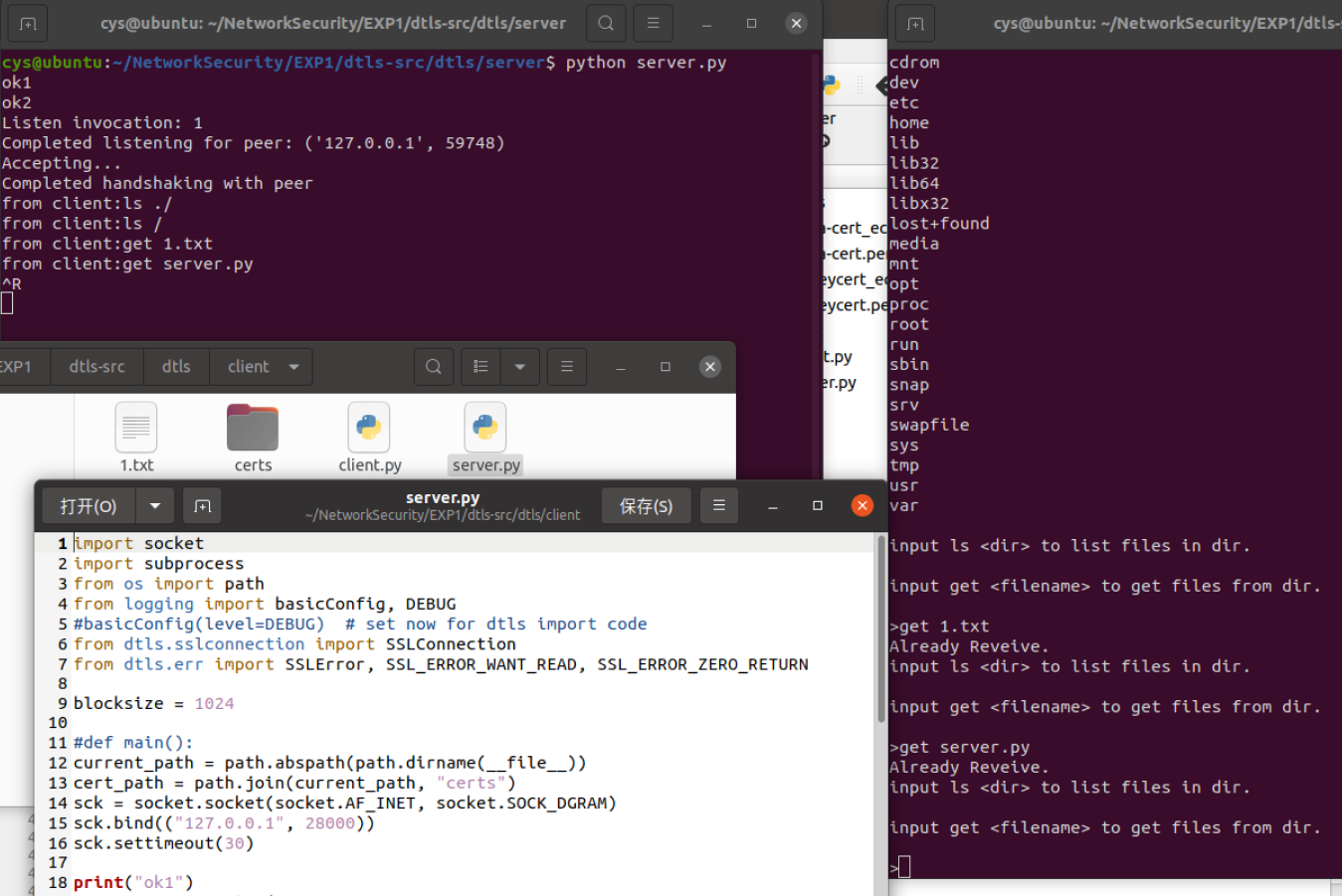
最终总的截图:
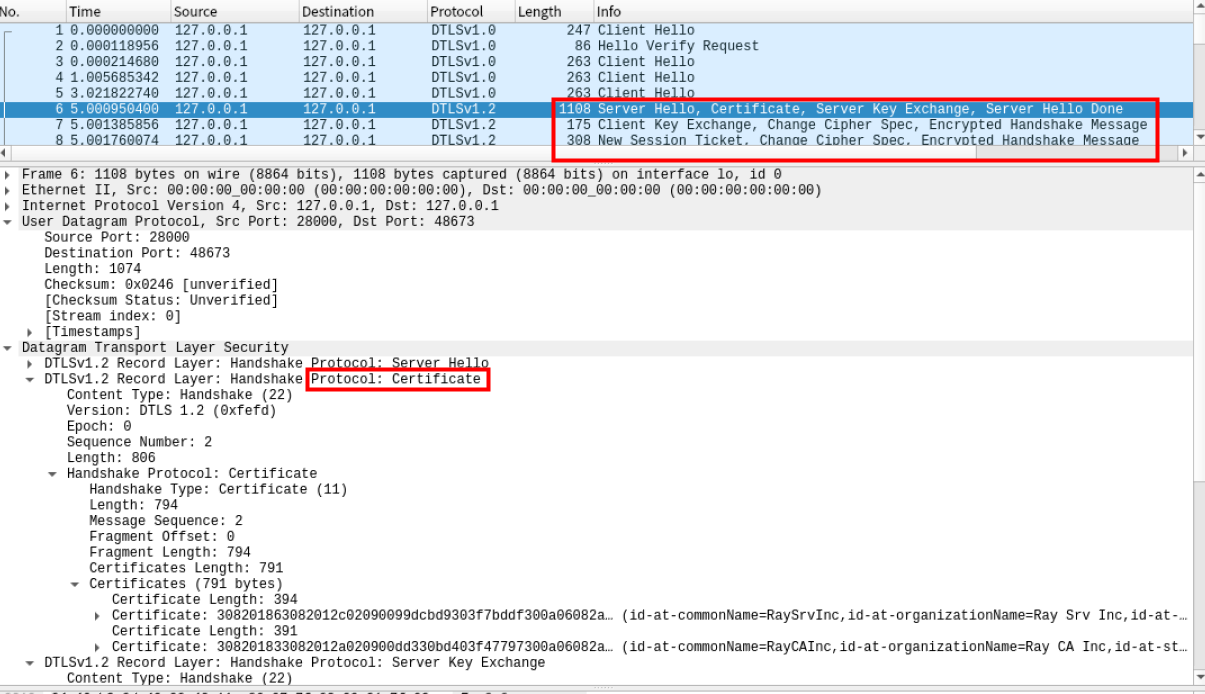
4)通过Wireshark分析DTLS协议握手及通信过程
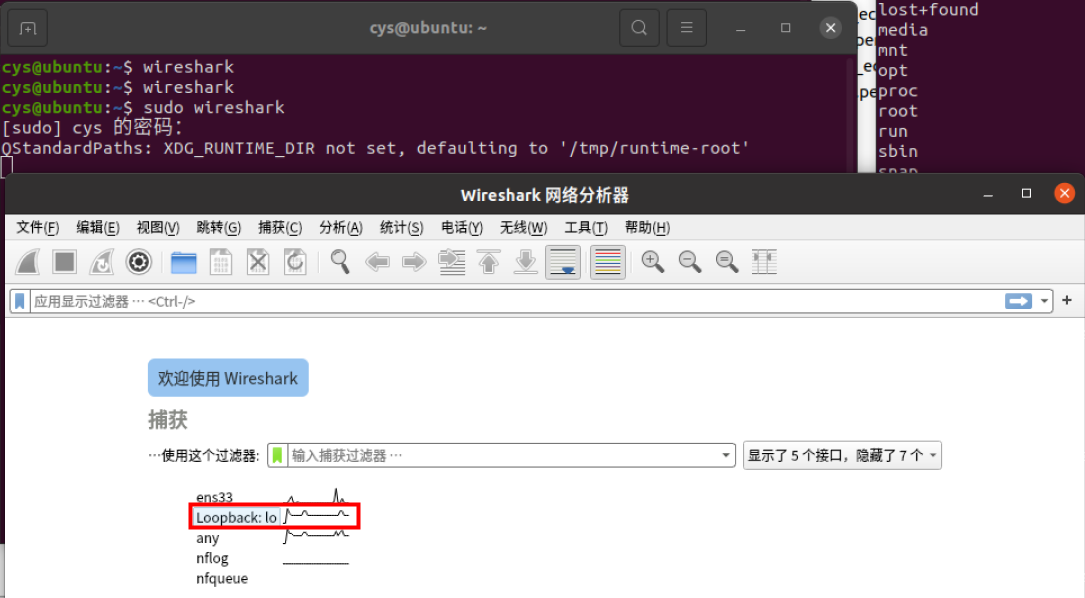
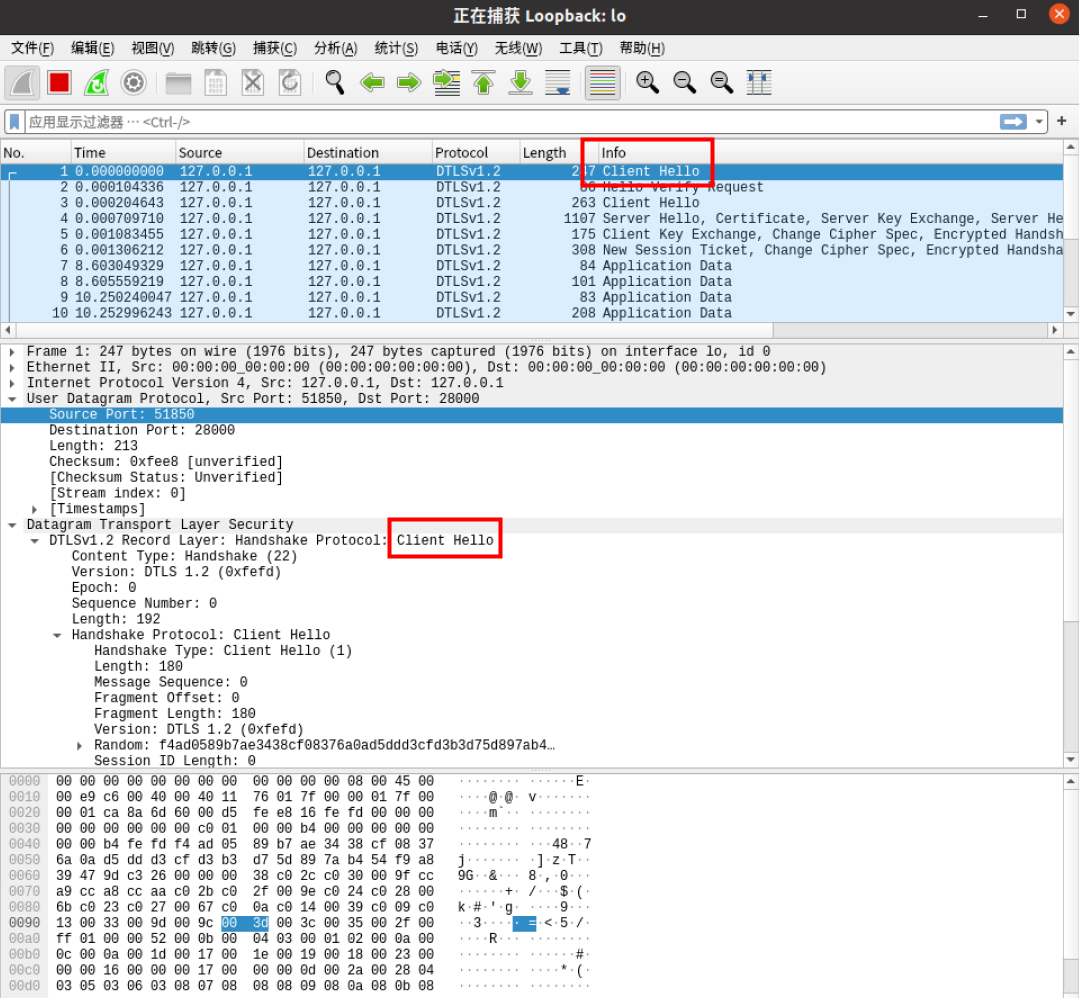
抓取到Hello报文
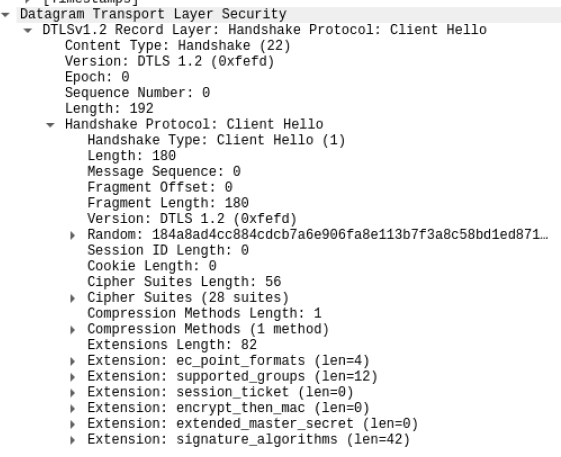

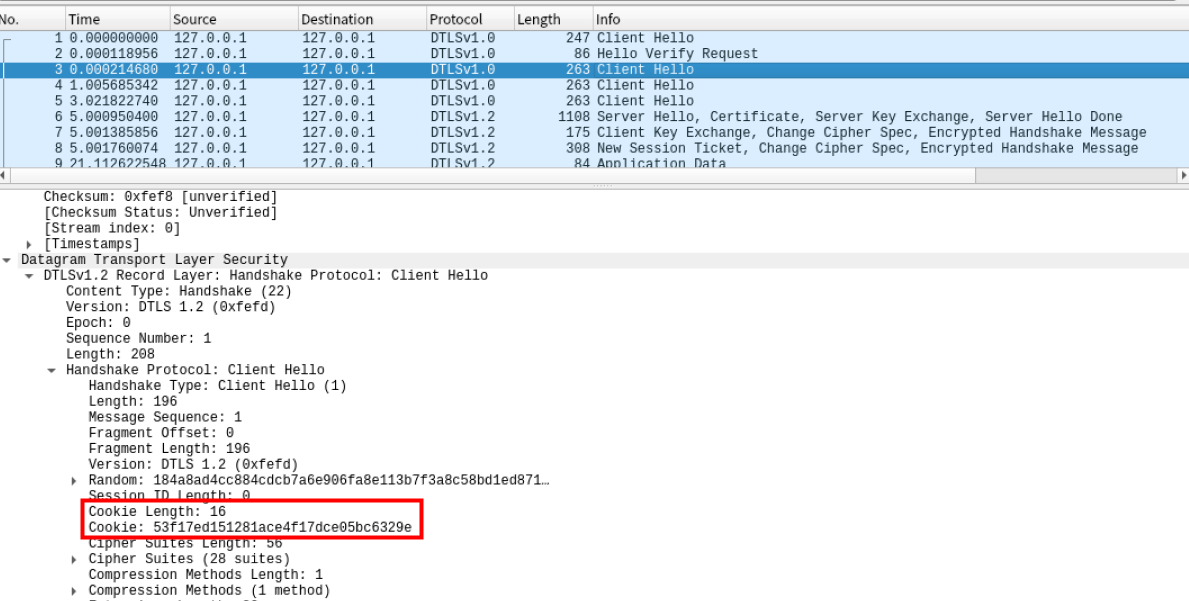
抓取到cookie
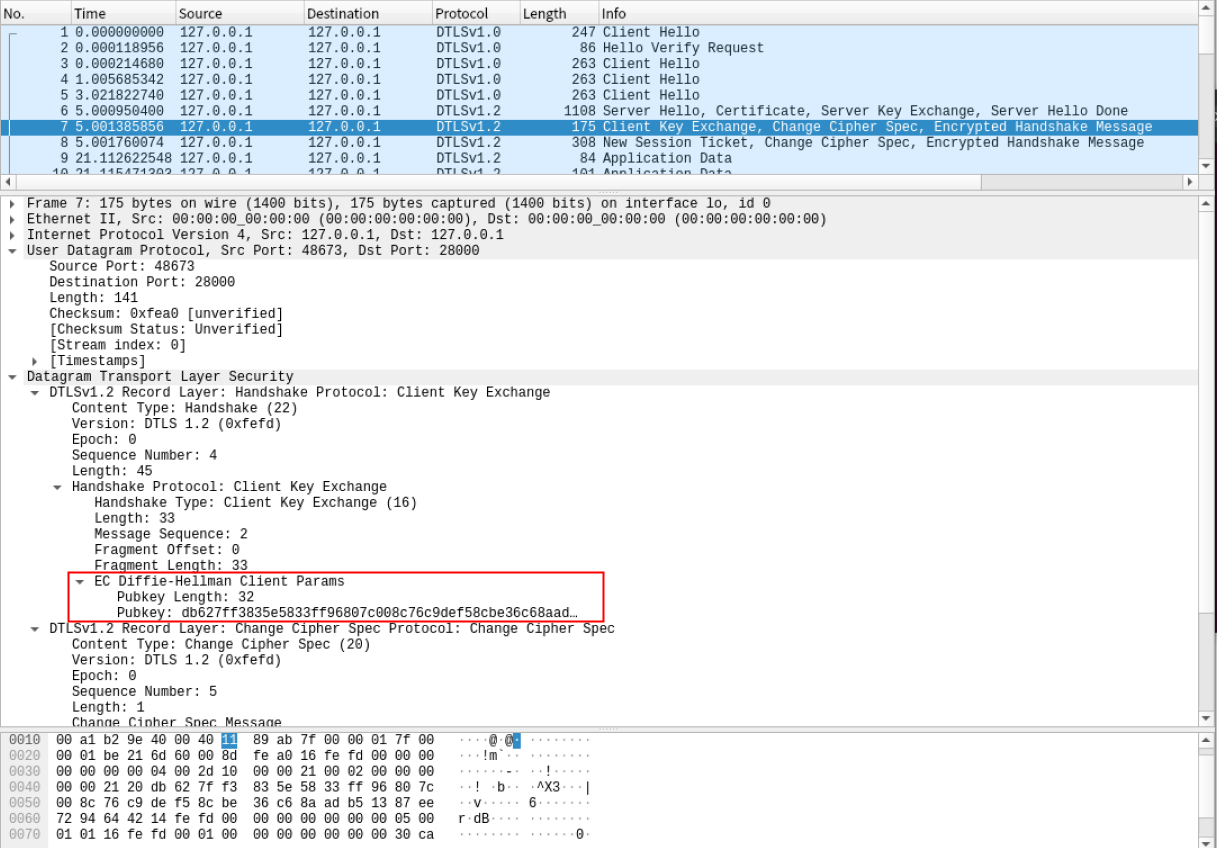
抓取到密钥协商过程
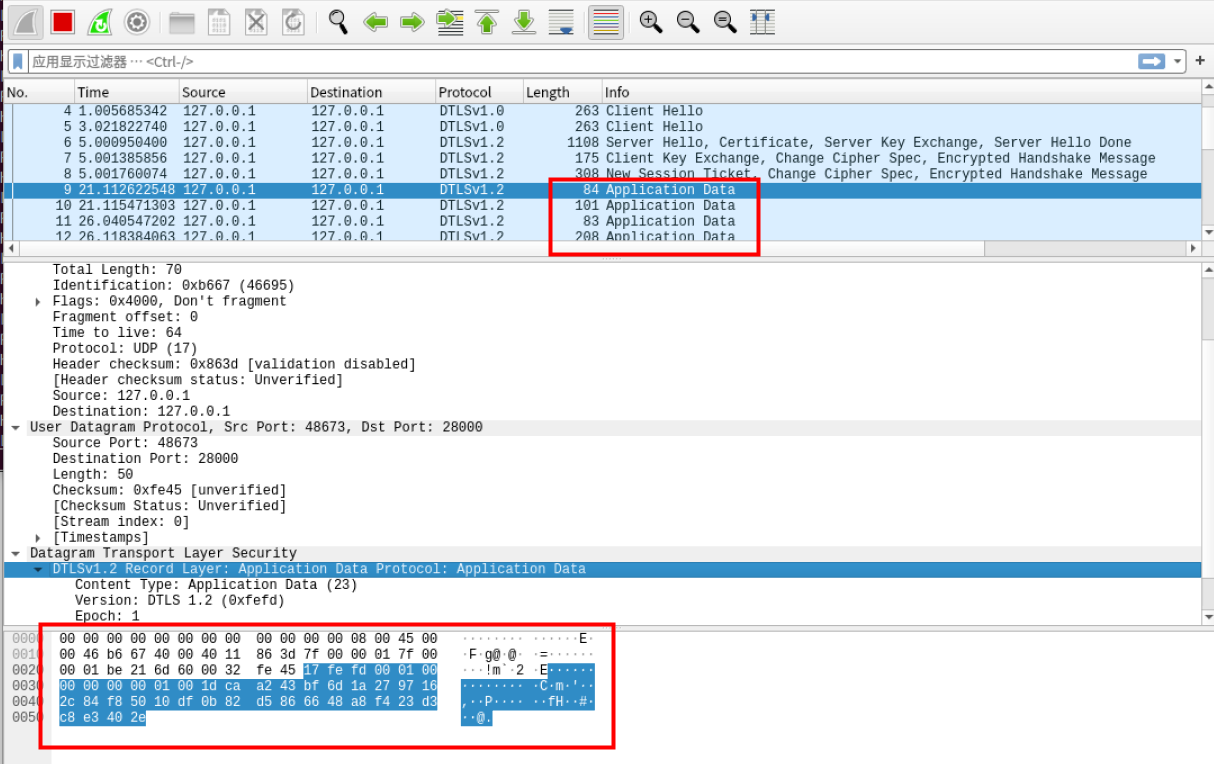
抓取到加密通信的内容
python3.6安装
apt-get install -y software-properties-common
add-apt-repository ppa:deadsnakes/ppa
apt-get update
apt-get install python3.6cys@ubuntu:~$ python3.6 -m pip install python3-dtls
Collecting python3-dtls
Using cached python3_dtls-1.3.0-py3-none-any.whl (102 kB)
Installing collected packages: python3-dtls
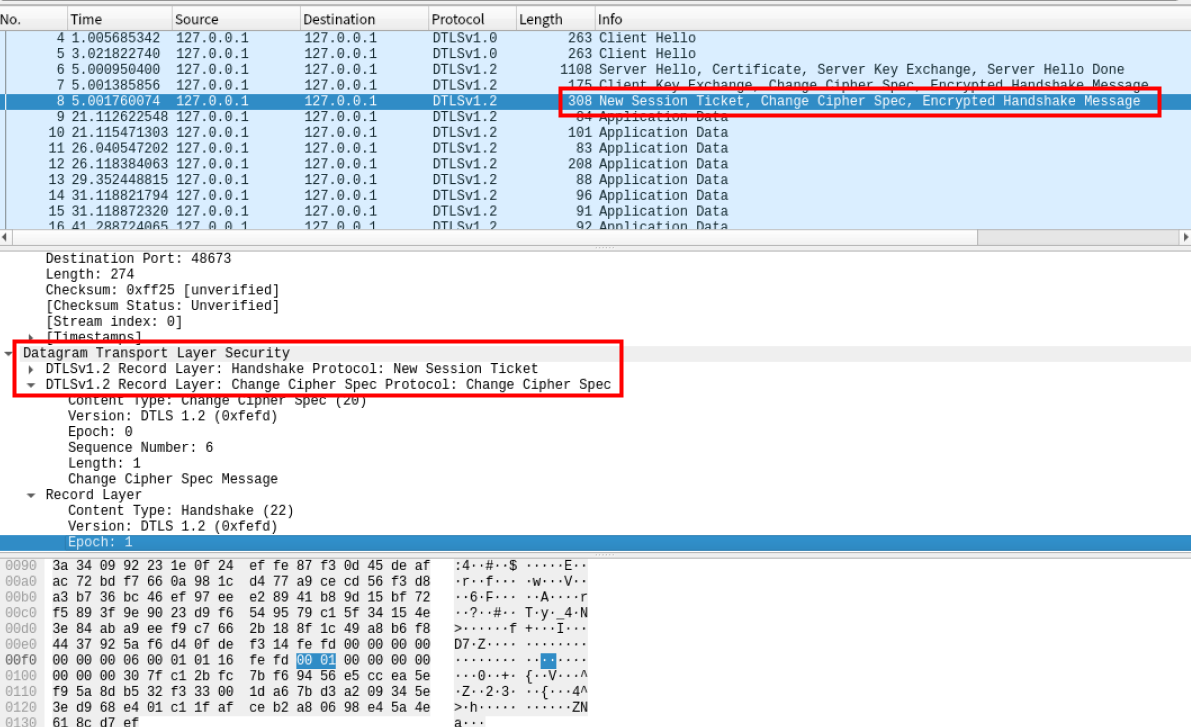
Successfully installed python3-dtls-1.3.010 发送Change Cipher Spec消息和Encrypted Handshake消息的目的是什么?
1.通知对端改变当前使用的加密方式,change cipher spec 实际可用于通知对端改版当前使用的加密通信方式。
2.告诉对端自己在整个握手中收到了什么数据,发送了什么数据,保证中间没人篡改报文。首先,无论是客户端还是服务端,都会在握手完成之后,发送 Encrypted handshake message,且各自收到对端的Encrypted handshake message后会去验证这个数据。 具体 这个 Encrypted handshake message 怎么计算,就是把当前(准备发送Encrypted handshake message)前,自己收到的数据和发送的数据进行一次简单运算(hash+)。如果中间有人篡改了报文,比如,把客户端的client hello中的提供的加密套件改成了 一个弱秘钥算法,那么对于server而言,收到的client hello 和 客户端实际发送的是不同的



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语 ── 封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· 地球OL攻略 —— 某应届生求职总结
· 提示词工程——AI应用必不可少的技术
· Open-Sora 2.0 重磅开源!
· 周边上新:园子的第一款马克杯温暖上架
2021-04-02 2021国防科技大学计算机学院无军籍考研经验贴
2019-04-02 问题 B: 【例9.3】求最长不下降序列(基础dp)
2019-04-02 问题 H: 老管家的忠诚(线段树)
2019-04-02 问题 H: 老管家的忠诚(线段树)