实验三:类和对象
【实验结论】
#1.在画布上可以上下左右移动的小球

#ifndef BALL_H #define BALL_H class Ball { public: Ball(int x0=0, int y0=0); // 在坐标(x,y)处构造一个小球(小球用字符O表示) void move(); //小球移动的实现 void judgemove(char get,int step=1); //判断小球的移动方向 private: int x; // x坐标 int y; // y坐标 }; #endif

#include "ball.h" #include <iostream> #include <cstdlib> // 因为使用了system("cls"); 所以需要包含这个头文件 using std::cout; using std::endl; const int SIZE_X=50; // 小球x轴移动范围0~SIZE_X const int SIZE_Y=50; // 小球y轴移动范围0~SIZE_Y // void Ball::move() { // 清屏 system("cls"); // 打印y0-1行空行 for(int line=1;line<=y-1;line++) cout<<endl; // 打印x0-1个空格 for(int col=1;col<=x-1;col++) cout<<" "; // 打印小球 cout<<"O"<<endl; } // Ball::Ball(int x0, int y0):x(x0),y(y0) { move(); } void Ball::judgemove(char get,int step) { switch(get) { case 'W': { y=y-step; if(y<=0) y=0; move(); break; } case 'S': { y=y+step; if(y>=SIZE_Y) y=SIZE_Y; move(); break; } case 'A': { x=x-step; if(x<=0) x=0; move(); break; } case 'D': { x=x+step; if(x>=SIZE_X) x=SIZE_X; move(); break; } } }

#ifndef CANVAS_H #define CANVAS #include <string> using std::string; class Canvas { public: Canvas(string bg0="0", string fg0="A"); void setcanvas(); //设置画布颜色的具体实现 void changeCanvasBg(string bg0); void changeCanvasFg(string fg0); void changeCanvasColor(string bg0, string fg0); private: string bg; // background color string fg; // foreground color }; #endif

#include "canvas.h" #include <cstdlib> //设置画布颜色 void Canvas::setcanvas() { string color="color "; color+=bg; color+=fg; system(color.c_str()); } // Canvas::Canvas(string bg0, string fg0):bg(bg0), fg(fg0) { setcanvas(); } void Canvas::changeCanvasBg(string bg0) { bg=bg0; // 更新画布背景色 setcanvas(); } void Canvas::changeCanvasFg(string fg0) { fg=fg0; // 更新画布前景色 setcanvas(); } void Canvas::changeCanvasColor(string bg0, string fg0) { bg=bg0; // 更新画布背景色 fg=fg0; // 更新画布前景色 setcanvas(); }

#include <iostream> #include "canvas.h" #include "Ball.h" int main() { Canvas canvas; Ball ball1(10,10); system("pause"); ball1.judgemove('A',5); system("pause"); ball1.judgemove('W',20); system("pause"); canvas.changeCanvasFg("E"); // 更新画布前景色 system("pause"); canvas.changeCanvasBg("D"); // 更新画布背景色 system("pause"); return 0; }
[运行结果]






#2.graph类的实现

#ifndef GRAPH_H #define GRAPH_H #include<string> using std::string; // 类Graph的声明 class Graph { public: Graph(char ch, int n); // 带有参数的构造函数 void draw(); // 绘制图形 void reset(char newch,int newn); //重新设置图形参数 void color(string background="A",string foreground="E"); void changecolor(string newbackground,string newforeground); void move(char get,int n); private: char symbol; int size; }; #endif

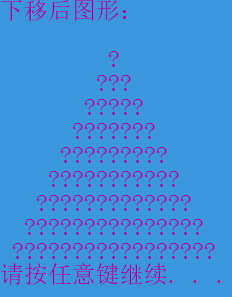
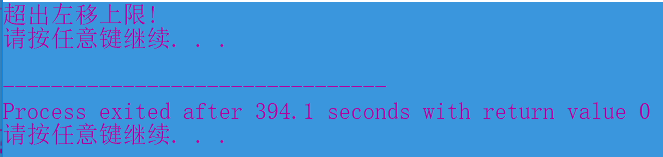
#include<cstdlib> using namespace std; static int top=1,left0=1; // 带参数的构造函数的实现 Graph::Graph(char ch,int n):symbol(ch),size(n) { } //重新设置字符和尺寸,并输出 void Graph::reset(char newch,int newn) { symbol=newch; size=newn; draw(); } //前景色,背景色的设置 void Graph::color(string background,string foreground) { string color="color "; color+=background; color+=foreground; system(color.c_str()); } //前景、背景色的修改 void Graph::changecolor(string newbackground,string newforeground) { string color="color "; color+=newbackground; color+=newforeground; system(color.c_str()); } //图形移动 void Graph::move(char get,int n) { switch(get) { case 'W': { if(top==1) cout<<"图形已经置顶,无法上移!"<<endl; else if(top<n+1) cout<<"超出上移上限!"<<endl; else { cout<<"上移后图形:"<<endl; top-=n; draw(); } break; } case 'S': { cout<<"下移后图形:"<<endl; top++; draw(); break; } case 'A': { if(left0==1) cout<<"图形已经在最左端,无法左移!"<<endl; else if(left0<n+1) cout<<"超出左移上限!"<<endl; else { cout<<"左移后图形:"<<endl; left0-=n; draw(); } break; } case 'D': { cout<<"右移后图形:" <<endl; left0+=n; draw(); break; } } } // 成员函数draw()的实现 // 功能:绘制size行,显示字符为symbol的指定图形样式 void Graph::draw() { for(int i=2;i<=top;i++) cout<<endl; for(int i=1;i<=size;i++) { cout<<setfill(' ')<<setw(size-i+1+left0); for(int j=1;j<=2*i-1;j++) { cout<<symbol; } cout<<endl; } }

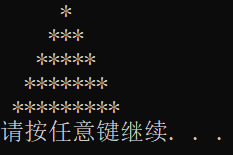
#include <iostream> #include "graph.h" #include<string> using namespace std; int main() { Graph graph1('*',5); graph1.draw(); system("pause"); system("cls"); Graph graph2('$',7); graph2.draw(); system("pause"); system("cls"); // Graph graph3('#',6); graph3.draw(); system("pause"); system("cls"); //设置背景、前景色 graph3.color(); system("pause"); system("cls"); //修改背景、前景色 graph3.changecolor("3","D"); system("pause"); system("cls"); //重新设置图形参数 graph3.reset('?',9); system("pause"); system("cls"); //上移 graph3.move('W',1); system("pause"); system("cls"); //下移 graph3.move('S',2); system("pause"); system("cls"); //右移 graph3.move('D',5); system("pause"); system("cls"); //左移 graph3.move('A',6); system("pause"); return 0; }
[运行结果]








#3.分数类的实现

#ifndef Fraction_H #define Fraction_H #include<iostream> using namespace std; class Fraction { public: Fraction(int top0=0,int bottom0=1); void polish(); void add(Fraction a,Fraction b); void disadd(Fraction a,Fraction b); void multipy(Fraction a,Fraction b); void dismultipy(Fraction a,Fraction b); void compare(Fraction a); void show(); ~Fraction(); private: int top; int bottom; }; #endif

#include<iostream> #include"Fraction.h" #include<cstdlib> using namespace std; //输入 Fraction::Fraction(int top0,int bottom0):top(top0),bottom(bottom0) { } //最大公约数 int gongyue(int a,int b) { if(a>b) { int t=a; a=b; b=t; } while(a!=0) { int t=b%a; b=a; a=t; } return b; } //最小公倍数 int gongbei(int a,int b) { int t=gongyue(a,b); return a*b/t; } //对所得结果进行改善 void Fraction::polish() { //约分 int gongyue0=gongyue(top,bottom); //最大公约数 top/=gongyue0; bottom/=gongyue0; //正负号 if(top*bottom<0) { if(top>0) { bottom=0-bottom; top=0-top; } } if(top<0&&bottom<0) { top=0-top; bottom=0-bottom; } } //加法 void Fraction::add(Fraction a,Fraction b) { bottom=gongbei(a.bottom,b.bottom); top=a.top*bottom/a.bottom+b.top*bottom/b.bottom; polish(); show(); } //减法 void Fraction::disadd(Fraction a,Fraction b) { bottom=gongbei(a.bottom,b.bottom); top=a.top*bottom/a.bottom-b.top*bottom/b.bottom; polish(); show(); } //乘法 void Fraction::multipy(Fraction a,Fraction b) { top=a.top*b.top; bottom=a.bottom*b.bottom; polish(); show(); } //除法 void Fraction::dismultipy(Fraction a,Fraction b) { top=a.top*b.bottom; bottom=a.bottom*b.top; polish(); show(); } //比较大小 void Fraction::compare(Fraction a) { int bottom1=gongbei(bottom,a.bottom); if(top*bottom1/bottom<a.top*bottom1/a.bottom) cout<<" 后者大" <<endl; else if(top*bottom1/bottom>a.top*bottom1/a.bottom) cout<<" 前者大" <<endl; else cout<<" 一样大" <<endl; } //输出格式 void Fraction::show() { //分母为0 if(bottom==0) cout<<" 无意义"<<endl; //输出 else { if(bottom==1) cout<<" "<<top<<endl; else { cout<<" 分数形式:"<<top<<"/"<<bottom<<endl; cout<<" 小数形式:"<<static_cast<double>(top)/static_cast<double>(bottom)<<endl; } } } Fraction::~Fraction() { }

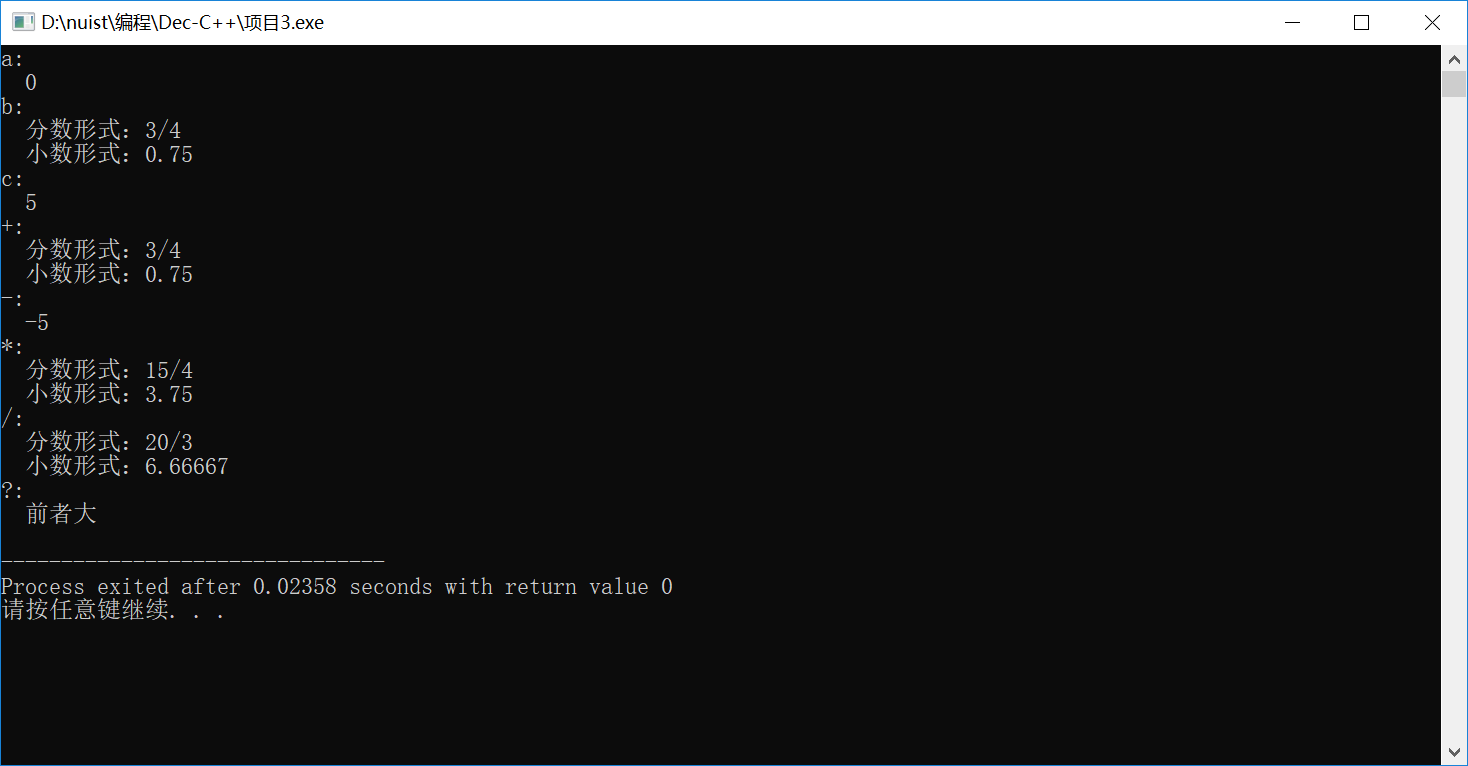
#include<iostream> #include"Fraction.h" using namespace std; int main() { //输出初始值 Fraction a; cout<<"a:"<<endl; a.show(); Fraction b(3,4); cout<<"b:"<<endl; b.show(); Fraction c(5); cout<<"c:"<<endl; c.show(); //计算 Fraction d; //加法a+b cout<<"+:"<<endl; d.add(a,b); //减法a-c cout<<"-:"<<endl; d.disadd(a,c); //乘法b*c cout<<"*:"<<endl; d.multipy(b,c); //除法c/b cout<<"/:"<<endl; d.dismultipy(c,b); //比较大小c&a cout<<"?:"<<endl; c.compare(a); return 0; }
[运行结果]
【实验总结】
运行结果的截图见谅,本来想录个视频直接发上来的,但是过程一言难尽。。。
嗯,因为写实验的时候大体看了一下,发现小球类涉及的知识点覆盖了graph类和分数类,所以就先跳过了小球类写下面的两个类的实现,所以看程序的话,会发现越往下看越不成熟。本来在写完小球类后是想修改一下graph类和分数类的程序的,但是,我感觉虽然最开始写的不怎么成熟,但是有些想法和小球类的立足点不太一样,以后可以回过来看一下,所以就没有改了。
至于将小球类写成一个小游戏的改进,emmm,如果可以的话会写好发上来,不过因为不知道弹球是怎么弹的,如果要设定轨迹的话能力有限,暂时写不出来,然后因为参考的是贪吃蛇的程序,所以最后可能会写成小球吃小球这种的。。。
感觉吧,这次实验最大的收获还是会尝试着自己设计一个算法再写程序吧,感觉这样确实会比直接写的时候天马行空要方便一点,逻辑方面也比较合理。emmm,就这样吧。
顺便附一下system()的详解:(图片信息来自:https://blog.csdn.net/sinat_34707539/article/details/51946210)

嗯,那个小球的程序最后有点一言难尽,只能在开始进入的时候弹出菜单,游戏中途可以是可以,但是弹出来之后会字会留在屏幕上,就没办法继续进行游戏了。嗯,如果有人知道怎么局部清屏可以分享一下~程序因为游戏规则嵌了文件,所以就不放上来嘞。
【评论地址】
https://www.cnblogs.com/xiaobailong123/p/10744236.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/zxz2425405395/p/10745209.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/aitxy899/p/10745690.htm





