Wemos D1入门


ESP8266特点介绍
- 802.11 b/g/n
- 内置Tensilica L106 超低功耗 32 位微型 MCU,主频支持 80 MHz 和160 MHz,支持 RTOS
- 内置10 bit高精度ADC
- 内置TCP/IP协议栈
- 内置TR 开关、balun、LNA、功率放大器和匹配网络
- 内置PLL、稳压器和电源管理组件,802.11b 模式下+20 dBm的输出功率
- A-MPDU 、 A-MSDU 的聚合和 0.4 s的保护间隔
- WiFi @ 2.4 GHz,支持 WPA/WPA2 安全模式
- 支持AT远程升级及云端OTA升级
- 支持 STA/AP/STA+AP 工作模式
- 支持 Smart Config 功能(包括 Android 和 iOS 设备)
- HSPI 、UART、I2C、I2S、IR Remote Control、PWM、GPIO
- 深度睡眠保持电流为 10 uA,关断电流小于 5 uA
- 2 ms 之内唤醒、连接并传递数据包
- 待机状态消耗功率小于1.0 mW (DTIM3)
- 工作温度范围:-40℃- 125℃
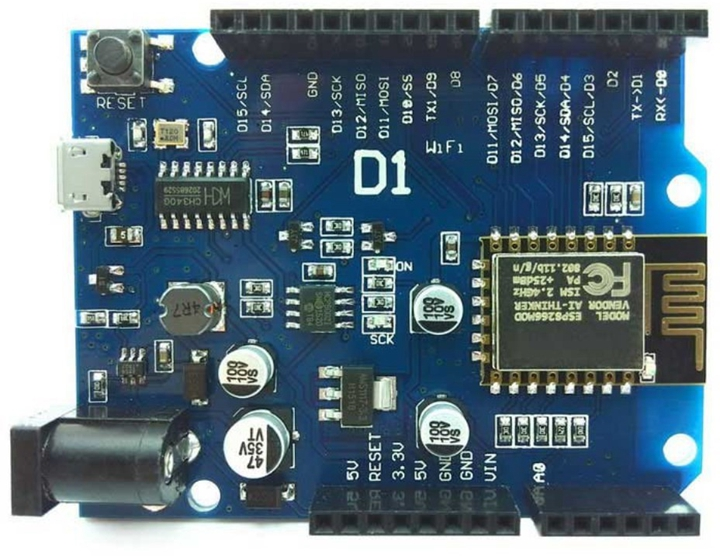
WeMos D1开发板
全称是WeMos D1 WiFI UNO R3开发板,基于ESP-8266,兼容Arduino。
有了这款物联网开发板,我们就可以愉快的使用arduino方式开发ESP8266,玩转物联网项目。
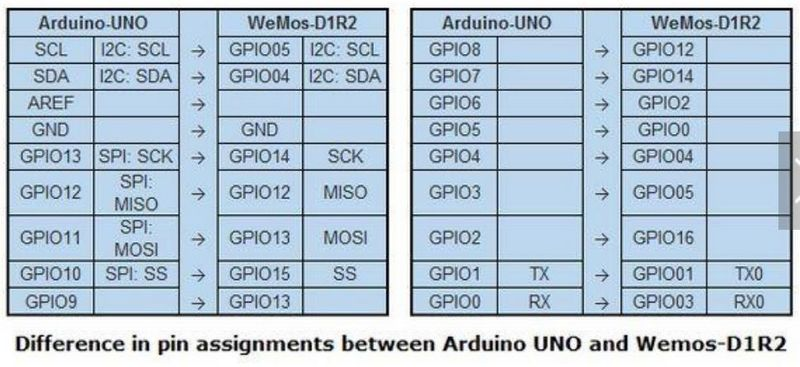
引脚
WeMos D1包含:
数字IO引脚11个。除了D0引脚外,其余引脚均支持pwm、I2C、中断、单总线。
模拟输入引脚1个(最大支持3.3v输入)。
模拟引脚仅有1个。数字引脚(包括RX,TX)共有11个
需要注意的一点是:WeMos D1上数字引脚的一侧引脚数量远大于11个,
这是因为该板上D3与D15、D4与D14、D5与D13、D6与D12、D7与D11、D9与板载LED 它们两两之间是互通的。
具体引脚的定义可以参考我整理的引脚定义库。
1.Arduino IDE下载
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1ig6psM6GvWJk0CwqaIqs7A
提取码:uyy4
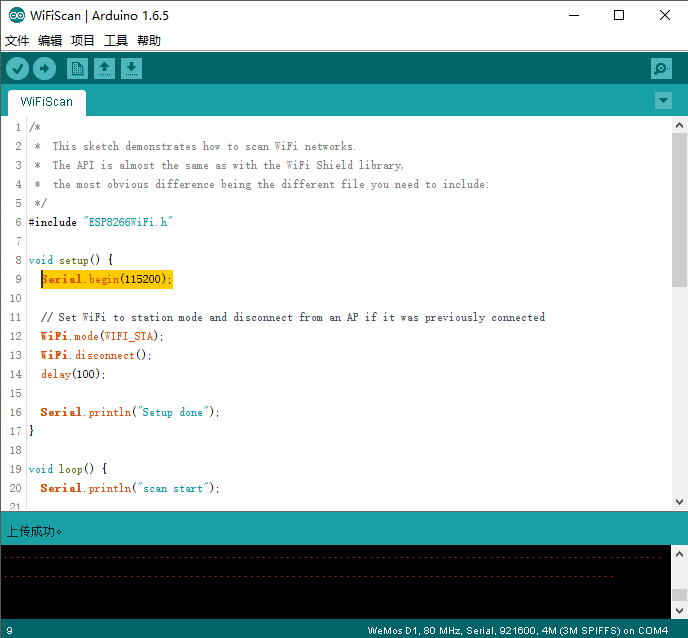
2.示例(搜索WIFI)
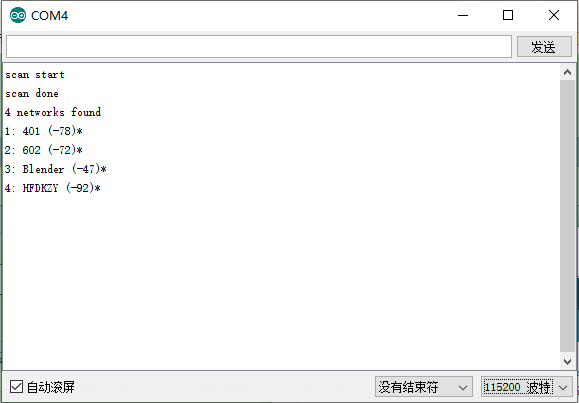
1 /* 2 * This sketch demonstrates how to scan WiFi networks. 3 * The API is almost the same as with the WiFi Shield library, 4 * the most obvious difference being the different file you need to include: 5 */ 6 #include "ESP8266WiFi.h" 7 8 void setup() { 9 Serial.begin(115200); 10 11 // Set WiFi to station mode and disconnect from an AP if it was previously connected 12 WiFi.mode(WIFI_STA); 13 WiFi.disconnect(); 14 delay(100); 15 16 Serial.println("Setup done"); 17 } 18 19 void loop() { 20 Serial.println("scan start"); 21 22 // WiFi.scanNetworks will return the number of networks found 23 int n = WiFi.scanNetworks(); 24 Serial.println("scan done"); 25 if (n == 0) 26 Serial.println("no networks found"); 27 else 28 { 29 Serial.print(n); 30 Serial.println(" networks found"); 31 for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) 32 { 33 // Print SSID and RSSI for each network found 34 Serial.print(i + 1); 35 Serial.print(": "); 36 Serial.print(WiFi.SSID(i)); 37 Serial.print(" ("); 38 Serial.print(WiFi.RSSI(i)); 39 Serial.print(")"); 40 Serial.println((WiFi.encryptionType(i) == ENC_TYPE_NONE)?" ":"*"); 41 delay(10); 42 } 43 } 44 Serial.println(""); 45 46 // Wait a bit before scanning again 47 delay(5000); 48 }
3.WIFI搜索
4.点灯控制
/* * This sketch demonstrates how to set up a simple HTTP-like server. * The server will set a GPIO pin depending on the request * http://server_ip/gpio/0 will set the GPIO2 low, * http://server_ip/gpio/1 will set the GPIO2 high * server_ip is the IP address of the ESP8266 module, will be * printed to Serial when the module is connected. */ #include <ESP8266WiFi.h> const char* ssid = "your-ssid"; const char* password = "your-password"; // Create an instance of the server // specify the port to listen on as an argument WiFiServer server(80); void setup() { Serial.begin(115200); delay(10); // prepare GPIO2 pinMode(2, OUTPUT); digitalWrite(2, 0); // Connect to WiFi network Serial.println(); Serial.println(); Serial.print("Connecting to "); Serial.println(ssid); WiFi.begin(ssid, password); while (WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED) { delay(500); Serial.print("."); } Serial.println(""); Serial.println("WiFi connected"); // Start the server server.begin(); Serial.println("Server started"); // Print the IP address Serial.println(WiFi.localIP()); } void loop() { // Check if a client has connected WiFiClient client = server.available(); if (!client) { return; } // Wait until the client sends some data Serial.println("new client"); while(!client.available()){ delay(1); } // Read the first line of the request String req = client.readStringUntil('\r'); Serial.println(req); client.flush(); // Match the request int val; if (req.indexOf("/gpio/0") != -1) val = 0; else if (req.indexOf("/gpio/1") != -1) val = 1; else { Serial.println("invalid request"); client.stop(); return; } // Set GPIO2 according to the request digitalWrite(2, val); client.flush(); // Prepare the response String s = "HTTP/1.1 200 OK\r\nContent-Type: text/html\r\n\r\n<!DOCTYPE HTML>\r\n<html>\r\nGPIO is now "; s += (val)?"high":"low"; s += "</html>\n"; // Send the response to the client client.print(s); delay(1); Serial.println("Client disonnected"); // The client will actually be disconnected // when the function returns and 'client' object is detroyed }

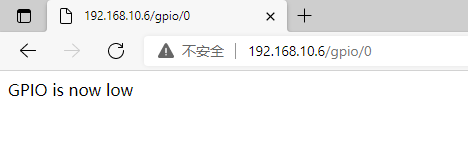
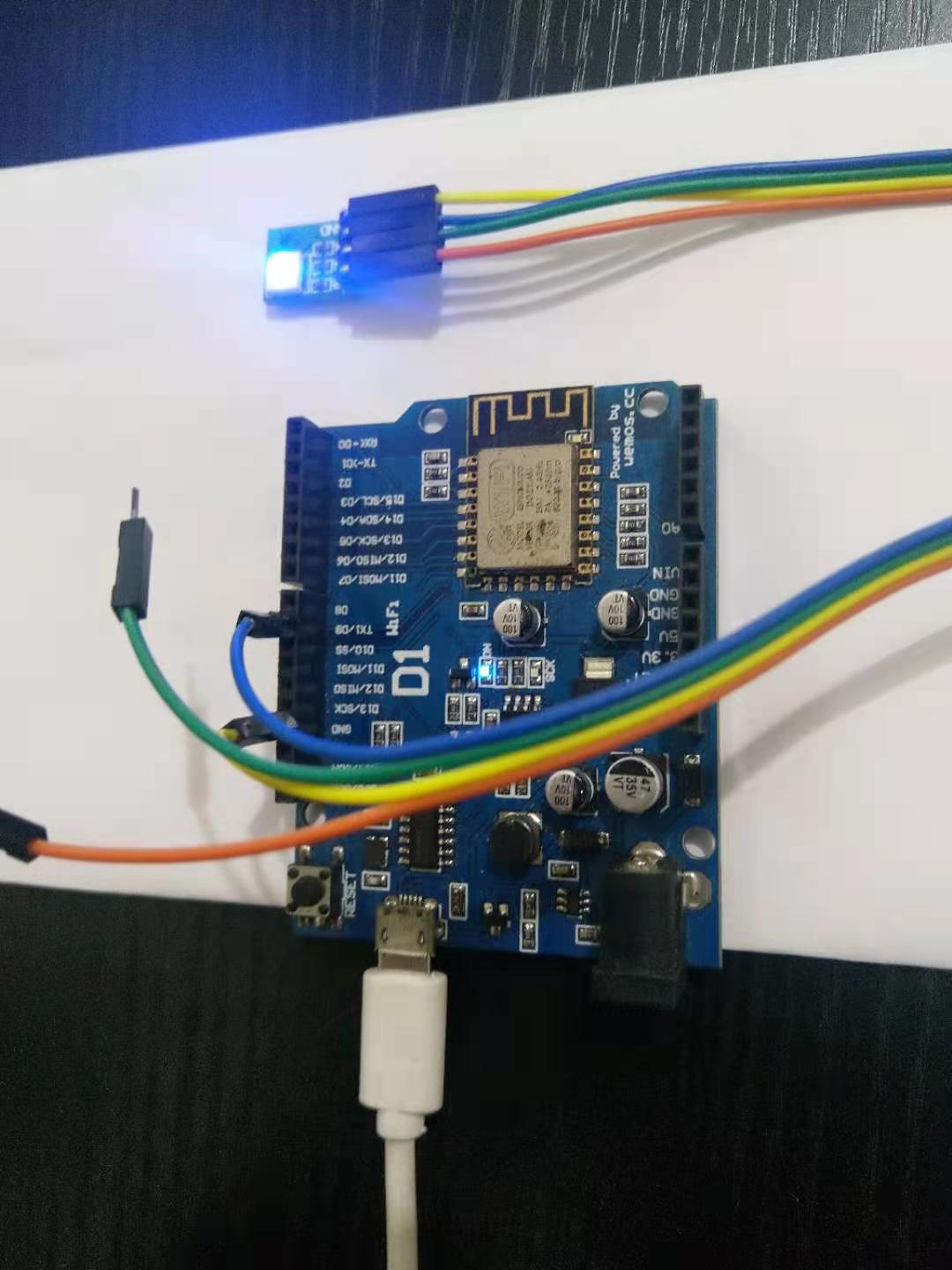
作者:儒良设计
-------------------------------------------
个性签名:独学而无友,则孤陋而寡闻。做一个灵魂有趣的人!
万水千山总是情,打赏一分行不行,所以如果你心情还比较高兴,也是可以扫码打赏博主,哈哈哈(っ•̀ω•́)っ✎⁾⁾!




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号