排序总结
各种排序方法的C++实现以及复杂度。
#include <iostream> using namespace std; void bubble_sort(int num[], int len); void select_sort(int num[], int len); void insert_sort(int num[], int len); void merge_sort(int num[], int len); void quick_sort(int num[], int len); void quick_sort(int arr[], int start, int end); int main() { const int n = 10; int num[n] = { 3,1,4,6,9,5,2,7,8,10 }; quick_sort(num, 0,n-1); for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){ cout << num[i] << ' '; } cout << endl; system("pause"); return 0; } void bubble_sort(int num[], int len){ for (int i = len - 1; i >= 0; i--){ bool swapped = false; for (int j = 0; j < i; j++){ if (num[j]>num[j + 1]){ swap(num[j], num[j + 1]); swapped = true; } } if (!swapped) break; } } void select_sort(int num[], int len){ for (int i = 0; i < len; i++){ int min_index = i; for (int j = i + 1; j < len; j++){ if (num[j] < num[min_index]) min_index = j; } if (i != min_index) swap(num[i], num[min_index]); } } void insert_sort(int num[], int len){ for (int i = 0; i < len; i++){ int cur = num[i]; int j; for (j = i - 1; j >= 0; j--){ if (cur < num[j]){ num[j + 1] = num[j]; } else{ break; } } num[j + 1] = cur; } } void merge_sort(int num[], int len){ if (len <= 1) return; int len1 = len / 2, len2 = len - len1; int *p1 = num, *p2 = num + len1; merge_sort(p1, len1); merge_sort(p2, len2); int *tmp = new int[len]; for (int cnt = 0, i = 0, j = 0; cnt < len; cnt++){ if (i == len1) tmp[cnt] = p2[j++]; else if (j == len2) tmp[cnt] = p1[i++]; else tmp[cnt] = p1[i]<p2[j] ? p1[i++] : p2[j++]; } for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) num[i] = tmp[i]; delete[] tmp; } void quick_sort(int num[], int len) { if (len <= 1) return; int x = num[len - 1]; int i = 0; for (int j = 0; j < len - 1; j++){ if (num[j] <= x){ swap(num[i++], num[j]); } } swap(num[i], num[len - 1]); quick_sort(num, i); quick_sort(num + i + 1, len - i - 1); } void quick_sort(int arr[], int start, int end) { if (start < end){ int x = arr[end]; int i = start; for (int j = start; j < end; j++){ if (arr[j] <= x){ swap(arr[i++], arr[j]); } } swap(arr[i], arr[end]); quick_sort(arr, start, i - 1); quick_sort(arr, i + 1, end); } }
下面摘录维基上的排序的比较
| Name | Best | Average | Worst | Memory | Stable | Method | Other notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quicksort | 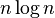 variation is  |
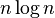 |
 |
 on average, worst case is on average, worst case is  ; Sedgewick variation is ; Sedgewick variation is  worst case worst case |
typical in-place sort is not stable; stable versions exist | Partitioning | Quicksort is usually done in place with O(log n) stack space.[2][3] |
| Merge sort | 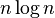 |
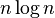 |
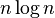 |
 |
Yes | Merging | Highly parallelizable (up to O(log n) using the Three Hungarians' Algorithm[4] or, more practically, Cole's parallel merge sort) for processing large amounts of data. |
| In-place merge sort | — | — | 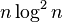 |
 |
Yes | Merging | Can be implemented as a stable sort based on stable in-place merging.[5] |
| Heapsort | 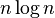 |
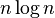 |
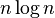 |
 |
No | Selection | |
| Insertion sort |  |
 |
 |
 |
Yes | Insertion | O(n + d), in the worst case over sequences that have d inversions. |
| Selection sort |  |
 |
 |
 |
No | Selection | Stable with O(n) extra space, for example using lists.[6] |
| Bubble sort |  |
 |
 |
 |
Yes | Exchanging | Tiny code size. |
| Binary tree sort | 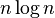 |
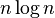 |
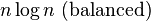 |
 |
Yes | Insertion | When using a self-balancing binary search tree. |
posted on 2015-10-24 11:39 caiminfeng 阅读(218) 评论(0) 收藏 举报


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号