实验四:类的继承,派生和多态(1)
【实验结论】
#1.车辆基本信息管理

#ifndef BATTERY_H #define BATTERY_H class Battery { public: Battery(int batterSize0=70); int getbatterysize(); ~Battery(); private: int batterySize; }; #endif

#include"Battery.h" Battery::Battery(int batterySize0):batterySize(batterySize0) {} int Battery::getbatterysize() { return batterySize; } Battery::~Battery() {}

#ifndef CAR_H #define CAR_H #include<iostream> using std::string; using std::ostream; class Car { public: Car(string maker0,string model0,int year0); friend ostream &operator<<(ostream &out,const Car &c); void updateOdometer(int updatemeter); string getmaker() const; string getmodel() const; int getyear() const; int getodometer() const; ~Car(); private: string maker; string model; int year; int odometer; }; #endif

#include<iostream> #include"Car.h" using namespace std; Car::Car(string maker0,string model0,int year0):maker(maker0),model(model0),year(year0) { odometer=0; } ostream &operator<<(ostream &out,const Car &c) { out<<"maker:\t\t"<<c.maker<<endl <<"model:\t\t"<<c.model<<endl <<"year:\t\t"<<c.year<<endl <<"odometer:\t"<<c.odometer<<endl; return out; } void Car::updateOdometer(int updatemeter) { if(updatemeter<odometer) { cout<<"Warning:Wrong!"<<endl; } else odometer=updatemeter; } string Car::getmaker() const { return maker; } string Car::getmodel() const { return model; } int Car::getyear() const { return year; } int Car::getodometer() const { return odometer; } Car::~Car() { }

#ifndef ElectricCar_H #define ElectricCar_H #include<iostream> #include"Car.h" #include"Battery.h" using std::string; using std::ostream; class ElectricCar:public Car { public: ElectricCar(string maker0,string model0,int year0); friend ostream &operator<<(ostream &out,const ElectricCar &e); ~ElectricCar(); private: Battery battery; int batterySize; }; #endif

#include<iostream> #include"ElectricCar.h" #include"Car.h" #include"Battery.h" using namespace std; ElectricCar::ElectricCar(string maker0,string model0,int year0):Car(maker0,model0,year0) { batterySize=battery.getbatterysize(); } ostream &operator<<(ostream &out,const ElectricCar &e) { out<<"maker:\t\t"<<e.getmaker()<<endl <<"model:\t\t"<<e.getmodel()<<endl <<"year:\t\t"<<e.getyear()<<endl <<"odometer:\t"<<e.getodometer()<<endl <<"batterySize:\t"<<e.batterySize<<"-kWh"<<endl; return out; } ElectricCar::~ElectricCar() { }

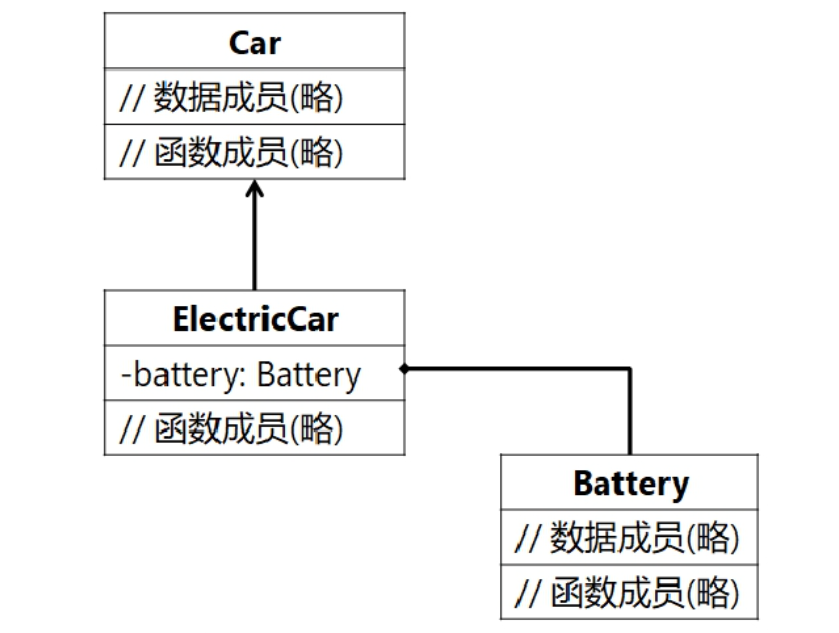
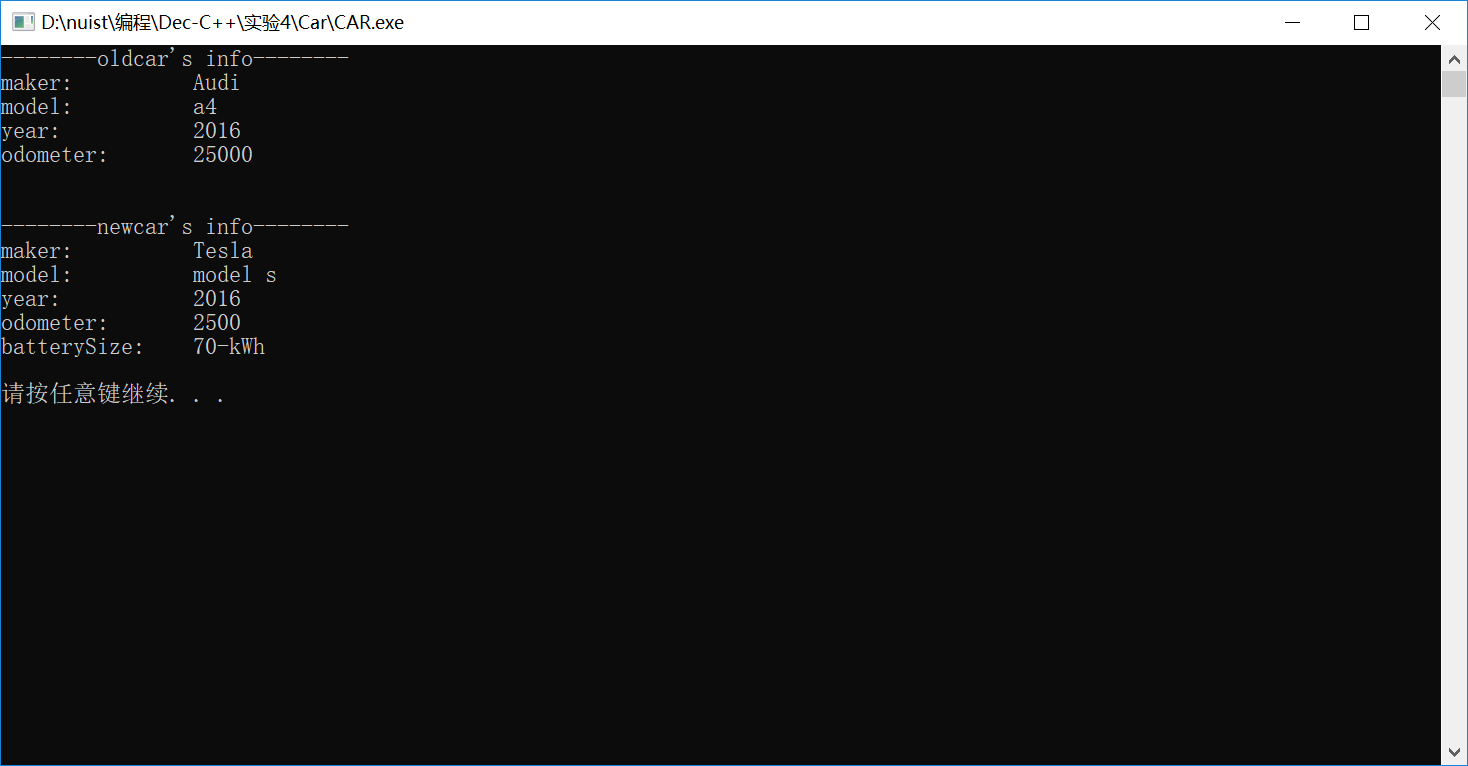
#include <iostream> using namespace std; #include "Car.h" #include "ElectricCar.h" int main() { // 测试Car类 Car oldcar("Audi","a4",2016); cout << "--------oldcar's info--------" << endl; oldcar.updateOdometer(25000); cout << oldcar << endl; // 测试ElectricCar类 ElectricCar newcar("Tesla","model s",2016); newcar.updateOdometer(2500); cout << "\n--------newcar's info--------\n"; cout << newcar << endl; system("pause"); return 0; }
[修改]
因为上面被折叠了,我这里也不好改(也许好改,但是找不到),所以在这里说明一下,这段程序中,用到string的地方要加头文件#include<string>~(这里说一下,该头文件是要加using namespace std的,或者std::string的,还有,他和#include<cstring>/<string.h>不是一个头文件)。
[运行结果]
[扩充]
ostream &operator<<(ostream &out,const ElectricCar &e) { out<<Car(e) <<"batterySize:\t"<<e.batterySize<<"-kWh"<<endl; return out; }
这样也行,调用了Car类中声明的<<重载运算符友元函数。
#2.重载运算符[ ]

#ifndef ARRAY_INT_H #define ARRAY_INT_H class ArrayInt{ public: ArrayInt(int n, int value=0); ~ArrayInt(); int &operator[](int i); void print(); private: int *p; int size; }; #endif

#include "arrayInt.h" #include <iostream> #include <cstdlib> using std::cout; using std::endl; ArrayInt::ArrayInt(int n, int value):size(n) { p=new int[size]; if(p==0) { cout<<"fail to mallocate memory"<<endl; exit(0); } for(int i=0;i<size;i++) p[i]=value; } ArrayInt::~ArrayInt() { delete[] p; } void ArrayInt::print() { for(int i=0;i<size;i++) cout<<p[i]<<" "; cout<<endl; } int &ArrayInt::operator[](int i) { return p[i]; }

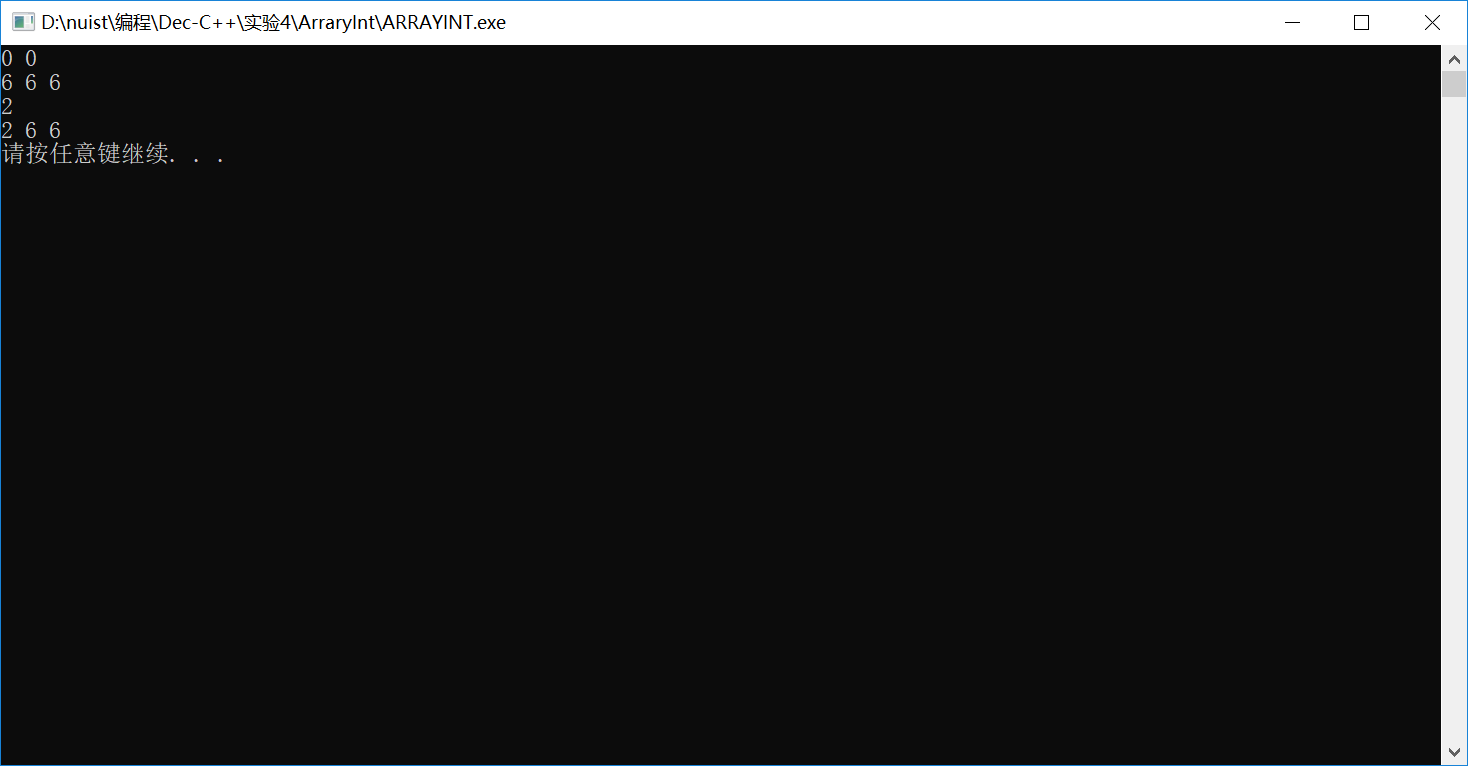
#include <iostream> using namespace std; #include "arrayInt.h" int main() { // 定义动态整型数组对象a,包含2个元素,初始值为0 ArrayInt a(2); a.print(); // 定义动态整型数组对象b,包含3个元素,初始值为6 ArrayInt b(3,6); b.print(); // 通过对象名和下标方式访问并修改对象元素 b[0]=2; cout<<b[0]<<endl; b.print(); system("pause"); return 0; }
[运行结果]
【实验总结】
嗯,第一个汽车相关的实现,Battery和ElectricCar之间是组合关系,ElectricCar和Car之间是继承关系,这里解释一下组合和继承:(由于最近时间关系没有来得及整理知识点,所以就先现写一下,将就一下,下次写好发上来~)
组合关系相当于has—it,即ElectricCar里面有Battery,简单点来说,就是如果有一个教室,它是由桌椅,风扇,多媒体构成的,那么教室,桌椅,风扇,空调之间就是组合关系。
继承关系相当于is—it,即ElectricCar是Car,这个比较好理解一点,比如枫树和树,枫树是树,所以枫树和树是继承关系。
关于第二个[ ] 的重载,思路就是要让计算机知道b[0]是一个数组(大概是这么解释的趴?)
附两个最开始学继承和组合时的blog:https://www.cnblogs.com/shmilxu/p/4849097.html(继承),https://blog.csdn.net/ForestRound/article/details/52726984(组合)
再附一个<<和>>重载的blog:https://www.cnblogs.com/wuchanming/p/3879159.html
【评论地址】
https://www.cnblogs.com/mzy-1229/p/10889880.html#4264060
https://www.cnblogs.com/wyy0204/p/10891409.html#4264065
https://www.cnblogs.com/Kun-520/p/10896481.html#4264069







