Spring对IOC的理解
一、IOC控制反转和DI依赖注入
1.控制反转,字面可以理解为:主动权的转移,原来一个应用程序内的对象是类通过new去主动创建并实例化的,对对像创建的主动权在程序代码中。程序不仅要管理业务逻辑也要管理对的象创建和依赖关系。这是很累的,也跟软件工程 "低耦合高内聚" 的概念不十分符合。
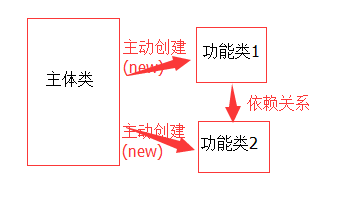
有了spring的ioc容器之后,对象的实例化和依赖关系管理都由IOC容器进行统一管理,主体类只要依赖ioc容器就够了,需要啥,容器会给他注入进去,也就是只要声明对象不用再主动去new,ioc容器帮忙把相应的对象注入到声明对象中,使其变成实例化对象。(类似主体类提供一个躯体,ioc容器把灵魂注入进去,使其变成一个生命体,激活他),这样创建对象的主动权就转移交接了,
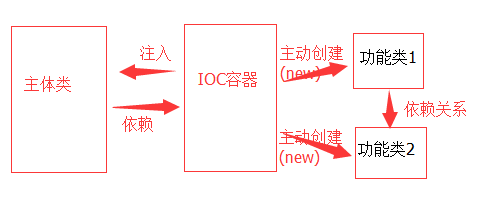
二、使用xml配置方式实现IOC
1.在ioc容器中配置了dao实现类和service类的bean,在容器加载的时候就会实例化这些bean到内存中。(bean.xml配置如下)
1 <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" 2 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" 3 xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans 4 http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd 5 "> 6 7 <!-- BookDao Bean --> 8 <bean id="bookDao" class="com.study.DaoImpl.BookDaoImpl"></bean> 9 10 <!-- BookService Bean--> 11 <bean id="bookService" class="com.study.Service.BookService"> 12 <!-- BookService中的声明了BookDao对象,通过ref属性将BookDao的bean注入到对象中 --> 13 <property name="bookDao" ref="bookDao"/> 14 </bean> 15 </beans>
2. service类中需要用到dao类的实例(正常情况下需要new一个dao类对象),但是用ioc容器接管后只需要声明dao接口对象即可,然后写一个dao对象的set方法。(要注入的对象必须要有set方法,否则将报错 Bean property 'bookDao' is not writable or has an invalid setter method)因为spring注入是根据反射机制实现的,他在反射注入的时候会调用该方法名的set方法,如果set方法写错,或者根本没写,那么注入就会失败。(BookService类如下)
1 public class BookService { 2 private BookDao bookDao; 3 4 public BookService() { 5 System.out.println("BookService实例化"); 6 } 7 8 public void setBookDao(BookDao bookDao) { 9 System.out.println("BookService属性初始化装配成功"); 10 this.bookDao = bookDao; 11 } 12 13 public void storeBook(String bookname){ 14 System.out.println("图书上架"); 15 System.out.println(bookDao.addBook(bookname)); 16 } 17 }
如上代码:BookSerivce类需要用到BookDao对象,但是却没有new对象,只有一个set方法,这个set方法就是ioc容器注入的入口(必不可少),
3.此处我们用ApplicationContext作为容器,初始化配置文件,然后从容器中根据id名取出容器中已经帮我们实例化好的对象。
1 public class TestDmeo { 2 BookService bookService; 3 4 @Test 5 public void testStoreBook(){ 6 System.out.println("容器初始化"); 7 ApplicationContext app = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml"); 8 bookService = (BookService) app.getBean("bookService");//将对象注入到声明好的BookService对象中。(bookService就是配置文件中的id) 9 bookService.storeBook("Spring MVC"); 10 } 11 }
getBean中的参数就是配置文件中的bean的id名,这个id在spring进行反射实例化的时候,相当于实例化对象的名称:

4.dao类和实现类如下:
接口类:
1 public interface BookDao { 2 public String addBook(String BookName); 3 }
实现类:
1 public class BookDaoImpl implements BookDao { 2 3 public BookDaoImpl() { 4 System.out.println("BookDao实例化"); 5 } 6 7 public String addBook(String BookName) { 8 return BookName+"添加成功"; 9 } 10 }
5.运行测试结果:
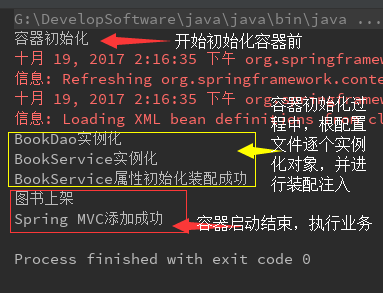
6.大体思路如下图:
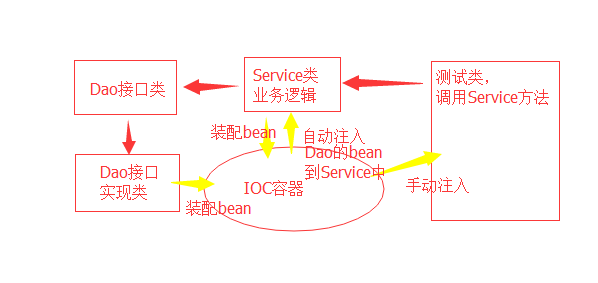
程序中除了初始化容器用了new对象,其余的基本没有new的存在。
二、注解方式配置IOC
注解配置方式目的和xml配置的目的一样,都是为了实现bean的创建。常用的注解如下:
-
-
- @Component 在类定义之前添加@Component注解,他会被spring容器识别,并转为bean。
- @Repository 对Dao实现类进行注解 (特殊的@Component)
- @Service 用于对业务逻辑层进行注解, (特殊的@Component)
- @Controller 用于控制层注解 , (特殊的@Component)
-
装配注解如下:
-
-
- @Autowired 默认按照类型装配注入,想按照名称来装配的话要结合@Qualifier(“name”)一起使用,使用@Autowired注解可以不用set方法。@Autowired 注释进行自动注入时,Spring 容器中匹配的候选 Bean 数目必须有且仅有一个
- @Qualifier("name") 中的name是bean的名字,也就是id,和@Autowired可以作为限定专配对象的名称
- @Resource 默认按照名称装配注入,当找不到对应名成的bean的时候就按照类型匹配,如果还是找不到的话就会报错,@Autowired是spring提供的,@Resource是javaee提供,使用@Resource可以减少对spring的依赖
-
范例:
1.例子同上,只是配置bean的方式从xml文件中转移到了代码中,用注解体现。
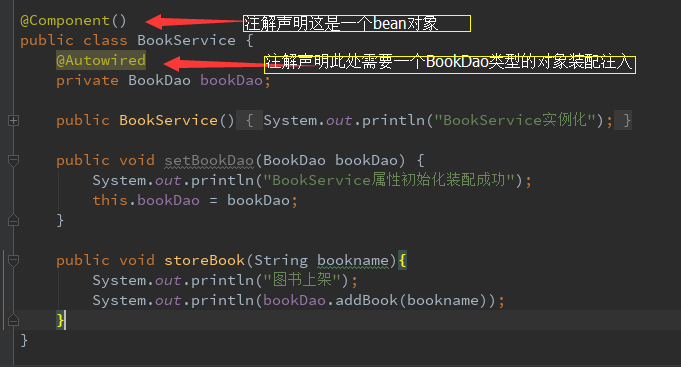
2.除了把配置文件中<bean id="" class=""/>变成对应的注解外,另外一个区别在于,bean.xml文件中的修改,需要做如下,配置才能够使注解生效
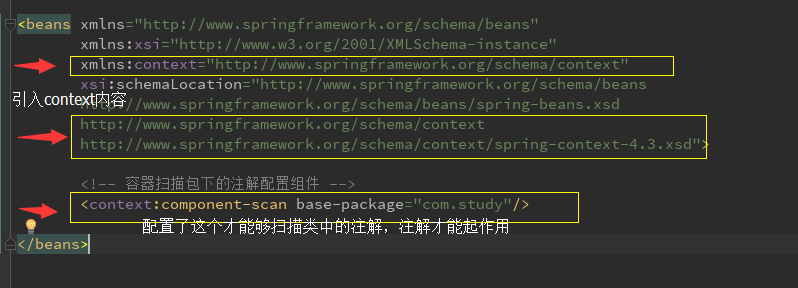
context的配置有如下方法:
1.仅扫描特定包下的特定类:
1 <context:component-scan base-package="com.study" resource-pattern="Service/B*.class"/>
这是扫描Service包下B开头的所有类。
2.使用<context:include-filter .../>和<context:exclude-filter .../>配置那些需要和不需要的扫描的包
| 过滤器类型 | 描述 |
| annotation | 过滤器扫描使用注解所标注的那些类,通过expression属性指定要扫描的注释 |
| assignable | 过滤器扫描派生于expression属性所指定类型的那些类 |
| aspectj | 过滤器扫描与expression属性所指定的AspectJ表达式所匹配的那些类 |
| custom | 使用自定义的org.springframework.core.type.TypeFliter实现类,该类由expression属性指定 |
| regex | 过滤器扫描类的名称与expression属性所指定正则表示式所匹配的那些类 |
1 <!-- 容器扫描包下的注解配置组件 --> 2 <context:component-scan base-package="com.study" use-default-filters="false"><!--- user-default-filters="false"必须要设置成false,不然下面配置的过滤规则会被默认的注解过滤方式覆盖 ——> 3 <context:include-filter type="aspectj" expression="com.study.Service.*"/> <!-- 过滤器扫描与expression属性所指定的AspectJ表达式所匹配的那些类 --> 4 <context:include-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Component"/><!-- 过滤指定的注解 --> 5 <context:include-filter type="assignable" expression="com.study.Service.BookService"/><!-- 过滤指定的类或接口,路径要完整,如果是接口的话,所有派生类都会被过滤 --> 6 <context:include-filter type="regex" expression="com.*"/><!-- 过滤器扫描类的名称与expression属性所指定正则表示式所匹配的那些类 --> 7 </context:component-scan>
<context:exclude-filter ../>要配在<context:include-filter .../>的后面。
配置了<context:include-filter .../>,他会把符合过滤条件的类转化成bean,并不是只有@Component、@Service。。。等注解才能注解bean,通过过滤器也可以达到转换成bean的效果。
最后:aspectj表达式可参考:http://blog.csdn.net/peng658890/article/details/7223046




