【luffy】登录注册前端页面,腾讯短信功能验证,短信验证码,登录接口
目录
1. 登录接口两个问题
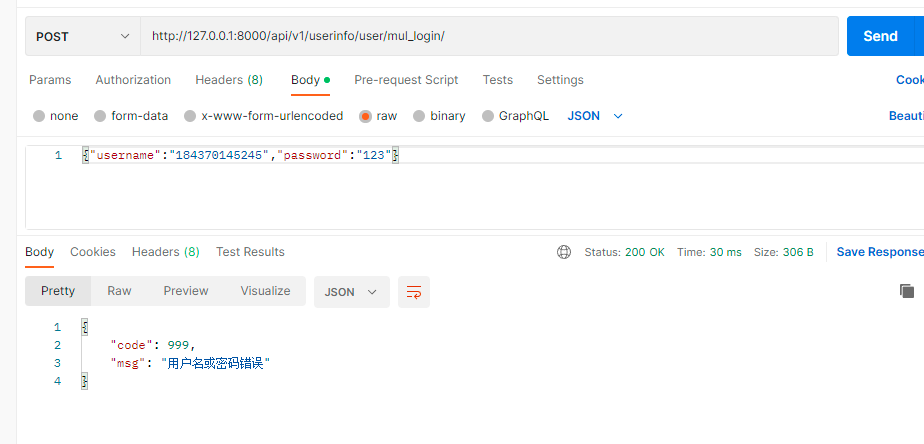
1. 使用authenticate 只能使用username和password去校验用户
使用手机号mobile和邮箱email去校验是不能对的
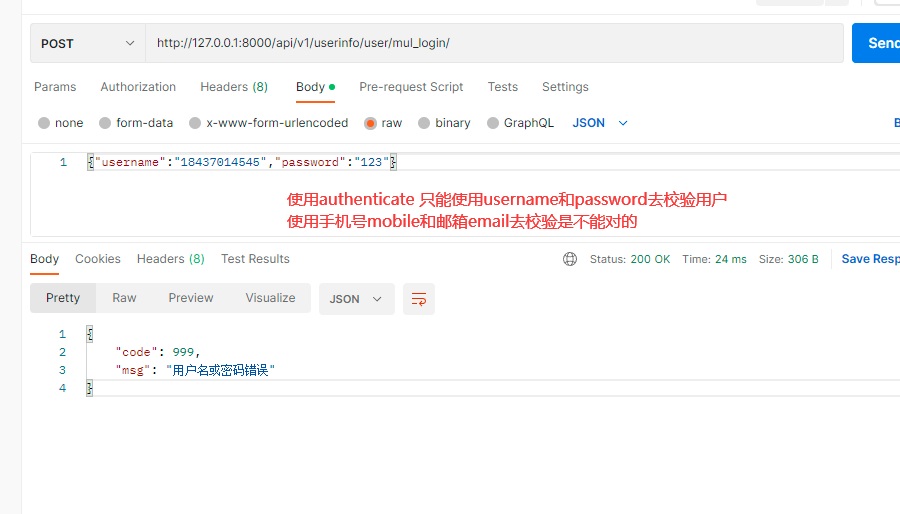
def _get_user(self, attrs):
# attrs是校验过后的数据:字段自己有规则(字段有自己规则有坑)和局部钩子
username = attrs.get('username')
password = attrs.get('password')
# username 可能是手机号,邮箱,用户名--->使用正则判断
if re.match(r'^1[3-9][0-9]{9}$', username):
# authenticate 只能使用username和password去校验用户
# user = authenticate(mobile=username, password=password)
user = UserInfo.objects.filter(mobile=username).first()
elif re.match(r'^.+@.+$', username): # adsa@adsf 会有bug,用户名中如果有@,登录不了了
# user = authenticate(email=username, password=password)
user = UserInfo.objects.filter(email=username).first()
else:
# user = authenticate(username=username, password=password)
user = UserInfo.objects.filter(username=username).first()
if user and user.check_password(password):
return user
else:
# raise ValidationError('用户名或密码错误') non_fields_error
raise APIException('用户名或密码错误')
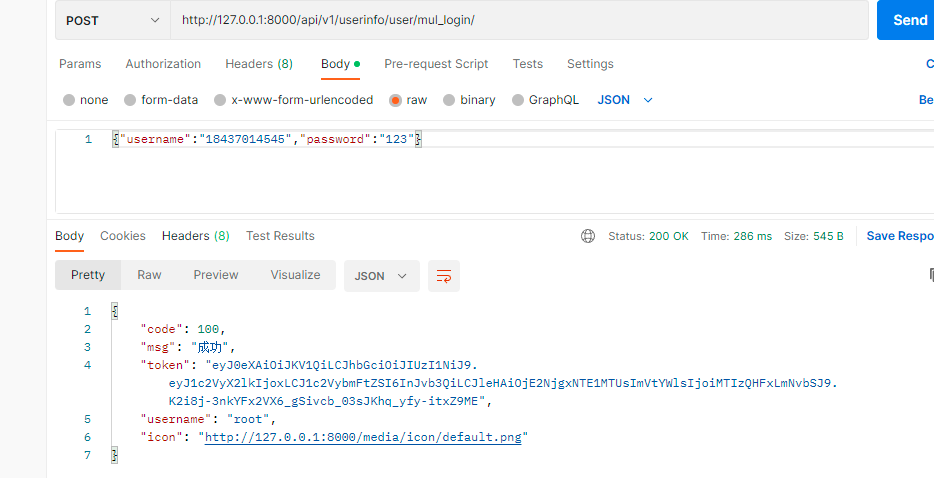
2. 使用ValidationError,会出现服务器出错,请联系系统管理员
而在登录接口中应该是用户名或密码错问等所以使用APIException
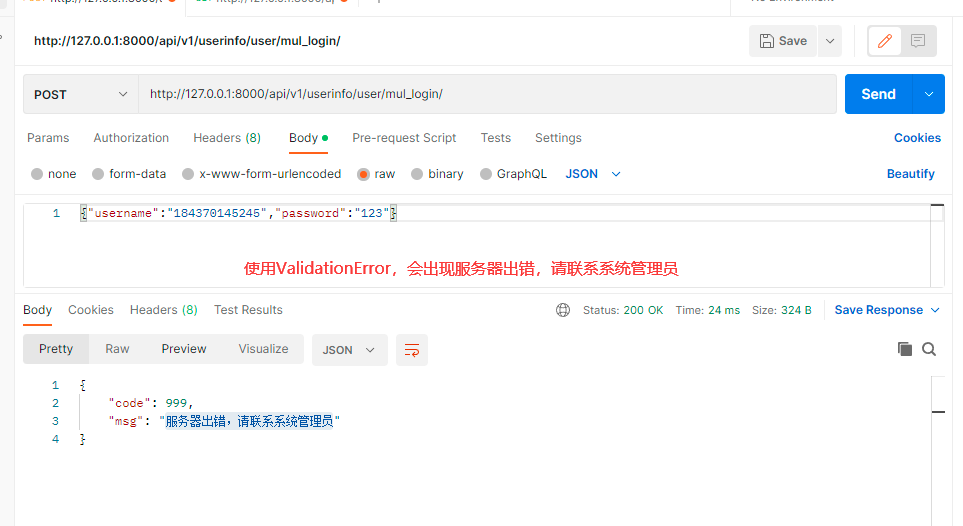
if user and user.check_password(password):
return user
else:
# raise ValidationError('用户名或密码错误') # non_fields_error
raise APIException('用户名或密码错误')
2. 登录注册模拟框
1. 如果点击是跳转新的页面(这里不用)
路由中配置一个路由
写一个视图组件
2. 点击登录是弹出弹窗,盖在主页上-->模拟框
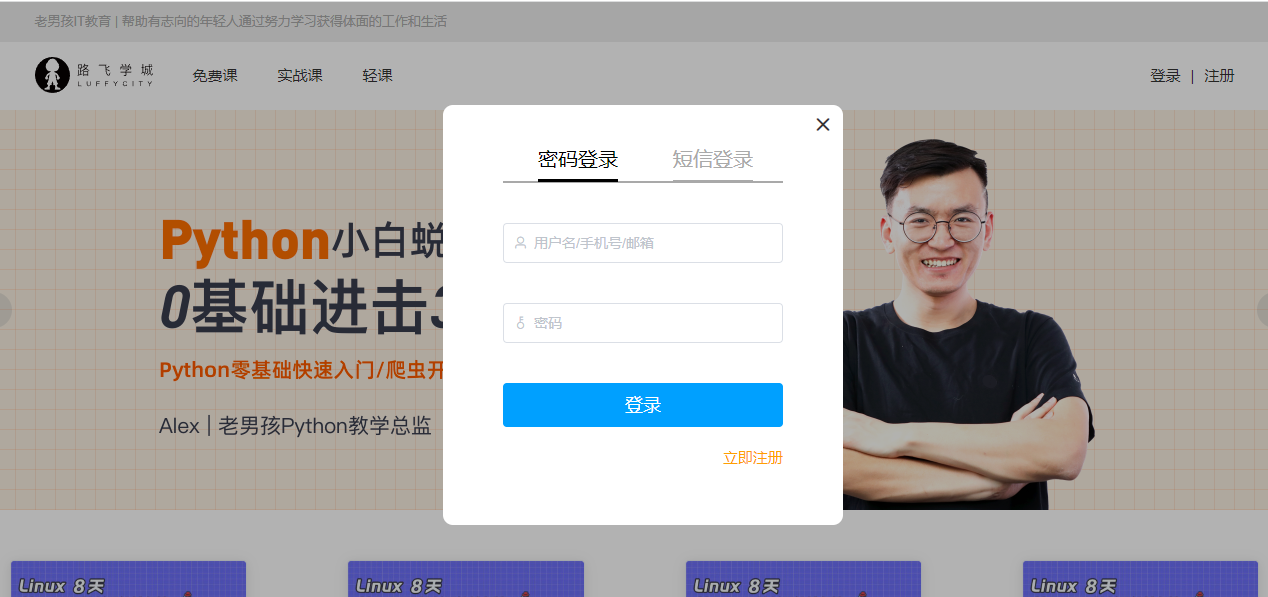
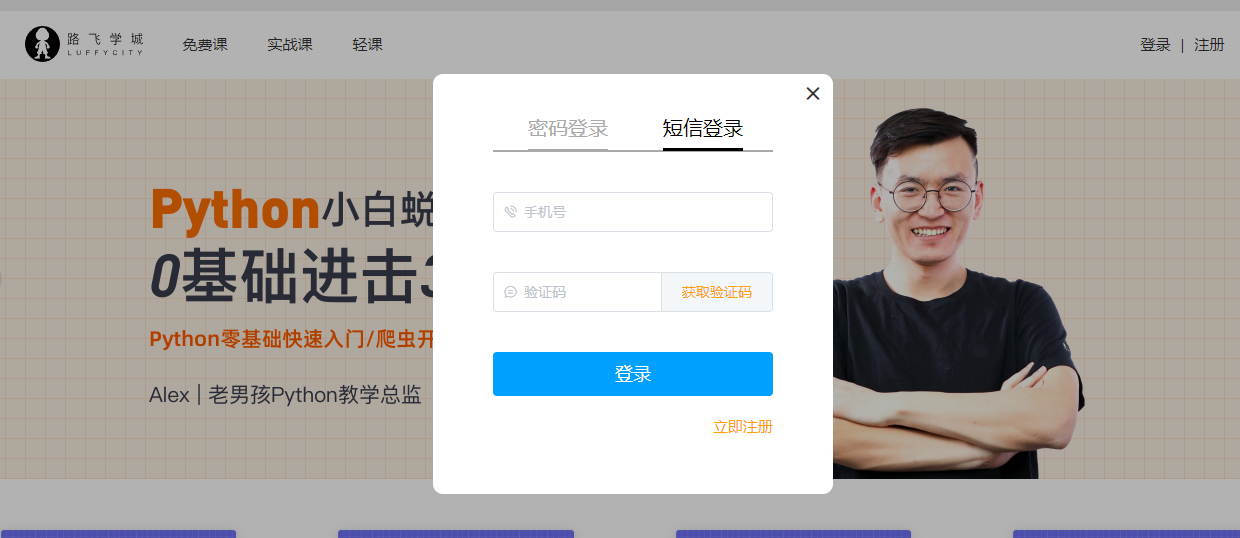

Header.vue
<template>
<div class="header">
<div class="slogan">
<p>老男孩IT教育 | 帮助有志向的年轻人通过努力学习获得体面的工作和生活</p>
</div>
<div class="nav">
<ul class="left-part">
<li class="logo">
<router-link to="/">
<img src="../assets/img/head-logo.svg" alt="">
</router-link>
</li>
<li class="ele">
<span @click="goPage('/free-course')" :class="{active: url_path === '/free-course'}">免费课</span>
</li>
<li class="ele">
<span @click="goPage('/actual-course')" :class="{active: url_path === '/actual-course'}">实战课</span>
</li>
<li class="ele">
<span @click="goPage('/light-course')" :class="{active: url_path === '/light-course'}">轻课</span>
</li>
</ul>
<div class="right-part">
<div>
<span @click="put_login">登录</span>
<span class="line">|</span>
<span @click="put_register">注册</span>
</div>
<Login v-if="is_login" @close="close_login" @go="put_register"></Login>
<Register v-if="is_register" @close="close_register" @go="put_login"></Register>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Login from "@/components/Login";
import Register from "@/components/Register";
export default {
name: "Header",
data() {
return {
url_path: sessionStorage.url_path || '/',
is_login: false,
is_register: false,
}
},
methods: {
goPage(url_path) {
// 已经是当前路由就没有必要重新跳转
if (this.url_path !== url_path) {
// 传入的参数,如果不等于当前路径,就跳转
this.$router.push(url_path)
}
sessionStorage.url_path = url_path;
},
goLogin() {
this.loginShow = true
},
put_login() {
this.is_login = true;
this.is_register = false;
},
put_register() {
this.is_login = false;
this.is_register = true;
},
close_login() {
this.is_login = false;
},
close_register() {
this.is_register = false;
}
},
created() {
sessionStorage.url_path = this.$route.path
this.url_path = this.$route.path
},
components: {
Login,
Register
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.header {
background-color: white;
box-shadow: 0 0 5px 0 #aaa;
}
.header:after {
content: "";
display: block;
clear: both;
}
.slogan {
background-color: #eee;
height: 40px;
}
.slogan p {
width: 1200px;
margin: 0 auto;
color: #aaa;
font-size: 13px;
line-height: 40px;
}
.nav {
background-color: white;
user-select: none;
width: 1200px;
margin: 0 auto;
}
.nav ul {
padding: 15px 0;
float: left;
}
.nav ul:after {
clear: both;
content: '';
display: block;
}
.nav ul li {
float: left;
}
.logo {
margin-right: 20px;
}
.ele {
margin: 0 20px;
}
.ele span {
display: block;
font: 15px/36px '微软雅黑';
border-bottom: 2px solid transparent;
cursor: pointer;
}
.ele span:hover {
border-bottom-color: orange;
}
.ele span.active {
color: orange;
border-bottom-color: orange;
}
.right-part {
float: right;
}
.right-part .line {
margin: 0 10px;
}
.right-part span {
line-height: 68px;
cursor: pointer;
}
</style>
Login.vue
<template>
<div class="login">
<div class="box">
<i class="el-icon-close" @click="close_login"></i>
<div class="content">
<div class="nav">
<span :class="{active: login_method === 'is_pwd'}"
@click="change_login_method('is_pwd')">密码登录</span>
<span :class="{active: login_method === 'is_sms'}"
@click="change_login_method('is_sms')">短信登录</span>
</div>
<el-form v-if="login_method === 'is_pwd'">
<el-input
placeholder="用户名/手机号/邮箱"
prefix-icon="el-icon-user"
v-model="username"
clearable>
</el-input>
<el-input
placeholder="密码"
prefix-icon="el-icon-key"
v-model="password"
clearable
show-password>
</el-input>
<el-button type="primary">登录</el-button>
</el-form>
<el-form v-if="login_method === 'is_sms'">
<el-input
placeholder="手机号"
prefix-icon="el-icon-phone-outline"
v-model="mobile"
clearable
@blur="check_mobile">
</el-input>
<el-input
placeholder="验证码"
prefix-icon="el-icon-chat-line-round"
v-model="sms"
clearable>
<template slot="append">
<span class="sms" @click="send_sms">{{ sms_interval }}</span>
</template>
</el-input>
<el-button type="primary">登录</el-button>
</el-form>
<div class="foot">
<span @click="go_register">立即注册</span>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "Login",
data() {
return {
username: '',
password: '',
mobile: '',
sms: '',
login_method: 'is_pwd',
sms_interval: '获取验证码',
is_send: false,
}
},
methods: {
close_login() {
this.$emit('close')
},
go_register() {
this.$emit('go')
},
change_login_method(method) {
this.login_method = method;
},
check_mobile() {
if (!this.mobile) return;
if (!this.mobile.match(/^1[3-9][0-9]{9}$/)) {
this.$message({
message: '手机号有误',
type: 'warning',
duration: 1000,
onClose: () => {
this.mobile = '';
}
});
return false;
}
this.is_send = true;
},
send_sms() {
if (!this.is_send) return;
this.is_send = false;
let sms_interval_time = 60;
this.sms_interval = "发送中...";
let timer = setInterval(() => {
if (sms_interval_time <= 1) {
clearInterval(timer);
this.sms_interval = "获取验证码";
this.is_send = true; // 重新回复点击发送功能的条件
} else {
sms_interval_time -= 1;
this.sms_interval = `${sms_interval_time}秒后再发`;
}
}, 1000);
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.login {
width: 100vw;
height: 100vh;
position: fixed;
top: 0;
left: 0;
z-index: 10;
background-color: rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.3);
}
.box {
width: 400px;
height: 420px;
background-color: white;
border-radius: 10px;
position: relative;
top: calc(50vh - 210px);
left: calc(50vw - 200px);
}
.el-icon-close {
position: absolute;
font-weight: bold;
font-size: 20px;
top: 10px;
right: 10px;
cursor: pointer;
}
.el-icon-close:hover {
color: darkred;
}
.content {
position: absolute;
top: 40px;
width: 280px;
left: 60px;
}
.nav {
font-size: 20px;
height: 38px;
border-bottom: 2px solid darkgrey;
}
.nav > span {
margin: 0 20px 0 35px;
color: darkgrey;
user-select: none;
cursor: pointer;
padding-bottom: 10px;
border-bottom: 2px solid darkgrey;
}
.nav > span.active {
color: black;
border-bottom: 3px solid black;
padding-bottom: 9px;
}
.el-input, .el-button {
margin-top: 40px;
}
.el-button {
width: 100%;
font-size: 18px;
}
.foot > span {
float: right;
margin-top: 20px;
color: orange;
cursor: pointer;
}
.sms {
color: orange;
cursor: pointer;
display: inline-block;
width: 70px;
text-align: center;
user-select: none;
}
</style>
Register.vue
<template>
<div class="register">
<div class="box">
<i class="el-icon-close" @click="close_register"></i>
<div class="content">
<div class="nav">
<span class="active">新用户注册</span>
</div>
<el-form>
<el-input
placeholder="手机号"
prefix-icon="el-icon-phone-outline"
v-model="mobile"
clearable
@blur="check_mobile">
</el-input>
<el-input
placeholder="密码"
prefix-icon="el-icon-key"
v-model="password"
clearable
show-password>
</el-input>
<el-input
placeholder="验证码"
prefix-icon="el-icon-chat-line-round"
v-model="sms"
clearable>
<template slot="append">
<span class="sms" @click="send_sms">{{ sms_interval }}</span>
</template>
</el-input>
<el-button type="primary">注册</el-button>
</el-form>
<div class="foot">
<span @click="go_login">立即登录</span>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "Register",
data() {
return {
mobile: '',
password: '',
sms: '',
sms_interval: '获取验证码',
is_send: false,
}
},
methods: {
close_register() {
this.$emit('close', false)
},
go_login() {
this.$emit('go')
},
check_mobile() {
if (!this.mobile) return;
if (!this.mobile.match(/^1[3-9][0-9]{9}$/)) {
this.$message({
message: '手机号有误',
type: 'warning',
duration: 1000,
onClose: () => {
this.mobile = '';
}
});
return false;
}
this.is_send = true;
},
send_sms() {
if (!this.is_send) return;
this.is_send = false;
let sms_interval_time = 60;
this.sms_interval = "发送中...";
let timer = setInterval(() => {
if (sms_interval_time <= 1) {
clearInterval(timer);
this.sms_interval = "获取验证码";
this.is_send = true; // 重新回复点击发送功能的条件
} else {
sms_interval_time -= 1;
this.sms_interval = `${sms_interval_time}秒后再发`;
}
}, 1000);
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.register {
width: 100vw;
height: 100vh;
position: fixed;
top: 0;
left: 0;
z-index: 10;
background-color: rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.3);
}
.box {
width: 400px;
height: 480px;
background-color: white;
border-radius: 10px;
position: relative;
top: calc(50vh - 240px);
left: calc(50vw - 200px);
}
.el-icon-close {
position: absolute;
font-weight: bold;
font-size: 20px;
top: 10px;
right: 10px;
cursor: pointer;
}
.el-icon-close:hover {
color: darkred;
}
.content {
position: absolute;
top: 40px;
width: 280px;
left: 60px;
}
.nav {
font-size: 20px;
height: 38px;
border-bottom: 2px solid darkgrey;
}
.nav > span {
margin-left: 90px;
color: darkgrey;
user-select: none;
cursor: pointer;
padding-bottom: 10px;
border-bottom: 2px solid darkgrey;
}
.nav > span.active {
color: black;
border-bottom: 3px solid black;
padding-bottom: 9px;
}
.el-input, .el-button {
margin-top: 40px;
}
.el-button {
width: 100%;
font-size: 18px;
}
.foot > span {
float: right;
margin-top: 20px;
color: orange;
cursor: pointer;
}
.sms {
color: orange;
cursor: pointer;
display: inline-block;
width: 70px;
text-align: center;
user-select: none;
}
</style>
3. 腾讯短信功能二次封装
3.1 脚本测试发短信
sdk:https://cloud.tencent.com/document/product/382/43196#
使用步骤:
-下载模块:pip3 install tencentcloud-sdk-python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from tencentcloud.common import credential
from tencentcloud.common.exception.tencent_cloud_sdk_exception import TencentCloudSDKException
# 导入对应产品模块的client models。
from tencentcloud.sms.v20210111 import sms_client, models
# 导入可选配置类
from tencentcloud.common.profile.client_profile import ClientProfile
from tencentcloud.common.profile.http_profile import HttpProfile
try:
# 必要步骤:
# 实例化一个认证对象,入参需要传入腾讯云账户密钥对secretId,secretKey。
# 这里采用的是从环境变量读取的方式,需要在环境变量中先设置这两个值。
# 你也可以直接在代码中写死密钥对,但是小心不要将代码复制、上传或者分享给他人,
# 以免泄露密钥对危及你的财产安全。
# SecretId、SecretKey 查询: https://console.cloud.tencent.com/cam/capi
cred = credential.Credential("secretId", "secretKey")
# cred = credential.Credential(
# os.environ.get(""),
# os.environ.get("")
# )
# 实例化一个http选项,可选的,没有特殊需求可以跳过。
httpProfile = HttpProfile()
# 如果需要指定proxy访问接口,可以按照如下方式初始化hp(无需要直接忽略)
# httpProfile = HttpProfile(proxy="http://用户名:密码@代理IP:代理端口")
httpProfile.reqMethod = "POST" # post请求(默认为post请求)
httpProfile.reqTimeout = 30 # 请求超时时间,单位为秒(默认60秒)
httpProfile.endpoint = "sms.tencentcloudapi.com" # 指定接入地域域名(默认就近接入)
# 非必要步骤:
# 实例化一个客户端配置对象,可以指定超时时间等配置
clientProfile = ClientProfile()
clientProfile.signMethod = "TC3-HMAC-SHA256" # 指定签名算法
clientProfile.language = "en-US"
clientProfile.httpProfile = httpProfile
# 实例化要请求产品(以sms为例)的client对象
# 第二个参数是地域信息,可以直接填写字符串ap-guangzhou,支持的地域列表参考 https://cloud.tencent.com/document/api/382/52071#.E5.9C.B0.E5.9F.9F.E5.88.97.E8.A1.A8
client = sms_client.SmsClient(cred, "ap-guangzhou", clientProfile)
# 实例化一个请求对象,根据调用的接口和实际情况,可以进一步设置请求参数
# 你可以直接查询SDK源码确定SendSmsRequest有哪些属性可以设置
# 属性可能是基本类型,也可能引用了另一个数据结构
# 推荐使用IDE进行开发,可以方便的跳转查阅各个接口和数据结构的文档说明
req = models.SendSmsRequest()
# 基本类型的设置:
# SDK采用的是指针风格指定参数,即使对于基本类型你也需要用指针来对参数赋值。
# SDK提供对基本类型的指针引用封装函数
# 帮助链接:
# 短信控制台: https://console.cloud.tencent.com/smsv2
# 腾讯云短信小助手: https://cloud.tencent.com/document/product/382/3773#.E6.8A.80.E6.9C.AF.E4.BA.A4.E6.B5.81
# 短信应用ID: 短信SdkAppId在 [短信控制台] 添加应用后生成的实际SdkAppId,示例如1400006666
# 应用 ID 可前往 [短信控制台](https://console.cloud.tencent.com/smsv2/app-manage) 查看
req.SmsSdkAppId = "1400787878"
# 短信签名内容: 使用 UTF-8 编码,必须填写已审核通过的签名
# 签名信息可前往 [国内短信](https://console.cloud.tencent.com/smsv2/csms-sign) 或 [国际/港澳台短信](https://console.cloud.tencent.com/smsv2/isms-sign) 的签名管理查看
req.SignName = "腾讯云"
# 模板 ID: 必须填写已审核通过的模板 ID
# 模板 ID 可前往 [国内短信](https://console.cloud.tencent.com/smsv2/csms-template) 或 [国际/港澳台短信](https://console.cloud.tencent.com/smsv2/isms-template) 的正文模板管理查看
req.TemplateId = "449739"
# 模板参数: 模板参数的个数需要与 TemplateId 对应模板的变量个数保持一致,,若无模板参数,则设置为空
req.TemplateParamSet = ["1234"]
# 下发手机号码,采用 E.164 标准,+[国家或地区码][手机号]
# 示例如:+8613711112222, 其中前面有一个+号 ,86为国家码,13711112222为手机号,最多不要超过200个手机号
req.PhoneNumberSet = ["+8613711112222"]
# 用户的 session 内容(无需要可忽略): 可以携带用户侧 ID 等上下文信息,server 会原样返回
req.SessionContext = ""
# 短信码号扩展号(无需要可忽略): 默认未开通,如需开通请联系 [腾讯云短信小助手]
req.ExtendCode = ""
# 国际/港澳台短信 senderid(无需要可忽略): 国内短信填空,默认未开通,如需开通请联系 [腾讯云短信小助手]
req.SenderId = ""
resp = client.SendSms(req)
# 输出json格式的字符串回包
print(resp.to_json_string(indent=2))
# 当出现以下错误码时,快速解决方案参考
# - [FailedOperation.SignatureIncorrectOrUnapproved](https://cloud.tencent.com/document/product/382/9558#.E7.9F.AD.E4.BF.A1.E5.8F.91.E9.80.81.E6.8F.90.E7.A4.BA.EF.BC.9Afailedoperation.signatureincorrectorunapproved-.E5.A6.82.E4.BD.95.E5.A4.84.E7.90.86.EF.BC.9F)
# - [FailedOperation.TemplateIncorrectOrUnapproved](https://cloud.tencent.com/document/product/382/9558#.E7.9F.AD.E4.BF.A1.E5.8F.91.E9.80.81.E6.8F.90.E7.A4.BA.EF.BC.9Afailedoperation.templateincorrectorunapproved-.E5.A6.82.E4.BD.95.E5.A4.84.E7.90.86.EF.BC.9F)
# - [UnauthorizedOperation.SmsSdkAppIdVerifyFail](https://cloud.tencent.com/document/product/382/9558#.E7.9F.AD.E4.BF.A1.E5.8F.91.E9.80.81.E6.8F.90.E7.A4.BA.EF.BC.9Aunauthorizedoperation.smssdkappidverifyfail-.E5.A6.82.E4.BD.95.E5.A4.84.E7.90.86.EF.BC.9F)
# - [UnsupportedOperation.ContainDomesticAndInternationalPhoneNumber](https://cloud.tencent.com/document/product/382/9558#.E7.9F.AD.E4.BF.A1.E5.8F.91.E9.80.81.E6.8F.90.E7.A4.BA.EF.BC.9Aunsupportedoperation.containdomesticandinternationalphonenumber-.E5.A6.82.E4.BD.95.E5.A4.84.E7.90.86.EF.BC.9F)
# - 更多错误,可咨询[腾讯云助手](https://tccc.qcloud.com/web/im/index.html#/chat?webAppId=8fa15978f85cb41f7e2ea36920cb3ae1&title=Sms)
except TencentCloudSDKException as err:
print(err)

3.2 把发送短信封装成包
1. 后期别的项目,也有用到发送短信,只要把包copy到项目即可
2. 封装包:
目录结构
send_tx_sms #包名
__init__.py
settings.py # 配置文件
sms.py # 核心文件
init.py
from .sms import get_code, send_sms_by_phone
settings.py
SECRET_ID = ''
SECRET_KEY = ''
APP_ID = ''
SIGN_NAME=''
TEMPLATE_ID=''
sms.py
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from tencentcloud.common import credential
from tencentcloud.common.exception.tencent_cloud_sdk_exception import TencentCloudSDKException
# 导入对应产品模块的client models。
from tencentcloud.sms.v20210111 import sms_client, models
# 导入可选配置类
from tencentcloud.common.profile.client_profile import ClientProfile
from tencentcloud.common.profile.http_profile import HttpProfile
try:
# 必要步骤:
# 实例化一个认证对象,入参需要传入腾讯云账户密钥对secretId,secretKey。
# 这里采用的是从环境变量读取的方式,需要在环境变量中先设置这两个值。
# 你也可以直接在代码中写死密钥对,但是小心不要将代码复制、上传或者分享给他人,
# 以免泄露密钥对危及你的财产安全。
# SecretId、SecretKey 查询: https://console.cloud.tencent.com/cam/capi
cred = credential.Credential("AKIDgEcmHiwwiKisoWzMVQ7ZnbDblmY8WklY", "d2D9sMgngLmzyjGaicHzUlnaAWdWBbmj")
# cred = credential.Credential(
# os.environ.get(""),
# os.environ.get("")
# )
# 实例化一个http选项,可选的,没有特殊需求可以跳过。
httpProfile = HttpProfile()
# 如果需要指定proxy访问接口,可以按照如下方式初始化hp(无需要直接忽略)
# httpProfile = HttpProfile(proxy="http://用户名:密码@代理IP:代理端口")
httpProfile.reqMethod = "POST" # post请求(默认为post请求)
httpProfile.reqTimeout = 30 # 请求超时时间,单位为秒(默认60秒)
httpProfile.endpoint = "sms.tencentcloudapi.com" # 指定接入地域域名(默认就近接入)
# 非必要步骤:
# 实例化一个客户端配置对象,可以指定超时时间等配置
clientProfile = ClientProfile()
clientProfile.signMethod = "TC3-HMAC-SHA256" # 指定签名算法
clientProfile.language = "en-US"
clientProfile.httpProfile = httpProfile
# 实例化要请求产品(以sms为例)的client对象
# 第二个参数是地域信息,可以直接填写字符串ap-guangzhou,支持的地域列表参考 https://cloud.tencent.com/document/api/382/52071#.E5.9C.B0.E5.9F.9F.E5.88.97.E8.A1.A8
client = sms_client.SmsClient(cred, "ap-guangzhou", clientProfile)
# 实例化一个请求对象,根据调用的接口和实际情况,可以进一步设置请求参数
# 你可以直接查询SDK源码确定SendSmsRequest有哪些属性可以设置
# 属性可能是基本类型,也可能引用了另一个数据结构
# 推荐使用IDE进行开发,可以方便的跳转查阅各个接口和数据结构的文档说明
req = models.SendSmsRequest()
# 基本类型的设置:
# SDK采用的是指针风格指定参数,即使对于基本类型你也需要用指针来对参数赋值。
# SDK提供对基本类型的指针引用封装函数
# 帮助链接:
# 短信控制台: https://console.cloud.tencent.com/smsv2
# 腾讯云短信小助手: https://cloud.tencent.com/document/product/382/3773#.E6.8A.80.E6.9C.AF.E4.BA.A4.E6.B5.81
# 短信应用ID: 短信SdkAppId在 [短信控制台] 添加应用后生成的实际SdkAppId,示例如1400006666
# 应用 ID 可前往 [短信控制台](https://console.cloud.tencent.com/smsv2/app-manage) 查看
req.SmsSdkAppId = "1400763885"
# 短信签名内容: 使用 UTF-8 编码,必须填写已审核通过的签名
# 签名信息可前往 [国内短信](https://console.cloud.tencent.com/smsv2/csms-sign) 或 [国际/港澳台短信](https://console.cloud.tencent.com/smsv2/isms-sign) 的签名管理查看
req.SignName = "张的不坏公众号"
# 模板 ID: 必须填写已审核通过的模板 ID
# 模板 ID 可前往 [国内短信](https://console.cloud.tencent.com/smsv2/csms-template) 或 [国际/港澳台短信](https://console.cloud.tencent.com/smsv2/isms-template) 的正文模板管理查看
req.TemplateId = "1603745"
# 模板参数: 模板参数的个数需要与 TemplateId 对应模板的变量个数保持一致,,若无模板参数,则设置为空
req.TemplateParamSet = ["1234", "5"]
# 下发手机号码,采用 E.164 标准,+[国家或地区码][手机号]
# 示例如:+8613711112222, 其中前面有一个+号 ,86为国家码,13711112222为手机号,最多不要超过200个手机号
req.PhoneNumberSet = ["+8618437014545"]
# 用户的 session 内容(无需要可忽略): 可以携带用户侧 ID 等上下文信息,server 会原样返回
req.SessionContext = ""
# 短信码号扩展号(无需要可忽略): 默认未开通,如需开通请联系 [腾讯云短信小助手]
req.ExtendCode = ""
# 国际/港澳台短信 senderid(无需要可忽略): 国内短信填空,默认未开通,如需开通请联系 [腾讯云短信小助手]
req.SenderId = ""
resp = client.SendSms(req)
# 输出json格式的字符串回包
print(resp.to_json_string(indent=2))
# 当出现以下错误码时,快速解决方案参考
# - [FailedOperation.SignatureIncorrectOrUnapproved](https://cloud.tencent.com/document/product/382/9558#.E7.9F.AD.E4.BF.A1.E5.8F.91.E9.80.81.E6.8F.90.E7.A4.BA.EF.BC.9Afailedoperation.signatureincorrectorunapproved-.E5.A6.82.E4.BD.95.E5.A4.84.E7.90.86.EF.BC.9F)
# - [FailedOperation.TemplateIncorrectOrUnapproved](https://cloud.tencent.com/document/product/382/9558#.E7.9F.AD.E4.BF.A1.E5.8F.91.E9.80.81.E6.8F.90.E7.A4.BA.EF.BC.9Afailedoperation.templateincorrectorunapproved-.E5.A6.82.E4.BD.95.E5.A4.84.E7.90.86.EF.BC.9F)
# - [UnauthorizedOperation.SmsSdkAppIdVerifyFail](https://cloud.tencent.com/document/product/382/9558#.E7.9F.AD.E4.BF.A1.E5.8F.91.E9.80.81.E6.8F.90.E7.A4.BA.EF.BC.9Aunauthorizedoperation.smssdkappidverifyfail-.E5.A6.82.E4.BD.95.E5.A4.84.E7.90.86.EF.BC.9F)
# - [UnsupportedOperation.ContainDomesticAndInternationalPhoneNumber](https://cloud.tencent.com/document/product/382/9558#.E7.9F.AD.E4.BF.A1.E5.8F.91.E9.80.81.E6.8F.90.E7.A4.BA.EF.BC.9Aunsupportedoperation.containdomesticandinternationalphonenumber-.E5.A6.82.E4.BD.95.E5.A4.84.E7.90.86.EF.BC.9F)
# - 更多错误,可咨询[腾讯云助手](https://tccc.qcloud.com/web/im/index.html#/chat?webAppId=8fa15978f85cb41f7e2ea36920cb3ae1&title=Sms)
except TencentCloudSDKException as err:
print(err)
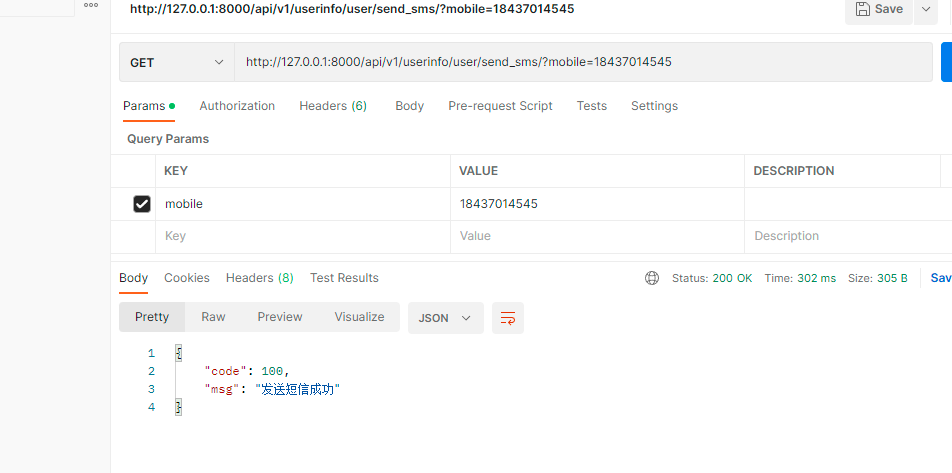
4. 短信验证码接口
前端通过 get http://127.0.0.1:8000/api/v1/userinfo/user/send_sms/?mobile=12324344
class UserView(ViewSet):
@action(methods=['GET'], detail=False)
def send_sms(self, request):
mobile = request.query_params.get('mobile')
if re.match(r'^1[3-9][0-9]{9}$', mobile):
code = get_code()
print(code) # 保存验证码---》能存,不能丢,后期能取---》缓存--》django自带缓存框架
# 放在内存中了,只要重启就没了----》后期学完redis,放到redis中,重启项目,还在
cache.set('sms_code_%s' % mobile, code)
# cache.get('sms_code_%s'%mobile)
res = send_sms_by_phone(mobile, code)
if res:
return APIResponse(msg='发送短信成功')
else:
# raise APIException('发送短信失败')
return APIResponse(msg='发送短信失败', code=101)
else:
return APIResponse(msg='手机号不合法', code=102)
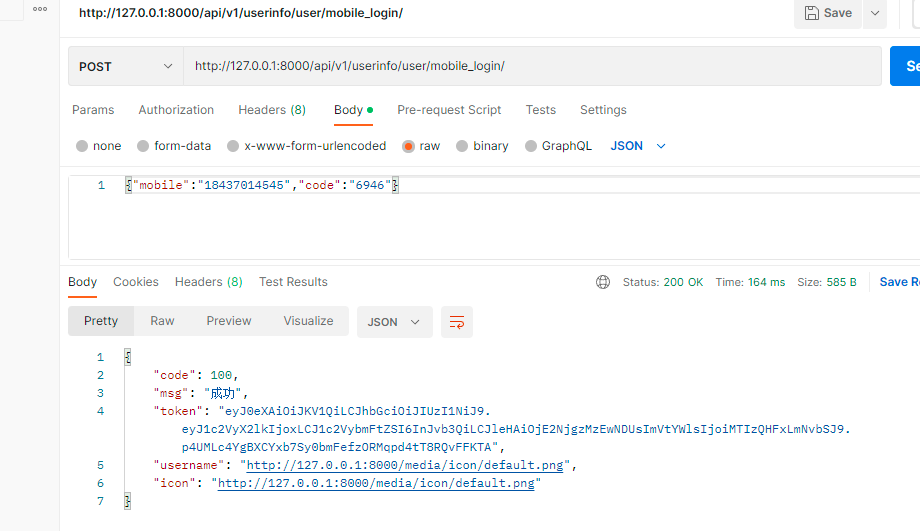
5. 短信登录接口
http://127.0.0.1:8000/api/v1/userinfo/user/mobile_login/
views.py
import re
from django.shortcuts import render
# Create your views here.
from rest_framework.exceptions import APIException
from rest_framework.viewsets import ViewSet, GenericViewSet, ViewSetMixin
from rest_framework.decorators import action
from .models import UserInfo
from .serializer import UserMulLoginSerializer, UserMobileLoginSerializer
from libs.send_tx_sms import get_code, send_sms_by_phone
from django.core.cache import cache
from utils.response import APIResponse
class UserView(ViewSet):
def get_serializer(self, data):
# 判断如果请求的action是:mul_login,返回UserMulLoginSerializer
# 判断如果请求的action是:mobile_login,返回UserMobileLoginSerializer
if self.action == 'mul_login':
return UserMulLoginSerializer(data=data)
else:
return UserMobileLoginSerializer(data=data)
def common_login(self, request):
ser = self.get_serializer(data=request.data)
ser.is_valid(raise_exception=True)
token = ser.context.get('token')
username = ser.context.get('icon')
icon = ser.context.get('icon')
return APIResponse(token=token, username=username, icon=icon)
@action(methods=['POST'], detail=False)
def mul_login(self, request):
return self.common_login(request)
# # # 1. 老写法
# # username=request.data.get('username')
# # password=request.data.get('password')
# # # 2. 查询用户
# # UserInfo.objects.filter(username=username,password=password)
# # # 3. 签发token
# # # 4. 返回
# # 1. 新写法,使用序列化类
# ser = UserMulLoginSerializer(data=request.data)
# # jwt 模块的登录就是这么写的
# ser.is_valid(raise_exception=True) # 会执行:序列化类字段自己的校验规则,局部钩子,全局钩子
# # 用户名密码校验通过了,在序列化类中--->签发token
# token = ser.context.get('token')
# username = ser.context.get('username')
# icon = ser.context.get('icon') # icon是个对象 字符串
# return APIResponse(token=token, username=username,
# icon=icon) # 前端看到的样子{code:100,msg:成功,token:adsfa,username:root,icon:http://adsfasd.png}
@action(methods=['POST'], detail=False)
def mobile_login(self, request):
return self.common_login(request)
@action(methods=['GET'], detail=False)
def mobile(self, request):
try:
mobile = request.query_params.get('mobile')
UserInfo.objects.get(mobile=mobile) # 有且只有一个才不报错,
return APIResponse(msg='手机号存在') # {code:100,msg:手机号存在}
except Exception as e:
raise APIException('手机号不存在') # {code:999,msg:手机号不存在}
@action(methods=['GET'], detail=False)
def send_sms(self, request):
mobile = request.query_params.get('mobile')
if re.match(r'^1[3-9][0-9]{9}$', mobile):
code = get_code()
print(code) # 保存验证码-->能存,不能丢,后期能取-->缓存-->django自带缓存框架
# 放在内存中了,只要重启就没了-->后期学完redis,放到redis中,重启项目,还在
cache.set('sms_code_%s' % mobile, code)
# cache.get('sms_code_%s'%mobile)
res = send_sms_by_phone(mobile, code)
if res:
return APIResponse(msg='发送短信成功')
else:
# raise APIException('发送短信失败')
return APIResponse(msg='发送短信失败', code=101)
else:
return APIResponse(msg='手机号不合法', code=102)
serializer.py
from rest_framework import serializers
from .models import UserInfo
import re
from django.contrib.auth import authenticate
from rest_framework.exceptions import ValidationError, APIException
from rest_framework_jwt.settings import api_settings
jwt_payload_handler = api_settings.JWT_PAYLOAD_HANDLER
jwt_encode_handler = api_settings.JWT_ENCODE_HANDLER
from django.core.cache import cache
# 这个序列类,只用来做登录校验,不做序列化,不做反序列化
class UserMulLoginSerializer(serializers.ModelSerializer):
username = serializers.CharField() # 重写,优先用现在的,就没有unique的限制了
class Meta:
model = UserInfo
fields = ['username', 'password']
# 封装之隐藏属性 __表示隐藏, _并不是隐藏,公司里约定俗成用 _ 表示只在内部用,如果外部想用,也可以用
def _get_user(self, attrs):
# attrs 是校验过后的数据:字段自己的规则【字段自己有规则:坑】和局部钩子
username = attrs.get('username')
password = attrs.get('password')
# username可能是用户名,邮箱,手机号---》使用正则判断
if re.match(r'^1[3-9][0-9]{9}$', username):
# authenticate:只能使用username和password去校验用户
# user = authenticate(mobile=username, password=password)
user = UserInfo.objects.filter(mobile=username).first()
elif re.match(r'^.+@.+$', username): # adsa@adsf 会有bug,用户名中如果有@,登录不了了
# user = authenticate(email=username, password=password)
user = UserInfo.objects.filter(email=username).first()
else:
# user = authenticate(username=username, password=password)
user = UserInfo.objects.filter(username=username).first()
if user and user.check_password(password):
return user
else:
# raise ValidationError('用户名或密码错误') non_fields_error
raise APIException('用户名或密码错误') # 读了源码,抛出APIException也会被捕获
def _get_token(self, user):
try:
payload = jwt_payload_handler(user)
token = jwt_encode_handler(payload)
return token
except Exception as e:
raise APIException(str(e))
# 还要写别的
def validate(self, attrs):
# 1 取出用户名和密码,校验用户是否存在
user = self._get_user(attrs)
# 2 签发token
token = self._get_token(user)
# 3 把token放到序列化类对象中
self.context['token'] = token
self.context['username'] = user.username
self.context['icon'] = 'http://127.0.0.1:8000/media/' + str(user.icon) # 这是个对象,可能会有问题
# self.context['icon'] = user.icon # 这是个对象,可能会有问题
# 以后如果有问题,都抛异常
# 如没有问题,返回attrs
return attrs
class UserMobileLoginSerializer(serializers.ModelSerializer):
code = serializers.CharField() # code 不是UserInfo表的字段,一定要重写一下
mobile = serializers.CharField()
class Meta:
model = UserInfo
fields = ['mobile', 'code']
def _get_user(self, attrs):
mobile = attrs.get('mobile')
code = attrs.get('code')
# 校验code是否正确
old_code = cache.get('sms_code_%s' % mobile)
cache.set('sms_code_%s' % mobile, '') # 验证码用过了要清除
if code == old_code: # 万能验证码,在测试阶段,测试用的
user = UserInfo.objects.filter(mobile=mobile).first()
return user
raise APIException('验证码错误')
def _get_token(self, user):
try:
payload = jwt_payload_handler(user)
token = jwt_encode_handler(payload)
return token
except Exception as e:
raise APIException(str(e))
def validate(self, attrs):
# 1 手机号和code
user = self._get_user(attrs)
# 2 签发token
token = self._get_token(user)
# 3 把token放到序列化类对象中
self.context['token'] = token
self.context['username'] = user.username
self.context['icon'] = 'http://127.0.0.1:8000/media/' + str(user.icon)
return attrs
6. python的深浅copy
浅拷贝,指的是重新分配一块内存,创建一个新的对象,但里面的元素是原对象中各个子对象的引用。
深拷贝,是指重新分配一块内存,创建一个新的对象,并且将原对象中的元素,以递归的方式,通过创建新的子对象拷贝到新对象中。因此,新对象和原对象没有任何关联。
浅拷贝
使用数据类型本身的构造器
对于可变的序列,还可以通过切片操作符 : 来完成浅拷贝
Python 还提供了对应的函数 copy.copy() 函数,适用于任何数据类型
深拷贝
Python 中以 copy.deepcopy() 来实现对象的深度拷贝
7. __new__和__init__的区别
【同】
二者均是Python面向对象语言中的函数,__new__比较少用,__init__则用的比较多。
【异】
__new__是在实例创建之前被调用的,因为它的任务就是创建实例然后返回该实例对象,是个静态方法。
__init__是当实例对象创建完成后被调用的,然后设置对象属性的一些初始值,通常用在初始化一个类实例的时候。是一个实例方法。
也就是: __new__先被调用,__init__后被调用,__new__的返回值(实例)将传递给__init__方法的第一个参数,然后__init__给这个实例设置一些参数。
1、继承自object的新式类才有__new__
2、__new__至少要有一个参数cls,代表当前类,此参数在实例化时由Python解释器自动识别
3、__new__必须要有返回值,返回实例化出来的实例,这点在自己实现__new__时要特别注意,可以return父类(通过super(当前类名, cls))__new__出来的实例,或者直接是object的__new__出来的实例
4、__init__有一个参数self,就是这个__new__返回的实例,__init__在__new__的基础上可以完成一些其它初始化的动作,__init__不需要返回值
5、如果__new__创建的是当前类的实例,会自动调用__init__函数,通过return语句里面调用的__new__函数的第一个参数是 cls 来保证是当前类实例,如果是其他类的类名,;那么实际创建返回的就是其他类的实例,其实就不会调用当前类的__init__函数,也不会调用其他类的__init__函数。
6、在定义子类时没有重新定义__new__()时,Python默认是调用该类的直接父类的__new__()方法来构造该类的实例,如果该类的父类也没有重写__new__(),那么将一直按此规矩追溯至object的__new__()方法,因为object是所有新式类的基类。
7、而如果子类中重写了__new__()方法,那么你可以自由选择任意一个的其他的新式类(必定要是新式类,只有新式类必定都有__new__(),因为所有新式类都是object的后代,而经典类则没有__new__()方法)的__new__()方法来制造实例,包括这个新式类的所有前代类和后代类,只要它们不会造成递归死循环。反正肯定不能调用自己的__new__,这肯定是死循环。
8、对于子类的__init__,其调用规则跟__new__是一致的,当然如果子类和父类的__init__函数都想调用,可以在子类的__init__函数中加入对父类__init__函数的调用。
9、我们在使用时,尽量使用__init__函数,不要去自定义__new__函数,因为这两者在继承派生时的特性还是很不一样的。
10、将类比作制造商,__new__方法就是前期的原材料购买环节,__init__方法就是在有原材料的基础上,加工,初始化商品环节
8. python 是值传递还是引用传递
python参数传递统一使用的是引用传递方式,因为python对象分为分为可变对象(list,dict,set等)和不可变对象(number,string,tuple等)
当传递参数是可变对象的引用时,因为可变对象的值可以修改,因此可以通过修改参数值而修改原对象
当传递参数是不可变对象的引用时,虽然传递的是引用,参数变量和原变量都指向同一内存地址,但是不可变对象无法修改,所以参数的重新赋值不会影响原对象
9. 什么是可变类型和不可变类型?
可变的:列表、集合、字典(可以进行更改,并且更改后物理地址不会发生改变)
不可变的:数字、字符串、元组(不可以进行更改,更改后就是一个新的对象了,物理地址发生了变化)


