机器人系统仿真(十四)——机器人运动控制以及里程计信息显示
参考视频:【奥特学园】ROS机器人入门课程《ROS理论与实践》零基础教程_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
参考文档:http://www.autolabor.com.cn/book/ROSTutorials/
机器人运动控制以及里程计信息显示
1 ros_control 简介
场景:同一套 ROS 程序,如何部署在不同的机器人系统上,比如:开发阶段为了提高效率是在仿真平台上测试的,部署时又有不同的实体机器人平台,不同平台的实现是有差异的,如何保证 ROS 程序的可移植性?ROS 内置的解决方式是 ros_control。
ros_control:是一组软件包,它包含了控制器接口,控制器管理器,传输和硬件接口。ros_control 是一套机器人控制的中间件,是一套规范,不同的机器人平台只要按照这套规范实现,那么就可以保证 与ROS 程序兼容,通过这套规范,实现了一种可插拔的架构设计,大大提高了程序设计的效率与灵活性。
gazebo 已经实现了 ros_control 的相关接口,如果需要在 gazebo 中控制机器人运动,直接调用相关接口即可
在 urdf 文件夹下新建 gazebo 文件夹,在 gazebo 文件夹下新建 move.xacro
2.运动控制实现流程(Gazebo)
承上,运动控制基本流程:
-
已经创建完毕的机器人模型,编写一个单独的 xacro 文件,为机器人模型添加传动装置以及控制器
-
将此文件集成进xacro文件
-
启动 Gazebo 并发布 /cmd_vel 消息控制机器人运动
2.1 为 joint 添加传动装置以及控制器
两轮差速配置
在 urdf 新建 gazebo 文件夹,再在文件夹下新建 move.xacro
2.2 xacro文件集成
在 car.urdf.xacro 里设置 move.xacro
<robot name="my_base" xmlns:xacro="http://www.ros.org/wiki/xacro"> <!--包含惯性矩阵文件--> <xacro:include filename="head.xacro" /> <!--包含底盘、摄像头与雷达的 xacro 文件--> <xacro:include filename="demo05_car_base.urdf.xacro" /> <xacro:include filename="demo06_car_camera.urdf.xacro" /> <xacro:include filename="demo07_car_laser.urdf.xacro" /> <!--运动控制--> <xacro:include filename="gazebo/move.xacro" /> </robot>
复用之前的 demo03_env.launch
<launch> <!--1.需要在参数服务器中载入 urdf --> <param name="robot_description" command="$(find xacro)/xacro $(find urdf02_gazebo)/urdf/car.urdf.xacro" /> <!--2.启动 Gazebo 仿真环境 --> <include file="$(find gazebo_ros)/launch/empty_world.launch" > <arg name="world_name" value="$(find urdf02_gazebo)/worlds/box_house.world" /> </include> <!--3.在 Gazebo 中添加机器人模型 --> <node pkg="gazebo_ros" type="spawn_model" name="spawn_model" args="-urdf -model car -param robot_description" /> </launch>
编写 move.xacro
<robot name="my_car_move" xmlns:xacro="http://wiki.ros.org/xacro"> <!-- 传动实现:用于连接控制器与关节 --> <xacro:macro name="joint_trans" params="joint_name"> <!-- Transmission is important to link the joints and the controller --> <transmission name="${joint_name}_trans"> <type>transmission_interface/SimpleTransmission</type> <joint name="${joint_name}"> <hardwareInterface>hardware_interface/VelocityJointInterface</hardwareInterface> </joint> <actuator name="${joint_name}_motor"> <hardwareInterface>hardware_interface/VelocityJointInterface</hardwareInterface> <mechanicalReduction>1</mechanicalReduction> </actuator> </transmission> </xacro:macro> <!-- 每一个驱动轮都需要配置传动装置 --> <xacro:joint_trans joint_name="left_wheel2base_link" /> <xacro:joint_trans joint_name="right_wheel2base_link" /> <!-- 控制器 --> <gazebo> <plugin name="differential_drive_controller" filename="libgazebo_ros_diff_drive.so"> <rosDebugLevel>Debug</rosDebugLevel> <publishWheelTF>true</publishWheelTF> <robotNamespace>/</robotNamespace> <publishTf>1</publishTf> <publishWheelJointState>true</publishWheelJointState> <alwaysOn>true</alwaysOn> <updateRate>100.0</updateRate> <legacyMode>true</legacyMode> <leftJoint>left_wheel2base_link</leftJoint> <!-- 左轮 --> <rightJoint>right_wheel2base_link</rightJoint> <!-- 右轮 --> <wheelSeparation>${base_link_radius * 2}</wheelSeparation> <!-- 车轮间距 --> <wheelDiameter>${wheel_radius * 2}</wheelDiameter> <!-- 车轮直径 --> <broadcastTF>1</broadcastTF> <wheelTorque>30</wheelTorque> <wheelAcceleration>1.8</wheelAcceleration> <commandTopic>cmd_vel</commandTopic> <!-- 运动控制话题 --> <odometryFrame>odom</odometryFrame> <odometryTopic>odom</odometryTopic> <!-- 里程计话题 --> <robotBaseFrame>base_footprint</robotBaseFrame> <!-- 根坐标系 --> </plugin> </gazebo> </robot>
一些配置参考 demo05_car_base.urdf.xacro

<!-- 使用 xacro 优化 URDF 版的小车底盘实现: 实现思路: 1.将一些常量、变量封装为 xacro:property 比如:PI 值、小车底盘半径、离地间距、车轮半径、宽度 .... 2.使用 宏 封装驱动轮以及支撑轮实现,调用相关宏生成驱动轮与支撑轮 --> <!-- 根标签,必须声明 xmlns:xacro --> <robot name="my_base" xmlns:xacro="http://www.ros.org/wiki/xacro"> <!-- 封装变量、常量 --> <xacro:property name="PI" value="3.141"/> <!-- 宏:黑色设置 --> <material name="black"> <color rgba="0.0 0.0 0.0 1.0" /> </material> <!-- 底盘属性 --> <xacro:property name="base_footprint_radius" value="0.001" /> <!-- base_footprint 半径 --> <xacro:property name="base_link_radius" value="0.1" /> <!-- base_link 半径 --> <xacro:property name="base_link_length" value="0.08" /> <!-- base_link 长 --> <xacro:property name="base_link_mass" value="2" /> <!-- base_link 长 --> <xacro:property name="earth_space" value="0.015" /> <!-- 离地间距 --> <!-- 底盘 --> <link name="base_footprint"> <visual> <geometry> <sphere radius="${base_footprint_radius}" /> </geometry> </visual> </link> <link name="base_link"> <visual> <geometry> <cylinder radius="${base_link_radius}" length="${base_link_length}" /> </geometry> <origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="0 0 0" /> <material name="green"> <color rgba="0.0 0.8 0.3 0.5" /> </material> </visual> <!--设置惯性矩阵--> <collision> <geometry> <cylinder radius="${base_link_radius}" length="${base_link_length}" /> </geometry> <origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="0 0 0" /> </collision> <!--调用惯性矩阵函数--> <xacro:cylinder_inertial_matrix m="${base_link_mass}" r="${base_link_radius}" h="${base_link_length}" /> </link> <gazebo reference="base_link"> <material>Gazebo/Yellow</material> </gazebo> <joint name="base_link2base_footprint" type="fixed"> <parent link="base_footprint" /> <child link="base_link" /> <origin xyz="0 0 ${earth_space + base_link_length / 2 }" /> </joint> <!-- 驱动轮 --> <!-- 驱动轮属性 --> <xacro:property name="wheel_radius" value="0.0325" /><!-- 半径 --> <xacro:property name="wheel_length" value="0.015" /><!-- 宽度 --> <xacro:property name="wheel_mass" value="0.05" /><!-- 宽度 --> <!-- 驱动轮宏实现 --> <xacro:macro name="add_wheels" params="name flag"> <link name="${name}_wheel"> <visual> <geometry> <cylinder radius="${wheel_radius}" length="${wheel_length}" /> </geometry> <origin xyz="0.0 0.0 0.0" rpy="${PI / 2} 0.0 0.0" /> <material name="black" /> </visual> <collision> <geometry> <cylinder radius="${wheel_radius}" length="${wheel_length}" /> </geometry> <origin xyz="0.0 0.0 0.0" rpy="${PI / 2} 0.0 0.0" /> </collision> <xacro:property name="wheel_mass" value="0.05" /><!-- 宽度 --> <xacro:cylinder_inertial_matrix m="${wheel_mass}" r="${wheel_radius}" h="${wheel_length}" /> </link> <gazebo reference="${name}_wheel"> <material>Gazebo/Red</material> </gazebo> <joint name="${name}_wheel2base_link" type="continuous"> <parent link="base_link" /> <child link="${name}_wheel" /> <origin xyz="0 ${flag * base_link_radius} ${-(earth_space + base_link_length / 2 - wheel_radius) }" /> <axis xyz="0 1 0" /> </joint> </xacro:macro> <xacro:add_wheels name="left" flag="1" /> <xacro:add_wheels name="right" flag="-1" /> <!-- 支撑轮 --> <!-- 支撑轮属性 --> <xacro:property name="support_wheel_radius" value="0.0075" /> <!-- 支撑轮半径 --> <xacro:property name="support_wheel_mass" value="0.01" /> <!-- 支撑轮半径 --> <!-- 支撑轮宏 --> <xacro:macro name="add_support_wheel" params="name flag" > <link name="${name}_wheel"> <visual> <geometry> <sphere radius="${support_wheel_radius}" /> </geometry> <origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="0 0 0" /> <material name="black" /> </visual> <collision> <geometry> <sphere radius="${support_wheel_radius}" /> </geometry> <origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="0 0 0" /> </collision> <xacro:sphere_inertial_matrix m="${support_wheel_mass}" r="${support_wheel_radius}" /> </link> <gazebo reference="${name}_wheel"> <material>Gazebo/Red</material> </gazebo> <joint name="${name}_wheel2base_link" type="continuous"> <parent link="base_link" /> <child link="${name}_wheel" /> <origin xyz="${flag * (base_link_radius - support_wheel_radius)} 0 ${-(base_link_length / 2 + earth_space / 2)}" /> <axis xyz="1 1 1" /> </joint> </xacro:macro> <xacro:add_support_wheel name="front" flag="1" /> <xacro:add_support_wheel name="back" flag="-1" /> </robot>
2.3 启动 gazebo并控制机器人运动
运行:
cys@ubuntu:~/demo05_ws$ source ./devel/setup.bash
cys@ubuntu:~/demo05_ws$ roslaunch urdf02_gazebo demo03_env.launch
新建命令窗口:
rostopic list
rosrun teleop_twist_keyboard teleop_twist_keyboard.py
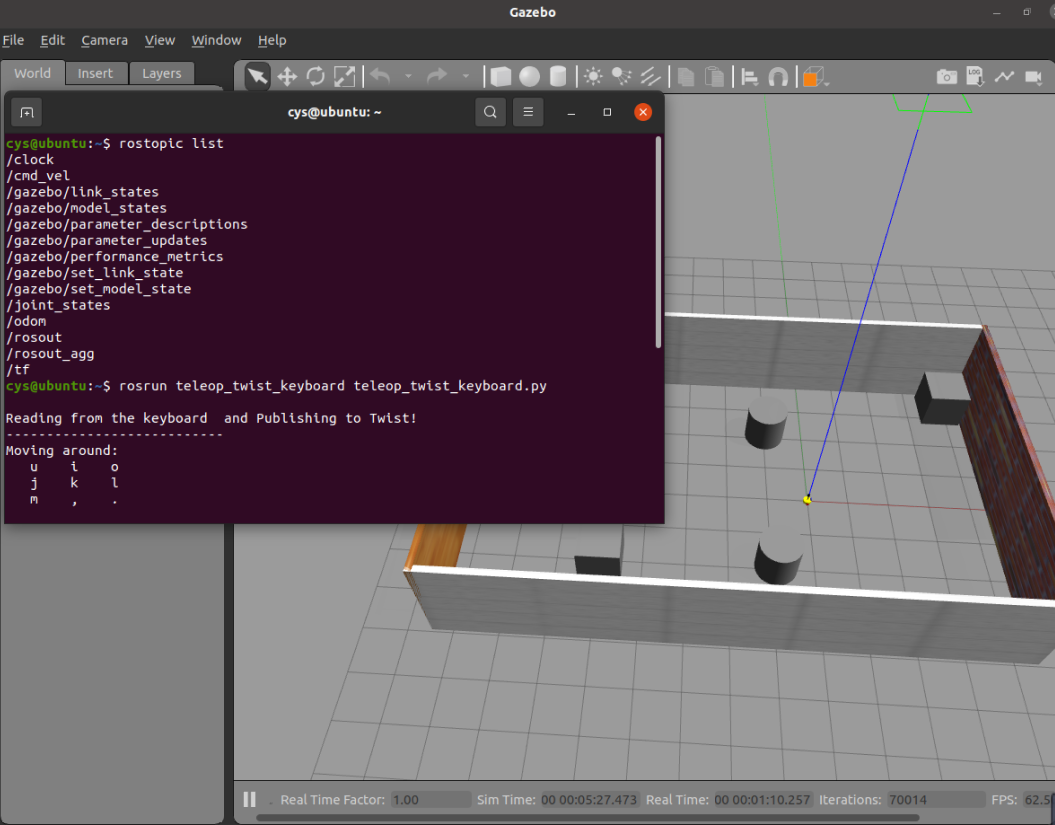
键盘控制运动 i 向前走,k 停止,“,”后退
更改速度
rosrun teleop_twist_keyboard teleop_twist_keyboard.py _speed:=0.3 _turn:=0.5
3.Rviz查看里程计信息
在 Gazebo 的仿真环境中,机器人的里程计信息以及运动朝向等信息是无法获取的,可以通过 Rviz 显示机器人的里程计信息以及运动朝向
里程计: 机器人相对出发点坐标系的位姿状态(X 坐标 Y 坐标 Z坐标以及朝向)。
在 launch 文件夹下新建 demo04_sensor.launch
<launch> <!--启动rviz--> <node pkg="rviz" name="rviz" type="rviz" args="-d $(find urdf01_rviz)/config/show_mycar.rviz"/> <!--关节状态发布节点--> <node pkg="joint_state_publisher" type="joint_state_publisher" name="joint_state_publisher"/> <!--机器人状态发布节点--> <node pkg="robot_state_publisher" type="robot_state_publisher" name="robot_state_publisher"/> </launch>
同时运行两个 launch 文件
cys@ubuntu:~/demo05_ws$ source ./devel/setup.bash
cys@ubuntu:~/demo05_ws$ roslaunch urdf02_gazebo demo03_env.launch
cys@ubuntu:~/demo05_ws$ source ./devel/setup.bash
cys@ubuntu:~/demo05_ws$ roslaunch urdf02_gazebo demo04_sensor.launch
开启里程计
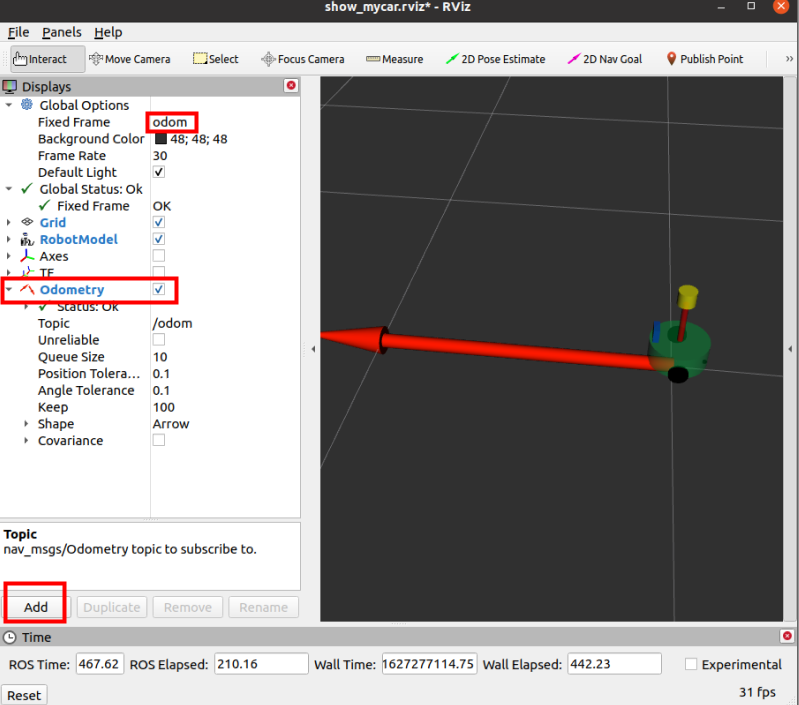
新建命令行,开启键盘同时控制 rviz 和 gazebo 里的机器人小车
rosrun teleop_twist_keyboard teleop_twist_keyboard.py




