day45——存储引擎、数据类型、约束条件
今日内容
- 存储引擎
- 数据类型
- 约束条件
一、存储引擎
在日常生活中,文件的格式以有很多种,不同类型的文件有不同的存储方式和处理机制(图片:png、音乐:MP3、文档:word)。
针对不同的数据应该用不同的处理机制来存储,而存储引擎就是存储的处理机制。
mysql主要的 存储引擎
-
Innodb
是Mysql5.5版本之后默认的存储引擎, 存储数据更加的安全,确保数据的安全选性
-
myisam
是MySQL5.5版本之前的存储引擎,存储的速度比Inondb快,但是无法保证数据的安全性,速度虽快,但是我们一般注重的是数据的安全性
-
memory
为内存引擎(数据存放在内存中),数据断电即丢失
-
blackhole
听名字就知道,黑洞嘛,无论放入什么数据,都会消失。
各引擎存数据的异同点
# 查看所有的存储引擎
show engines;
# 用四种不同的存储引擎创建表
create table t1(id int) engine=innodb;
create table t2(id int) engine=myisam;
create table t3(id int) engine=blackhole;
create table t4(id int) engine=memory;
存数据的文件中看不同存储引擎创建的表都有哪些数据,如下图
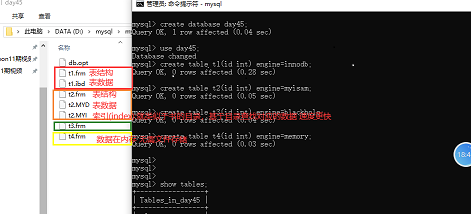
# 往每张表中存数据,并查看表中的数据
insert t1 values(1);
select * from t1;
"""
+------+
| id |
+------+
| 1 |
+------+"""
insert t2 values(1);
select * from t2;
"""
+------+
| id |
+------+
| 1 |
+------+"""
insert t3 values(1);
select * from t3;
"""
Empty set (0.00 sec) # 因为写的数据都会消失,所以表中无数据为空
"""
insert t4 values(1);
select * from t4;
"""
+------+
| id |
+------+
| 1 |
+------+ # 数据存在内存中,查询表中有数据
"""
select * form t4; # 重启服务端,再查
"""
Empty set (0.00 sec) # 数据存于内存中重启数据丢失,表为空
"""
创建表的完整语法
# 语法
create tabel 表名(
字段名1 类型(宽度) 约束条件,
字段名2 类型(宽度) 约束条件
)
# 注意
1 在同一张表中字段名不能重复
2 宽度和约束条件是可选的,可写可不写,而字段名和字段类型是必须写的
约束条件还可以写多个
3 最后一行不能有逗号
create table t6(
id int,
name char,
); 报错
# 补充
宽度一般情况下指的是对存储数据的限制
create table t7(name char); 默认宽度是1
insert into t7 values('jason');
insert into t7 values(null); 关键字NULL
针对不同的版本会出现不同的效果
5.6 版本默认没有开启严格模式 规定只能存一个字符你给了多个字符,那么会自动帮你截取
"""
+------+
| name |
+------+
| j | # 给多个字符自动截取第一个字符
| NULL | # 空
"""
5.7 版本及以上或者开启了严格模式 那么规定只能存几个,不能超出,一旦超出范围立刻报错 Data too long for ....
# 严格模式需不需要开
MySQL5.7之后的版本是默认开启严格模式的
使用数据库的准则:能尽量人啊过数据库少干存取数据之外的其他事,不要给数据库增加额外的压力。
# 约束条件 null 、not null后者限制不能插入null
create table t8 (id int, name char null);
insert into t8 values(1,null);
"""
ERROR 1048 (23000): Column 'name' cannot be null"""
"""
宽度和约束条件到底是什么关系
宽度是用来限制数据的存储,约束条件是在宽度的基础上增加的额外的约束
"""
二、数据类型
整形
-
分类
TINYINT、SMALLINT、MEDUIMINT、INT、BIGINT
-
作用
主要用来存储年龄、等级、id、号码等
"""
以TINYINT为例
1 默认情况下都是带符号的
2 超出存储限制只存最大可接受值"""
create table t9(id tinyint);
insert into t9 values(-129),(256);
select * from t9;
"""
+------+
| id |
+------+
| -128 |
| 127 |
+------+ # 无符号范围-128到127
"""
# 约束条件unsigned 无符号
create table t10(id tinyint unsigned);
select * from t10;
"""
+------+
| id |
+------+
| 0 |
| 255 | # 无符号范围0到255
"""
"""整型INT"""
create table t11(id int);
# int 默认也是有符号的,也就是说整型默认情况下都是有符号的。
# 上述提到,括号内的宽度一般是用来限制存储数据的位数,那整型括号内的也是如此嘛?
create table t12(id int(8));
insert into t12 values(123456789); # 存九位的数据
select * from t12;
"""
+-----------+
| id |
+-----------+
| 123456789 | # 九位数都显示了,也就是说括号内的参数不是用来限制储存位数的
+-----------+"""
# 用0填充
create table t13(id int(8) unsigned zerofill);
insert into t13 values(1);
select * from t13;
"""
+----------+
| id |
+----------+
| 00000001 |
+----------+"""
# 总结
"""
整型是个特例,括号里的数字不是用来限制位数的
id int(8)
如果数字没有超过8位,用空格填充至八位
如果超出八位,那么有几位就存几位,前提在最大范围内"""
针对整型字段 括号内无需指定宽度 因为它默认的宽度以及足够显示所有的数据了
严格模式
# 如果查看严格模式
show variables like "%mode";
"""
sql_mode | NO_ENGINE_SUBSTITUTION |
+----------------------------+------------------------+
"""
ps:模糊匹配/查询
"""
关键字 like
%:匹配任意多个字符
_: 匹配任意单个字符
"""
# 修改严格模式
set session # 只在当前窗口有效
set global # 全局有效
set global sql_mode='STRICT_TRANS_TABLES'; # 修改后需重新进入服务端即可,刷新一下
浮点型
-
分类
FLOAT、DOUBLE、DECIMAL
-
作用
记录身高、体重、薪资等带有小时的数字
# 存储限制
float (255,30) # 总共255位,小数部分占30位
double(255,30) # 总共255位,小数部分占30位
decimale(65,30) # 总共65位,小数 部分占30位
# 精确度验证
create table t15(id float(255,30));
create table t16(id double(255,30));
create table t17(id decimal(65,30));
# 往表中插入浮点数,查看精确度
insert into t15 values(1.111111111111111111111111111111);
select * from t15;
"""
+----------------------------------+
| id |
+----------------------------------+
| 1.111111164093017600000000000000 |
+----------------------------------+
"""
insert into t16 values(1.111111111111111111111111111111);
select * from t16;
"""
+----------------------------------+
| 1.111111111111111200000000000000 |
+----------------------------------+"""
insert into t17 values(1.111111111111111111111111111111);
select * from t17;
"""
+----------------------------------+
| id |
+----------------------------------+
| 1.111111111111111111111111111111 |
+----------------------------------+"""
# 要结合实际应用场景 三者都能使用
字符类型
分类 :
-
char
定长
char(4) 数据超过四个字符直接报错,不够四个字符用空格补全
-
varchar
变长
varchar(4) 数据超过四个也是直接报错,不够四个字符有几个存几个
create table t18(name char(4));
create table t19(name varchar(4));
insert into t18 values('a');
insert into t19 values('a');
#char_length统计字段长度
select char_length(name) from t18;
"""
+-------------------+
| char_length(name) |
+-------------------+
| 1 |
+-------------------+"""
select char_length(name) from t19;
"""
+-------------------+
| char_length(name) |
+-------------------+
| 1 |
+-------------------+"""
"""
长度都为一这是为什么呢?
首先可以肯定的是 char硬盘上存的绝对是带有空格的数据,
但是在显示的时候MySQL会自动的将多余的空格剔除"""
# 再次修改sql_mode 让MySQL不要做自动剔除的操作
set global sql_mode=
'STRICT_TRANS_TABLES,PAD_CHAR_TO_FULL_LENGTH';
# 修改模式后重复上述操作,重新进入服务端在查询的第一个表name字符的长度位4,第二个为1。
char、varcahr对比
"""
char
缺点:浪费空间
优点:存取都很简单
直接按照固定的字符存取数据即可
jason egon alex wusir tank
存按照五个字符存 取也直接按照五个字符取
varchar
优点:节省空间
缺点:存取较为麻烦
1bytes+jason 1bytes+egon 1bytes+alex 1bytes+tank
存的时候需要制作报头
取的时候也需要先读取报头 之后才能读取真实数据
以前基本上都是用的char 其实现在用varchar的也挺多
"""
补充:
进来公司之后你完全不需要考虑字段类型和字段名
因为产品经理给你发的邮件上已经全部指明了
时间类型
分类:
- date——年月日 2020-5-4
- datetime——年月日时分秒 2020-5-4 11:11:11
- time——时分秒 11:11:11
- year——年 2020
create table student(
id int,
name varchar(16),
born_year year,
birth datE,
study_time time,
reg_time datetime
);
insert into student values(1,'tom','2000','2000-1-1','11:11:11','2000-1-1 11:11:11');
select * from student;
"""
+------+------+-----------+------------+------------+---------------------+
| id | name | born_year | birth | study_time | reg_time |
+------+------+-----------+------------+------------+---------------------+
| 1 | tom | 2000 | 2000-01-01 | 11:11:11 | 2000-01-01 11:11:11 |
+------+------+-----------+------------+------------+---------------------+"""
枚举与集合类型
- 枚举(enum) 多选一
- 集合(set) 多选多
具体使用:
# 枚举
create table user(
id int,
name char(16),
gender enum('male','female','others')
);
insert into user values(1,'user_1','male'); # 正常
insert into user values(2,'user_2','female'); # 正常
insert into user values(3,'user_3','others'); # 正常
insert into user values(4,'user_4','xxxxxxx'); # 报错
"""
ERROR 1265 (01000): Data truncated for column 'gender' at row 1
枚举字段在存数据的时候只能从枚举里面选择一个存储,存储没有列举的数据就会报错"""
# 集合
create table teacher(
id int,
name char(16),
gender enum('male','female'),
hobby set('read','shopping','play_basketball')
);
insert into teacher values (1,'tea_1','male','play_basketball');
insert into teacher values(2,'tea_2','female','shopping,read');
insert into teacher values(2,'tea_3','female','你们是我教过最差的一届...') # 报错
"""
集合可以写一个或者多个,但是不能写没有列举的"""


