RocketMQ消费者设置了instanceName属性后消息竟不翼而飞
背景
RocketMQ使用过程中为了快速搭建消费服务,于是在同一个机器集群消费的方式起了多个消费者实例,结果发现部分消息没被消费到!本文是对问题产生原因的跟踪和分析,下面会将项目中遇到的问题简化成官方demo来说明。
问题重现
生产者代码
Producer.java
/* * Instantiate with a producer group name. * 默认分配4个消息队列 */ DefaultMQProducer producer = new DefaultMQProducer("producer_group"); producer.setNamesrvAddr("localhost:9876"); /* * Launch the instance. */ producer.start(); for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { try { /* * Create a message instance, specifying topic, tag and message body. */ Message msg = new Message("TopicTest" /* Topic */, "TagA" /* Tag */, ("Hello RocketMQ " + i).getBytes(RemotingHelper.DEFAULT_CHARSET) /* Message body */ ); SendResult sendResult = producer.send(msg); System.out.printf("%s%n", sendResult); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); Thread.sleep(1000); } }
启动一个producer实例发送10条消息到4个消息队列。
消息发送情况:
消息发送结果: queueId=2,消息内容: Hello RocketMQ 0 消息发送结果: queueId=3,消息内容: Hello RocketMQ 1 消息发送结果: queueId=0,消息内容: Hello RocketMQ 2 消息发送结果: queueId=1,消息内容: Hello RocketMQ 3 消息发送结果: queueId=2,消息内容: Hello RocketMQ 4 消息发送结果: queueId=3,消息内容: Hello RocketMQ 5 消息发送结果: queueId=0,消息内容: Hello RocketMQ 6 消息发送结果: queueId=1,消息内容: Hello RocketMQ 7 消息发送结果: queueId=2,消息内容: Hello RocketMQ 8 消息发送结果: queueId=3,消息内容: Hello RocketMQ 9
从发送结果可以看出消息发送的队列分配情况如下所示:

消费者代码
Consumer.java
/* * Instantiate with specified consumer group name. */ DefaultMQPushConsumer consumer = new DefaultMQPushConsumer("consumer_group"); consumer.setNamesrvAddr("localhost:9876"); //自定义instanceName consumer.setInstanceName("XUJIAN_MACBOOK"); /* * Subscribe one more more topics to consume. */ consumer.subscribe("TopicTest", "*"); /* * Register callback to execute on arrival of messages fetched from brokers. */ consumer.registerMessageListener(new MessageListenerConcurrently() { @Override public ConsumeConcurrentlyStatus consumeMessage(List<MessageExt> msgs, ConsumeConcurrentlyContext context) { System.out.printf("%s Receive New Messages: %s %n", Thread.currentThread().getName(), msgs); System.out.printf("msgBody: %s %n",new String(msgs.get(0).getBody())); return ConsumeConcurrentlyStatus.CONSUME_SUCCESS; } }); /* * Launch the consumer instance. */ consumer.start();
本地启动两个消费者实例,即consumer启动两次,设置为集群消费模式,且两个消费者实例属于同一个消费者组。
紊乱的消费结果
consumer1
ConsumeMessageThread_11 接收到新消息: queueId=0,消息内容: Hello RocketMQ 2 ConsumeMessageThread_14 接收到新消息: queueId=1,消息内容: Hello RocketMQ 6 ConsumeMessageThread_15 接收到新消息: queueId=0,消息内容: Hello RocketMQ 3 ConsumeMessageThread_16 接收到新消息: queueId=1,消息内容: Hello RocketMQ 7
consumer2
ConsumeMessageThread_6 接收到新消息: queueId=0,消息内容: Hello RocketMQ 2 ConsumeMessageThread_7 接收到新消息: queueId=1,消息内容: Hello RocketMQ 6 ConsumeMessageThread_8 接收到新消息: queueId=0,消息内容: Hello RocketMQ 3 ConsumeMessageThread_9 接收到新消息: queueId=1,消息内容: Hello RocketMQ 7
从消费结果可以看出消息消费的队列分配情况如下所示:

两个消费者消费了相同队列的相同消息,且部分消息没被消费到。这和预期的集群消费模式下消费者组内的消费者均分消息队列不符!
原因分析
当发现消费者消费异常时,首先应该排查消费负载均衡是否正常。
消费负载均衡
集群消费的时候会根据统一消费者组内消费者的数量、队列数量以及不同的策略来为每个消费者分配要消费的消息。
消费者的默认队列分配策略是“均分”,源码如下:
/** * Constructor specifying consumer group. * * @param consumerGroup Consumer group. */ public DefaultMQPushConsumer(final String consumerGroup) { this(null, consumerGroup, null, new AllocateMessageQueueAveragely()); }
其中AllocateMessageQueueAveragely就是平均分配策略,其他的还有随机等,均实现了AllocateMessageQueueStrategy接口。
RebalanceImpl.java
该类就是消息消费均衡类。
相关核心源码如下:
public void doRebalance(final boolean isOrder) { Map<String, SubscriptionData> subTable = this.getSubscriptionInner(); if (subTable != null) { for (final Map.Entry<String, SubscriptionData> entry : subTable.entrySet()) { final String topic = entry.getKey(); try { //根据topic进行reblance this.rebalanceByTopic(topic, isOrder); } catch (Throwable e) { if (!topic.startsWith(MixAll.RETRY_GROUP_TOPIC_PREFIX)) { log.warn("rebalanceByTopic Exception", e); } } } } this.truncateMessageQueueNotMyTopic(); } private void rebalanceByTopic(final String topic, final boolean isOrder) { ... //获取分配的结果 allocateResult = strategy.allocate( this.consumerGroup, this.mQClientFactory.getClientId(), mqAll, cidAll); ... }
又回到AllocateMessageQueueAveragely.java,上文提到这个类的策略是均分,那就来看看他是怎么做的。源码如下:AllocateMessageQueueAveragely.java
public List<MessageQueue> allocate(String consumerGroup/*消费者组*/, String currentCID/*clientId*/, List<MessageQueue> mqAll/*消息队列集合*/, List<String> cidAll/*消费者组里面的所有消费者的clientId*/) { if (currentCID == null || currentCID.length() < 1) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("currentCID is empty"); } if (mqAll == null || mqAll.isEmpty()) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("mqAll is null or mqAll empty"); } if (cidAll == null || cidAll.isEmpty()) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("cidAll is null or cidAll empty"); } List<MessageQueue> result = new ArrayList<MessageQueue>(); //如果消费者组里的消费者不包含当前这个消费者,直接返回 if (!cidAll.contains(currentCID)) { log.info("[BUG] ConsumerGroup: {} The consumerId: {} not in cidAll: {}", consumerGroup, currentCID, cidAll); return result; } //当前消费者在消费者集合里面的位置 int index = cidAll.indexOf(currentCID); //队列数对消费者数取模 int mod = mqAll.size() % cidAll.size(); //求当前消费者应该消费几个队列 int averageSize = mqAll.size() <= cidAll.size() ? 1 : (mod > 0 && index < mod ? mqAll.size() / cidAll.size() + 1 : mqAll.size() / cidAll.size()); //求当前消费者应该从哪个队列开始消费消息 int startIndex = (mod > 0 && index < mod) ? index * averageSize : index * averageSize + mod; int range = Math.min(averageSize, mqAll.size() - startIndex); //将当前消费者应该消费的队列一个一个放进返回结果列表 for (int i = 0; i < range; i++) { result.add(mqAll.get((startIndex + i) % mqAll.size())); } return result; }
可以发现消费者消费哪些队列是由
clientId决定的。
所以当两个消费者的clientId一样时,调用indexOf方法返回的是一样的结果,所以他们消费的队列是一样的。如上面的例子,总共有4个队列,2个消费者,所以两个消费者只消费了同样的两个队列:queueId=0、queueId=1。
clientId怎么生成
上面说了消费队列负载均衡的结果和clientId有关,那clientId是怎么生成的?
构建clientId的源码如下:
/** * clientId格式:ip+@+instanceName[+@unitName],通常你会看到形如127.0.0.1@32531这样的clientId * @return */ public String buildMQClientId() { StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); sb.append(this.getClientIP()); sb.append("@"); sb.append(this.getInstanceName()); if (!UtilAll.isBlank(this.unitName)) { sb.append("@"); sb.append(this.unitName); } return sb.toString(); }
clientId用来唯一标识一个
MQClientInstance。
可见clientId是根据instanceName属性、ip、unitName(可选)生成的。
为什么会生成相同的clientId
根据上面clientId的生成规则,两个消费者都在本地启动,意味着有相同的ip,unitName没有设置。
正巧两个消费者设置了相同的instanceName,那生成的clientId必然相同!,这就是问题的关键所在。
解决方案
经过上面分析知道了是clientId相同是问题所在,那解决方案就是让两个消费者的clientId不相同。
根据
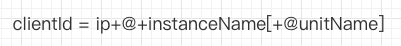
那最简单的解决方案有如下三种:
方案一:不设置instanceName属性
因为集群模式下instanceName默认值为进程id,源码如下:
/** * 如果是集群消费模式,如果instanceName是默认值(即没有自定义该属性)则通过进程id来替换该属性 */ public void changeInstanceNameToPID() { if (this.instanceName.equals("DEFAULT")) { this.instanceName = String.valueOf(UtilAll.getPid()); } }
两个消费者的进程id肯定是不同的。
方案二:两个消费者设置不同的instanceName属性
这个很容易能想到,不必多说。
方案三:两个消费者在不同的机器上启动
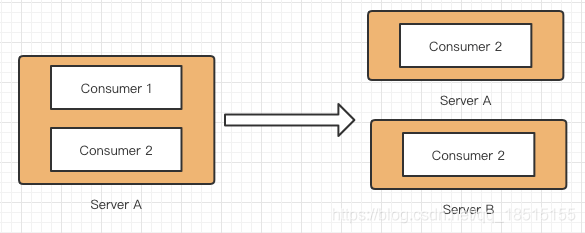
在不同机器上启动意味着ip是不一样的,也可以使生成的clientId不同。正常的消费结果
通过上述解决方案,最终得到了正确的消费结果。
consumer1:
ConsumeMessageThread_16 接收到新消息: queueId=0,消息内容: Hello RocketMQ 2 ConsumeMessageThread_17 接收到新消息: queueId=1,消息内容: Hello RocketMQ 3 ConsumeMessageThread_18 接收到新消息: queueId=0,消息内容: Hello RocketMQ 6 ConsumeMessageThread_19 接收到新消息: queueId=1,消息内容: Hello RocketMQ 7
consumer2:
ConsumeMessageThread_6 接收到新消息: queueId=2,消息内容: Hello RocketMQ 0 ConsumeMessageThread_7 接收到新消息: queueId=3,消息内容: Hello RocketMQ 1 ConsumeMessageThread_8 接收到新消息: queueId=2,消息内容: Hello RocketMQ 4 ConsumeMessageThread_9 接收到新消息: queueId=3,消息内容: Hello RocketMQ 5 ConsumeMessageThread_10 接收到新消息: queueId=2,消息内容: Hello RocketMQ 8 ConsumeMessageThread_11 接收到新消息: queueId=3,消息内容: Hello RocketMQ 9
10条消息被两个消费者消费完成,从消费结果可以看出消息消费的队列分配情况如下所示:
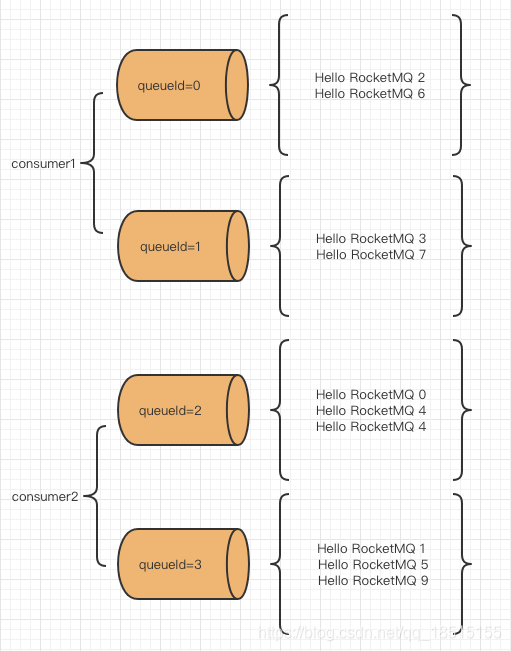
队列被两个消费者平均分配,但是注意,队列均分不代表消息均分!
总结
通过这次的问题跟踪排查和解决,越来越意识到对一个中间件原理甚至源码熟悉的重要性。当了解了其整体架构、运作原理以及模块源码以后就能够很快判断出大概是哪里出了问题,这最终也会沉淀为我们的个人经验。
转载:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_18515155/article/details/106175901




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 阿里最新开源QwQ-32B,效果媲美deepseek-r1满血版,部署成本又又又降低了!
· 开源Multi-agent AI智能体框架aevatar.ai,欢迎大家贡献代码
· Manus重磅发布:全球首款通用AI代理技术深度解析与实战指南
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧