自定义线程池拒绝策略
一、Executors提供四种线程池配置方案
1、构造一个固定线程数目的线程池,核心线程数与最大线程数相同,同时使用了一个无界LinkedBlockingQueue存放阻塞任务,因此多余的任务将存在阻塞队列,不会由RejectedExecutionHandler处理
//固定线程数目的线程池源码 public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads) { return new ThreadPoolExecutor(nThreads, nThreads, 0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>()); } //无界LinkedBlockingQueue源码 默认是Integer.MAX_VALUE大小,也可以指定大小 public LinkedBlockingQueue() { this(Integer.MAX_VALUE); } public LinkedBlockingQueue(int capacity) { if (capacity <= 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException(); this.capacity = capacity; last = head = new Node<E>(null); }
2、构造一个缓冲功能的线程池,配置核心线程数corePoolSize=0,最大线程数maximumPoolSize=Integer.MAX_VALUE,keepAliveTime=60s,以及一个无容量的阻塞队列 SynchronousQueue,因此任务提交之后,将会创建新的线程执行;线程空闲超过60s将会销毁
//缓冲功能的线程池源码 public static ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool() { return new ThreadPoolExecutor(0, Integer.MAX_VALUE, 60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>()); }
3、构造一个只支持一个线程的线程池,配置corePoolSize=maximumPoolSize=1,无界阻塞队列LinkedBlockingQueue;保证任务由一个线程串行执行
public static ExecutorService newSingleThreadExecutor() { return new FinalizableDelegatedExecutorService (new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1, 0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>())); }
4、构造有定时功能的线程池,配置corePoolSize,无界延迟阻塞队列DelayedWorkQueue;有意思的是:maximumPoolSize=Integer.MAX_VALUE,由于DelayedWorkQueue是无界队列,所以这个值是没有意义的
public static ScheduledExecutorService newScheduledThreadPool(int corePoolSize) { return new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(corePoolSize); } public static ScheduledExecutorService newScheduledThreadPool( int corePoolSize, ThreadFactory threadFactory) { return new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(corePoolSize, threadFactory); } public ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize, ThreadFactory threadFactory) { super(corePoolSize, Integer.MAX_VALUE, 0, TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS, new DelayedWorkQueue(), threadFactory); }
注意:阿里巴巴开发手册强调在日常编写代码时不要使用Executors显示的去创建线程池。

二 线程池执行流程
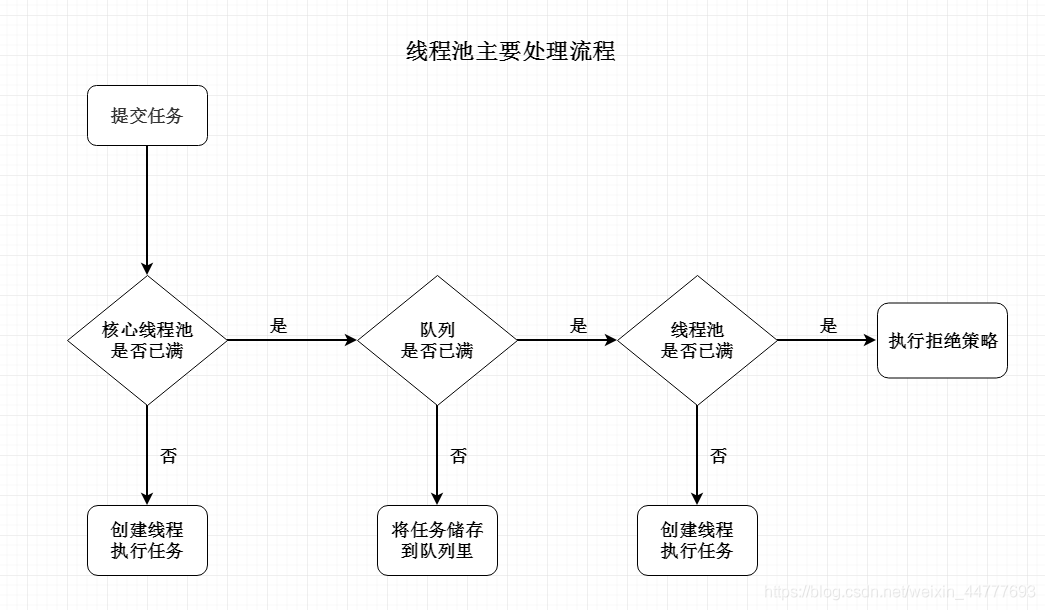
ThreadPoolExecutor最核心的构造方法源码
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize, //核心线程数 int maximumPoolSize, //最大线程数 long keepAliveTime, //线程池中超过核心线程数目的空闲线程最大存活时间 TimeUnit unit, //时间单位 BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,//阻塞任务队列 ThreadFactory threadFactory, //新建线程工厂 RejectedExecutionHandler handler //拒绝策略 //当提交任务数超过最大线程数+队列(maxmumPoolSize+workQueue)之和时, //任务会交给RejectedExecutionHandler来处理 ) { if (corePoolSize < 0 || maximumPoolSize <= 0 || maximumPoolSize < corePoolSize || keepAliveTime < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException(); if (workQueue == null || threadFactory == null || handler == null) throw new NullPointerException(); this.acc = System.getSecurityManager() == null ? null : AccessController.getContext(); this.corePoolSize = corePoolSize; this.maximumPoolSize = maximumPoolSize; this.workQueue = workQueue; this.keepAliveTime = unit.toNanos(keepAliveTime); this.threadFactory = threadFactory; this.handler = handler; }
//四种拒绝策略
RejectedExecutionHandler rejected = null;
rejected = new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy();//默认,队列满了丢任务抛出异常
rejected = new ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardPolicy();//队列满了丢任务不异常
rejected = new ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardOldestPolicy();//将最早进入队列的任务删,之后再尝试加入队列
rejected = new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy();//如果添加到线程池失败,那么主线程会自己去执行该任务
自定义线程池和自定义拒绝策略
import java.util.concurrent.*; import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger; public class MyThreadPoolExecutor { private ThreadPoolExecutor pool = null; public void init() { pool = new ThreadPoolExecutor( 1, 3, 5, TimeUnit.MINUTES, new ArrayBlockingQueue<Runnable>(5), new CustomThreadFactory(), new CustomRejectedExecutionHandler()); } public void destory() { if(pool != null) { pool.shutdownNow(); } } public ExecutorService getMyThreadPoolExecutor() { return this.pool; } /** * 自定义创建线程工厂 */ private class CustomThreadFactory implements ThreadFactory { private AtomicInteger count = new AtomicInteger(0); @Override public Thread newThread(Runnable r) { Thread t = new Thread(r); String threadName = MyThreadPoolExecutor.class.getSimpleName() + count.addAndGet(1); //System.out.println(threadName); t.setName(threadName); return t; } } /** * 自定义拒绝策略 */ private class CustomRejectedExecutionHandler implements RejectedExecutionHandler { @Override public void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor executor) { try { // 核心改造点,由blockingqueue的offer改成put阻塞方法 executor.getQueue().put(r); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } // 测试构造的线程池 public static void main(String[] args) { MyThreadPoolExecutor exec = new MyThreadPoolExecutor(); // 1.初始化 exec.init(); ExecutorService pool = exec.getMyThreadPoolExecutor(); MyTask task = new MyTask(); for(int i=0; i<1000; i++) { pool.execute(task); } try { Thread.sleep(5000); // 2.销毁----留点时间给线程池执行,因为任务没有提交执行完,如果销毁线程池,任务也就无法执行了 exec.destory(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } class MyTask implements Runnable{ public AtomicInteger i = new AtomicInteger(0); @Override public void run() { System.out.println("第"+i.getAndIncrement()+"次执行任务"); } }
执行结果:

//excute执行源码 public void execute(Runnable command) { if (command == null) throw new NullPointerException(); int c = ctl.get(); if (workerCountOf(c) < corePoolSize) { if (addWorker(command, true)) return; c = ctl.get(); } if (isRunning(c) && workQueue.offer(command)) { int recheck = ctl.get(); if (! isRunning(recheck) && remove(command)) reject(command); else if (workerCountOf(recheck) == 0) addWorker(null, false); } else if (!addWorker(command, false)) // 进入拒绝机制, 我们把runnable任务拿出来,重新用阻塞操作put,来实现提交阻塞功能 reject(command); }
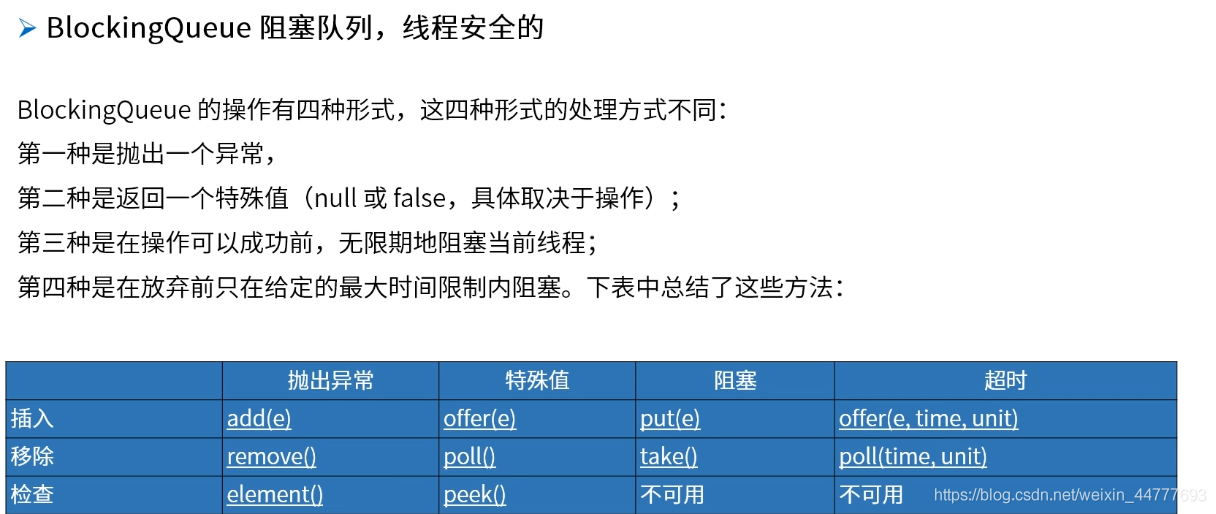
阻塞队列常见操作方法:
总结:
1、用ThreadPoolExecutor自定义线程池,看线程是的用途,如果任务量不大,可以用无界队列,如果任务量非常大,要用有界队列,防止OOM
2、如果任务量很大,还要求每个任务都处理成功,要对提交的任务进行阻塞提交,重写拒绝机制,改为阻塞提交。保证不抛弃一个任务
3、最大线程数一般设为2N+1最好,N是CPU核数,可以通过Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors();来获取
4、核心线程数,看应用,如果是任务,一天跑一次,设置为0,合适,因为跑完就停掉了,如果是常用线程池,看任务量,是保留一个核心还是几个核心线程数
转载:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_44777693/article/details/104569711




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 阿里最新开源QwQ-32B,效果媲美deepseek-r1满血版,部署成本又又又降低了!
· 开源Multi-agent AI智能体框架aevatar.ai,欢迎大家贡献代码
· Manus重磅发布:全球首款通用AI代理技术深度解析与实战指南
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
2017-04-22 集合对象与自定义javabean对象接收数据库查询的数据 (基础知识扫盲)