C++ 提高编程
一、string
二、vector
三、deque
四、stack
五、queue
六、list
九、函数对象/仿函数
十、常用算法
一、模板
C++ 除了面向对象编程外,还有一种编程思想为泛型编程
模板的作用:建立通用函数,返回类型与参数类型都不指定,用虚拟的类型代表
语法
template <typename T>
#include<iostream> using namespace std; template<typename T> void swapNumber(T &a, T &b) { T temp = a; a = b; b = temp; } int main() { int a = 10; int b = 20; //1.隐士类型转换 //swapNumber(a,b); //2.显示类型指定 swapNumber<int>(a, b); cout << a << endl; cout << b << endl; return 0; }
普通函数可以发生隐式类型转换
函数模板自动类型推导不会发生隐式类型转换,但是显示指定类型可以发生隐士类型转换
普通函数与函数模板的调用规则
- 普通函数与函数模板都可以调用,优先调用普通函数
- 可以通过空模板参数列表强制调用函数模板
- 函数模板可以发生函数重载
- 如果函数模板有更好的匹配,优先调用函数模板
类模板:类模板没有自动类型推导,类模板参数列表可以有默认参数
定义: template<T> 类
类模板成员函数的创建时机1
类模板成员函数在调用时才创建
备注:
typeid() 获取指定数据的类型
climit 头文件包含数据类型的极值
类模板与继承
子类继承父类,如果父类是类模板,那么需要指定父类的模板类型
二、string
string 本质上是一个类,内部维护了一个 char *
string 赋值可以通过 = 或者 assign
string 字符串拼接 , 通过 += 或者 appent
查找与替换 find rfind ,区别是find 从左往右边查,rfind 从右往左查询 。replace ,替换,可以将指定位置的字符替换为目标字符串
string 字符串比较 compare ,相等为0 ,逐个字符比较
string 内部重载了 [] , 也可以通过 at 访问单个字符
字符串插入与删除 insert ,erase 删除 ,下标都是从 0 开始计数
子串,substr ,指定开始位置与长度,截取子串
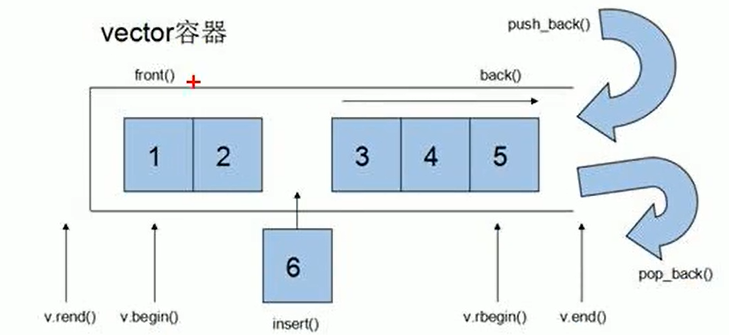
三、vector 容器
特点:
Vector 数据结构和数组非常相似,称为单端数组
vector 可以动态扩展
使用需要包含头文件 <vector>
void printVector(vector<int> &v) { for (vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++) { cout << *it << " "; } } int main() { vector<int> v1; for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { v1.push_back(i); } printVector(v1); return 0; }
四、deque
使用需要先包含头文件 <deque>
双端数组,可以对头端与尾端进行操作
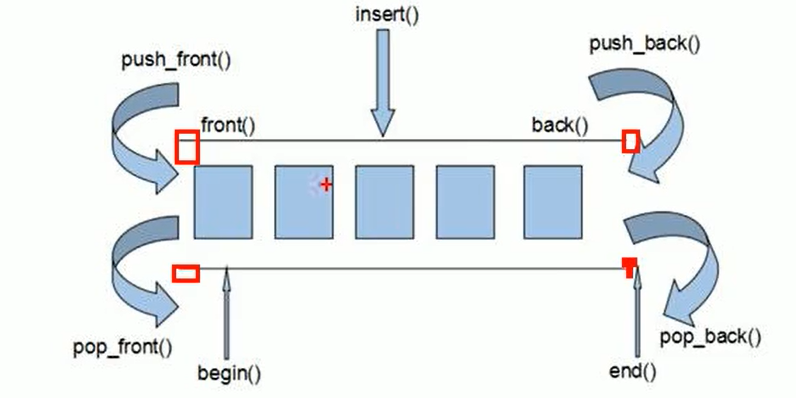
deque 内部工作原理:
deque 内部有个中控器,维护每端缓冲区的地址
deque 容器的迭代器也支持随机访问
deque 没有容量的概念,可以无限扩大
算法头文件 <algorithm> ,可以使用 sort 排序 ,支持随机访问的容器都可以通过 sort 进行排序
rand() 可以获取随机数, 伪随机,
rand((unsigned int)time(null))
void printDeque(deque<int> &d) { for (deque<int>::iterator it = d.begin(); it != d.end(); it++) { cout << *it << " "; } } void printDeque2(const deque<int>& d) { for (deque<int>::const_iterator it = d.begin(); it != d.end(); it++) { cout << *it << " "; } } int main() { deque<int>d; d.push_front(10); }
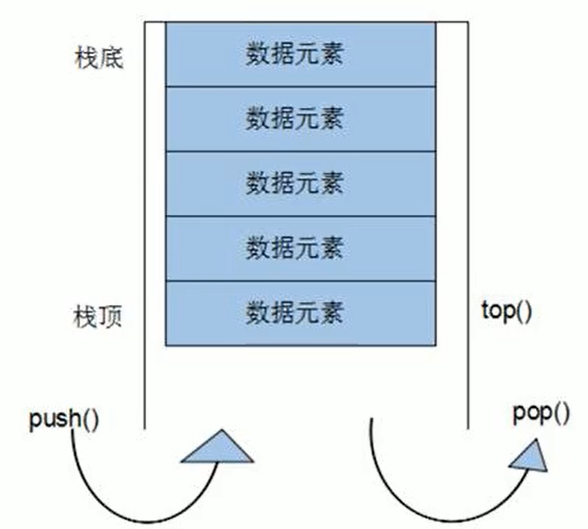
五、stack
栈容器 stack ,是一种 先进后出 FILO 的数据结构,栈不允许有遍历的行为,每次只能访问栈顶元素
int main() { using namespace std; stack<int>s; s.push(10); s.push(20);while (!s.empty()) { cout << s.top() << endl; s.pop(); } return 0; }
STL 中使用栈,需要包含头文件 <stack>
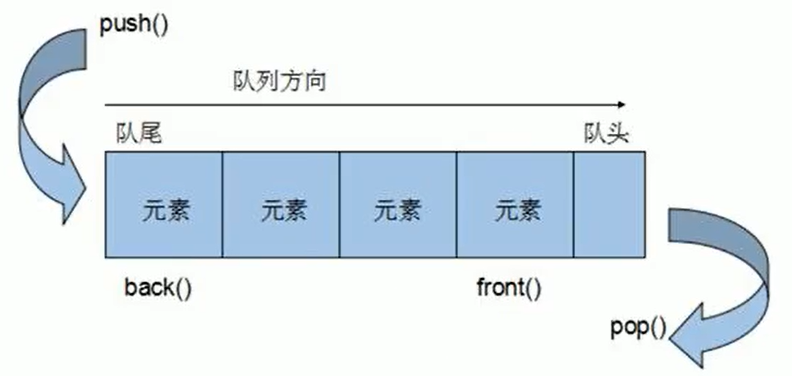
六、queue
队列,是一种先进先出的数据结构 FIFO,一端只能进数据,一端只能出数据。访问数据也只能访问2端的数据
int main() { queue<int>q; q.push(30); q.push(40);while (!q.empty()) { cout << q.front() << endl; q.pop(); } return 0; }
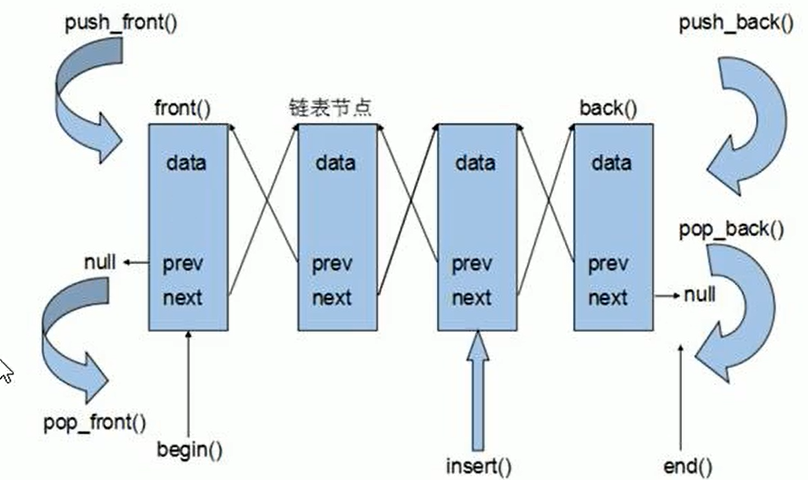
七、list
功能:将数据进行链式存储
链表:是一种物理上存储非连续的存储结构,数据元素的逻辑顺序是通过链表中的指针实现的
int main() { list<int> in; in.push_back(50); in.push_back(10); in.push_back(20);in.sort(); in.reverse(); for (list<int>::iterator it = in.begin(); it != in.end(); it++) { cout << *it<<endl; } //sort(); 标准算法的排序只能够随机访问的数据结构 return 0; }
八、set /multiset
包含头文件 <set>
set 容器,不允许存储重复的元素 multiset 允许插入重复的元素
set 容器特点
- 容器元素插入会自动排序
- 不允许插入重复元素
int main() { set<int, MyCompare> s; s.insert(10); s.insert(40); s.insert(20);for (set<int, MyCompare>::iterator it = s.begin(); it != s.end(); it++) { cout << *it << " "; } cout << endl; return 0; }
在 visio studio 下编译会报错,需要在仿函数中加入 const
九、map / multimap
包含头文件 <map>
map 中所有的元素都是 pair(对组)
所有的元素都会根据元素的键自动排序
map 与 multimap 区别是key 值是否允许重复
队组: pair<int,int>(1,10) ,make_pair(1,20)
class Mycompare { public: bool operator()(int x,int y)const { return x > y; } }; int main() { map<int, int, Mycompare>m; m.insert(make_pair(1, 10)); m.insert(make_pair(2, 20)); m.insert(make_pair(3, 30)); m.insert(make_pair(4, 40)); for (map<int, int, Mycompare>::iterator it = m.begin(); it != m.end(); it++) { cout << it->first << "," << it->second << endl; } return 0; }
十 、函数对象(仿函数)
函数对象/仿函数是一个类
重载函数调用操作符,其对象常称为函数对象
函数对象使用重载 () 时,行为类似函数调用,叫做仿函数
谓词
如果bool 类型作为返回值的仿函数
一元谓词
operator() 接收一个参数
二元谓词
operator() 接收2个参数
内建函数对象
包含头文件 <functional>
- 算术仿函数
- 关系仿函数
- 逻辑仿函数
算术仿函数
negate 取反
plus 加法
关系仿函数
equal
less
greater_equal
逻辑仿函数
logical_and
logical_or
logical_not
注意:transform 算法函数搬运
十一、常用算法
算法需要导入头文件
#include<algorithm>
11.1 遍历算法foreach
函数可以是普通函数/
class Print { public: void operator()(int i) { cout << i<<" "; } }; void myPrint(int i) { cout << i << " "; } int main() { vector<int> v; for (int i = 1; i < 10; i++) { v.push_back(i); } for_each(v.begin(),v.end(), Print()); cout << endl; for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), myPrint); return 0; }
11.2 transform 搬运到另一个容器
#include<iostream> #include<algorithm> #include<vector> using namespace std; int transInt(int i) { return i+100; } void myPrint(int i) { cout << i << " "; } int main() { vector<int> v1; for (int i = 1; i < 10; i++) { v1.push_back(i); } vector<int>v2; v2.resize(v1.size()); transform(v1.begin(),v1.end(),v2.begin(), transInt); for_each(v1.begin(), v1.end(), myPrint); cout << endl; for_each(v2.begin(), v2.end(), myPrint); return 0; }
11.3 find 查找元素,返回迭代器
#include<iostream> #include<algorithm> #include<vector> using namespace std; int main() { vector<int> v1; for (int i = 1; i < 10; i++) { v1.push_back(i); } vector<int>::iterator it = find(v1.begin(), v1.end(), 1); if (it != v1.end()) { cout << "找到元素:" << *it << endl; } else { cout << "未找到元素" << endl; } return 0; }
11.4 find_if 按条件查找
#include<iostream> #include<algorithm> #include<vector> using namespace std; class Greater20 { public: bool operator()(int i) { return i > 20; } }; int main() { vector<int> v1; for (int i = 1; i < 30; i++) { v1.push_back(i); } vector<int>::iterator it = find_if(v1.begin(), v1.end(), Greater20()); if (it != v1.end()) { cout << "找到元素:" << *it << endl; } else { cout << "未找到元素" << endl; } return 0; }
11.5 adjacent_find 查询相邻重复元素
#include<iostream> #include<algorithm> #include<vector> using namespace std; int main() { vector<int> v1; v1.push_back(10); v1.push_back(30); v1.push_back(30); v1.push_back(10); v1.push_back(50); vector<int>::iterator it = adjacent_find(v1.begin(), v1.end()); if (it != v1.end()) { cout << "找到元素:" << *it << endl; } else { cout << "未找到元素" << endl; } return 0; }
11.6 binary_search 二分查找有序数组是否存在某元素
#include<iostream> #include<algorithm> #include<vector> using namespace std; int main() { vector<int> v1; v1.push_back(10); v1.push_back(20); v1.push_back(30); v1.push_back(40); v1.push_back(50); bool res = binary_search(v1.begin(), v1.end(),30); if (res) { cout << "找到元素:" << endl; } else { cout << "未找到元素" << endl; } return 0; }
11.7 count 统计数据出现次数
#include<iostream> #include<algorithm> #include<vector> using namespace std; int main() { vector<int> v1; v1.push_back(10); v1.push_back(20); v1.push_back(30); v1.push_back(10); v1.push_back(50); int res = count(v1.begin(), v1.end(),10); cout << res << endl; return 0; }
参考笔记:https://blog.csdn.net/ClaireSy/article/details/108423061



