Trees on the level UVA - 122 (二叉树的层次遍历)
题目链接:https://vjudge.net/problem/UVA-122
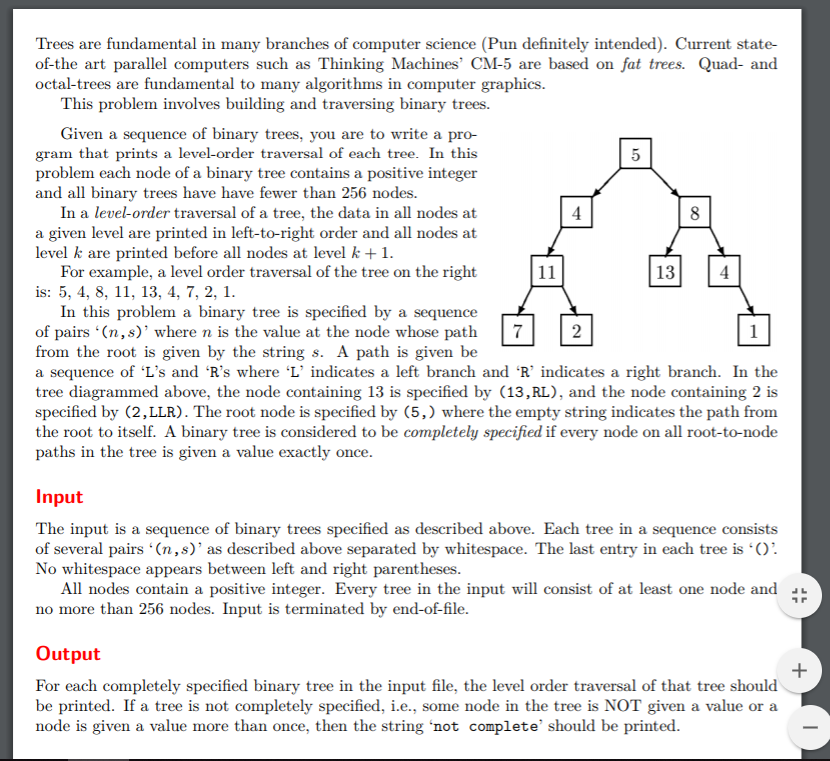

题目大意:输入一颗二叉树,你的任务是按从上到下,从左到右的顺序输出各个结点的值。每个结点都按照从根节点到它的移动序列给出(L表示左,R表示右) 在输入中,每个结点的左括号
和右括号之间没有空格,相邻结点之间用一个空格隔开。每棵树的输入用一对空括号)()结束 入上图所示:
注意:如果从根结点到某个叶节点的路径有的结点没有在输入中给出,或者给出超过一次,输出not complete。 结点个数不超过256
思路:显然是二叉树的层次遍历。
首先看一下输入部分:
bool read_input()//读入字符 { failed=false;//记录是否输入有误 remove_tree(root);//释放内存空间 root=newnode();//创建根节点 for(;;) { if(scanf("%s",s)!=1) return false;//整个输入结束 if(!strcmp(s,"()")) break;//读到结束标志 退出循环 int v; sscanf(&s[1],"%d",&v);//读入节点值 addnode(v,strchr(s,',')+1);// } return true; }
这里要学一下sscanf的用法 strchr的用法
接下来看一下建树的代码:
void addnode(int v,char* s) { int len=strlen(s); Node* u=root;//从根节点往下走 for(int i=0;i<len;i++)//找到当前位置 { if(s[i]=='L') { if(u->Left==NULL) u->Left=newnode();//节点不存在 建立新节点 u=u->Left; } else if(s[i]=='R') { if(u->Right==NULL) u->Right=newnode(); u=u->Right; } //忽略其他情况 即最后多余的那个空格 } if(u->have_value) failed=true;//已经赋过值 表明输入有误 u->v=v;//没有误 给节点赋值 u->have_value=true;//标记已经赋值 }
建完树之后便是层次遍历的过程了,这里用bfs来写:
bool bfs(vector<int>& ans) { queue<Node*> q; ans.clear(); q.push(root);//初始时只有一个根节点 while(!q.empty()) { Node* u=q.front(); q.pop(); if(!u->have_value) return false;//有节点没有被赋值过 表明输入有误 ans.push_back(u->v);//增加到输出序列尾部 if(u->Left!=NULL) q.push(u->Left); if(u->Right!=NULL) q.push(u->Right); } return true; }
这里有一块代码 是释放内存的 没有也不会错
void remove_tree(Node* u) { if(u==NULL) return ; remove_tree(u->Left);//递归释放左子树的空间 remove_tree(u->Right);// delete u; }
下面看完整代码:
#include<iostream> #include<string.h> #include<stdio.h> #include<vector> #include<queue> using namespace std; const int maxn=256+5; char s[maxn];//保存读入的节点 bool failed; struct Node{ bool have_value;//是否被赋值过 int v;//结点值 Node *Left,*Right; Node() { have_value=false; Left=NULL; Right=NULL; } }; Node *root; void remove_tree(Node* u) { if(u==NULL) return ; remove_tree(u->Left);//递归释放左子树的空间 remove_tree(u->Right);// delete u; } Node* newnode() { return new Node(); } void addnode(int v,char* s) { int len=strlen(s); Node* u=root;//从根节点往下走 for(int i=0;i<len;i++)//找到当前位置 { if(s[i]=='L') { if(u->Left==NULL) u->Left=newnode();//节点不存在 建立新节点 u=u->Left; } else if(s[i]=='R') { if(u->Right==NULL) u->Right=newnode(); u=u->Right; } //忽略其他情况 即最后多余的那个空格 } if(u->have_value) failed=true;//已经赋过值 表明输入有误 u->v=v;//没有误 给节点赋值 u->have_value=true;//标记已经赋值 } bool read_input()//读入字符 { failed=false;//记录是否输入有误 remove_tree(root);//释放内存空间 root=newnode();//创建根节点 for(;;) { if(scanf("%s",s)!=1) return false;//整个输入结束 if(!strcmp(s,"()")) break;//读到结束标志 退出循环 int v; sscanf(&s[1],"%d",&v);//读入节点值 addnode(v,strchr(s,',')+1);// } return true; } /* 这样一来 输入和建树部分就已经结束了 接下来只需要按照层次顺序遍历这棵树 此处使用一个队列来完成这个任务 初始时只有一个根节点 然后每次取出一个节点 就把它的左右子结点放入队列中 */ bool bfs(vector<int>& ans) { queue<Node*> q; ans.clear(); q.push(root);//初始时只有一个根节点 while(!q.empty()) { Node* u=q.front(); q.pop(); if(!u->have_value) return false;//有节点没有被赋值过 表明输入有误 ans.push_back(u->v);//增加到输出序列尾部 if(u->Left!=NULL) q.push(u->Left); if(u->Right!=NULL) q.push(u->Right); } return true; } int main() { while(read_input()) { vector<int>ans; vector<int>::iterator it; if(failed||(!bfs(ans))) printf("not complete\n"); else { it=ans.begin(); printf("%d",*it); it++; for(it;it!=ans.end();it++) printf(" %d",*it); printf("\n"); } } return 0; }
当初的梦想实现了吗,事到如今只好放弃吗~




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号