【模板】网络流的求法
posted on 2022-08-12 14:14:05 | under 模板 | source
感谢讲师 LQS 带来的网络流专题。
本文非常不严谨,请不要把它当作入门博客。
codes
最大流:Dinic 实现(version 1)
typedef long long LL;
template <int N, int M, class T = int>
struct graph {
int head[N + 10], nxt[M * 2 + 10], cnt, tot;
struct edge {
int u, v;
T w;
edge(int u = 0, int v = 0, T w = 0) : u(u), v(v), w(w) {}
} e[M * 2 + 10];
graph() { memset(head, tot = cnt = 0, sizeof head); }
edge& operator[](int i) { return e[i]; }
void add(int u, int v, T w = 0) {
e[++cnt] = edge(u, v, w), nxt[cnt] = head[u], head[u] = cnt;
}
void link(int u, int v, T w = 0) { add(u, v, w), add(v, u, w); }
};
template <int N, int M, class T = int>
struct maxflow_g : public graph<N, M, T> {
graph<N, M, T>& g = *this;
maxflow_g() { g.add(0, 0, 0); }
void insert(int u, int v, T w) { g.add(u, v, w), g.add(v, u, 0); }
int dep[N + 10], cur[N + 10];
bool bfs(int s, int t) {
queue<int> q;
memset(dep, 0x3f, sizeof dep);
for (q.push(s), dep[s] = 0; !q.empty();) {
int u = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int i = g.head[u]; i; i = g.nxt[i]) {
int v = g[i].v;
if (!g[i].w) continue;
if (dep[v] > dep[u] + 1) q.push(v), dep[v] = dep[u] + 1;
}
}
return dep[t] != dep[0];
}
T dfs(int u, T flow, int t) {
if (u == t || !flow) return flow;
T rest = flow;
for (int& i = cur[u]; i; i = g.nxt[i]) {
int v = g[i].v;
if (dep[v] != dep[u] + 1 || !g[i].w) continue;
T run = dfs(v, min(rest, g[i].w), t);
if (g[i].w -= run, g[i ^ 1].w += run, !(rest -= run)) break;
}
if (rest == flow) dep[u] = -1;
return flow - rest;
}
T maxflow(int s, int t, T inf) {
T flow = 0;
while (bfs(s, t)) memcpy(cur, g.head, sizeof cur), flow += dfs(s, inf, t);
return flow;
}
};
最大流:Dinic 实现(version 2)
template <int N, int M, class T>
struct graph {
int head[N + 10], nxt[M << 1], cnt;
struct edge {
int u, v;
T w;
} e[M << 1];
graph() : cnt(0) { memset(head, 0, sizeof head); }
edge& operator[](int i) { return e[i]; }
void add(int u, int v, const T &w) {
e[++cnt] = {u, v, w};
nxt[cnt] = head[u];
head[u] = cnt;
}
void link(int u, int v, const T &w) {
add(u, v, w);
add(v, u, w);
}
};
template <int N, int M, class Cap>
struct maxflow {
graph<N, M, Cap> g;
maxflow() { ++g.cnt; }
void add(int u, int v, Cap cap) {
g.add(u, v, cap);
g.add(v, u, 0);
}
int dep[N + 10], cur[N + 10];
bool bfs(int s, int t) {
queue<int> q;
memset(dep, -1, sizeof dep);
for (q.push(s), dep[s] = 0; !q.empty(); ) {
int u = q.front(); q.pop();
for (int i = g.head[u]; i; i = g.nxt[i]) {
int v = g[i].v;
if (g[i].w && dep[v] == -1) {
dep[v] = dep[u] + 1;
q.push(v);
}
}
}
return dep[t] != -1;
}
Cap dfs(int u, Cap flw, int t) {
if (u == t) return flw;
Cap res = flw;
for (int &i = cur[u]; i; i = g.nxt[i]) {
int v = g[i].v;
if (g[i].w && dep[v] == dep[u] + 1) {
Cap run = dfs(v, min(res, g[i].w), t);
g[i].w -= run, g[i ^ 1].w += run;
res -= run;
if (res == 0) break;
}
}
if (res == flw) dep[u] = -1;
return flw - res;
}
Cap flow(int s, int t, Cap limit) {
Cap flw = 0;
while (flw < limit && bfs(s, t)) {
memcpy(cur, g.head, sizeof cur);
flw += dfs(s, limit - flw, t);
}
return flw;
}
};
最大流:Dinic 实现(version 3)
template <int N, class T>
struct graph {
struct edge {
int u, v;
T w;
};
int head[N + 10];
vector<edge> e;
vector<int> nxt;
edge& operator[](int i) { return e[i]; }
graph() { memset(head, -1, sizeof head); }
void add(int u, int v, T w) {
nxt.push_back(exchange(head[u], e.size()));
e.push_back((edge){u, v, w});
}
void link(int u, int v, T w) { add(u, v, w), add(v, u, w); }
};
template <int N, class Cap>
struct mf_graph {
graph<N, Cap> g;
int dep[N + 10];
int cur[N + 10];
void add(int u, int v, Cap cap) { g.add(u, v, cap), g.add(v, u, 0); }
bool bfs(int s, int t) {
memset(dep, -1, sizeof dep);
queue<int> q;
q.push(s);
dep[s] = 0;
while (!q.empty()) {
int u = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int i = g.head[u]; ~i; i = g.nxt[i]) {
int v = g[i].v;
if (g[i].w && dep[v] == -1) dep[v] = dep[u] + 1, q.push(v);
}
}
return dep[t] != -1;
}
Cap dfs(int u, Cap flw, int t) {
if (u == t) return flw;
Cap res = flw;
for (int& i = cur[u]; ~i; i = g.nxt[i]) {
int v = g[i].v;
if (g[i].w && dep[v] == dep[u] + 1) {
Cap run = dfs(v, min(res, g[i].w), t);
g[i].w -= run, g[i ^ 1].w += run;
res -= run;
if (!res) break;
}
}
if (res == flw) dep[u] = -1;
return flw - res;
}
Cap flow(int s, int t, Cap lim = numeric_limits<Cap>::max()) {
Cap flw = 0;
while (lim && bfs(s, t)) {
memcpy(cur, g.head, sizeof cur);
Cap run = dfs(s, lim, t);
flw += run, lim -= run;
}
return flw;
}
};
最大流:Dinic 实现(version 4,完全 vector)
template <class T>
struct graph {
struct edge {
int u, v;
T w;
};
vector<edge> e;
vector<int> head, nxt;
edge& operator[](int i) { return e[i]; }
graph(int n = 0) : head(n, -1) {}
size_t size() const { return head.size(); }
void add(int u, int v, T w = T{}) {
nxt.push_back(exchange(head[u], e.size()));
e.push_back((edge){u, v, w});
}
void link(int u, int v, T w = T{}) { add(u, v, w), add(v, u, w); }
int newnode() { head.push_back(-1); return head.size() - 1; }
};
template <class Cap>
struct mf_graph {
graph<Cap> g;
vector<int> dep, cur;
mf_graph(int n = 0) : g(n) {}
int newnode() { return g.newnode(); }
void add(int u, int v, Cap cap) { g.add(u, v, cap), g.add(v, u, 0); }
bool bfs(int s, int t) {
dep.assign(g.size(), -1);
queue<int> q;
q.push(s);
dep[s] = 0;
while (!q.empty()) {
int u = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int i = g.head[u]; ~i; i = g.nxt[i]) {
int v = g[i].v;
if (g[i].w && dep[v] == -1) dep[v] = dep[u] + 1, q.push(v);
}
}
return dep[t] != -1;
}
Cap dfs(int u, Cap flw, int t) {
if (u == t) return flw;
Cap res = flw;
for (int& i = cur[u]; ~i; i = g.nxt[i]) {
int v = g[i].v;
if (g[i].w && dep[v] == dep[u] + 1) {
Cap run = dfs(v, min(res, g[i].w), t);
g[i].w -= run, g[i ^ 1].w += run;
res -= run;
if (!res) break;
}
}
if (res == flw) dep[u] = -1;
return flw - res;
}
Cap flow(int s, int t, Cap lim = numeric_limits<Cap>::max()) {
Cap flw = 0;
while (lim && bfs(s, t)) {
cur = g.head;
Cap run = dfs(s, lim, t);
flw += run, lim -= run;
}
return flw;
}
};
最大流:Dinic 实现(version 5,ac-library style,完全 vector)
template <class Cap>
struct mf_graph {
struct edge {
int v, rid;
Cap cap;
};
int n;
vector<vector<edge>> g;
mf_graph() = default;
mf_graph(int _n) : n(_n), g(_n) {}
void addedge(int u, int v, Cap cap) {
int fid = (int)g[u].size(), tid = (int)g[v].size() + (u == v);
g[u].push_back({v, tid, cap});
g[v].push_back({u, fid, 0});
}
vector<int> dep, cur;
bool bfs(int s, int t) {
dep.assign(n, -1);
queue<int> q;
dep[s] = 0;
q.push(s);
while (!q.empty()) {
int u = q.front(); q.pop();
for (auto&& e : g[u]) {
if (e.cap && dep[e.v] == -1) {
dep[e.v] = dep[u] + 1, q.push(e.v);
}
}
}
return dep[t] != -1;
}
Cap dfs(int u, Cap flw, int t) {
if (u == t) return flw;
Cap res = 0;
for (int &i = cur[u]; i < (int)g[u].size(); i++) {
auto &e = g[u][i];
if (e.cap && dep[e.v] == dep[u] + 1) {
Cap run = dfs(e.v, min(flw - res, e.cap), t);
e.cap -= run, g[e.v][e.rid].cap += run;
res += run;
if (res == flw) return res;
}
}
dep[u] = -1;
return res;
}
Cap flow(int s, int t, Cap lim = numeric_limits<Cap>::max()) {
Cap flw = 0;
while (flw < lim && bfs(s, t)) {
cur.assign(n, 0);
flw += dfs(s, lim - flw, t);
}
return flw;
}
};
最小费用最大流:Dinic + SPFA = SSP 实现
template <int N, int M, class T = int>
struct graph {
int head[N + 10], nxt[M * 2 + 10], cnt, tot;
struct edge {
int u, v;
T w;
edge(int u = 0, int v = 0, T w = {0, 0}) : u(u), v(v), w(w) {}
} e[M * 2 + 10];
graph() { memset(head, tot = cnt = 0, sizeof head); }
edge& operator[](int i) { return e[i]; }
void add(int u, int v, T w) {
e[++cnt] = edge(u, v, w), nxt[cnt] = head[u], head[u] = cnt;
}
void link(int u, int v, T w) { add(u, v, w), add(v, u, w); }
};
template <int N, int M, class T = int, class F = int>
struct mcmf_g : public graph<N, M, pair<T, F>> {
graph<N, M, pair<T, F>>& g = *this;
mcmf_g() { g.add(0, 0, {0, 0}); }
void insert(int u, int v, T w, F c) {
g.add(u, v, {w, c}), g.add(v, u, {0, -c});
}
F dis[N + 10];
int cur[N + 10], vis[N + 10];
bool bfs(int s, int t) {
queue<int> q;
memset(dis, 0x3f, sizeof dis), memset(vis, 0, sizeof vis);
for (q.push(s), dis[s] = 0; !q.empty();) {
int u = q.front();
q.pop(), vis[u] = 0;
for (int i = g.head[u]; i; i = g.nxt[i]) {
int v = g[i].v;
if (!g[i].w.first) continue;
if (dis[v] > dis[u] + g[i].w.second)
dis[v] = dis[u] + g[i].w.second, !vis[v] && (q.push(v), vis[v] = 1);
}
}
return dis[t] != dis[0];
}
T dfs(int u, T flow, int t) {
if (u == t || !flow) return flow;
T rest = flow;
vis[u] = 1;
for (int& i = cur[u]; i; i = g.nxt[i]) {
int v = g[i].v;
if (dis[v] != dis[u] + g[i].w.second || vis[v] || !g[i].w.first) continue;
T run = dfs(v, min(rest, g[i].w.first), t);
if (g[i].w.first -= run, g[i ^ 1].w.first += run, !(rest -= run)) break;
}
if (rest == flow) vis[u] = 0;
return flow - rest;
}
pair<T, F> mcmf(int s, int t, T inf) {
pair<T, F> flow = {0, 0};
while (bfs(s, t)) {
memcpy(cur, g.head, sizeof cur);
T run = dfs(s, inf, t);
flow.first += run, flow.second += run * dis[t];
}
return flow;
}
};
最小费用最大流:原始对偶 + EK 实现
template <class T>
using pqueue = priority_queue<T, vector<T>, greater<T>>;
template <int N, int M, class Type>
struct graph {
int head[N + 10], nxt[M << 1], cnt;
struct edge {
int u, v;
Type w;
} e[M << 1];
graph() { clear(); }
void clear() { cnt = 0, memset(head, 0, sizeof head); }
edge& operator[](int i) { return e[i]; }
void add(int u, int v, Type w) {
e[++cnt] = {u, v, w}, nxt[cnt] = head[u], head[u] = cnt;
}
void link(int u, int v, Type w) { add(u, v, w), add(v, u, w); }
};
template <int N, int M, class Cap, class Cost>
struct mincostflow {
graph<N, M, pair<Cap, Cost>> g;
int pre[N + 10], tot;
Cost h[N + 10], dis[N + 10];
bool vis[N + 10];
mincostflow() { clear(); }
void clear(int n = 0) { g.clear(), g.cnt += 1, tot = n; }
void add(int u, int v, Cap cap, Cost cost) {
g.add(u, v, {cap, cost});
g.add(v, u, {0, -cost});
}
bool spfa(int s, int t) {
static int app[N + 10];
queue<int> q;
memset(h, 0x3f, sizeof h);
memset(vis, 0, sizeof vis);
memset(app, 0, sizeof app);
for (q.push(s), h[s] = 0; !q.empty();) {
int u = q.front();
q.pop();
vis[u] = 0;
for (int i = g.head[u]; i; i = g.nxt[i]) {
int v = g[i].v;
if (g[i].w.first && h[v] > h[u] + g[i].w.second) {
h[v] = h[u] + g[i].w.second;
if (!vis[v]) {
if (++app[v] >= tot) return 0;
vis[v] = 1, q.push(v);
}
}
}
}
return h[t] < h[0];
}
bool dijkstra(int s, int t) {
pqueue<pair<Cost, int>> q;
memset(dis, 0x3f, sizeof dis);
memset(vis, 0, sizeof vis);
for (q.push({dis[s] = 0, s}); !q.empty();) {
int u = q.top().second;
q.pop();
if (vis[u]) continue;
vis[u] = 1;
for (int i = g.head[u]; i; i = g.nxt[i]) {
int v = g[i].v;
Cost w = g[i].w.second + h[u] - h[v];
if (g[i].w.first && dis[v] > dis[u] + w) {
pre[v] = i;
q.push({dis[v] = dis[u] + w, v});
}
}
}
return vis[t];
}
pair<Cap, Cost> mcmf(int s, int t, Cap flow) {
pair<Cap, Cost> res = {0, 0};
if (!spfa(s, t)) throw "The min-cost-flow problem can't be solved.";
while (flow && dijkstra(s, t)) {
for (int i = 1; i <= tot; i++) h[i] += dis[i];
Cap run = flow;
for (int i = pre[t]; i; i = pre[g[i].u])
run = min(run, g[i].w.first);
for (int i = pre[t]; i; i = pre[g[i].u])
g[i].w.first -= run, g[i ^ 1].w.first += run;
res.first += run, res.second += run * h[t];
}
return res;
}
};
最小费用最大流:SPFA + EK 实现
template <int N, int M, class T>
struct graph {
int head[N + 10], nxt[M << 1], cnt;
struct edge {
int u, v;
T w;
} e[M << 1];
graph() { memset(head, cnt = 0, sizeof head); }
edge& operator[](int i) { return e[i]; }
void add(int u, int v, T w) { e[++cnt] = {u, v, w}, nxt[cnt] = head[u], head[u] = cnt; }
void link(int u, int v, T w) { add(u, v, w), add(v, u, w); }
};
template <int N, int M, class Cap, class Cst>
struct mcmf {
int tot;
graph<N, M, pair<Cap, Cst>> g;
mcmf() : tot(0) { ++g.cnt; }
void add(int u, int v, Cap cap, Cst cst) {
g.add(u, v, make_pair(cap, cst));
g.add(v, u, make_pair(0, -cst));
}
int pre[N + 10];
Cst dis[N + 10];
bool vis[N + 10];
void spfa(int s) {
memset(pre, 0, sizeof pre);
memset(vis, false, sizeof vis);
memset(dis, 0x3f, sizeof dis);
queue<int> q;
q.push(s);
dis[s] = 0;
while (!q.empty()) {
int u = q.front(); q.pop();
vis[u] = false;
for (int i = g.head[u]; i; i = g.nxt[i]) {
int v = g[i].v;
auto w = g[i].w.second;
if (g[i].w.first && dis[v] > dis[u] + w) {
dis[v] = dis[u] + w;
pre[v] = i;
if (!vis[v]) vis[v] = true, q.push(v);
}
}
}
}
pair<Cap, Cst> flow(int s, int t, Cap lim) {
Cap flw = 0;
Cst cst = 0;
while (lim && (spfa(s), pre[t])) {
Cap run = lim;
for (int i = pre[t]; i; i = pre[g[i].u]) run = min(run, g[i].w.first);
flw += run, lim -= run;
cst += run * dis[t];
for (int i = pre[t]; i; i = pre[g[i].u]) g[i].w.first -= run, g[i ^ 1].w.first += run;
}
return make_pair(flw, cst);
}
};
最小费用最大流:原始对偶 + dinic 实现(完全 vector)
if (res != flw) vis[u] = false; 的解释 see below。
template <class T>
struct graph {
struct edge {
int u, v;
T w;
};
vector<edge> e;
vector<int> head, nxt;
edge& operator[](int i) { return e[i]; }
edge operator[](int i) const { return e[i]; }
graph(int n = 0) : head(n, -1) {}
size_t size() const { return head.size(); }
void add(int u, int v, T w = T{}) {
nxt.push_back(exchange(head[u], e.size()));
e.push_back((edge){u, v, w});
}
void link(int u, int v, T w = T{}) { add(u, v, w), add(v, u, w); }
int newnode() {
head.push_back(-1);
return head.size() - 1;
}
};
template <class T>
using pqueue = priority_queue<T, vector<T>, greater<T>>;
template <class Cap, class Cst>
struct mcmf_graph {
graph<pair<Cap, Cst>> g;
int newnode() { return g.newnode(); }
mcmf_graph(int n = 0) : g(n) {}
void add(int u, int v, Cap cap, Cst cst) {
g.add(u, v, make_pair(cap, cst));
g.add(v, u, make_pair(0, -cst));
}
vector<Cst> h, dis;
vector<int> vis;
bool spfa(int s) {
vis.assign(g.size(), false);
h.assign(g.size(), numeric_limits<Cst>::max());
queue<int> q;
vector<int> app(g.size());
q.push(s);
h[s] = 0;
while (!q.empty()) {
int u = q.front();
q.pop();
vis[u] = false;
for (int i = g.head[u]; ~i; i = g.nxt[i]) {
int v = g[i].v;
auto w = g[i].w.second;
if (g[i].w.first && h[v] > h[u] + w) {
h[v] = h[u] + w;
if (!vis[v]) {
if (++app[v] >= g.size()) return false;
vis[v] = true, q.push(v);
}
}
}
}
return true;
}
bool dijkstra(int s, int t) {
vis.assign(g.size(), false);
dis.assign(g.size(), numeric_limits<Cst>::max());
pqueue<pair<Cst, int>> q;
q.emplace(dis[s] = 0, s);
while (!q.empty()) {
int u = q.top().second;
q.pop();
if (vis[u]) continue;
vis[u] = true;
for (int i = g.head[u]; ~i; i = g.nxt[i]) {
int v = g[i].v;
if (!g[i].w.first) continue;
auto w = g[i].w.second + h[u] - h[v];
if (dis[v] > dis[u] + w) {
q.emplace(dis[v] = dis[u] + w, v);
}
}
}
return vis[t];
}
vector<int> cur;
Cap dfs(int u, Cap flw, int t) {
if (u == t) return flw;
Cap res = flw;
vis[u] = true;
for (int& i = cur[u]; ~i; i = g.nxt[i]) {
int v = g[i].v;
auto w = g[i].w.second + h[u] - h[v];
if (vis[v] || !g[i].w.first || dis[v] != dis[u] + w) continue;
Cap run = dfs(v, min(res, g[i].w.first), t);
g[i].w.first -= run, g[i ^ 1].w.first += run;
res -= run;
if (!res) break;
}
if (res != flw) vis[u] = false;
return flw - res;
}
pair<Cap, Cst> flow(int s, int t, Cap lim = numeric_limits<Cap>::max()) {
pair<Cap, Cst> res{0, 0};
if (!spfa(s)) throw logic_error("sorry, cannot solve this problem");
while (lim && dijkstra(s, t)) {
cur = g.head;
vis.assign(g.size(), false);
Cap run = dfs(s, lim, t);
res.first += run, res.second += run * (dis[t] - h[s] + h[t]);
lim -= run;
for (int i = 0; i < g.size(); i++) {
if (dis[i] != numeric_limits<Cst>::max()) h[i] += dis[i];
}
}
return res;
}
};
最小费用最大流:原始对偶 + dinic 实现(ac-library style,完全 vector)
template <class T>
using pqueue = priority_queue<T, vector<T>, greater<T>>;
template <class Cap, class Cst>
struct mcf_graph {
inline static constexpr auto MAXC = numeric_limits<Cst>::max();
struct edge {
int v, rid;
Cap cap;
Cst cst;
};
int n;
vector<vector<edge>> g;
mcf_graph() = default;
mcf_graph(int _n) : n(_n), g(_n) {}
void add(int u, int v, Cap cap, Cst cst) {
int fid = (int)g[u].size(), tid = (int)g[v].size() + (u == v);
g[u].push_back({v, tid, cap, cst});
g[v].push_back({u, fid, 0, -cst});
}
vector<Cst> h, dis;
vector<int> vis;
bool spfa(int s) {
vis.assign(n, false);
h.assign(n, MAXC);
vector<int> app(n, 0);
queue<int> q;
q.push(s), h[s] = 0;
while (!q.empty()) {
int u = q.front(); q.pop();
vis[u] = false;
for (auto&& e : g[u]) {
if (e.cap && h[e.v] > h[u] + e.cst) {
h[e.v] = h[u] + e.cst;
if (!vis[e.v]) {
if (++app[e.v] >= n) return false;
vis[e.v] = true, q.push(e.v);
}
}
}
}
return true;
}
bool dijkstra(int s, int t) {
vis.assign(n, false);
dis.assign(n, MAXC);
pqueue<pair<Cst, int>> q;
q.emplace(dis[s] = 0, s);
while (!q.empty()) {
int u = q.top().second; q.pop();
if (exchange(vis[u], true)) continue;
for (auto&& e : g[u]) {
if (!e.cap) continue;
auto w = e.cst + h[u] - h[e.v];
if (dis[e.v] > dis[u] + w) q.emplace(dis[e.v] = dis[u] + w, e.v);
}
}
return dis[t] != MAXC;
}
vector<int> cur;
Cap dfs(int u, Cap flw, int t) {
if (u == t) return flw;
Cap res = 0;
vis[u] = true;
for (int &i = cur[u]; i < (int)g[u].size(); i++) {
auto &e = g[u][i];
if (vis[e.v]) continue;
if (e.cap && h[e.v] == h[u] + e.cst) {
Cap run = dfs(e.v, min(flw - res, e.cap), t);
e.cap -= run, g[e.v][e.rid].cap += run;
res += run;
if (res == flw) return vis[u] = false, res;
}
}
return res;
}
pair<Cap, Cst> flow(int s, int t, Cap lim = numeric_limits<Cap>::max()) {
if (!spfa(s)) throw logic_error("sorry, cannot solve :(");
Cap flw = 0;
Cst sum = 0;
while (flw < lim && dijkstra(s, t)) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (dis[i] != MAXC) h[i] += dis[i];
}
cur.assign(n, 0);
vis.assign(n, false);
Cap run = dfs(s, lim - flw, t);
flw += run, sum += run * h[t];
}
return make_pair(flw, sum);
}
};
有负圈的费用流:原始对偶 + dinic 实现(ac-library style,完全 vector)
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#ifdef LOCAL
#define debug(...) fprintf(stderr, ##__VA_ARGS__)
#else
#define endl "\n"
#define debug(...) void(0)
#endif
using LL = long long;
template <class T>
using pqueue_less = priority_queue<T, vector<T>, greater<T>>;
template <class Cap, class Cst>
struct mcf_graph {
const Cst maxc = numeric_limits<Cst>::max();
struct edge {
int v, rid;
Cap cap;
Cst cst;
};
int n;
vector<vector<edge>> g;
vector<Cst> h, dis;
vector<int> pre;
mcf_graph() = default;
mcf_graph(int _n) : n(_n), g(_n) {}
void addedge(int u, int v, Cap cap, Cst cst) {
int tid = (int)g[u].size(), rid = (int)g[v].size() + (u == v);
g[u].push_back({v, rid, cap, cst});
g[v].push_back({u, tid, 0, -cst});
}
bool dijkstra(int s, int t) {
vector<int> vis(n);
pre.assign(n, -1);
dis.assign(n, maxc);
pqueue_less<pair<Cst, int>> q;
q.emplace(dis[s] = 0, s);
while (!q.empty()) {
int u = q.top().second;
q.pop();
if (exchange(vis[u], true)) continue;
for (auto e : g[u]) {
auto w = h[u] - h[e.v] + e.cst;
if (e.cap && dis[e.v] > dis[u] + w) {
assert(w >= 0);
pre[e.v] = e.rid;
q.emplace(dis[e.v] = dis[u] + w, e.v);
}
}
}
return vis[t];
}
vector<int> vis, cur;
Cap dfs(int u, Cap flw, int t) {
if (u == t) return flw;
vis[u] = true;
Cap run = 0;
for (int &i = cur[u]; i < (int)g[u].size(); i++) {
auto &e = g[u][i];
if (e.cap && !vis[e.v] && h[e.v] == h[u] + e.cst) {
auto f = dfs(e.v, min(flw - run, e.cap), t);
run += f, e.cap -= f, g[e.v][e.rid].cap += f;
if (run == flw) break;
}
}
if (run == flw) vis[u] = false;
return run;
}
struct result_type {
Cap cap;
Cst cst;
};
result_type flow(int s, int t, Cap lim = numeric_limits<Cap>::max()) {
Cap flw = 0;
Cst cst = 0;
if (h.empty()) h.assign(n, 0);
dijkstra(s, t);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
if (dis[i] < maxc) h[i] += dis[i];
auto hs = h[s];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) h[i] -= hs;
while (flw < lim && dijkstra(s, t)) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
if (dis[i] < maxc) h[i] += dis[i];
// Cap run = lim - flw;
// for (int v = t, u; v != s; v = u) {
// u = g[v][pre[v]].v;
// run = min(run, g[u][g[v][pre[v]].rid].cap);
// }
// for (int v = t, u; v != s; v = u) {
// u = g[v][pre[v]].v;
// g[u][g[v][pre[v]].rid].cap -= run;
// g[v][pre[v]].cap += run;
// }
vis.assign(n, false);
cur.assign(n, 0);
auto run = dfs(s, lim - flw, t);
flw += run, cst += run * h[t];
}
return {flw, cst};
}
};
template <class Cap, class Cst>
struct mcf_interface {
int n;
vector<Cap> d;
mcf_graph<Cap, Cst> mf;
Cap cap{};
Cst val{};
mcf_interface() = default;
mcf_interface(int _n) : n(_n), d(_n), mf(_n + 2) {}
void addedge(int u, int v, Cap f, Cst c) {
if (c >= 0)
mf.addedge(u, v, f, c);
else
mf.addedge(v, u, f, -c), val += f * c, d[u] -= f, d[v] += f;
}
auto flow(int s, int t, Cap lim = numeric_limits<Cap>::max()) {
int s1 = n, t1 = n + 1;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (d[i] > 0)
mf.addedge(s1, i, d[i], 0);
else if (d[i] < 0)
mf.addedge(i, t1, -d[i], 0);
}
mf.addedge(t, s, lim, 0);
auto ret = mf.flow(s1, t1);
cap = mf.g[s].back().cap, val += ret.cst;
mf.g[s].pop_back(), mf.g[t].pop_back();
ret = mf.flow(s, t, lim - cap);
ret.cap += cap, ret.cst += val;
return ret;
}
};
int main() {
#ifndef LOCAL
cin.tie(nullptr)->sync_with_stdio(false);
#endif
int n, m, s0, t0;
cin >> n >> m, s0 = 0, t0 = n - 1;
mcf_interface<int, int> g(n);
for (int i = 1, u, v, f, c; i <= m; i++) {
cin >> u >> v >> f >> c, --u, --v;
g.addedge(u, v, f, c);
}
auto ret = g.flow(s0, t0);
cout << ret.cap << " " << ret.cst << endl;
return 0;
}
网络是一张边带权的有向图,这是一个例子:
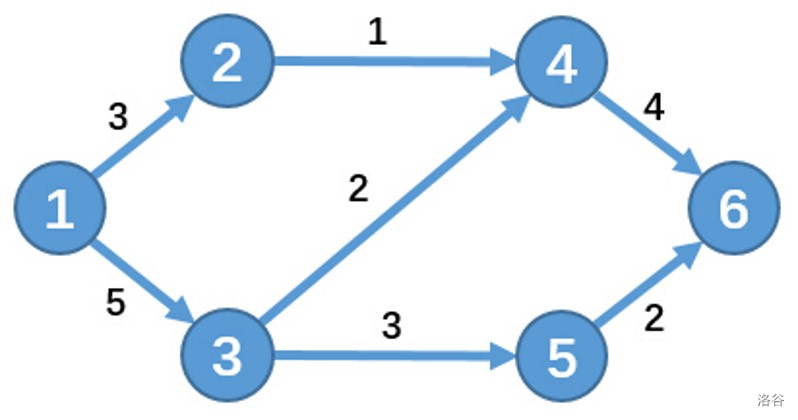
其中有一个源点 \(S\),一个汇点 \(T\)。流量从 \(S\) 源源不断地流出,每条边可以承载边权这么多的流量,每个点(除了 \(S,T\))要把它接受的流量全部流出(不能剩余),最后汇集到 \(T\),就像一个排水系统在工作。
我们将最后到达 \(T\) 的最大流量称为这个网络的最大流(Maxinum Flow)。
如果边上还有一个费用,每有一个流量流过都要支付这么多费用,最后使 \(T\) 接受最大流量的前提下,所使用的最小费用,称作这个网络的最小费用最大流(Mininum Cost & Maxinum Flow)。
0x01 暴力最大流:Ford-Fulkerson 算法
我们有一个 naive 的想法:每次从 \(S\) 发出一个流量,让它一直流到 \(T\),直到它不能流为止。在流的过程中,每流过一条边,我们就减少这条边的容量,避免下次流爆这条边。
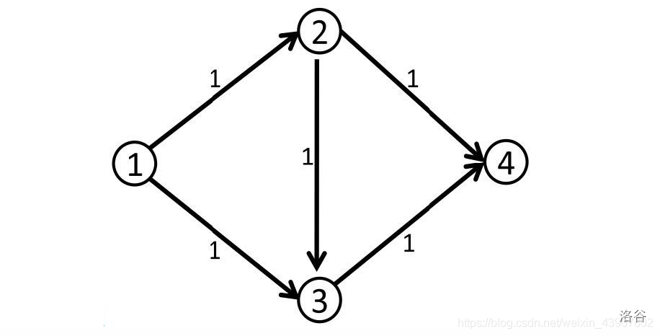
Hacked!如果我们不幸访问了 \(1\to 2\to 3\to 4\),你就寄了。明明有 \(maxflow=2\),我们却只有 \(1\),到底是什么地方出了问题?
观察到,不一定每条路径流过去都是最优的,那么我们加一条反悔边:当一条边 \((u,v)\) 流过了 \(w\) 的流量,我们就添加一条反向边 \((v,u)=w\)。如果以后我们发现走 \((u,v)\) 是不优的,我们就反悔,把这条路径分裂开,但是最大流不变。例如:
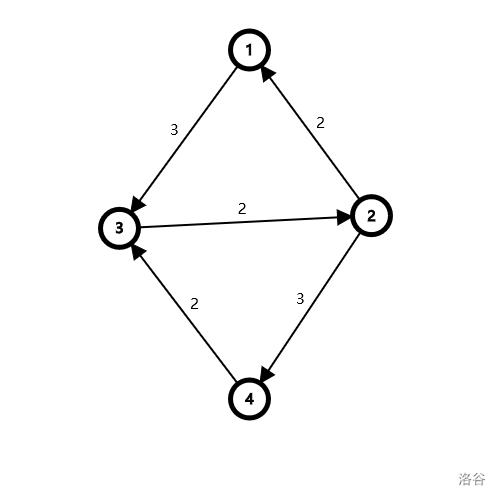
想象我们已经流了两个流量 \(1\to 2\to 3\to 4\),加上 \((2,1),(3,2),(4,3)\) 这些反悔边。现在试图走 \(1\to 3\to 2\to 4\),有了这个反悔边就可以成功流两个流量,现在真实的路径已经成为了 \(1\to 3\to 4\) 和 \(1\to2\to4\),达到了 \(maxflow=4\)。再来一个:
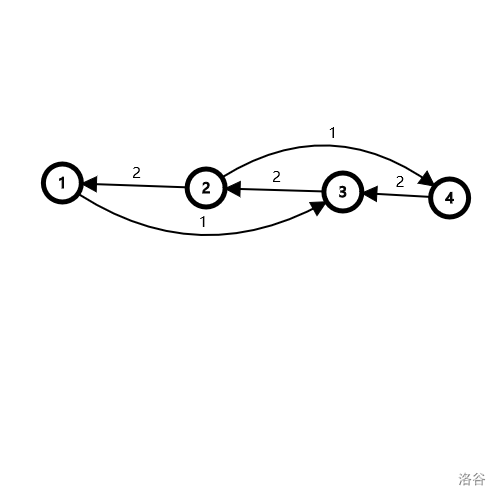
我们走了 \(1\to2\to3\to4\) 流了两个流量,现在试图走 \(1\to3\to2\to4\),是可以走过去的,且 \((3,2)\) 的反悔边没反悔完,所以最后实际上是拆成三条路径 \(1\to2\to3\to4\) 和 \(1\to3\to4\) 和 \(1\to 2\to 4\),最终 \(maxflow=3\)。
总而言之,它是正确的!于是我们可以开始模拟这个过程,得到了 FF 算法,它的复杂度是 \(O(Fm)\) 其中 \(F=maxflow\)。这样的复杂度随便卡。
0x02 最大流:Edmord-Karp 算法
为什么 FF 算法这么慢?
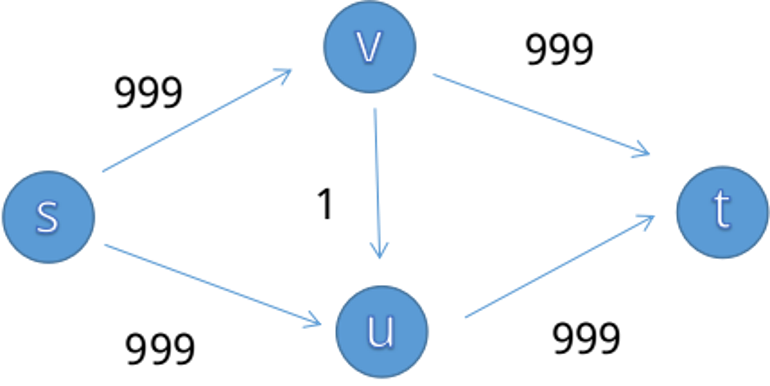
考虑优化一下,每次不要流一个流量这么少,我们使用 BFS,随便找一条路径,记录一路上最小的容量(不要走没有容量的边,可以当作不存在),再倒着回去流过来,这就是 EK 算法。复杂度 \(O(nm^2)\) 但跑不满。
0x03 最大流:Dinic 算法
为什么 EK 算法慢?我们发现,EK 一次只增广一条路径。考虑多条路径同时增广,我们先把图变成 DAG,一种可行的方法是求出每个节点的深度(BFS),增广时只走 \(dep_v=dep_u+1\) 的边,这样就没有环了,于是可以这样模拟增广的过程。
这就是 Dinic 算法,复杂度 \(O(n^2m)\)。为了吊打 EK,我们可以加入一些优化:
优化 1:当前弧优化
首先放一下原始代码:
LL dfs(int u,LL flow,int t){
if(u==t||!flow) return flow;
LL rest=flow;
for(int i=g.head[u];i;i=g.nxt[i]){
int v=g[i].v;
if(!g[i].v||dep[v]!=dep[u]+1) continue;
if(LL ans=dfs(v,min(rest,g[i].w),t)){
g[i].w-=ans,g[i^1].w+=ans;
rest-=ans;
if(!rest) break;
}
}
return flow-rest;
}
注意到一个点是会被重复走的(DAG),考虑第一次访问点 \(u\),它会放掉一部分流量给下一些点 \(v\),这些点 \(v\) 显然已经流完了,再给他们流量是没有意义的,所以第一次点 \(u\) 访问过的点 \(v\) 不需要再走,可以跳过。实现到代码里就是加一个 &,跳下一条边的同时删边。
注意,当前弧优化要把 if(!rest) break; 移到 if 里面,这条边可能没有流满,下一次仍要访问。
优化 2:炸点优化
考虑一个点 \(u\),它真的流不出流量,重复访问它是没有意义的,这时我们可以把这个点炸了,当它不存在。
0x04 最小费用最大流:EK/Dinic + SPFA = SSP
现在我们加入了费用!
怎么反悔?反悔可以理解成退钱,所以我们反悔可以把之前给的钱减掉,用一个负数即可。
考虑继续使用 EK 算法,现在我们不仅要管流量,还要管费用。可以贪心地选一条 \(S\to T\) 的最短路,把流量从这条最短路流过去,这就是最小费用最大流。
注意到费用可能为负(你自己定义的反悔边),可以使用 Bellman-Ford,复杂度是窒息的 \(O(Fnm)\)。如果有负环,SSP 将直接去世,需要消圈算法。
code EK + SPFA
template Dinic + SPFA
0x05 最小费用最大流:Dinic + Johnson 最短路 = 原始对偶
回忆一下我们怎样在负权图上跑 Dijkstra。
Recall:Johnson 全源最短路
首先我们跑一次 Bellman-Ford,判一下有没有负环,同时求出点 \(S\) 到点 \(u\) 的最短距离 \(h_u\)(距离定义为每条边的费用)。接下来是关键:将边 \((u,v)=w\) 的权值重定义为 \(w+h_u-h_v\)。最后跑 Dijkstra,所有 \(dis_u\) 更改为 \(dis_u-h_S+h_u\)。有几个问题:
为什么这些边有非负边权?考虑 \(h_u\) 是最短路长度,根据三角形不等式有 \(h_u+w(u,v)\geq h_v\),移项有 \(w(u,v)+h_u-h_v\geq 0\),证毕。
为什么最终答案为 \(dis_u-h_S+h_u\)?考虑这其实是错位相减,对于一条路径,前面的 \(-h_v\) 被后面来的 \(+h_u\) 抵消,最后剩下 \(h_S-h_u\),我们减掉这一部分就好了。
回到网络流
现在我们会了 Johnson,有个问题是怎么更新 \(h_u\),可以用这一次跑出来的最短路更新(\(h_u=dis_u-h_S+h_u\),注意到 \(h_S=0\))。考虑套上 Dinic,多路增广在最短路图上进行。我们需要换一下炸点优化,当前点 \(u\) 在栈里的时候炸掉它(\(vis_u=1\)),最后访问完再重构它(\(vis_u=0\)),如果它真的流不出去,炸了,这样就正确了。因为有可能存在零边权导致 dinic 转圈。
细节
在最短路图上要怎么判断呢?如果先写 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) h[i]+=dis[i];,那就要写 \(w(u,v)+h_u-h_v=0\) 为在最短路图上。原来是 \(dis_u+w(u,v)+h_u-h_v=dis_v\),移项并合并同类项后就是这个式子。
复杂度 \(O(Fm\log m)\),但实际表现不是很好(太长了)。
说句闲话,SSP 和原始对偶的区别在于最短路的求法,与增广路算法无关。应该是的。
本文来自博客园,作者:caijianhong,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/caijianhong/p/template-maxflow.html


