题解 ARC142E【Pairing Wizards】
problem
给定 \(n\) 个元素,每个元素有两个属性 \(a_i, b_i\)。
你可以花费 1 的代价使得其中一个元素的 \(a\) 属性 +1。
问最少多少代价,可以使得给定的 \(m\) 组 \((i,j)\) 关系符合:
- 要么满足 \(a_i >= b_i \land a_j >= b_j\);
- 要么满足 \(a_i >= b_j \land a_j >= b_i\)。
- \(2 \leq N \leq 100\)
- \(1 \leq a_i,b_i \leq 100\)
- \(1 \leq M \leq \frac{N(N-1)}{2}\)
- \(1 \leq x_i \lt y_i \leq N\)
- \((x_i,y_i) \neq (x_j,y_j)\), if \(i\neq j\).
- All values in input are integers.
solution
限制相当于 \(\max(a_i, a_j)\geq \max(b_i, b_j)\land\min(a_i, a_j)\geq \min(b_i, b_j)\)。我们通过强制调整使得第二个限制被满足(直接将 \(\min(b_i, b_j)\) 分别对 \(a_i, a_j\) chkmax),这样只需要考虑第一个限制。这时候就有:\(a_i\geq b_i\) 或者 \(a_i\geq b_j\),如果 \(a_i\geq b_i\land a_j\geq b_j\) 跳过,否则就是其中有一个 \(a_i\geq b_i\),另外一个 \(a_i\leq a_j<b_j\)。我们将 \(a_i\geq b_i\) 划归 A 类点,\(a_i<b_i\) 划归 B 类点,则限制是在 A 类点和 B 类点之间的边,竟然是二分图。
于是对于 \(\max(a_i, a_j)\geq \max(b_i, b_j)\),因为后面是常数,所以我们可以做最小割。
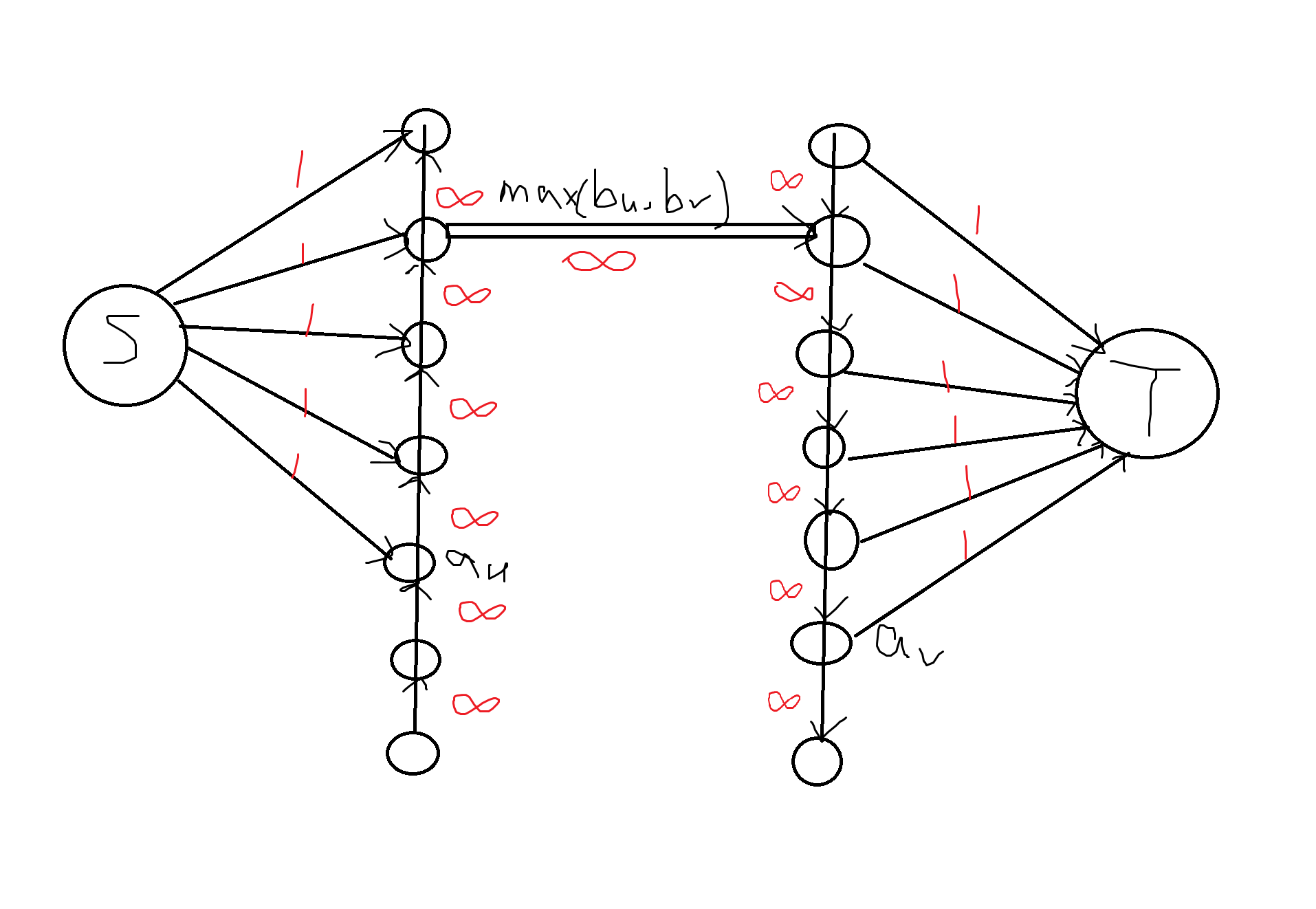
S 连 A 类点,T 连 B 类点,左边正链右边反链,就能完成题目限制。红色数字是边权。切完以后刚好是这样的。非常优美。
code
#include <queue>
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
#include <cstring>
#include <cassert>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
#ifdef LOCAL
#define debug(...) fprintf(stderr, ##__VA_ARGS__)
#else
#define debug(...) void(0)
#endif
typedef long long LL;
typedef long long LL;
template<int N,int M,class T=int> struct graph{
int head[N+10],nxt[M*2+10],cnt,tot;
struct edge{
int u,v;T w;
edge(int u=0,int v=0,T w=0):u(u),v(v),w(w){}
} e[M*2+10];
graph(){memset(head,tot=cnt=0,sizeof head);}
edge& operator[](int i){return e[i];}
void add(int u,int v,T w=0){e[++cnt]=edge(u,v,w),nxt[cnt]=head[u],head[u]=cnt;}
void link(int u,int v,T w=0){add(u,v,w),add(v,u,w);}
};
template<int N,int M,class T=int> struct maxflow_g:public graph<N,M,T>{
graph<N,M,T>&g=*this;
maxflow_g(){g.add(0,0,0);}
void insert(int u,int v,T w){debug("%d %d %d\n", u, v, w), g.add(u,v,w),g.add(v,u,0);}
int dep[N+10],cur[N+10];
bool bfs(int s,int t){
queue<int> q; memset(dep,0x3f,sizeof dep);
for(q.push(s),dep[s]=0;!q.empty();){
int u=q.front(); q.pop();
for(int i=g.head[u];i;i=g.nxt[i]){
int v=g[i].v; if(!g[i].w) continue;
if(dep[v]>dep[u]+1) q.push(v),dep[v]=dep[u]+1;
}
}
return dep[t]!=dep[0];
}
T dfs(int u,T flow,int t){
if(u==t||!flow) return flow;
T rest=flow;
for(int &i=cur[u];i;i=g.nxt[i]){
int v=g[i].v; if(dep[v]!=dep[u]+1||!g[i].w) continue;
T run=dfs(v,min(rest,g[i].w),t);
if(g[i].w-=run,g[i^1].w+=run,!(rest-=run)) break;
}
if(rest==flow) dep[u]=-1;
return flow-rest;
}
T maxflow(int s,int t,T inf){
T flow=0;
while(bfs(s,t)) memcpy(cur,g.head,sizeof cur),flow+=dfs(s,inf,t);
return flow;
}
};
int n, a[110], b[110], c[110], id[110][110], m;
int V = 100;
bool islimed[110][110];
maxflow_g<100010, 300010, int> g;
int main() {
scanf("%d", &n);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) scanf("%d%d", &a[i], &b[i]), c[i] = a[i];
scanf("%d", &m);
for (int i = 1, u, v; i <= m; i++) {
scanf("%d%d", &u, &v);
islimed[u][v] = islimed[v][u] = 1;
a[u] = max(a[u], min(b[u], b[v]));
a[v] = max(a[v], min(b[u], b[v]));
}
int S = ++g.tot, T = ++g.tot;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
//debug(">>> i = %d\n", i);
//id[i][j - 1] <=> id[i][j] is the real edge
if (a[i] < b[i]) {
for (int j = 0; j <= V; j++) id[i][j] = ++g.tot;
g.insert(S, id[i][0], 1e9), g.insert(id[i][V], T, 1e9);
for (int j = 1; j < a[i]; j++) g.insert(id[i][j - 1], id[i][j], 1e9);
for (int j = a[i]; j <= V; j++) g.insert(id[i][j - 1], id[i][j], j - c[i]);
} else {
for (int j = 1; j <= V + 1; j++) id[i][j] = ++g.tot;
g.insert(S, id[i][V + 1], 1e9), g.insert(id[i][1], T, 1e9);
for (int j = 1; j < a[i]; j++) g.insert(id[i][j + 1], id[i][j], 1e9);
for (int j = a[i]; j <= V; j++) g.insert(id[i][j + 1], id[i][j], j - c[i]);
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
if (!islimed[i][j]) continue;
if ((a[i] >= b[i] && a[j] >= b[j]) || (a[i] >= b[j] && a[j] >= b[i])) continue;
if (a[i] >= b[i]) continue;
//a[i] < b[i], a[j] >= b[j]
int maxb = max(b[i], b[j]);
g.insert(id[i][maxb], id[j][maxb - 1], 1e9);
g.insert(id[j][maxb], id[i][maxb - 1], 1e9);
}
}
printf("%d\n", g.maxflow(S, T, 1e9));
return 0;
}
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#ifdef LOCAL
#define debug(...) fprintf(stderr, ##__VA_ARGS__)
#else
#define endl "\n"
#define debug(...) void(0)
#endif
typedef long long LL;
template <class T>
struct graph {
struct edge {
int u, v;
T w;
};
vector<edge> e;
vector<int> head, nxt;
edge& operator[](int i) { return e[i]; }
edge operator[](int i) const { return e[i]; }
graph(int n = 0) : head(n, -1) {}
size_t size() const { return head.size(); }
void add(int u, int v, T w = T{}) {
nxt.push_back(exchange(head[u], e.size()));
e.push_back((edge){u, v, w});
}
void link(int u, int v, T w = T{}) { add(u, v, w), add(v, u, w); }
int newnode() { head.push_back(-1); return head.size() - 1; }
};
template <class Cap>
struct mf_graph {
graph<Cap> g;
vector<int> dep, cur;
mf_graph(int n = 0) : g(n) {}
int newnode() { return g.newnode(); }
void add(int u, int v, Cap cap) { debug("%d %d %d\n", u, v, cap), g.add(u, v, cap), g.add(v, u, 0); }
bool bfs(int s, int t) {
dep.assign(g.size(), -1);
queue<int> q;
q.push(s);
dep[s] = 0;
while (!q.empty()) {
int u = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int i = g.head[u]; ~i; i = g.nxt[i]) {
int v = g[i].v;
if (g[i].w && dep[v] == -1) dep[v] = dep[u] + 1, q.push(v);
}
}
return dep[t] != -1;
}
Cap dfs(int u, Cap flw, int t) {
if (u == t) return flw;
Cap res = flw;
for (int& i = cur[u]; ~i; i = g.nxt[i]) {
int v = g[i].v;
if (g[i].w && dep[v] == dep[u] + 1) {
Cap run = dfs(v, min(res, g[i].w), t);
g[i].w -= run, g[i ^ 1].w += run;
res -= run;
if (!res) break;
}
}
if (res == flw) dep[u] = -1;
return flw - res;
}
Cap flow(int s, int t, Cap lim = numeric_limits<Cap>::max()) {
Cap flw = 0;
while (lim && bfs(s, t)) {
cur = g.head;
Cap run = dfs(s, lim, t);
flw += run, lim -= run;
}
return flw;
}
};
int n, a[110], b[110], ans, m, tot, id[110];
bool vis[110][110];
mf_graph<int> mf(10010);
int main() {
#ifndef LOCAL
cin.tie(nullptr)->sync_with_stdio(false);
#endif
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> a[i] >> b[i], ans -= a[i];
cin >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
int u, v;
cin >> u >> v;
vis[u][v] = vis[v][u] = true;
a[u] = max(a[u], min(b[u], b[v]));
a[v] = max(a[v], min(b[u], b[v]));
}
int s0 = tot++, t0 = tot++, V = 100;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
ans += a[i];
tot += V;
id[i] = tot;
if (a[i] >= b[i]) {
for (int j = 1; j < V; j++) mf.add(tot - j, tot - j - 1, 1e9);
for (int j = a[i] + 1; j <= V; j++) mf.add(s0, tot - j, 1);
} else {
for (int j = 1; j < V; j++) mf.add(tot - j - 1, tot - j, 1e9);
for (int j = a[i] + 1; j <= V; j++) mf.add(tot - j, t0, 1);
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j <= n; j++) {
if (!vis[i][j]) continue;
if (a[i] >= b[i] && a[j] >= b[j]) continue;
if (a[i] >= b[j] && a[j] >= b[i]) continue;
int mx = max(b[i], b[j]);
if (a[i] >= b[i]) mf.add(id[i] - mx, id[j] - mx, 1e9);
else mf.add(id[j] - mx, id[i] - mx, 1e9);
}
}
debug("ans = %d\n", ans);
cout << ans + mf.flow(s0, t0) << endl;
return 0;
}
本文来自博客园,作者:caijianhong,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/caijianhong/p/solution-ARC142E.html


