实验六:流类库与I/O
【实验结论】
#Part1

#include <iostream> #include <fstream> #include <string> #include <cstdlib> using namespace std; int main() { string filename1, filename2, newfilename; cout << "输入要合并的两个文件名: " ; cin >> filename1 >> filename2; cout << "输入合并后新文件名: " ; cin >> newfilename; ofstream fout; // 输出文件流对象 ifstream fin; // 输入文件流对象 fin.open(filename1); // 将输入文件流对象fin与文件filename1建立关联 if(!fin.is_open()) { // 如果打开文件失败,则输出错误提示信息并退出 cerr << "fail to open file " << filename1 << endl; system("pause"); exit(0); } fout.open(newfilename); // 将输出文件流对象fout与文件newfilename建立关联 if(!fin.is_open()) { // 如果创建/打开文件失败,输出错误提示信息并退出 cerr << "fail to open file " << newfilename << endl; system("pause"); exit(0); } char ch; // 从文件输入流对象fin中获取字符,并将其插入到文件输出流对象fout中 while(fin.get(ch)) fout << ch; fin.close(); // 关闭文件输入流对象fin与文件filename1的关联 fout << endl; // 向文件输出流对象fout中插入换行 fin.open(filename2); // 将输入文件流对象fin与文件filename2建立关联 if(!fin.is_open()) { // 如果打开文件失败,则输出错误提示信息并退出 cerr << "fail to open file " << filename2 << endl; system("pause"); exit(0); } // 从文件输入流对象fin中获取字符,并将其插入到文件输出流对象fout中 while(fin.get(ch)) fout << ch; fin.close(); // 关闭文件输入流对象fin与文件filename2的关联 fout.close(); // 关闭文件输出流对象fout与文件newfilename的关联 system("pause"); return 0; }
[运行结果]
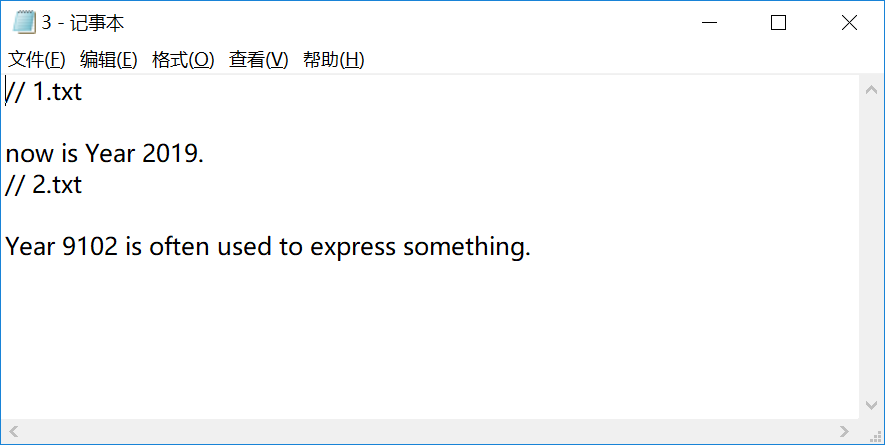
#Part2

#include <iostream> #include <fstream> #include <string> #include <cstdlib> using namespace std; int main() { string filename; cout<<"打开文件:"; cin>>filename; ofstream fout(filename,ios_base::app); //打开文件,写指针位于文件末尾 if(!fout.is_open()) //判断是否打开成功 { cout<<"fail to open file "<<filename<<endl; system("pause"); exit(0); } fout<<endl<<"merge successfully."<<endl; //写入文字 fout.close(); //关闭文件 return 0; }
[运行结果]
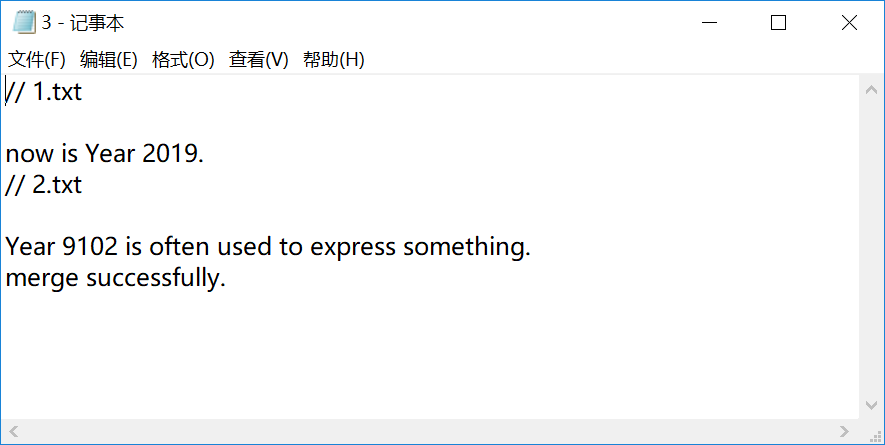
#Part3.1

//这个头文件里包含了可用工具函数的声明 #include <string> using std::string; // 函数声明 // 返回当前系统时间,格式诸如20190611 string getCurrentDate();

#include "utils.h" #include <ctime> using std::string; const int SIZE = 20; // 函数功能描述:返回当前系统日期 // 参数描述:无参数 // 返回值描述:以string类型返回系统当前日期,格式诸如20190611 string getCurrentDate() { time_t now = time(0); // 获取当前系统日历时间 struct tm *local_time = localtime(&now); // 把系统日历时间转换为当地时间 char date[SIZE]; strftime(date, SIZE, "%Y%m%d", local_time); return (string(date)); }

#include <iostream> #include<fstream> #include <string> #include<ctime> #include<cstdlib> #include<vector> #include "utils.h" using namespace std; static int is_choose[83]={0}; int main() { string list_filename; cout<<"输入名单列表文件名:"; cin>>list_filename; string filename; //获取当天系统日期为文件名 filename=getCurrentDate(); ifstream fin; fin.open(list_filename); //打开文件 ofstream fout; fout.open(filename); //打开文件 if(!fin.is_open()) //判断是否打开成功 { cout<<"fail to open file "<<list_filename<<endl; system("pause"); exit(0); } if(!fout.is_open()) //判断是否打开成功 { cout<<"fail to open file "<<filename<<endl; system("pause"); exit(0); } srand((unsigned)time(NULL)); //初始化 int n; cout<<"输入随机抽点人数:"; cin>>n; cout<<"随机抽点中..."<<endl; vector<string>num; string left_content; while(getline(fin,left_content)) num.push_back(left_content); //见下方总结 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) { int choose_num=rand()%83+1; if(is_choose[choose_num]==1) //判断是否重复 { i--; continue; } is_choose[choose_num]=1; cout<<num[choose_num]<<endl; //在运行窗口中显示 fout<<num[choose_num]<<endl; //存入文件中 } cout<<"存入文件:"<<filename<<endl; fin.close(); fout.close(); return 0; }
[运行结果]
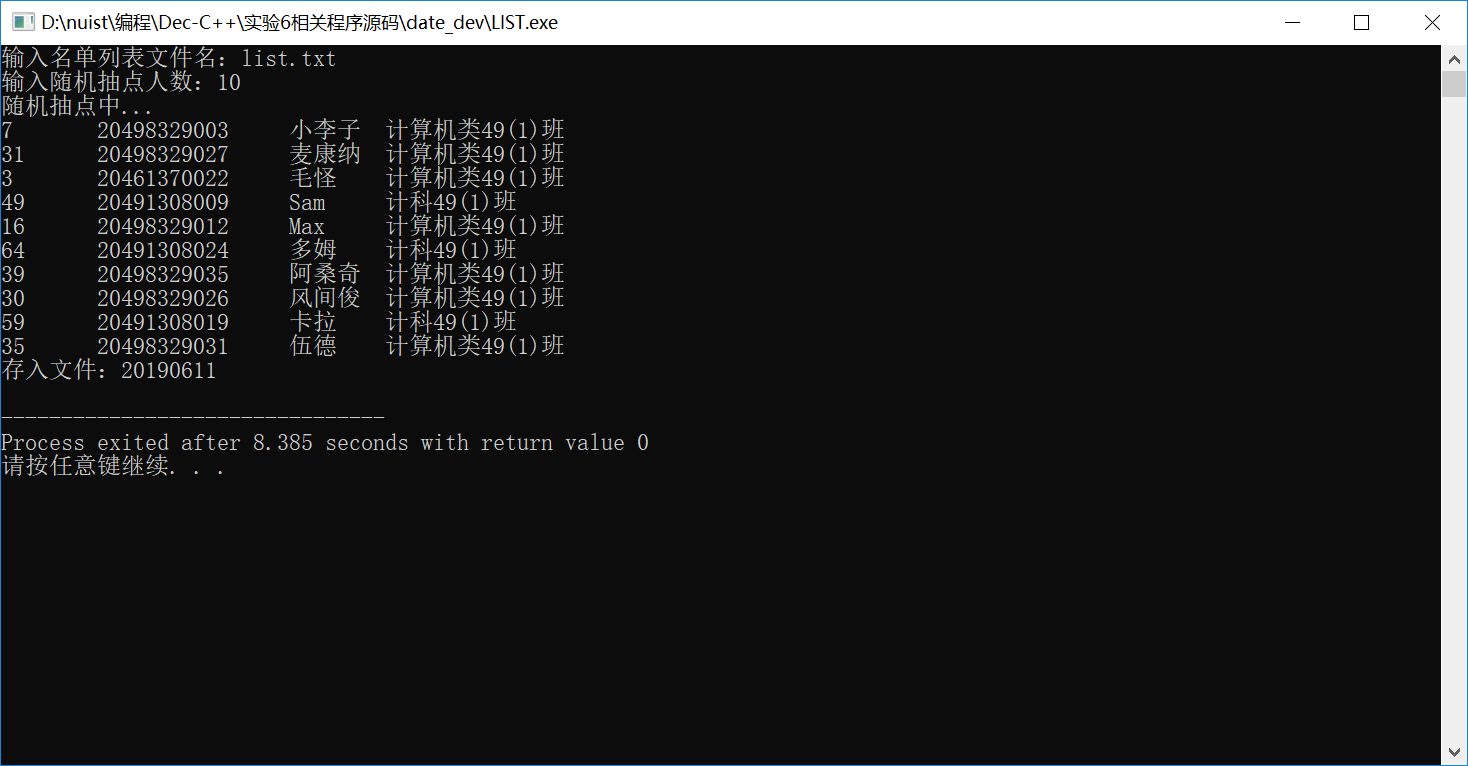
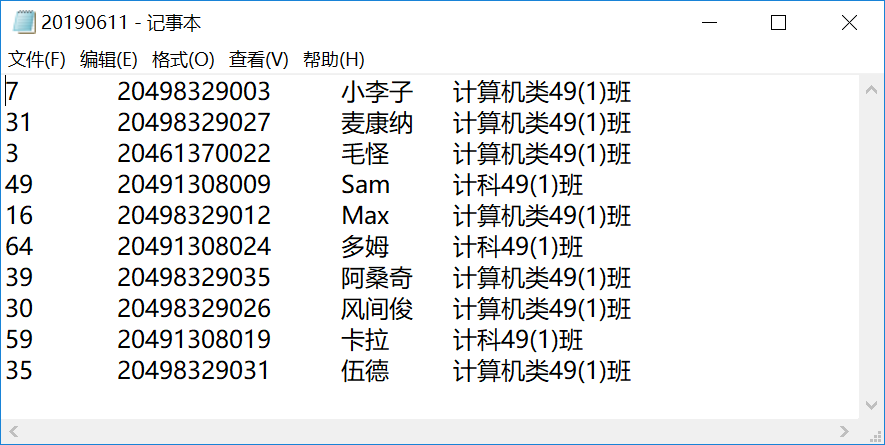
#Part3.2
//上面那个作废,请看下面的,谢谢~

#include<iostream> #include<fstream> #include<cstdlib> #include<string> #include<cstring> using namespace std; int main() { string filename; //打开文件 cout<<"输入要统计的英文文本文件名:"; cin>>filename; ifstream fin; fin.open(filename); if(!fin.is_open()) { cout<<"fail to open file "<<filename<<endl; system("pause"); exit(0); } long line=0,num_word=0,num_char=0; //统计各种 char p[1000]; while(fin.getline(p,1000)) { num_char+=strlen(p); for(int i=0;i<strlen(p);i++) { if(p[i]==' '&&p[i+1]!=' ') num_word++; } num_word++; line++; } int num; //选择统计的东西 cout<<"------------菜单------------"<<endl <<"请按照您的需要选择以下业务:"<<endl <<"1.统计字符数"<<endl <<"2.统计单词数"<<endl <<"3.统计行数"<<endl <<"4.退出"<<endl <<"请输入你所需要的业务序号:"; while(cin>>num) { switch(num) { case 1:cout<<"字符数: "<<num_char<<endl;break; case 2:cout<<"单词数: "<<num_word<<endl;break; case 3:cout<<"行数: "<<line<<endl;break; case 4: { char whether; cout<<"是否确定退出"<<endl <<"确定请输入Y,不确定请输入N"<<endl; while(cin>>whether) { if(whether=='Y') { fin.close(); exit(0); } if(whether=='N') break; else cout<<"错误,请重新输入!"<<endl; } if(whether=='N')break; } default:cout<<"错误,请重新输入!"<<endl;break; } cout<<"请输入你所需要的业务序号:"; } fin.close(); //关闭文件 return 0; }
//这里道个歉,后面统计的方法是临时改的,也没验证,直接发上来了,今天才发现改错了~
//这里默认标点符号按标准英文书写格式书写。
[运行结果]
【实验总结】
嗯,这里先说一下Part3.1中那个见下的注释,那一段是将文件中的数据整行输出,主要用的是push_back(),函数的详解可以看一下这个https://blog.csdn.net/XLJ_XLJ/article/details/52328695,如果vector那个理解又困难的话,可以看一下这个,其他还好就是有点秀:https://blog.csdn.net/isbnhao/article/details/8055359。如果感觉push_back()有点多余的话,可以用下面这个
string s,b[84]; for(int i=1;i<84;i++) { getline(fin,s); b[i]=s; } int it=rand()%83+1; cout<<b[it]<<endl; fout<<b[it]<<endl; /* 这里说一下这里用getline的一些问题。 1.getline就是字面意思,得到一整行的数据。 2.getline,嗯,至少在文件读取的时候,个人感觉是以指针的形式读取的,如果没有特殊的控制语句(比如seekg什么的)它的指针位置是不变的,会一直按顺序依次往下,所以这里要在开始的时候全部存入b数组中, 而不能在随机的时候,根据抽到的数再用getline获取那一行(除了每次循环结束用控制语句将读指针指向开头(这里说一下,用seekg的话,一定要用clear(),准确的说是重用同一个流对象的时候就要用clear(),
字面意思,清除(流的状态)),或者计算与上一次随机数的差,再balabala的,想了一下,比较麻烦) 。 最后,上文仅限个人暂时理解,单纯的为了以后好复习,有错误的地方可以指出。 */
还有就是Part2中的ios::app,详情可以看一下这个,这里和ios::ate区别了一下:https://blog.csdn.net/qwezhaohaihong/article/details/51559455。
嗯,文件这部分可能是时间跨度有点大,然后和学C的文件时一样,都在期末,所以也没怎么认真学,嗯,也可能是真的菜,特别是写第三部分一些细节方面的东西的时候查了蛮多资料的,嗯,这里有些资料:
https://blog.csdn.net/kingstar158/article/details/6859379,个人感觉如果使比较基础的话,看这个就够了,下面那个链接会比较冗杂,不过还是看的进去一点的,至少晕字的看了还行~
https://blog.csdn.net/Augusdi/article/details/8865378
一些改进我会在考完六级之后发上来,emmm........嗯,如果有什么链接进去不对的,可以说一下,因为,历史纪录有点多,一个个点进去,一言难尽......
【评论地址】
https://www.cnblogs.com/charlotte00/p/11031967.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/pink-fairy/p/11031372.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/xuexinyu/p/11040108.html







