c#并行编程
作者:释迦苦僧 出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/woxpp/p/3924476.html
本文版权归作者和博客园共有,欢迎转载,但未经作者同意必须保留此段声明,且在文章页面明显位置给出原文连接
一、相关概念
背景:当今计算机至少都有一颗双核的微处理器,带有四核、八核的计算机非常常见,在单个处理器上具有多个内核的时代正在来临,现代微处理器提供了新型的的多核架构,
因此软件设计和编码能够充分发挥这些架构的功能是非常重要的事情,也要与时俱进。
多核微处理器:
多核微处理器有很多不同的复杂微结构,意在提供更强的并行执行能力,提升云吐量,减少潜在的性能瓶颈,缩减电源消耗,并减少发热量,因此,现代很多的微处理器可以根据工作负载提升或
降低每个内核的时钟频率,甚至可以将不在使用中的内核进入睡眠状态,等需要这些内核的时候,操作系统又会唤醒它们。
硬件线程与软件线程
多核处理器带有一个以上的物理内核,每个物理内核 都可能会提供多个硬件线程,也称之为逻辑内核或者逻辑处理器。
windows中每个运行的程序都是一个进程,每个进程都会创建并运行一个或者多个线程,也被称为软件线程(software thread),在一个进程当中只要有一个线程,这个线程我们就称之为主线程。
操作系统的调度器在所有要运行的进程和线程之间公平的分享可用的处理资源,给每一个软件线程分配处理时间,当Windows调度器运行在多核微处理器上时,调度器必须从物理内核支持的硬件线程中分配时间给一个需要运行指令的软件线程。
并行任务的利与弊
1、并行任务的运行和管理都是需要开销的,在程序中需要执行的任务越多,并行的效果越好。
2、并行任务中对于共享的资源或数据越多,对并行任务的执行性能损耗越大,如果每个任务的资源都是独立存在的,性能会好很多。
多线程
多线程是指从软件或者硬件上实现多个线程并发执行的技术,具有多线程能力的计算机因有硬件支持而能够在同一时间执行多一个线程,进而提升处理能力。
多线程的作用不只是并行计算,还有其他的作用(如降低阻塞,在单核时代,多线程的这个消除阻塞的作用我们称之为"并发",)
二、Parallel
TPL中引入了一个新命名空间System.Threading.Tasks,在该命名空间下Task是主类,表示一个类的异步的并发的操作, 创建并行代码的时候不一定要直接使用task类,在某些情况下可以
直接使用Parallel静态类(System.Threading.Tasks.Parallel)下所提供的方法,而不用底层的Task实例。
Parallel.Invoke
试图将很多方法并行运行,如果传入的是4个方法,则至少需要4个逻辑内核才能足以让这四个方法并发运行,逻辑内核也称为硬件线程。
需要注意的是:1、即食拥有4个逻辑内核,也不一定能够保证所需要运行的4个方法并发运行,逻辑内核也称为硬件线程,如果其中的一个内核处于繁忙状态,那么底层的调度逻辑可能会延迟某些方法的初始化执行。
2、通过Parallel.Invoke编写的并发执行代码一定不能依赖于特定的执行顺序,因为它的并发顺序也是不定的。
3、使用Parallel.Invoke方法一定要测量运行结果、实现加速比比以及逻辑内核的使用率,这点很重要。
4.使用Parallel.Invoke,在运行并行方法前都会产生一些额外的开销,如分配硬件线程等。

class Program { private static List<Product> ProductList = null; /* coder:释迦苦僧 * 没有特定的执行顺序 * 示例中 基于电脑配置 采用了4个方法的并行编程 * Parallel.Invoke 首先会尝试并行启动4个方法,充分利用一个或多个物理处理器所提供的多个逻辑内核 * 但是在实际的并行执行中,至少要有4个逻辑内核才能满足4个方法的并行运行 * 如果有个或者多个逻辑内核处于繁忙状态,那么底层的调度逻辑可能会延迟某些方法的初始化执行 * 通过Parallel.Invoke编写的并发执行代码一定不能依赖与特定的执行顺序,因为它的并发执行顺序也是不定的。 */ static void Main(string[] args) { ProductList = new List<Product>(); Thread.Sleep(3000); Stopwatch swTask = new Stopwatch(); swTask.Start(); /*执行并行操作*/ Parallel.Invoke(SetProcuct1_500, SetProcuct2_500, SetProcuct3_500, SetProcuct4_500); swTask.Stop(); Console.WriteLine("500条数据 并行编程所耗时间:" + swTask.ElapsedMilliseconds); ProductList = new List<Product>(); Thread.Sleep(3000);/*防止并行操作 与 顺序操作冲突*/ Stopwatch sw = new Stopwatch(); sw.Start(); SetProcuct1_500(); SetProcuct2_500(); SetProcuct3_500(); SetProcuct4_500(); sw.Stop(); Console.WriteLine("500条数据 顺序编程所耗时间:" + sw.ElapsedMilliseconds); ProductList = new List<Product>(); Thread.Sleep(3000); swTask.Restart(); /*执行并行操作*/ Parallel.Invoke(() => SetProcuct1_10000(), () => SetProcuct2_10000(), () => SetProcuct3_10000(), () => SetProcuct4_10000()); swTask.Stop(); Console.WriteLine("10000条数据 并行编程所耗时间:" + swTask.ElapsedMilliseconds); ProductList = new List<Product>(); Thread.Sleep(3000); sw.Restart(); SetProcuct1_10000(); SetProcuct2_10000(); SetProcuct3_10000(); SetProcuct4_10000(); sw.Stop(); Console.WriteLine("10000条数据 顺序编程所耗时间:" + sw.ElapsedMilliseconds); Console.ReadLine(); } private static void SetProcuct1_500() { for (int index = 1; index < 500; index++) { Product model = new Product(); model.Category = "Category" + index; model.Name = "Name" + index; model.SellPrice = index; ProductList.Add(model); } Console.WriteLine("SetProcuct1 执行完成"); } private static void SetProcuct2_500() { for (int index = 500; index < 1000; index++) { Product model = new Product(); model.Category = "Category" + index; model.Name = "Name" + index; model.SellPrice = index; ProductList.Add(model); } Console.WriteLine("SetProcuct2 执行完成"); } private static void SetProcuct3_500() { for (int index = 1000; index < 2000; index++) { Product model = new Product(); model.Category = "Category" + index; model.Name = "Name" + index; model.SellPrice = index; ProductList.Add(model); } Console.WriteLine("SetProcuct3 执行完成"); } private static void SetProcuct4_500() { for (int index = 2000; index < 3000; index++) { Product model = new Product(); model.Category = "Category" + index; model.Name = "Name" + index; model.SellPrice = index; ProductList.Add(model); } Console.WriteLine("SetProcuct4 执行完成"); } private static void SetProcuct1_10000() { for (int index = 1; index < 20000; index++) { Product model = new Product(); model.Category = "Category" + index; model.Name = "Name" + index; model.SellPrice = index; ProductList.Add(model); } Console.WriteLine("SetProcuct1 执行完成"); } private static void SetProcuct2_10000() { for (int index = 20000; index < 40000; index++) { Product model = new Product(); model.Category = "Category" + index; model.Name = "Name" + index; model.SellPrice = index; ProductList.Add(model); } Console.WriteLine("SetProcuct2 执行完成"); } private static void SetProcuct3_10000() { for (int index = 40000; index < 60000; index++) { Product model = new Product(); model.Category = "Category" + index; model.Name = "Name" + index; model.SellPrice = index; ProductList.Add(model); } Console.WriteLine("SetProcuct3 执行完成"); } private static void SetProcuct4_10000() { for (int index = 60000; index < 80000; index++) { Product model = new Product(); model.Category = "Category" + index; model.Name = "Name" + index; model.SellPrice = index; ProductList.Add(model); } Console.WriteLine("SetProcuct4 执行完成"); } } class Product { public string Name { get; set; } public string Category { get; set; } public int SellPrice { get; set; } }
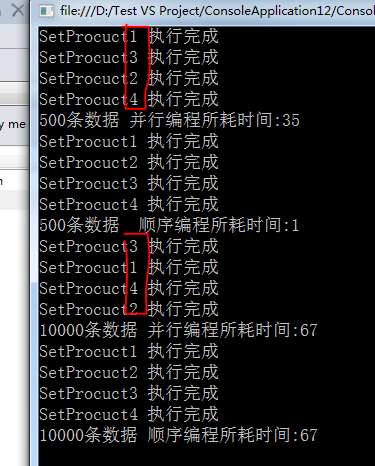
图中我们可以看出利用Parallel.Invoke编写的并发执行,它的并发执行顺序也是不定的。
但是所执行的时间上比不采用并行编程所耗的时间差不多。
这是因为我们在并行编程中操作了共享资源ProductList,如果把代码做出以下修改,采用并行编程的好处就显现出来了。

class Program { /* coder:释迦苦僧 * 没有特定的执行顺序 * 示例中 基于电脑配置 采用了4个方法的并行编程 * Parallel.Invoke 首先会尝试并行启动4个方法,充分利用一个或多个物理处理器所提供的多个逻辑内核 * 但是在实际的并行执行中,至少要有4个逻辑内核才能满足4个方法的并行运行 * 如果有个或者多个逻辑内核处于繁忙状态,那么底层的调度逻辑可能会延迟某些方法的初始化执行 * 通过Parallel.Invoke编写的并发执行代码一定不能依赖与特定的执行顺序,因为它的并发执行顺序也是不定的。 */ static void Main(string[] args) { Thread.Sleep(3000); Stopwatch swTask = new Stopwatch(); swTask.Start(); /*执行并行操作*/ Parallel.Invoke(SetProcuct1_500, SetProcuct2_500, SetProcuct3_500, SetProcuct4_500); swTask.Stop(); Console.WriteLine("500条数据 并行编程所耗时间:" + swTask.ElapsedMilliseconds); Thread.Sleep(3000);/*防止并行操作 与 顺序操作冲突*/ Stopwatch sw = new Stopwatch(); sw.Start(); SetProcuct1_500(); SetProcuct2_500(); SetProcuct3_500(); SetProcuct4_500(); sw.Stop(); Console.WriteLine("500条数据 顺序编程所耗时间:" + sw.ElapsedMilliseconds); Thread.Sleep(3000); swTask.Restart(); /*执行并行操作*/ Parallel.Invoke(() => SetProcuct1_10000(), () => SetProcuct2_10000(), () => SetProcuct3_10000(), () => SetProcuct4_10000()); swTask.Stop(); Console.WriteLine("10000条数据 并行编程所耗时间:" + swTask.ElapsedMilliseconds); Thread.Sleep(3000); sw.Restart(); SetProcuct1_10000(); SetProcuct2_10000(); SetProcuct3_10000(); SetProcuct4_10000(); sw.Stop(); Console.WriteLine("10000条数据 顺序编程所耗时间:" + sw.ElapsedMilliseconds); Console.ReadLine(); } private static void SetProcuct1_500() { List<Product> ProductList = new List<Product>(); for (int index = 1; index < 500; index++) { Product model = new Product(); model.Category = "Category" + index; model.Name = "Name" + index; model.SellPrice = index; ProductList.Add(model); } Console.WriteLine("SetProcuct1 执行完成"); } private static void SetProcuct2_500() { List<Product> ProductList = new List<Product>(); for (int index = 500; index < 1000; index++) { Product model = new Product(); model.Category = "Category" + index; model.Name = "Name" + index; model.SellPrice = index; ProductList.Add(model); } Console.WriteLine("SetProcuct2 执行完成"); } private static void SetProcuct3_500() { List<Product> ProductList = new List<Product>(); for (int index = 1000; index < 2000; index++) { Product model = new Product(); model.Category = "Category" + index; model.Name = "Name" + index; model.SellPrice = index; ProductList.Add(model); } Console.WriteLine("SetProcuct3 执行完成"); } private static void SetProcuct4_500() { List<Product> ProductList = new List<Product>(); for (int index = 2000; index < 3000; index++) { Product model = new Product(); model.Category = "Category" + index; model.Name = "Name" + index; model.SellPrice = index; ProductList.Add(model); } Console.WriteLine("SetProcuct4 执行完成"); } private static void SetProcuct1_10000() { List<Product> ProductList = new List<Product>(); for (int index = 1; index < 20000; index++) { Product model = new Product(); model.Category = "Category" + index; model.Name = "Name" + index; model.SellPrice = index; ProductList.Add(model); } Console.WriteLine("SetProcuct1 执行完成"); } private static void SetProcuct2_10000() { List<Product> ProductList = new List<Product>(); for (int index = 20000; index < 40000; index++) { Product model = new Product(); model.Category = "Category" + index; model.Name = "Name" + index; model.SellPrice = index; ProductList.Add(model); } Console.WriteLine("SetProcuct2 执行完成"); } private static void SetProcuct3_10000() { List<Product> ProductList = new List<Product>(); for (int index = 40000; index < 60000; index++) { Product model = new Product(); model.Category = "Category" + index; model.Name = "Name" + index; model.SellPrice = index; ProductList.Add(model); } Console.WriteLine("SetProcuct3 执行完成"); } private static void SetProcuct4_10000() { List<Product> ProductList = new List<Product>(); for (int index = 60000; index < 80000; index++) { Product model = new Product(); model.Category = "Category" + index; model.Name = "Name" + index; model.SellPrice = index; ProductList.Add(model); } Console.WriteLine("SetProcuct4 执行完成"); } } class Product { public string Name { get; set; } public string Category { get; set; } public int SellPrice { get; set; } }
将每个方法中的资源隔离,性能显而易见。
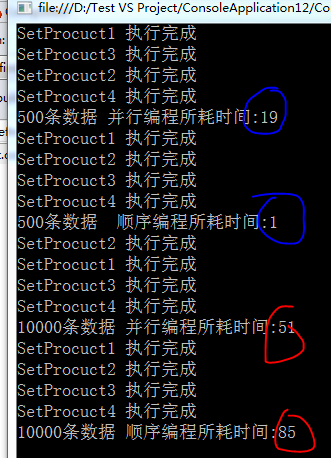
但是在操作500条数据时,显然采用并行操作并不明智,并行所带来的损耗比较大,在实际的开发中,还是要注意下是否有必要进行并行编程。
Parallel.For
将for循环替换成Parallel.For,并采用适合这个新方法的参数,就可以对这个已有的for循环进行重构,使其能够充分利用并行化优势。
需要注意的是:1、Parallel.For不支持浮点数的步进,就可以对这个已有的for循环进行重构,使其能够充分利用并行化优势。
2、由于循环体是并行运行,去迭代执行的顺序无法保证。

class Program { /* coder:释迦苦僧*/ static void Main(string[] args) { Thread.Sleep(3000); ForSetProcuct_100(); Thread.Sleep(3000); ParallelForSetProcuct_100(); Console.ReadLine(); } private static void ForSetProcuct_100() { Stopwatch sw = new Stopwatch(); sw.Start(); List<Product> ProductList = new List<Product>(); for (int index = 1; index < 100; index++) { Product model = new Product(); model.Category = "Category" + index; model.Name = "Name" + index; model.SellPrice = index; ProductList.Add(model); Console.WriteLine("for SetProcuct index: {0}", index); } sw.Stop(); Console.WriteLine("for SetProcuct 10 执行完成 耗时:{0}", sw.ElapsedMilliseconds); } private static void ParallelForSetProcuct_100() { Stopwatch sw = new Stopwatch(); sw.Start(); List<Product> ProductList = new List<Product>(); Parallel.For(1, 100, index => { Product model = new Product(); model.Category = "Category" + index; model.Name = "Name" + index; model.SellPrice = index; ProductList.Add(model); Console.WriteLine("ForSetProcuct SetProcuct index: {0}", index); }); sw.Stop(); Console.WriteLine("ForSetProcuct SetProcuct 20000 执行完成 耗时:{0}", sw.ElapsedMilliseconds); } } class Product { public string Name { get; set; } public string Category { get; set; } public int SellPrice { get; set; } }
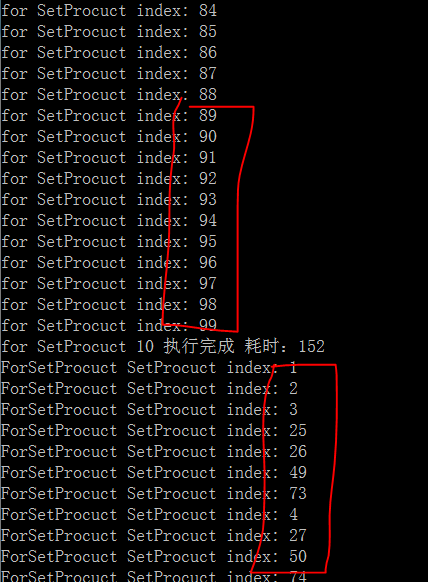
由图中我们可以看出,使用Parallel.For所迭代的顺序是无法保证的
Parallel.ForEach
Parallel.ForEach提供一个并行处理一组数据的机制,可以利用一个范围的整数作为一组数据,然后通过一个自定义的区分器将这个范围转换为一组数据块,每一块数据都通过循环的方式进行处理,而这些循环是并行执行的。

class Program { /* coder:释迦苦僧*/ static void Main(string[] args) { List<Product> ProductList =GetProcuctList(); Parallel.ForEach(ProductList, (model) => { Console.WriteLine(model.Name); }); Console.ReadLine(); } private static List<Product> GetProcuctList() { List<Product> result = new List<Product>(); for (int index = 1; index < 100; index++) { Product model = new Product(); model.Category = "Category" + index; model.Name = "Name" + index; model.SellPrice = index; result.Add(model); } return result; } } class Product { public string Name { get; set; } public string Category { get; set; } public int SellPrice { get; set; } }
ParallelLoopState
ParallelLoopState该实例提供了以下两个方法用于停止Parallel.For,Parallel.ForEach
Break-这个方法告诉并行循环应该在执行了当前迭代后尽快地停止执行。如果调用break时正在处理迭代100,那么循环仍然会处理所有小于100的迭代。
Stop-这个方法告诉并行循环应该尽快停止执行,如果调用stop时迭代100正在被处理,那么循环无法保证处理完所有小于100的迭代
下面代码:

class Program { /* coder:释迦苦僧*/ static void Main(string[] args) { List<Product> productList = GetProcuctList_500(); Thread.Sleep(3000); Parallel.For(0, productList.Count, (i, loopState) => { if (i < 100) { Console.WriteLine("采用Stop index:{0}", i); } else { /* 满足条件后 尽快停止执行,无法保证小于100的索引数据全部输出*/ loopState.Stop(); return; } }); Thread.Sleep(3000); Parallel.For(0, productList.Count, (i, loopState) => { if (i < 100) { Console.WriteLine("采用Break index:{0}", i); } else { /* 满足条件后 尽快停止执行,保证小于100的索引数据全部输出*/ loopState.Break(); return; } }); Thread.Sleep(3000); Parallel.ForEach(productList, (model, loopState) => { if (model.SellPrice < 10) { Console.WriteLine("采用Stop index:{0}", model.SellPrice); } else { /* 满足条件后 尽快停止执行,无法保证满足条件的数据全部输出*/ loopState.Stop(); return; } }); Thread.Sleep(3000); Parallel.ForEach(productList, (model, loopState) => { if (model.SellPrice < 10) { Console.WriteLine("采用Break index:{0}", model.SellPrice); } else { /* 满足条件后 尽快停止执行,保证满足条件的数据全部输出*/ loopState.Break(); return; } }); Console.ReadLine(); } private static List<Product> GetProcuctList_500() { List<Product> result = new List<Product>(); for (int index = 1; index < 500; index++) { Product model = new Product(); model.Category = "Category" + index; model.Name = "Name" + index; model.SellPrice = index; result.Add(model); } return result; } }
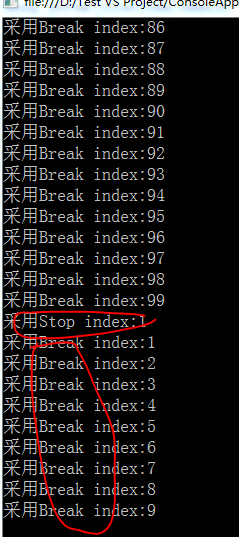
由图中可以看出Break可以保证输出满足所有条件的数据,而stop则无法保证。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号