并发编程学习笔记(二十二、DelayQueue源码分析)
目录:
- 什么是DelayQueue
- 如何使用DelayQueue
- 总结
什么是DelayQueue
DelayQueue是一个支持延时获取元素的无界阻塞队列,队列使用PriorityQueue来实现。
队列中的元素必须实现Delayed接口,在创建元素时可以指定多久才能从队列中获取当前元素,只有在延迟期满时才能从队列中提取元素。
DelayQueue非常有用,可以运用在以下两个应用场景:
- 缓存系统的设计:使用DelayQueue保存缓存元素的有效期,使用一个线程循环查询DelayQueue,一旦能从DelayQueue中获取元素时,就表示有缓存到期了。
- 定时任务调度:使用DelayQueue保存当天要执行的任务和执行时间,一旦从DelayQueue中获取到任务就开始执行,比如Timer就是使用DelayQueue实现的。
如何使用DelayQueue
既然上面说到了DelayQueue可以用于缓存系统的设计,那么我这里的demo就来模拟一下上面的场景。
使用DelayQueue保存缓存元素的有效期,使用一个线程循环查询DelayQueue,一旦能从DelayQueue中获取元素时,就表示有缓存到期了
1、首先有个CacheData,实现Delayed接口,用作DelayQueue的数据源。
1 /** 2 * 缓存数据源 3 * 4 * @author zhoude 5 * @date 2020/6/29 21:09 6 */ 7 public class CacheData implements Delayed { 8 9 /** 10 * 缓存过期时间,<= 0表示已过期 11 */ 12 private long remaining; 13 14 /** 15 * 缓存数据的key 16 */ 17 private String key; 18 19 /** 20 * 缓存数据的值 21 */ 22 private String value; 23 24 public CacheData(long remaining, String key, String value) { 25 this.remaining = System.currentTimeMillis() + remaining; 26 this.key = key; 27 this.value = value; 28 } 29 30 @Override 31 public String toString() { 32 return "CacheData{" + 33 "remaining=" + remaining + 34 ", key='" + key + '\'' + 35 ", value='" + value + '\'' + 36 '}'; 37 } 38 39 @Override 40 public long getDelay(TimeUnit unit) { 41 return remaining - System.currentTimeMillis(); 42 } 43 44 @Override 45 public int compareTo(Delayed o) { 46 CacheData data = (CacheData) o; 47 long diff = this.remaining - data.remaining; 48 if (diff > 0) { 49 return 1; 50 } 51 return -1; 52 } 53 54 // getter and setter 55 56 public String getKey() { 57 return key; 58 } 59 60 public String getValue() { 61 return value; 62 } 63 64 }
2、然后提供一个缓存的操作器。
1 /** 2 * 操作缓存的template 3 * 4 * @author zhoude 5 * @date 2020/6/29 21:21 6 */ 7 public class CacheTemplate extends Thread { 8 9 /** 10 * 原始数据(模拟DB) 11 */ 12 private Map<String, CacheData> data; 13 14 /** 15 * 缓存数据 16 */ 17 private DelayQueue<CacheData> delayQueue; 18 19 public CacheTemplate(List<CacheData> source) { 20 data = new HashMap<>(source.size()); 21 source.forEach(item -> data.put(item.getKey(), item)); 22 delayQueue = new DelayQueue<>(source); 23 } 24 25 @Override 26 public void run() { 27 for (; ; ) { 28 try { 29 // 一直从delayQueue拿数据,拿到则说明有缓存过期了 30 CacheData queue = delayQueue.take(); 31 String key = queue.getKey(); 32 String value = queue.getValue(); 33 System.out.println(MessageFormat.format("缓存{0}已到期,value={1}", key, value)); 34 } 35 catch (InterruptedException e) { 36 e.printStackTrace(); 37 } 38 } 39 } 40 41 public void put(String key, CacheData value) { 42 data.put(key, value); 43 } 44 45 /** 46 * 重新设置值到delayQueue中,用于模拟缓存过期后重新获取 47 * 48 * @param key 缓存key 49 */ 50 public void reset(String key) { 51 CacheData queue = data.get(key); 52 delayQueue.add(queue); 53 } 54 55 }
3、然后我们来测试下。
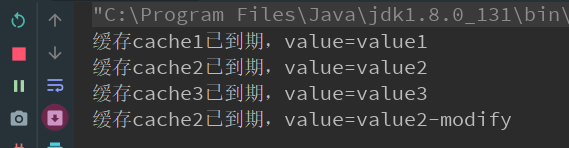
1 public class CacheTest { 2 3 public static CacheTemplate template; 4 5 public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { 6 template = new CacheTemplate(getTemplateInitData()); 7 template.start(); 8 // 休眠7秒,用于模拟程序开始后用户的行为,改变DB中的数据 9 TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(7L); 10 template.put("cache2", new CacheData(10000L, "cache2", "value2-modify")); 11 template.reset("cache2"); 12 } 13 14 private static List<CacheData> getTemplateInitData() { 15 List<CacheData> result = new ArrayList<>(); 16 result.add(new CacheData(5000L, "cache1", "value1")); 17 result.add(new CacheData(10000L, "cache2", "value2")); 18 result.add(new CacheData(15000L, "cache3", "value3")); 19 return result; 20 } 21 22 }
从结果我们可以看出来,cache2第二次的值会变成value2-modify,也就是从DB中获取的。
从demo看来,我们可以利用DelayQueue中take()方法的队列无值会一直阻塞获取的特性来达到缓存过期的目的。
总结(源码和ArrayBlockingQueue类似)
DelayQueue是阻塞队列中非常有用的一种队列,经常被用于缓存或定时任务等的设计。
以下类似的场景也可以使用:
1、异步通知的重试。
-
在很多系统中,当用户完成服务调用后, 系统有时需要将结果异步通知到用户的某个UR。由于网络等原因,很多时候会通知失败,这个时候就需要一种重试机制。
-
这时可以用DelayQueue保存通知失败的请求,失效时间可以根据已通知的次数来设定(比如: 2s、 5s、10s、 20s) ,这样每次从队列中take获取的就是剩余时间最短的请求,如果已重复通知次数超过一定阈值,则可以把消息抛弃。
- 像JUC线程池框架中的Schedu JedThreadPoolExecu tor.DelayedWorkQueu e就是一种延时阻塞队列。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号