SpringBoot(一)
在Spring Boot中优雅的实现定时任务
在日常的项目开发中,往往会涉及到一些需要做到定时执行的代码,例如自动将超过24小时的未付款的单改为取消状态,自动将超过14天客户未签收的订单改为已签收状态等等,那么为了在Spring Boot中实现此类需求,我们要怎么做呢?
Spring Boot早已考虑到了这类情况,先来看看要怎么做。第一种方式是比较简单的,先搭建好Spring Boot微服务,加上这个注解 @EnableScheduling :
/** * @author yudong * @date 2019/8/24 */ @EnableCaching // 启用缓存功能 @EnableScheduling // 开启定时任务功能 @ComponentScan(basePackages = "org.javamaster.b2c") @EnableTransactionManagement @SpringBootApplication public class ScheduledApplication { private static Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ScheduledApplication.class); public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(ScheduledApplication.class, args); logger.info("定时任务页面管理地址:{}", "http://localhost:8089/scheduled/task/taskList"); } }
然后编写定时任务类:
/** * @author yudong * @date 2019/8/24 */ @Component public class FixedPrintTask { private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(getClass()); private int i; @Scheduled(cron = "*/15 * * * * ?") public void execute() { logger.info("thread id:{},FixedPrintTask execute times:{}", Thread.currentThread().getId(), ++i); } }
@Scheduled(cron ="*/15 * * * * ?")注解表明这是一个需要定时执行的方法,里面的cron属性接收的是一个cron表达式,这里我给的是 */15 * * * * ? ,这个的意思是每隔15秒执行一次方法,对cron表达式不熟悉的同学可以百度一下用法。项目跑起来后可以看到方法被定时执行了:
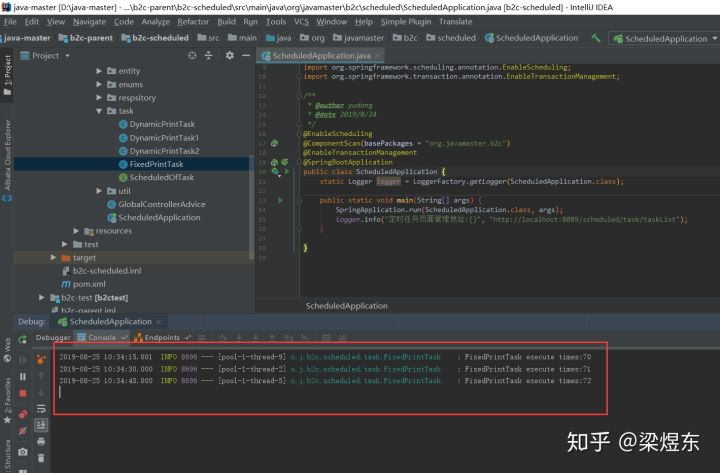
这种方式有个缺点,那就是执行周期写死在代码里了,没有办法动态改变,要想改变只能修改代码在重新部署启动微服务。其实Spring也考虑到了这个,所以给出了另外的解决方案,就是我下面说的第二种方式。
第二种方式需要用到数据库,先来建立一个定时任务表并插入三条定时任务记录:
drop table if exists `spring_scheduled_cron`; create table `spring_scheduled_cron` ( `cron_id` int primary key auto_increment comment '主键id', `cron_key` varchar(128) not null unique comment '定时任务完整类名', `cron_expression` varchar(20) not null comment 'cron表达式', `task_explain` varchar(50) not null default '' comment '任务描述', `status` tinyint not null default 1 comment '状态,1:正常;2:停用', unique index cron_key_unique_idx(`cron_key`) ) ENGINE = InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET = utf8mb4 COMMENT = '定时任务表'; insert into `spring_scheduled_cron` values (1, 'org.javamaster.b2c.scheduled.task.DynamicPrintTask', '*/5 * * * * ?', '定时任务描述', 1); insert into `spring_scheduled_cron` values (2, 'org.javamaster.b2c.scheduled.task.DynamicPrintTask1', '*/5 * * * * ?', '定时任务描述1', 1); insert into `spring_scheduled_cron` values (3, 'org.javamaster.b2c.scheduled.task.DynamicPrintTask2', '*/5 * * * * ?', '定时任务描述2', 1);
编写一个配置类:
@Configuration public class ScheduledConfig implements SchedulingConfigurer { @Autowired private ApplicationContext context; @Autowired private SpringScheduledCronRepository cronRepository; @Override public void configureTasks(ScheduledTaskRegistrar taskRegistrar) { for (SpringScheduledCron springScheduledCron : cronRepository.findAll()) { Class<?> clazz; Object task; try { clazz = Class.forName(springScheduledCron.getCronKey()); task = context.getBean(clazz); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("spring_scheduled_cron表数据" + springScheduledCron.getCronKey() + "有误", e); } catch (BeansException e) { throw new IllegalArgumentException(springScheduledCron.getCronKey() + "未纳入到spring管理", e); } Assert.isAssignable(ScheduledOfTask.class, task.getClass(), "定时任务类必须实现ScheduledOfTask接口"); // 可以通过改变数据库数据进而实现动态改变执行周期 taskRegistrar.addTriggerTask(((Runnable) task), triggerContext -> { String cronExpression = cronRepository.findByCronKey(springScheduledCron.getCronKey()).getCronExpression(); return new CronTrigger(cronExpression).nextExecutionTime(triggerContext); } ); } } @Bean public Executor taskExecutor() { return Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(10); } }
这里我为了做到可以灵活处理,自定义了一个接口ScheduledOfTask:
/** * @author yudong * @date 2019/5/11 */ public interface ScheduledOfTask extends Runnable { /** * 定时任务方法 */ void execute(); /** * 实现控制定时任务启用或禁用的功能 */ @Override default void run() { SpringScheduledCronRepository repository = SpringUtils.getBean(SpringScheduledCronRepository.class); SpringScheduledCron scheduledCron = repository.findByCronKey(this.getClass().getName()); if (StatusEnum.DISABLED.getCode().equals(scheduledCron.getStatus())) { // 任务是禁用状态 return; } execute(); } }
所有定时任务类只需要实现这个接口并相应的在数据库插入一条记录,那么在微服务启动的时候,就会被自动注册到Spring的定时任务里,也就是这行代码所起的作用:
// 可以通过改变数据库数据进而实现动态改变执行周期 taskRegistrar.addTriggerTask(((Runnable) task), triggerContext -> { String cronExpression = cronRepository.findByCronKey(springScheduledCron.getCronKey()).getCronExpression(); return new CronTrigger(cronExpression).nextExecutionTime(triggerContext); } );
具体的定时任务类(一共有三个,这里我只列出一个):
/** * @author yudong * @date 2019/5/10 */ @Component public class DynamicPrintTask implements ScheduledOfTask { private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(getClass()); private int i; @Override public void execute() { logger.info("thread id:{},DynamicPrintTask execute times:{}", Thread.currentThread().getId(), ++i); } }
项目跑起来后,可以看到类被定时执行了:

那么,要如何动态改变执行周期呢,没有理由去手工改动数据库吧?开发测试环境可以这么搞,生产环境就不可以了,所以为了做到动态改变数据库数据,很简单,提供一个Controller类供调用:
/** * 管理定时任务(需要做权限控制),具体的业务逻辑应 * 该写在Service里,良好的设计是Controller本身 * 只处理很少甚至不处理工作,业务逻辑均委托给 * Service进行处理,这里我偷一下懒,都写在Controller * @author yudong * @date 2019/5/10 */ @Controller @RequestMapping("/scheduled/task") public class TaskController { @Autowired private ApplicationContext context; @Autowired private SpringScheduledCronRepository cronRepository; /** * 查看任务列表 */ @RequestMapping("/taskList") public String taskList(Model model) { model.addAttribute("cronList", cronRepository.findAll()); return "task-list"; } /** * 编辑任务cron表达式 */ @ResponseBody @RequestMapping("/editTaskCron") public Result<Void> editTaskCron(String cronKey, String newCron) { if (!CronUtils.isValidExpression(newCron)) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("失败,非法表达式:" + newCron); } cronRepository.updateCronExpressionByCronKey(newCron, cronKey); return new Result<>(AppConsts.SUCCESS, "更新成功"); } /** * 执行定时任务 */ @ResponseBody @RequestMapping("/runTaskCron") public Result<Void> runTaskCron(String cronKey) throws Exception { ((ScheduledOfTask) context.getBean(Class.forName(cronKey))).execute(); return new Result<>(AppConsts.SUCCESS, "执行成功"); } /** * 启用或禁用定时任务 */ @ResponseBody @RequestMapping("/changeStatusTaskCron") public Result<Void> changeStatusTaskCron(Integer status, String cronKey) { cronRepository.updateStatusByCronKey(status, cronKey); return new Result<>(AppConsts.SUCCESS, "操作成功"); } }
这里我为了方便调用Controller接口,使用thymeleaf技术写了一个简易的html管理页面:
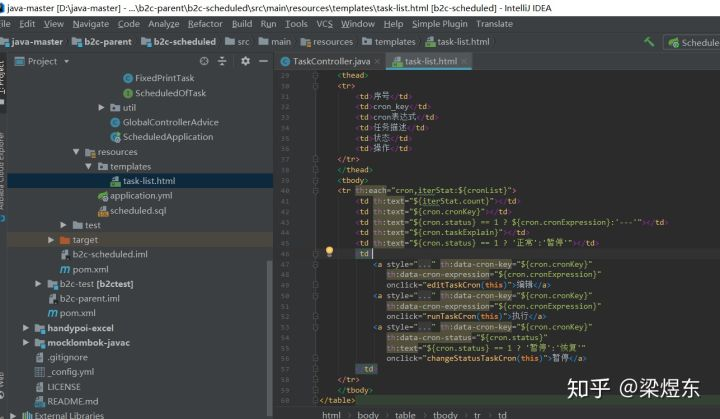
网页效果是这样的:
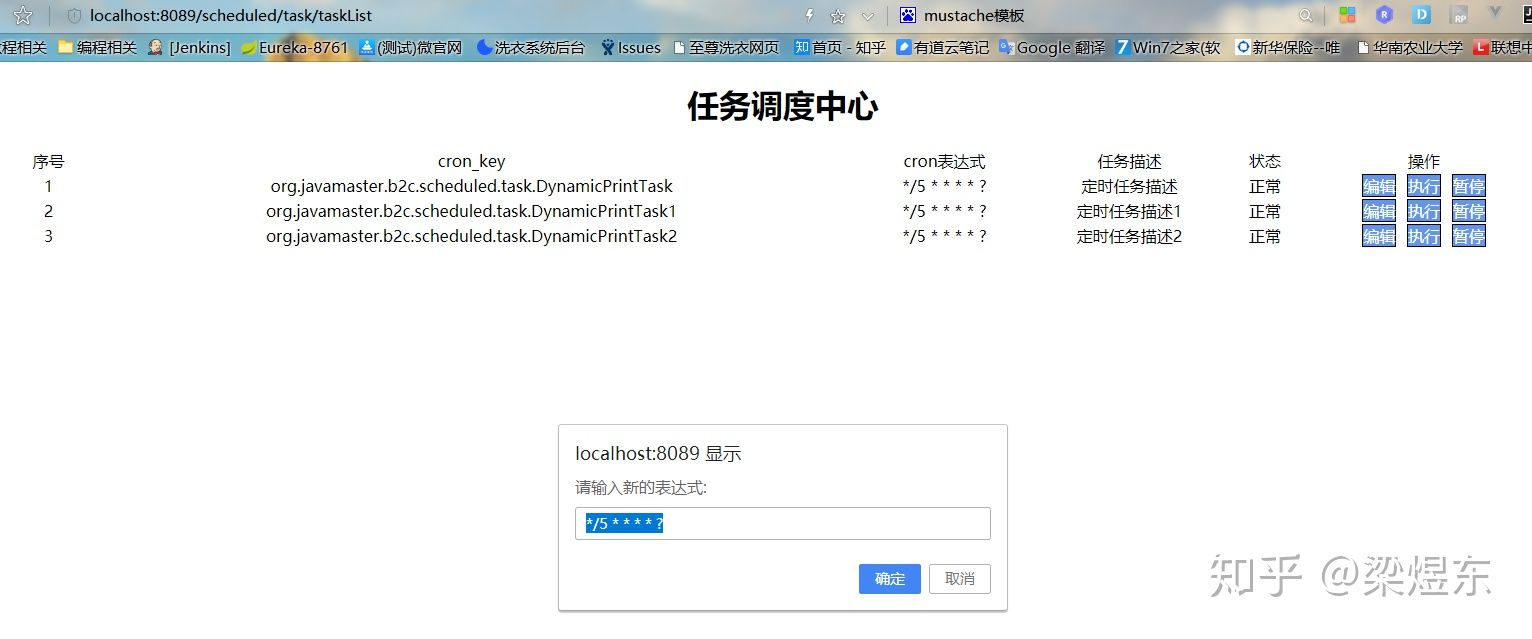
可以做到查看任务列表,修改任务cron表达式(也就实现了动态改变定时任务执行周期),暂停定时任务,以及直接执行定时任务。
最后如果对定时任务有更多其它要求,可以考虑使用xxljob这个开源的分布式任务调度平台,有兴趣的同学可以去了解,这里我就不展开了。
转载:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/79644891




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 记一次.NET内存居高不下排查解决与启示
· 阿里最新开源QwQ-32B,效果媲美deepseek-r1满血版,部署成本又又又降低了!
· 开源Multi-agent AI智能体框架aevatar.ai,欢迎大家贡献代码
· Manus重磅发布:全球首款通用AI代理技术深度解析与实战指南
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
2017-05-19 SpringMVC日期类型转换问题处理方法归纳
2017-05-19 SpringMVC的Date与String互转
2017-05-19 使用AJAX异步提交表单的几种方式
2017-05-19 ORACLE——日期时间格式化参数详解 之三
2017-05-19 ORACLE——日期时间格式化参数详解 之一
2017-05-19 ORACLE——日期时间格式化参数详解 之二