SpringBoot(二)
如何在springboot优雅的使用枚举
从数据库中读取枚举值
使用Mybatis-Plus3读取
借助MyBatis-Plus可以很容易的实现这一点。
首先需要在配置文件中加入type-enums-package指定枚举的扫描包,MyBatis-Plus将为包内(包含子包)所有枚举进行适配,可以使用逗号或封号分隔多个包名。
mybatis-plus: type-enums-package: [枚举包][,|;][枚举包]
接着在枚举类中指定数据库值所对应的属性。这里可以采用两种方式。
1、实现官方提供的IEnum接口,接口中的getValue方法与数据库值对应的属性。
@Getter//实现getValue public enum StatusEnum implements IEnum<Integer> { VALID(1, "有效"), INVALID(0, "无效"); StatusEnum(Integer value, String desc) { this.value = value; this.desc = desc; } //标记数据库存的值是value private final Integer value; private final String desc; }
2、将属性使用EnumValue注解标记数据库值对应的属性。
@Getter//实现getValue public enum StatusEnum { VALID(1, "有效"), INVALID(0, "无效"); StatusEnum(Integer value, String desc) { this.value = value; this.desc = desc; } //标记数据库存的值是value @EnumValue private final Integer value; private final String desc; }
在类的属性声明上直接将字段类型标记为枚举类型,读取时将自动转换数据库值为枚举对象。
@Data @Accessors(chain = true) @TableName("test") public class TestDO { private Integer id; private String username; private StatusEnum status; }
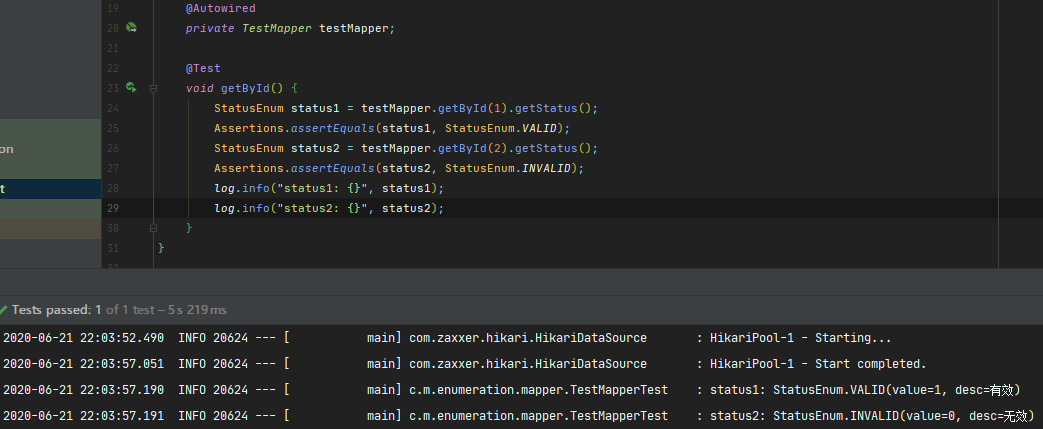
读取数据库中的两条数据进行测试,可以看到值被成功转换为了枚举。
MyBatis-Plus的实现
从MyBatis-Plus MybatisSqlSessionFactoryBean中可以找到它是如何实现的。
在buildSqlSessionFactory方法中可以看到,在配置了type-enums-package的情况下,
MyBatis-Plus将为该包下满足处理条件的枚举注册MybatisEnumTypeHandler类型转换处理器
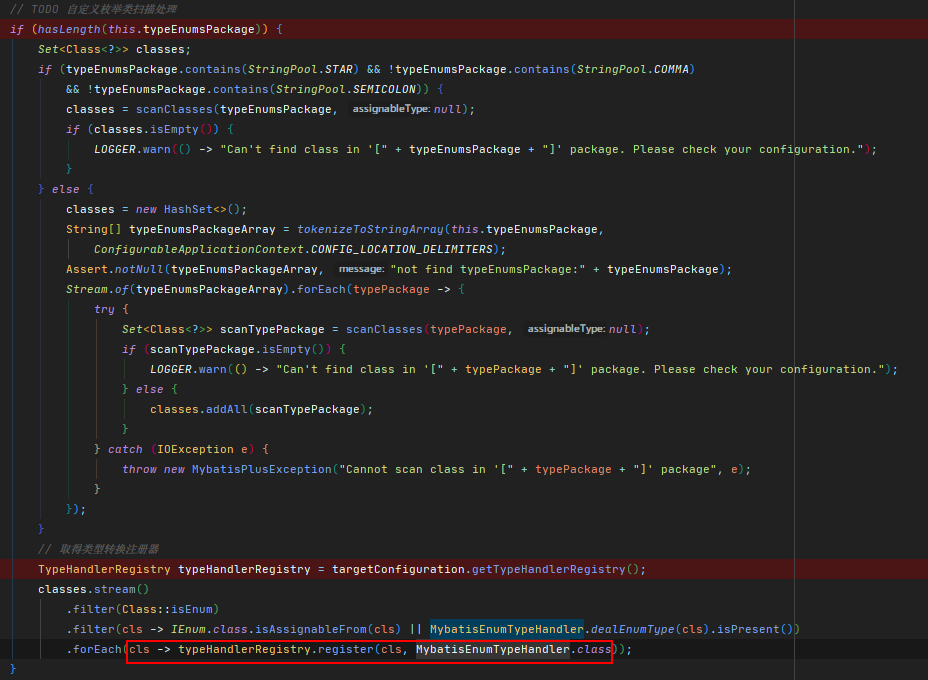
在MybatisEnumTypeHandler中将取出实现IEnum接口的枚举的getValue方法或使用EnumValue标记的字段的getter方法进行数据库值处理。
使用Mybatis实现
Mybatis提供了default-enum-type-handler配置用于改写默认的枚举处理器,这里简单粗暴的直接替换了默认处理器(MyBatis-Plus是满足条件的类才注册为该处理器处理,实际情况也应该如此)。
mybatis: configuration: default-enum-type-handler: com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.handlers.MybatisEnumTypeHandler
同样,这样也能完成枚举映射,相当于手动替换默认的处理器为mybatis-plus3的枚举处理器
或者在原有的Mybatis配置下追加类似的处理器注册操作。
@Configuration public class MybatisConfig implements InitializingBean { private final SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory; public MybatisConfig(SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory) { this.sqlSessionFactory = sqlSessionFactory; } @Override public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception { sqlSessionFactory.getConfiguration().getTypeHandlerRegistry().register(StatusEnum.class, MybatisEnumTypeHandler.class); } }
将请求值转换为枚举对象
虽然成功的将数据库值读为枚举属性,但如果不做处理,实体上的枚举类型将会成为累赘使请求值无法转换,因此需要处理使请求的字符串或数字值能够转换为枚举对象。
普通请求
对于诸如Get请求,Post表单请求的普通请求,可以使用自定义的转换器工厂进行处理,我们需要继承ConverterFactory类并指定想要处理的类型。
@Slf4j public class StringToEnumConverterFactory implements ConverterFactory<String, Enum<?>> { private static final Map<Class<?>, Converter<String, ? extends Enum<?>>> CONVERTER_MAP = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(); private static final Map<Class<?>, Method> TABLE_METHOD_OF_ENUM_TYPES = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(); @Override @SuppressWarnings("unchecked cast") public <T extends Enum<?>> Converter<String, T> getConverter(Class<T> targetType) { // 缓存转换器 Converter<String, T> converter = (Converter<String, T>) CONVERTER_MAP.get(targetType); if (converter == null) { converter = new StringToEnumConverter<>(targetType); CONVERTER_MAP.put(targetType, converter); } return converter; } static class StringToEnumConverter<T extends Enum<?>> implements Converter<String, T> { private final Map<String, T> enumMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(); StringToEnumConverter(Class<T> enumType) { Method method = getMethod(enumType); T[] enums = enumType.getEnumConstants(); // 将值与枚举对象对应并缓存 for (T e : enums) { try { enumMap.put(method.invoke(e).toString(), e); } catch (IllegalAccessException | InvocationTargetException ex) { log.error("获取枚举值错误!!! ", ex); } } } @Override public T convert(@NotNull String source) { // 获取 T t = enumMap.get(source); if (t == null) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("该字符串找不到对应的枚举对象 字符串:" + source); } return t; } } public static <T> Method getMethod(Class<T> enumType) { Method method; // 找到取值的方法 if (IEnum.class.isAssignableFrom(enumType)) { try { method = enumType.getMethod("getValue"); } catch (NoSuchMethodException e) { throw new IllegalArgumentException(String.format("类:%s 找不到 getValue方法", enumType.getName())); } } else { method = TABLE_METHOD_OF_ENUM_TYPES.computeIfAbsent(enumType, k -> { Field field = dealEnumType(enumType).orElseThrow(() -> new IllegalArgumentException(String.format( "类:%s 找不到 EnumValue注解", enumType.getName()))); return ReflectionKit.getMethod(enumType, field); }); } return method; } private static Optional<Field> dealEnumType(Class<?> clazz) { return clazz.isEnum() ? Arrays.stream(clazz.getDeclaredFields()).filter(field -> field.isAnnotationPresent(EnumValue.class)).findFirst() : Optional.empty(); } }
要使自定义的转换器工厂生效,需要实现WebMvcConfigurer接口并在addFormatters方法中进行追加。
@Configuration public class ConverterFactoryConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer { @Override public void addFormatters(FormatterRegistry registry) { registry.addConverterFactory(new StringToEnumConverterFactory()); } }
转换器生效,请求中的字符串类型,如果发现需要转换为枚举,则会触发自定义的转换器,并转换为对应的枚举。
@RestController @RequestMapping("/test") public class TestController{ @GetMapping public String getEnum(StatusEnum status) { return status.getDesc(); } @PostMapping("post") public String postEnum(StatusEnum status) { return status.getDesc(); } }
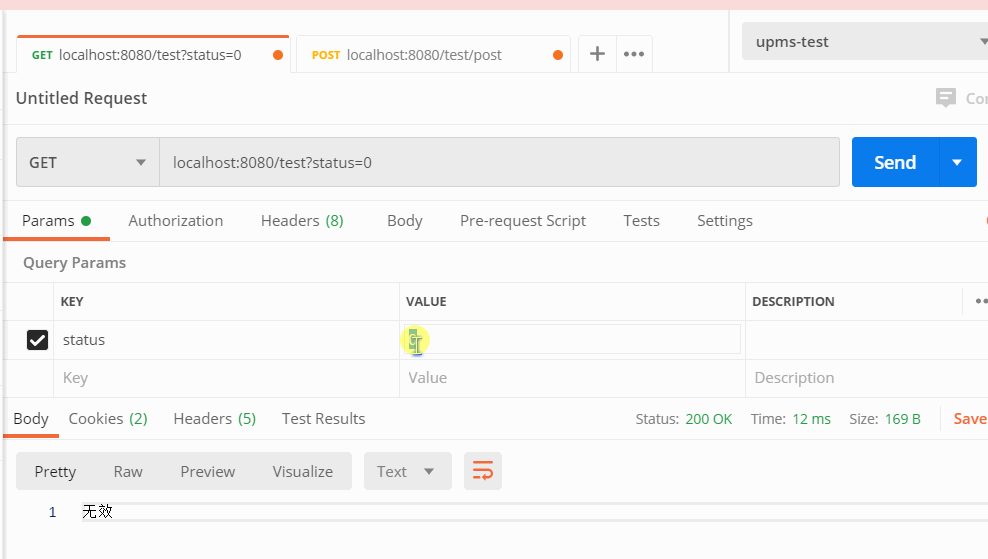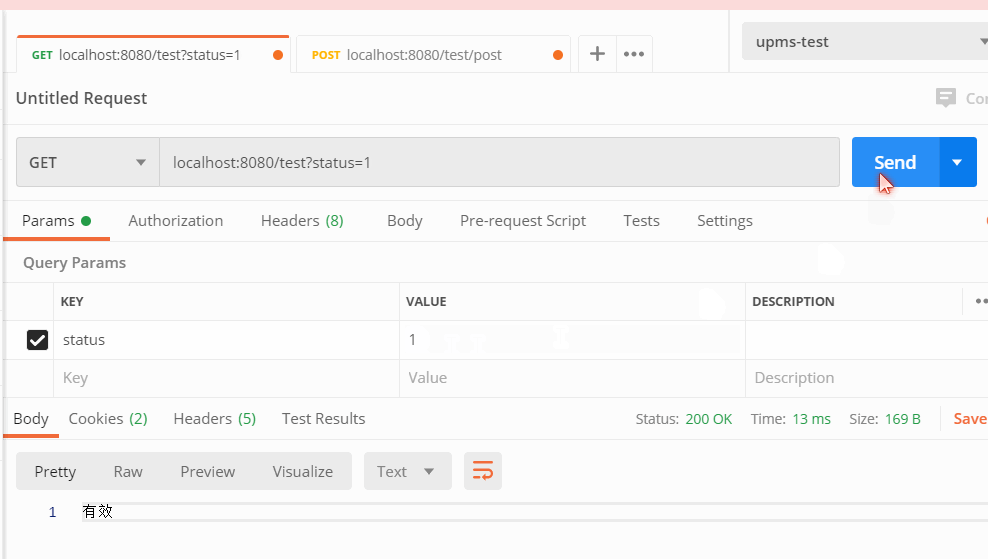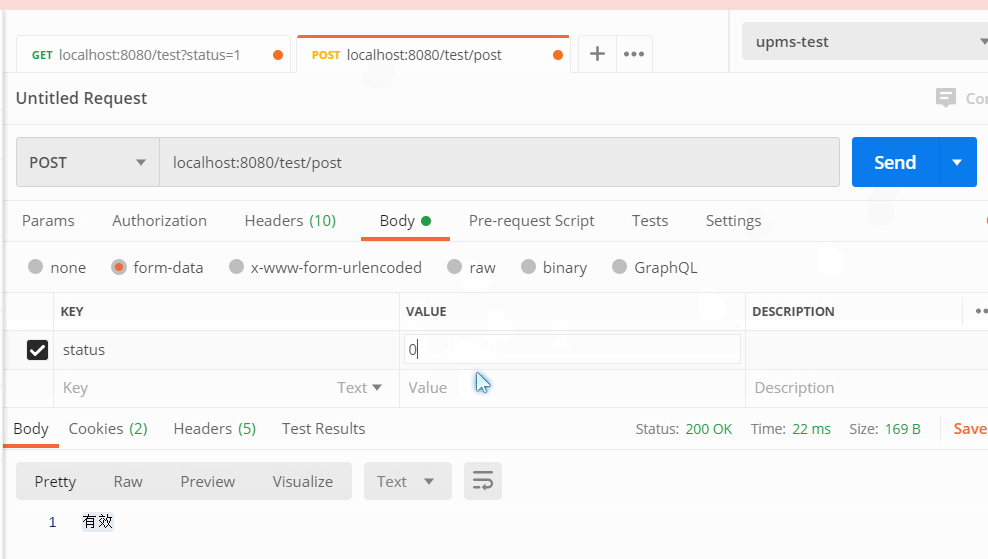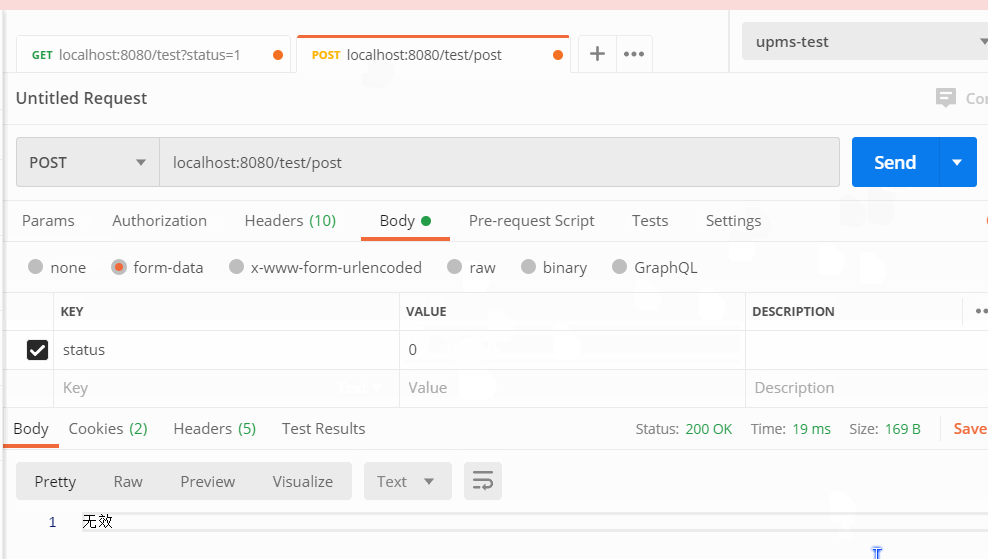
Json请求
Jackson
json请求使用RequestBody注解标记接收,处理器为项目中指定的消息转换器。在Springboot中默认为Jackson。
Jackson对枚举的默认行为为按枚举名或其所在的位置(从0开始计算),例如当传入0时获取的是枚举类中的第一个对象。
这显然不是我们要的,使用JsonCreator注解可以自定义枚举创建的方式。
增加枚举类方法:
@JsonCreator public static StatusEnum getItem(int code){ for(StatusEnum item : values()){ if(item.getValue() == code){ return item; } } return null; }
此时反序列化时将调用此方法创建枚举对象。
如果需要将转换的范围局限在某个实体字段,可以选择自定义JsonDeserializer。
@Slf4j public class JacksonStatusEnumDeserializer extends JsonDeserializer<StatusEnum> { @Override public StatusEnum deserialize(JsonParser jsonParser, DeserializationContext deserializationContext) throws IOException { String text = jsonParser.getText(); for (StatusEnum value : StatusEnum.values()) { if (Objects.equals(text, value.getValue().toString())) { return value; } } return null; } }
然后在实体字段上使用注解注明反序列化器。
@JsonDeserialize(using = JacksonStatusEnumConverter.class) private StatusEnum status;
由于在JsonDeserializer中DeserializationContext无法获取到实际的类信息,这意味着单独使用JsonDeserializer无法作为枚举的通用解决方案,我们必须为每一个枚举类定制一个反序列化处理方案。
要实现通用的解决方案,需要实现ContextualDeserializer辅助获取转换时的类信息(createContextual每个枚举类只会触发一次,之后都使用该方法返回的反序列化器处理)。
@Slf4j @Setter public class JacksonEnumDeserializer extends JsonDeserializer<Enum<?>> implements ContextualDeserializer { private Class<?> clazz; // ctx.getContextualType() 获取不到类信息 @Override public Enum<?> deserialize(JsonParser jsonParser, DeserializationContext ctx) throws IOException, JsonProcessingException { Class<?> enumType = clazz; if (Objects.isNull(enumType) || !enumType.isEnum()) { return null; } String text = jsonParser.getText(); Method method = StringToEnumConverterFactory.getMethod(clazz); Enum<?>[] enumConstants = (Enum<?>[]) enumType.getEnumConstants(); // 将值与枚举对象对应并缓存 for (Enum<?> e : enumConstants) { try { if (Objects.equals(method.invoke(e).toString(), text)) { return e; } } catch (IllegalAccessException | InvocationTargetException ex) { log.error("获取枚举值错误!!! ", ex); } } return null; } /** * 为不同的枚举获取合适的解析器 * * @param ctx ctx * @param property property */ @Override public JsonDeserializer<Enum<?>> createContextual(DeserializationContext ctx, BeanProperty property) throws JsonMappingException { Class<?> rawCls = ctx.getContextualType().getRawClass(); JacksonEnumDeserializer converter = new JacksonEnumDeserializer(); converter.setClazz(rawCls); return converter; } }
使用此序列化器备注的字段将能够被正确处理。
如果需要更大范围的采用此序列化器,将所有的枚举类型默认都委托给JacksonEnumDeserializer处理,可以修改默认的HttpMessageConverter。
@Configuration public class JacksonConfig { @Bean public HttpMessageConverter<?> httpMessageConverter(ObjectMapper objectMapper) { SimpleModule simpleModule = new SimpleModule(); simpleModule.addDeserializer(Enum.class, new JacksonEnumDeserializer());
objectMapper.registerModule(simpleModule); return new MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter(objectMapper);
}
}
或者在JacksonEnumDeserializer上使用JsonComponent注解标记。
@JsonComponent public class JacksonEnumDeserializer extends JsonDeserializer<Enum<?>> implements ContextualDeserializer
此时所有的枚举类型都将委托给该反序列化器处理。
FastJson
FastJson对枚举的默认行为同样为按枚举名或其所在的位置(从0开始计算),唯一不同的地方在于它强制要求按位置计算则需要传入的类型为数字类型(即不使用""包裹)。例如:
{ "fastJsonStatusEnum": 1 }
FastJson同样支持为枚举指定反序列化方式。
反序列化器需要实现ObjectDeserializer接口。
@Slf4j public class FastJsonEnumDeserializer implements ObjectDeserializer { @Override public <T> T deserialze(DefaultJSONParser parser, Type type, Object o) { final JSONLexer lexer = parser.lexer; Class<?> cls = (Class<?>) type; Object[] enumConstants = cls.getEnumConstants(); Method method = StringToEnumConverterFactory.getMethod(cls); if (!Enum.class.isAssignableFrom(cls)) { return null; } for (Object item : enumConstants) { try { String value = method.invoke(item).toString(); if (Objects.equals(value, lexer.stringVal()) || Objects.equals(Integer.valueOf(value), lexer.intValue())) { return (T)item; } } catch (IllegalAccessException | InvocationTargetException ex) { log.error("获取枚举值错误!!! ", ex); } } return null; } @Override public int getFastMatchToken() { return JSONToken.LITERAL_INT; } }
在枚举类上增加JSONType即可指定反序列化方式。(在类上注释)
@JSONType(deserializer = FastJsonEnumDeserializer.class)
反序列化器同样可以借助JSONField注解使其仅在实体字段生效。
@JSONField(deserializeUsing = FastJsonEnumDeserializer.class)
通过修改ParserConfig配置可以修改指定类的反序列化器,但由于FastJson获取序列化器时是直接从deserializers链表中直接按类型读取,并未做根类型的特殊处理,这意味着我们无法通过Enum类的配置覆盖所有枚举类,需要自行扫描所有枚举并加入配置,示例中借助hutool扫描指定包下的类。
<dependency>
<groupId>cn.hutool</groupId>
<artifactId>hutool-all</artifactId>
</dependency>
@Configuration public class FastJsonConfig { private static final String ENUM_BASE_PKG = "com.maple.enumeration.enums"; @Bean public HttpMessageConverter<?> httpMessageConverter() { FastJsonHttpMessageConverter fastConverter = new FastJsonHttpMessageConverter(); ParserConfig parserConfig = fastConverter.getFastJsonConfig().getParserConfig(); // 此方式不会生效 // parserConfig.putDeserializer(Enum.class, new FastJsonEnumDeserializer()); ClassUtil.scanPackage(ENUM_BASE_PKG).stream().filter(Class::isEnum).forEach(item -> parserConfig.putDeserializer(item, new FastJsonEnumDeserializer())); return fastConverter; } }
将枚举对象序列化为字符串
搞定了反序列化后,需要处理的便是序列化操作了。
Jackson
Jackson支持三个序列化枚举的SerializationFeature配置。
// 直接根据toString方法的返回值序列化 SerializationFeature.WRITE_ENUMS_USING_TO_STRING // 写出枚举序号 SerializationFeature.WRITE_ENUMS_USING_INDEX // 写出枚举名 默认 SerializationFeature.WRITE_ENUM_KEYS_USING_INDEX
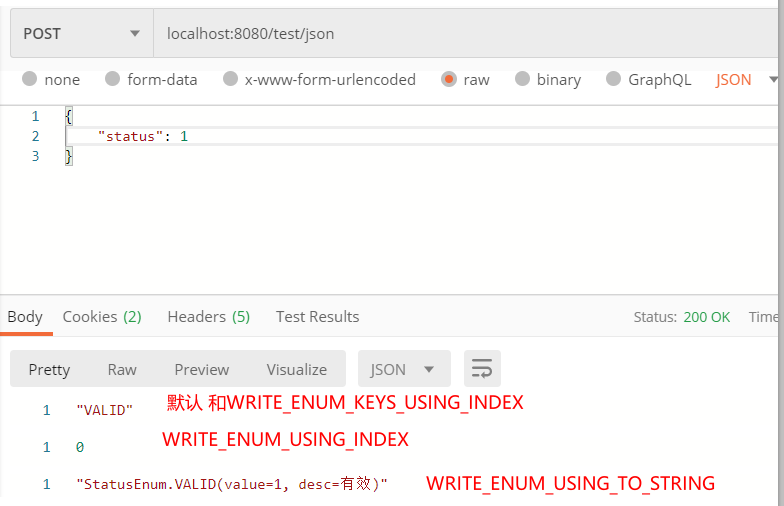
配置文件配置:
spring: jackson: serialization: WRITE_ENUMS_USING_TO_STRING: true # WRITE_ENUMS_USING_INDEX: true # WRITE_ENUM_KEYS_USING_INDEX: true
或者通过Bean配置:
@Configuration public class JacksonConfig { @Bean public Jackson2ObjectMapperBuilderCustomizer customizer() { return builder -> builder.featuresToEnable(SerializationFeature.WRITE_ENUMS_USING_TO_STRING); } }
若配置不满足需求,还可以使用JsonValue注解标记需要序列化返回的值(同一个类中不允许多个标记,标记字段则取字段实际值,标记方法则取方法返回值)。说明@JsonValue可以标记字段或方法。
@JsonValue private final String desc;
使用JsonFormat标记枚举类可以使枚举被序列化为对象形式。
@JsonFormat(shape = JsonFormat.Shape.OBJECT)
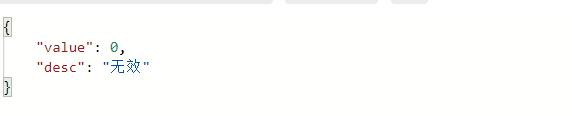
同样我们也可以通过继承JsonSerializer实现一个限定范围的序列化器,这里实现了序列化为对象形式的敷衍版本(工具类来自hutool)。
// 实体标记 @JsonSerialize(using = JacksonEnumSerializer.class) private StatusEnum status; @Slf4j public class JacksonEnumSerializer extends JsonSerializer<Enum<?>> { @Override public void serialize(Enum<?> value, JsonGenerator gen, SerializerProvider serializers) throws IOException { Method[] methods = ReflectUtil.getMethods(value.getClass(), item -> StrUtil.startWith(item.getName(), "get")); gen.writeStartObject(); for (Method method : methods) { String name = StrUtil.subAfter(method.getName(), "get", false); // 首字母小写 name = name.substring(0, 1).toLowerCase() + name.substring(1); String invokeStr = Objects.toString(ReflectUtil.invoke(value, method)); // 非数值类型写入字符串 if (!NumberUtil.isNumber(invokeStr)) { gen.writeStringField(name, invokeStr); continue; } // 是否小数 if (invokeStr.contains(".")) { gen.writeNumberField(name, Double.parseDouble(invokeStr)); continue; } gen.writeNumberField(name, Long.parseLong(invokeStr)); } gen.writeEndObject(); } }
将序列化器全局化:
@JsonComponent // 注册json序列化组件 public class JacksonEnumSerializer extends JsonSerializer<Enum<?>> // 或者bean配置 @Configuration public class JacksonConfig { @Bean public HttpMessageConverter<?> httpMessageConverter(ObjectMapper objectMapper) { SimpleModule simpleModule = new SimpleModule(); simpleModule.addSerializer(Enum.class, new JacksonEnumSerializer()); objectMapper.registerModule(simpleModule); return new MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter(objectMapper); } }
我们也可以将JsonFormat全局化,但此方式只支持到具体类,因此如果有需要也只能通过包扫描的形式进行全局定义。
@Configuration public class JacksonConfig { private static final String ENUM_BASE_PKG = "com.maple.enumeration.enums"; @Bean public HttpMessageConverter<?> httpMessageConverter(ObjectMapper objectMapper) { ClassUtil.scanPackage(ENUM_BASE_PKG).forEach(item -> objectMapper.configOverride(item) .setFormat(JsonFormat.Value.forShape(JsonFormat.Shape.OBJECT))); return new MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter(objectMapper); } }
附:各种场景的序列化优先级:
实体字段上的JsonSerialize配置 > 枚举上的JsonSerialize配置 > 全局JsonSerializer注册 > 枚举上的JsonValue配置 > 实体字段的JsonFormat配置> 全局的configOverride配置覆盖 > 枚举上的JsonFormat配置
FastJson
Jackson支持两个序列化枚举的SerializationFeature配置。
// 直接根据toString方法的返回值序列化 SerializerFeature.WriteEnumUsingToString // 默认 根据枚举名序列化 SerializerFeature.WriteEnumUsingName
bean配置:
@Bean public HttpMessageConverter<?> httpMessageConverter() { FastJsonHttpMessageConverter fastConverter = new FastJsonHttpMessageConverter(); fastConverter.getFastJsonConfig().setSerializerFeatures(SerializerFeature.WriteEnumUsingToString); return fastConverter; }
实现一个类似的序列化为对象的序列化器(还是敷衍版)。
@Slf4j public class FastJsonEnumSerializer implements ObjectSerializer { @Override public void write(JSONSerializer serializer, Object object, Object fieldName, Type fieldType, int features) throws IOException { Method[] methods = ReflectUtil.getMethods(object.getClass(), item -> StrUtil.startWith(item.getName(), "get")); Map<String, Object> objectMap = new HashMap<>(methods.length); for (Method method : methods) { String name = StrUtil.subAfter(method.getName(), "get", false); // 首字母小写 name = name.substring(0, 1).toLowerCase() + name.substring(1); objectMap.put(name, ReflectUtil.invoke(object, method)); } serializer.write(objectMap); } }
可以在类上使用JSONType注解标记或在类字段用JSONField标记。
@JSONField(serializeUsing = FastJsonEnumSerializer.class) private FastJsonStatusEnum fastJsonStatusEnum; @JSONType(serializer = FastJsonEnumSerializer.class) public enum FastJsonStatusEnum
配置为全局生效同样需要自行扫描添加。
@Bean public HttpMessageConverter<?> httpMessageConverter() { FastJsonHttpMessageConverter fastConverter = new FastJsonHttpMessageConverter(); ClassUtil.scanPackage(ENUM_BASE_PKG).stream().filter(Class::isEnum).forEach(item -> fastConverter.getFastJsonConfig().getSerializeConfig().put(FastJsonStatusEnum.class, new FastJsonEnumSerializer())); return fastConverter; }
附:各种场景的序列化优先级:
实体字段上的JSONField配置 > 全局SerializeConfig配置 > 枚举上的JSONType配置
转载:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_33306246/article/details/106933613




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 记一次.NET内存居高不下排查解决与启示
· 阿里最新开源QwQ-32B,效果媲美deepseek-r1满血版,部署成本又又又降低了!
· 开源Multi-agent AI智能体框架aevatar.ai,欢迎大家贡献代码
· Manus重磅发布:全球首款通用AI代理技术深度解析与实战指南
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
2017-05-19 SpringMVC日期类型转换问题处理方法归纳
2017-05-19 SpringMVC的Date与String互转
2017-05-19 使用AJAX异步提交表单的几种方式
2017-05-19 ORACLE——日期时间格式化参数详解 之三
2017-05-19 ORACLE——日期时间格式化参数详解 之一
2017-05-19 ORACLE——日期时间格式化参数详解 之二