Java学习--基本变量类型&科学计数法&Unicode编码
最开始的hello world
//一个源文件只能申明一个public class类 //空白符会被忽略掉 public class hello { int myrule = 0; //成员变量(实例变量) 对象销毁便不存在 可以理解成对象初始化的变量 static int class_rule = 1;//静态变量 类变量 随着类被卸载而销毁 public static void main(String[] args){ System.out.println("Hello, again Java!!"); int 年龄 = 18;//unicode编码 所以可以使用汉字来命名 System.out.println(年龄); } hello h = new hello(); }
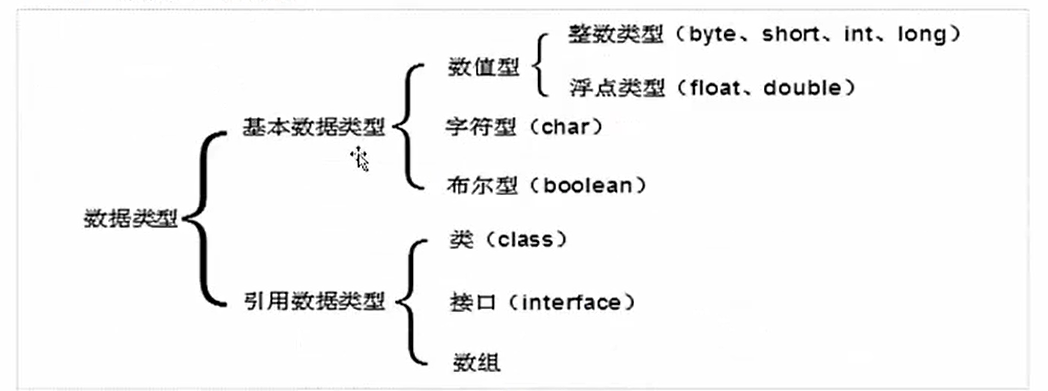
基本数据类型有8种
整数类型:byte short int long
浮点类型:float double
字符型:char
布尔型:boolean

整型
复习完类型再来过一遍不同整型对应的字节大小,1个字节对应的是8位(比特)

记得大约int也就是超过±21亿的范围才会溢出~~
public class TestConstants { public static void main (String[] args){ final double PI = 3.1415; //final 最终变量不能再赋值了! PI为符号常量 long f1 = 555555555555555L;//如果要使用long int 直接在变量后加个L long f2 = 555555555;//写一个long 也是默认的int 类型 int f3 = 555555555; System.out.println(f1); System.out.println(PI); } }
浮点型
顺带学以下科学计数法

public class TestFloatN { public static void main(String[] args){ double d1 = 3.14; double d2 = 3.14E-2;//科学计数法 System.out.println(d2); //float f1 = 1.55; //不能直接赋值float double f1 = 1.55F; float f2 = 1.55F; System.out.println(f1+"" +"||" +f2+""); //浮点数是不精确的 尽量不要用于直接比较 float f3 = 5616153546845576665L;//这里的float也是能定义成long 字节的 long f5 = 5000558888888888888L; float f4 = f3 +1 ; System.out.println(f3==f4);//输出为true } }
Java所用的是unicode编码
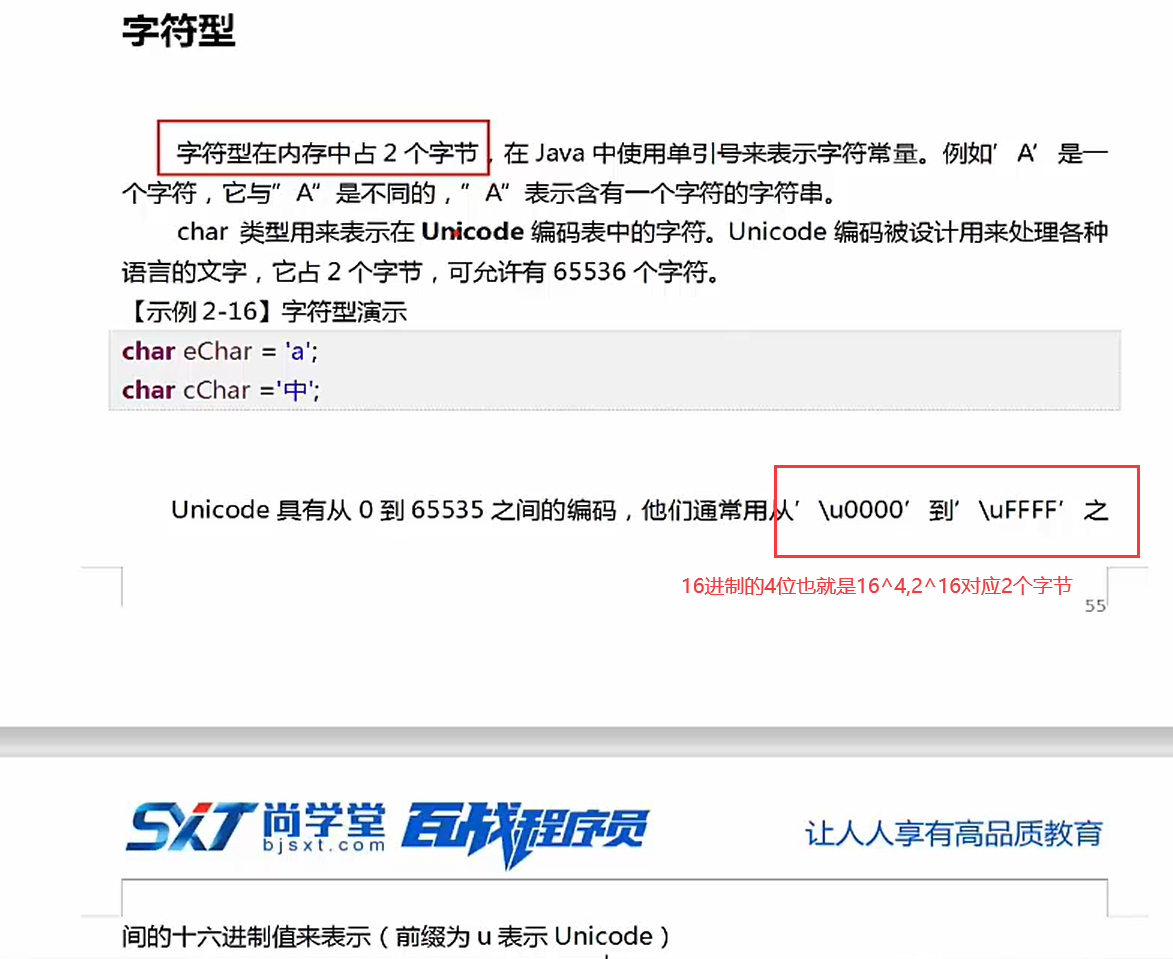
使用反斜杠来转移一些特殊字符,或者直接使用他们的Unicode编码

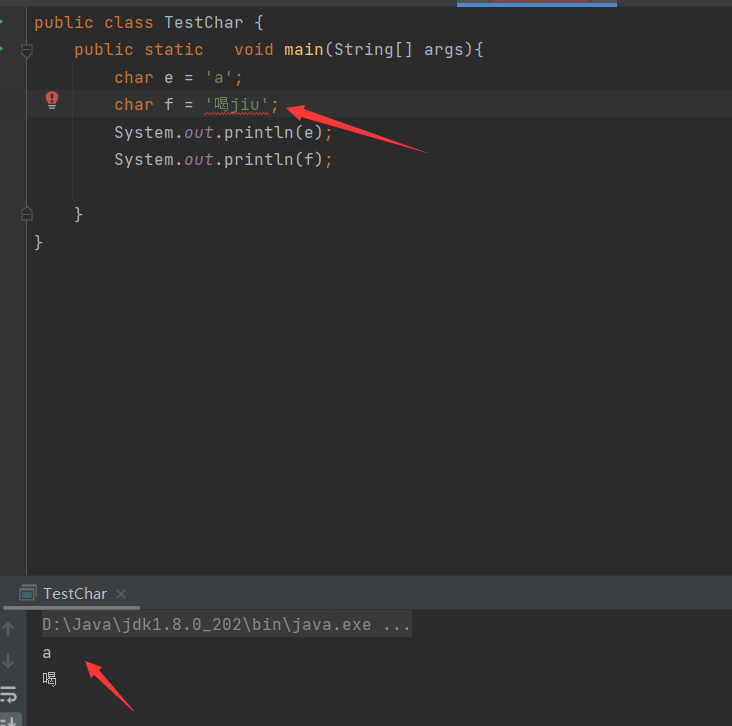
想使用超过1个字符的,就不能用char了,char只能表示1个字符的大小,而该使用String来定义了
Boolean类型
boolean类型有两个常量值,true和false,在内存中占一个字节或4个字节(取决于JVM在数组中占1个字节,其余在JVM中当作int处理 为4个字节),
不可以使用0或非0的整数替代 true 和false ,这点和C语言不同。
boolean类型用来判断逻辑条件,一般用于程序流程控制。


