Java入门笔记
Java
Java三大版本
JavaSE:标准版(桌面程序、控制台开发、……)
JavaME:嵌入式开发(手机、小家电、……)
JavaEE:企业级开发(web端、服务器端、……)
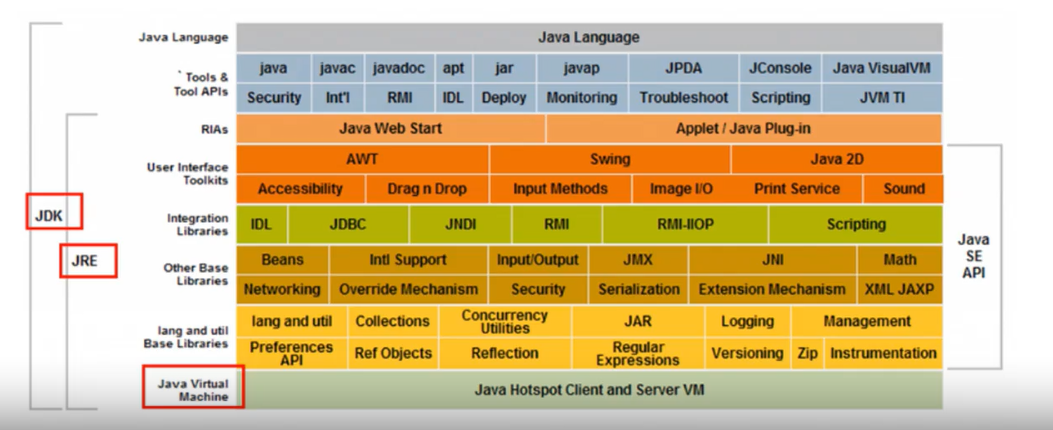
JDK、JRE、JVM
JDK:Java Development Kit (开发工具包)
JRE:Java Runtime Environment (编译器/运行环境)
JVM:Java Virtual Machine (虚拟机)
JDK内各文件夹功能
bin: 存放可执行的文件
include: 存放C/C++的头文件
lib: Java类库文件
Hello,World!
public class Hello{
public static void main(String[] args){
System.out.print("Hello,World!");
}
}
注:1.Java是大小写敏感的
2.文件名与类名必须保持一致,并且首字母大写
编译Java文件
javac xxx.java
运行class文件
java xxx
注:编译需要写全文件后缀 xxx.java,运行直接写文件名 xxx
注释
// 单行注释
/*
多
行
注
释
*/
//JavaDoc:文档注释
/**
* @Description HelloWorld
* @Author Java
* */
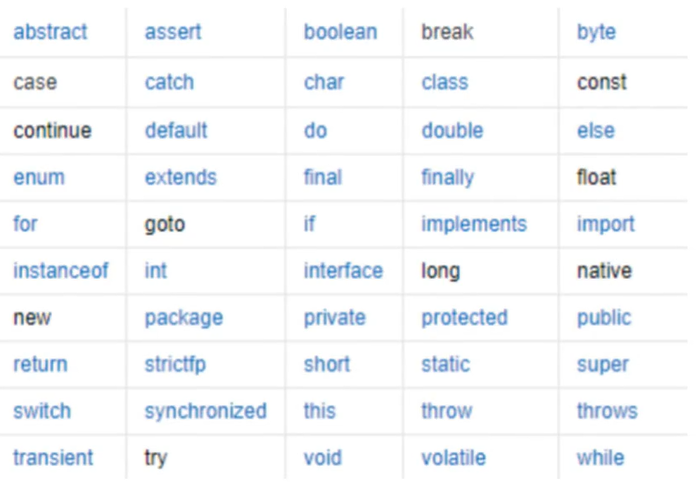
关键字
数据类型
Java的数据类型
Java是强类型语言(要求变量的使用要严格符合规定,所有变量都必须先定义再使用)

public class Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//八大基本数据类型
//整数
int num1 = 10; //最常用
byte num2 = 20;
short num3 = 30;
long num4 = 30L; //Long类型要在数字后面加个L
//小数:浮点数
float num5 = 50.1F; //float类型要在数字后面加个F
double num6 = 3.141592653589793238462643;
//字符
char name = 'A';
//字符串
String namea = "中国"; //String不是关键字,是类
//布尔值
boolean flag = true;
//boolean flag = false;
}
}
什么是字节

1bit 表示 1位
1Byte 表示一个字节 1B = 8b
1024B = 1KB
1024KB = 1M
1024M = 1G
数据类型扩展
public class Demo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//整数扩展: 进制 二进制--0b 十进制 八进制--0 十六进制--0x
int i1 = 10;
int i2 = 010; //八进制
int i3 = 0x10; //十六进制0x 0~9 A~F(10~16)
int i4 = 0x11;
System.out.println(i1); //10
System.out.println(i2); //8
System.out.println(i3); //16
System.out.println(i4); //17
System.out.println("========================================");
//============================================================================//
//浮点数拓展
//银行业务怎么表示?——钱
//BigDecimal 数学工具类
//float 有限 离散 舍入误差 大约 接近但不等于
//double
//最好完全使用浮点数进行比较
//最好完全使用浮点数进行比较
//最好完全使用浮点数进行比较
float f = 0.1f; //0.1
double d = 1.0/10; //0.1
System.out.println(f==d); //false
float d1 = 23121212312312313f;
float d2 = d1 + 1;
System.out.println(d1==d2); //true
System.out.println("========================================");
//============================================================================//
//字符拓展
char c1 = 'a';
char c2 = '中';
System.out.println(c1); //a
System.out.println((int)c1); //强制转换 //97
System.out.println(c2); //中
System.out.println((int)c2); //强制转换 //20013
//所有的字符本质还是数字
//编码 Unicode 表 (eg. 97 == a , 65 == A) 2字节 0~65536 Excel 2^16=65536
// U0000~UFFFF
char c3 = '\u0061';
System.out.println(c3); //a
//转义字符
// \t 制表符
// \n 换行
System.out.println("Hello\tWorld");
System.out.println("Hello\nWorld");
System.out.println("========================================");
String sa = new String("hello world");
String sb = new String("hello world");
System.out.println(sa==sb); //false
String sc = "hello world";
String sd = "hello world";
System.out.println(sc==sd); //true
//对象 从内存分析
System.out.println("========================================");
//============================================================================//
//布尔值扩展
boolean flag = true;
if (flag){
}
}
}
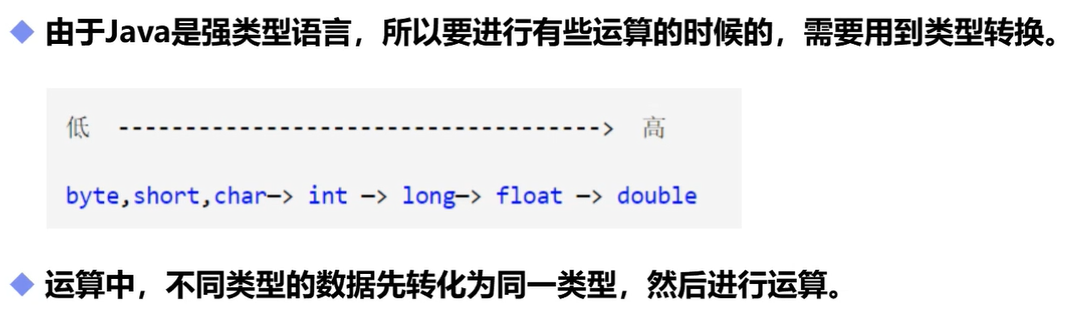
类型转换
public class Demo03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = 128;
byte b = (byte) i; //内存溢出
//强制转换 (类型)变量名 高——>低
System.out.println(i); //128
System.out.println(b); //-128
System.out.println("========================================");
int j = 128;
double c = j; //内存溢出
//自动转换 低——>高
System.out.println(j); //128
System.out.println(c); //128.0
/*
注意点:
1.不能对布尔值进行转换
2.不能把对象类型转换成不相干的类型
3.在把高容量转换到低容量的时候,强制转换
4.转换的时候可能存在内存溢出,或者精度问题
*/
System.out.println("========================================");
System.out.println((int)23.7); //23
System.out.println((int)-45.89f); //-45
System.out.println("========================================");
char u = 'a';
int r = u + 1;
System.out.println(r); //98
System.out.println((char)r); //b
System.out.println("========================================");
//操作比较大的数的时候,注意溢出问题
//JDK7新特性,数字之间可以用下划线分割
int money = 10_0000_0000;
int years = 20;
int total = money*years;
System.out.println(total); //-1474836480,计算的时候溢出了
long total2 = money*years;
System.out.println(total2); //-1474836480,默认是int,转换之前已经存在问题了
long total3 = money*((long)years); //先把一个数转换为long
System.out.println(total3); //20000000000
}
}
变量与常量
作用域
public class Demo04 {
//类变量 static
static double salary = 2500;
//属性:变量
//实例变量:从属于对象;如果不自行初始化,这个类型的默认值则为 0 或 0.0
//布尔值:默认为false
//除了基本类型,其余的默认值都是null
String name;
int age;
//常量
//(一般大写字母表示)
//修饰符不存在先后顺序
static final double PI = 3.14;
//main方法
public static void main(String[] args) {
//局部变量:必须声明和初始化
int i = 10;
System.out.println(i); //10
//变量类型 变量名字 = new Demo04();
Demo04 demo04 = new Demo04();
System.out.println(demo04.age); //0
System.out.println(demo04.name); //null
//类变量 static
System.out.println(salary); //2500.0
//常量
System.out.println(PI); //3.14
}
//其他方法
public void add(){
}
}
命名规范

运算符

二元运算符
package base;
public class Demo05 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 二元运算符
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
int c = 25;
int d = 25;
System.out.println(a+b); //30
System.out.println(a-b); //-10
System.out.println(a*b); //200
System.out.println(a/b); //0
System.out.println(a/(double)b); //0.5
System.out.println("====================================");
//不同类型变量运算后变化
long e = 12113253614456416L;
int f = 123;
short g = 10;
byte h = 8;
System.out.println(e+f+g+h); //Long 12113253614456557
System.out.println(f+g+h); //Int 141
System.out.println(g+h); //Int 18
}
}
关系运算符
package base;
public class Demo06 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//关系运算符返回的结果:正确,错误 布尔值
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
int c = 21;
//取余,模运算
System.out.println(c%a); // c/a 21/10 = 2 … 1
System.out.println(a>b); //false
System.out.println(a<b); //true
System.out.println(a==b); //false
System.out.println(a!=b); //true
}
}
自增、自减
package base;
public class Demo07 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//++ -- 自增,自减
int a = 3;
int b = a++; //执行玩这行代码后,先给b赋值,再自增
//a = a + 1;
System.out.println(a); //4
int c = ++a; //执行玩这行代码后,先自增,再给b赋值
System.out.println(a); //5
System.out.println(b); //3
System.out.println(c); //5
}
}
逻辑运算符
package base;
//逻辑运算符
public class Demo08 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 与(and) 或(or) 非(取反)
boolean a = true;
boolean b = false;
System.out.println("a && b : " + (a && b)); //a && b : false
//逻辑与运算:两个变量都为真,结果才为true
System.out.println("a || b : " + (a || b)); //a || b : true
//逻辑或运算:两个变量有一个为真,则结果为true
System.out.println("!(a && b) : " + !(a && b)); //!(a && b) : true
//逻辑非运算:如果是真,则变假,如果是假,则变真
//短路运算
int c = 5;
boolean d = (c<4)&&(c++<4);
System.out.println(d); //false
System.out.println(c); //5
}
}
位运算
package base;
public class Demo09 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/* 二进制
A = 0011 1100
B = 0000 1101
--------------------------
A&B = 0000 1100
A|B = 0011 1101
A^B = 0011 0001 //异或
~B = 1111 0010 //取反
*/
/*
2*8 = 16 2*2*2*2
<< *2
>> /2
0000 0000 0
0000 0001 1
0000 0010 2
0000 0011 3
0000 0100 4
0000 1000 8
0001 0000 16
*/
System.out.println(2<<3); //16
}
}
扩展赋值运算符、三元运算符
package base;
public class Demo10 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//扩展赋值运算符:+=, -=, *=, /=
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
a += b; //a = a+b
a -= b; //a = a-b
System.out.println(a); //30
//字符串连接符 + ,String
System.out.println("" + a + b); //1020
System.out.println(a + b + ""); //30
//三元运算符
/*
x ? y : z
如果x==true,则结果为y,否则结果为z
*/
int score = 50;
String type = score < 60 ? "不及格" : "及格";
System.out.println(type); //不及格
}
}
包机制
一般将域名倒置作为包名
定义包 package (eg,package com.baidu.www)
导入包 import (eg,import com.baidu.www)
JavaDoc生成文档
package com.baidu.base;
/**
* @author abc
* @version 1.0
* @since 1.8
*/
public class Doc {
String name;
/**
* @author abc
* @param name
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
public String test(String name) throws Exception{
return name;
}
}
javadoc -encoding UTF-8 -charset UTF-8 Doc.java
Scanner

next方法接收
package com.baidu.scanner;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建一个扫描器对象,用于接收键盘数据
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("使用next方式接收:");
//判断用户有没有输入字符串
if (scanner.hasNext()){
//使用next方式接收
String str = scanner.next();
System.out.println("输出的内容为:" + str);
}
//凡是属于IO流的类如果不关闭会一直占用资源,要养成良好的习惯用完就关掉
scanner.close();
}
}
nextLine方法接收
package com.baidu.scanner;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner2 = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("使用nextline方式接收:");
if (scanner2.hasNextLine()){
String str2 = scanner2.nextLine();
System.out.println("输出的内容为:" + str2);
}
scanner2.close();
}
}
判断小数、整数
package com.baidu.scanner;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
//从键盘接收数据
int i = 0;
float f = 0.0f;
System.out.println("请输入整数:");
if(scanner.hasNextInt()){
i = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println("整数数据:" + i);
}else {
System.out.println("输入的不是整数数据!");
}
System.out.println("请输入小数:");
if(scanner.hasNextFloat()){
f = scanner.nextFloat();
System.out.println("小数数据:" + f);
}else {
System.out.println("输入的不是小数数据!");
}
}
}
求和求平均值
package com.baidu.scanner;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 输入多个数字,并求其总和与平均数,每输入一个数字用回车确认,通过输入非数字来结束输入输出执行结果
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
// 和
double sum = 0;
// 计算输入了多少个数字
int m = 0;
System.out.println("请输入数据:");
while(scanner.hasNextDouble()) {
double x = scanner.nextDouble();
m += 1;
sum += x;
}
System.out.println(m + "个数的和为:" + sum);
System.out.println(m + "个数的平均值为:" + (sum / m));
scanner.close();
}
}
选择结构
if
单选择结构
if(……) {
……
}
package com.baidu.struct;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入内容:");
String s = scanner.nextLine();
//equals 判断字符串是否相等
if (s.equals("Hello")){
System.out.println(s);
}
System.out.println("End");
scanner.close();
}
}
双选择结构
if(……) {
……
}else {
……
}
package com.baidu.struct;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 考试分数大于等于60分就是及格,小于60就不及格
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入成绩:");
int score = scanner.nextInt();
if(score >= 60) {
System.out.println("及格");
}else {
System.out.println("不及格");
}
scanner.close();
}
}
多选择结构
if(……) {
……
}else if(……) {
……
}else {
……
}
package com.baidu.struct;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 考试分数大于等于60分就是及格,小于60就不及格
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入成绩:");
int score = scanner.nextInt();
if(score == 100) {
System.out.println("满分");
}else if(score < 100 && score >= 90) {
System.out.println("A");
}else if(score < 90 && score >= 80) {
System.out.println("B");
}else if(score < 80 && score >= 70) {
System.out.println("C");
}else if(score < 70 && score >= 60) {
System.out.println("D");
}else if(score < 60 && score >= 0) {
System.out.println("不及格");
}else {
System.out.println("成绩不合法");
}
scanner.close();
}
}
嵌套结构
if(……) {
if(……) {
……
}
}
switch
switch(……) {
case …… :
……
break;
case …… :
……
break;
default :
……
}
package com.baidu.struct;
public class Demo04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//
char grade = 'C';
switch (grade){
case 'A':
System.out.println("优秀");
break;
case 'B':
System.out.println("良好");
break;
case 'C':
System.out.println("中等");
break;
case 'D':
System.out.println("及格");
break;
case 'E':
System.out.println("挂科");
break;
default:
System.out.println("未知等级");
}
}
}
package com.baidu.struct;
public class Demo05 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String name = "小明";
// 反编译 java --- class(字节码文件) --- 反编译(IDEA)
switch (name) {
case "小明":
System.out.println("小明");
break;
case "小红":
System.out.println("小红");
break;
default:
System.out.println("未找到");
}
}
}
循环结构
while
while(……) {
……
}
package com.baidu.struct;
public class Demo06 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 输出1~100
int i = 0;
while (i < 100) {
i++;
System.out.println(i);
}
// 输出1+2+3+...+100
int j = 0;
int sum = 0;
while (j <= 100) {
sum += j;
j++;
}
System.out.println(sum);
}
}
do while
do {
……
}while(……)
package com.baidu.struct;
public class Demo07 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int j = 0;
int sum = 0;
do {
sum += j;
j++;
}while (j <= 100);
System.out.println(sum);
}
}
while 与 do while
while先判断后执行,do…while是先执行后判断
do…while总是保证循环体会被至少执行一次
package com.baidu.struct;
public class Demo08 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a= 0;
while (a < 0) {
System.out.println(a);
a++;
}
System.out.println("================================");
do {
System.out.println(a);
a++;
}while (a < 0);
}
}
for
for(……) {
……
}
package com.baidu.struct;
public class Demo09 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 1; // 初始条件
while (a <= 10) { // 条件判断
System.out.println(a); // 循环体
a += 2; // 迭代
}
System.out.println("while循环结束");
// 初始化; 条件判断; 迭代;
// 快捷键 10.for
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
System.out.println(i);
}
System.out.println("for循环结束");
}
}
0~100之间的奇数和与偶数和
package com.baidu.struct;
public class Demo12 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int oddSum = 0;
int evenSum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
if (i % 2 != 0) {
oddSum += i;
} else {
evenSum += i;
}
}
System.out.println("奇数和:" + oddSum); // 2500
System.out.println("偶数和:" + evenSum); // 2450
}
}
1~1000之间能被5整除的数(每行输出3个)
package com.baidu.struct;
public class Demo10 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
if (i % 5 == 0) {
System.out.print(i + "\t");
}
if (i % (5 * 3) == 0) {
System.out.println();
// System.out.println("\n");
}
}
}
}
打印九九乘法表
package com.baidu.struct;
public class Demo11 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 1; i <= 9; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++) {
System.out.print(i + "*" + j + "=" + (i*j) + "\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
打印正三角形
package com.baidu.struct;
public class Demo15 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i <= 5; i++) {
for (int j = 5; j >= i; j--) {
System.out.print(" ");
}
for (int j = 1; j <= 2*i-1; j++){
System.out.print("*");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
增强for循环
package com.baidu.struct;
public class Demo13 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] numbers = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50}; // 定义一个数组
// 遍历数组元素
for (int x:numbers) {
System.out.println(x);
}
}
}
break、continue
package com.baidu.struct;
public class Demo14 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = 0;
while (i < 100) {
i++;
if (i == 5) {
System.out.println();
continue;
}
System.out.println(i);
if (i == 10) {
break;
}
}
}
}
方法
基本概念
Java方法是语句的集合,它们在一起执行一个功能
方法是解决一类问题的步骤的有序组合
方法包含于类或对象中
方法在程序中被创建,在其他地方被引用
设计方法的原则
方法的本意是功能块,就是实现某个功能的语句块的集合
设计方法的时候,最好保持方法的原子性,就是一个方法只完成1个功能,这样利于我们后期的扩展
package com.baidu.method;
public class Demo01 {
// main方法
public static void main(String[] args) {
int sum = add(1, 2);
System.out.println(sum);
System.out.println("=================================");
fiveDiv();
}
// 加法
public static int add(int x, int y) {
return x + y;
}
// 1000以内能被5整除的数
public static void fiveDiv() {
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
if (i % 5 == 0) {
System.out.print(i + "\t");
}
if (i % (5 * 3) == 0) {
System.out.println();
}
}
}
}
定义
修饰符 返回值类型 方法名 (参数类型 参数名) {
……
方法体
……
return 返回值;
}
package com.baidu.method;
public class Demo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int max = max(50, -1);
System.out.println(max);
}
public static int max(int num1, int num2) {
int result;
if (num1 > num2) {
result = num1;
} else {
result = num2;
}
if (num1 == num2) {
System.out.println("num1 == num2");
return 0; // 终止方法
}
return result;
}
}
重载
重载就是在一个类中,有相同的函数名称,但形参不同的函数
重载的规则
方法名称必须相同
参数列表必须不同(个数不同、或类型不同、参数排列顺序不同等)
方法的返回类型可以相同也可以不相同
仅仅返回类型不同不足以成为方法的重载
重载的实现
方法名称相同时,编译器会根据调用方法的参数个数、参数类型等去逐个匹配,以选择对应的方法
如果匹配失败,则编译器报错
package com.baidu.method;
public class Demo03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int max1 = max(50, -1);
System.out.println(max1); // 50
double max2 = max(0.9, 5.6); // 5.6
System.out.println(max2);
int max3 = max(0, -1, 6);
System.out.println(max3); // 6
}
public static int max(int num1, int num2) {
int result;
if (num1 > num2) {
result = num1;
} else {
result = num2;
}
if (num1 == num2) {
System.out.println("num1 == num2");
return 0; // 终止方法
}
return result;
}
public static double max(double num1, double num2) {
double result;
if (num1 > num2) {
result = num1;
} else {
result = num2;
}
if (num1 == num2) {
System.out.println("num1 == num2");
return 0; // 终止方法
}
return result;
}
public static int max(int num1, int num2, int num3) {
int result;
if (num1 > num2) {
result = num1;
} else {
result = num2;
}
if (result < num3) {
result = num3;
}
if (num1 == num2) {
if (num2 == num3) {
System.out.println("num1 == num2 == num3");
return 0; // 终止方法
}
}
return result;
}
}
命令行传参
package com.baidu.method;
public class Demo04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// args.length 数组长度
for (int i = 0; i< args.length; i++) {
System.out.println("args[" + i + "]:" + args[i]);
}
}
}
src\com\baidu\method > javac Demo03.java
src\ > java com.baidu.method.Demo03 this is baidu
args[0]: this
args[1]: is
args[2]: baidu
可变参数
JDK1.5开始,Java支持传递同类型的可变参数给一个方法
在方法声明中,在指定参数类型后加一个省略号(…)
一个方法中只能指定一个可变参数,它必须是方法的最后一个参数,任何普通的参数必须在它之前声明
package com.baidu.method;
public class Demo05 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
printMax(100, 50, 23, 6.6, -1);
printMax(new double[]{1, 5.6, 8});
}
public static void printMax(double ...numbers) {
if (numbers.length == 0) {
System.out.println("No argument passed");
return;
}
double result = numbers[0];
for (int i = 0; i < numbers.length; i++) {
if (numbers[i] > result) {
result = numbers[i];
}
}
System.out.println("The max value is " + result);
}
}
递归
递归结构
递归头:表示什么时候不调用自身方法,如果没有头,将陷入死循环
递归体:表示什么时候需要调用自身方法
package com.baidu.method;
public class Demo06 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(f(5)); // 120
}
public static int f(int n) {
if (n == 1) {
return 1;
}else {
return n * f(n - 1);
}
}
}
数组
定义
数组是相同类型数据的有序集合
数组描述的是相同类型的若干个数据,按照一定的先后次序排列组合而成
每一个数据称作一个数组元素每个数组元素可以通过一个下标来访问它们
声明及创建
声明
dataType[] arrayRefVar; // 首选
dataType arrayRefVar[];
创建
dataType[] arrayRefVar = new dataType[arraySize];
package com.baidu.array;
public class Demo01 {
// 变量的类型 变量的名字 = 变量的值;
// 数组类型
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] nums; // 声明
int nums2[];
nums = new int[4]; // 创建
nums[0] = 1; // 赋值
nums[1] = 2;
nums[2] = 3;
System.out.println(nums[2]); // 3
System.out.println(nums[3]); // 为赋值默认为 0
// System.out.println(nums[4]); // 超出下标报错
// 计算所有元素总和
int sum = 0;
// 获取数组长度:array.length
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
sum += nums[i];
}
System.out.println(sum); // 6
}
}
初始化
package com.baidu.array;
public class Demo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 静态初始化
int[] a = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
System.out.println(a[0]); // 1
// 动态初始化
int[] b = new int[10];
b[0] = 10;
System.out.println(b[0]); // 10
}
}
使用
常见用法
package com.baidu.array;
public class Demo03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arrays = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
// 打印数组元素
for (int i = 0; i < arrays.length; i++) {
System.out.println(arrays[i]);
}
System.out.println("==========================");
// 计算所有元素之和
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < arrays.length; i++) {
sum += arrays[i];
}
System.out.println("sum = " + sum);
System.out.println("==========================");
// 查找最大元素
int max = arrays[0];
for (int i = 0; i < arrays.length; i++) {
if (arrays[i] > max) {
max = arrays[i];
}
}
System.out.println("max = " + max);
}
}
For-Each 循环
package com.baidu.array;
public class Demo04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arrays = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
// For-Each
// JDK1.5,没有下标
for (int array : arrays) {
System.out.println(array);
}
}
}
数组作方法入参
package com.baidu.array;
public class Demo05 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arrays = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
// 数组作方法入参
printArray(arrays);
}
public static void printArray(int[] arrays) {
for (int i = 0; i < arrays.length; i++) {
System.out.print(arrays[i] + " ");
}
}
}
数组作返回值
package com.baidu.array;
public class Demo06 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arrays = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
// 数组作返回值
int[] reverse = reverse(arrays);
for (int i = 0; i < arrays.length; i++) {
System.out.print(reverse[i] + " ");
}
}
// 反转数组
public static int[] reverse(int[] arrays) {
int[] result = new int[arrays.length];
for (int i = 0, j = result.length - 1; i < arrays.length; i++, j--) {
result[j] = arrays[i];
}
return result;
}
}
多维数组
package com.baidu.array;
public class Demo07 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] array = {{1, 2}, {3, 4}, {5, 6}};
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < array[i].length; j++) {
System.out.println(array[i][j]);
}
}
}
}
Arrays类
package com.baidu.array;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Demo08 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = {1, 2, -5, 666, 98, 8, -10};
// 直接输出
System.out.println(a); // [I@1540e19d
// 转换为字符串输出
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a)); // [1, 2, -5, 666, 98, 8, -10]
// 排序
Arrays.sort(a);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a)); // [-10, -5, 1, 2, 8, 98, 666]
// 填充
Arrays.fill(a, 0);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a)); // [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
Arrays.fill(a, 2, 4, 1);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a)); // [0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0]
// 相等
int[] array1 = new int[]{1, 2, 3};
int[] array2 = array1;
int[] array3 = new int[]{1, 2, 3};
int[] array4 = new int[]{4, 5, 6};
int[] array5 = new int[]{3, 2, 1};
System.out.println(Arrays.equals(array1, array2)); // true
System.out.println(Arrays.equals(array1, array3)); // true
System.out.println(Arrays.equals(array1, array4)); // false
System.out.println(Arrays.equals(array1, array5)); // false
}
}
冒泡排序
package com.baidu.array;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Demo09 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = {1, 6, 4, 5, -1, 0, 8};
int[] sort = sort(a);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(sort)); // [8, 6, 5, 4, 1, 0, -1]
}
public static int[] sort(int[] array) {
int temp = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < array.length - 1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < array.length - 1 - i; j++) {
if (array[j+1] > array[j]) {
temp = array[j];
array[j] = array[j+1];
array[j+1] = temp;
}
}
}
return array;
}
}
稀疏数组
当一个数组中大部分元素为0,或者为同一值的数组时,可以使用稀疏数组来保存该数组
稀疏数组的处理方式:
记录数组一共有几行几列,有多少个不同值
把具有不同值的元素和行列及值记录在一个小规模的数组中,从而缩小程序的规模
package com.baidu.array;
public class Demo10 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建一个二维数组 11*11
// 0:没有棋子, 1:黑棋, 2:白棋
int[][] array1 = new int[11][11];
array1[1][2] = 1;
array1[2][3] = 2;
// 输出原始数组
System.out.println("输出初始棋盘");
for (int[] ints : array1) {
for (int anInt : ints) {
System.out.print(anInt + "\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
// 转换为稀疏数组保存
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 11; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 11; j++) {
if (array1[i][j] != 0) {
sum++;
}
}
}
System.out.println("有效棋子为:" + sum + "个");
// 创建一个稀疏数组
int[][] array2 = new int[sum + 1][3];
array2[0][0] = 11;
array2[0][1] = 11;
array2[0][2] = sum;
// 遍历二维数组,将非零的值存放到稀疏数组中
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < array1.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < array1[i].length; j++) {
if (array1[i][j] != 0) {
count++;
array2[count][0] = i;
array2[count][1] = j;
array2[count][2] = array1[i][j];
}
}
}
System.out.println("==============================");
// 输出稀疏数组
System.out.println("输出稀疏数组");
for (int i = 0; i < array2.length; i++) {
System.out.println(array2[i][0] + "\t"
+ array2[i][1] + "\t"
+ array2[i][2] + "\t");
}
System.out.println("==============================");
// 还原
System.out.println("还原");
// 读取稀疏数组
int[][] array3 = new int[array2[0][0]][array2[0][1]];
// 还原元素的值
for (int i = 1; i < array2.length; i++) {
array3[array2[i][0]][array2[i][1]] = array2[i][2];
}
// 输出还原的数组
System.out.println("输出还原的数组(棋盘)");
for (int[] ints : array3) {
for (int anInt : ints) {
System.out.print(anInt + "\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
面向对象
面向对象编程(Object-Oriented Programming,OOP)
本质:以类的形式组织代码,以对象的形式封装数据
三大特性:封装、继承、多态
方法调用、值传递
package com.oop.demo01;
// Demo01 类
public class Demo01 {
// main 方法
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 调用Student类中静态方法
Student.sleep(); // go to bed
// 调用Student类中非静态方法
// 实例化这个类 new
// 对象类型 对象名 = 对象值;
Student student = new Student();
student.say(); // Hello
// 实际参数和形式参数的类型要对应
int add = Demo01.add(1, 2);
System.out.println(add); // 3
// 值传递
int a = 1;
System.out.println(a); // 1
Demo01.change(a);
System.out.println(a); // 1
// 引用传递:对象,本质还是值传递
Person person = new Person();
System.out.println(person.name); // null
Demo01.changeName(person);
System.out.println(person.name); // xiaoming
}
/*
修饰符 返回值类型 方法名(...) {
// 方法体
return 返回值;
}
*/
public String sayHello() {
return "Hello,World";
}
// return 结束方法,返回一个结果
public void print() {
return;
}
public int max(int a, int b) {
return a > b ? a : b;
}
// 非静态方法之间可以互相调用 例:a内调用b();
// 非静态方法可以调用静态方法 例:a内调用c();
public void a() {
b();
c();
}
public void b() {}
// 静态方法之间可以互相调用 例:c内调用d();
// 静态方法不可以调用非静态方法! 例:c内调用b();会报错
// 原因:静态方法是和类同时加载的,非静态方法是类实例化之后才存在的
public static void c() {
d();
// b();
}
public static void d() {}
public static int add(int a, int b) {
return a + b;
}
public static void change(int a) {
a = 10;
}
public static void changeName (Person person) {
person.name = "xiaoming";
}
}
// 定义一个Person类,有一个属性:name
class Person {
String name; // null
}
package com.oop.demo01;
// 学生类
public class Student {
// 非静态方法
public void say() {
System.out.println("Hello");
}
public static void sleep() {
System.out.println("go to bed");
}
}
类与对象
类是一种抽象的数据类型,是对某一类事物的整体描述/定义,但是并不能代表某一具体的事物
对象是抽象概念的具体实例
类是对象的模板
创建与初始化对象
使用new关键字创建对象
使用new关键字创建的时候,除了分配内存空间之外,还会给创建好的对象进行默认的初始化以及对类中构造器的调用
类中的构造器也称为构造方法,是在进行创建对象的时候必须要调用的
构造器特点:必须和类的名字相同,必须没有返回类型,也不能写void
package com.oop.demo02;
// 一个项目应该只存在一个main方法
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 类:抽象的,实例化
// 类实例化后会返回一个自己的对象
// student对象就是Student类的一个具体实例
Student xiaoming = new Student();
Student xiaohong = new Student();
System.out.println(xiaoming.name); // null
System.out.println(xiaoming.age); // 0
xiaoming.name = "小明";
xiaoming.age = 3;
System.out.println(xiaoming.name); // 小明
System.out.println(xiaoming.age); // 3
xiaohong.name = "小红";
xiaohong.age = 3;
System.out.println(xiaohong.name); // 小红
System.out.println(xiaohong.age); // 3
}
}
package com.oop.demo02;
// 学生类
public class Student {
// 属性:字段
String name;
int age;
// 方法
public void study() {
System.out.println(this.name + "在学习");
}
}
构造器
特点:和类名相同,没有返回值
作用:实例化初始值,使用new关键字,本质是在调用构造器
注意:定义有参构造后,如果想使用无参构造,需要显示的定义一个无参构造
package com.oop.demo02;
// 一个项目应该只存在一个main方法
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 实例化Person
Person person1 = new Person();
System.out.println(person1.name); // xiaoli
Person person2 = new Person("xiaoming");
System.out.println(person2.name); // xiaoming
}
}
package com.oop.demo02;
public class Person {
// 一个类即使不自定义,也会存在一个方法
// public Person() {} // class中可查看
String name;
// 显示的定义构造器
public Person() {
// 实例化初始值
// 使用new关键字,本质是在调用构造器
this.name = "xiaoli";
}
// 有参构造
public Person(String name) { // 重载
this.name = name;
}
}
创建对象的内存分析
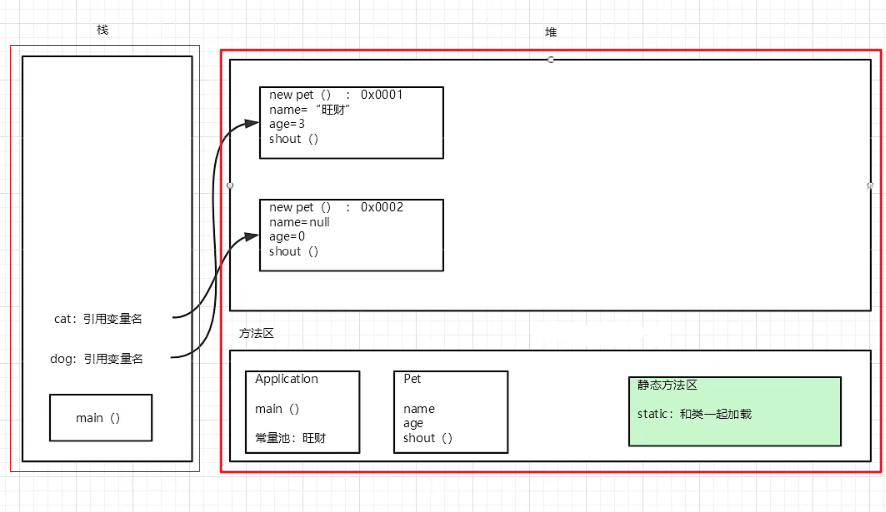
package com.oop.demo03;
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Pet dog = new Pet();
dog.name = "旺财";
dog.age = 3;
dog.shout();
System.out.println(dog.name);
System.out.println(dog.age);
Pet cat = new Pet();
}
}
package com.oop.demo03;
public class Pet {
String name;
int age;
// 无参构造
public void shout() {
System.out.println("叫了一声");
}
}
封装
封装的意义
提高程序的安全性,保护数据
隐藏代码的实现细节
统一接口
增加系统可维护性
package com.oop;
import com.oop.demo04.Student;
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student s1 = new Student();
s1.setName("小明");
System.out.println(s1.getName()); // 小明
s1.setAge(-1);
System.out.println(s1.getAge()); // 0
}
}
package com.oop.demo04;
public class Student {
// private 私有
// 属性私有
private String name;
private int id;
private char sex;
private int age;
// 提供一些可以操作私有属性的方法
// 提供一些 public 的 get、set方法
// get 获取数据
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
// set 设置数据
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
if (age > 120 || age < 0){ // 不合法
this.age = 0;
} else {
this.age = age;
}
}
}
继承
package com.oop;
import com.oop.demo05.Student;
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student student = new Student();
student.say();
System.out.println(student.money);
}
}
package com.oop.demo05;
// 在Java中,所有的类都默认直接或者间接的继承Object类
public class Person {
// public、protected、default、private
private int score = 10; // 私有属性不能继承
public int money = 10_0000_0000;
public void say() {
System.out.println("说了一句话");
}
public int getScore() {
return money;
}
public void setScore(int score) {
this.score = score;
}
}
package com.oop.demo05;
// 子类继承父类,就会拥有父类的全部方法
public class Student extends Person{
// Ctrl + H
}
package com.oop.demo05;
public class Teacher extends Person{
}
super( )
package com.oop;
import com.oop.demo06.Student;
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/* 先执行父类构造再执行子类 */
Student student = new Student(); // Person无参执行了 Student无参执行了
student.test("xiaoli");
student.testPrint();
}
}
package com.oop.demo06;
public class Person {
public Person() {
System.out.println("Person无参执行了");
}
protected String name = "xiaohong";
public void print() {
System.out.println("Person");
}
}
package com.oop.demo06;
public class Student extends Person{
// super必须只能出现在子类的方法或者构造方法中
// super和this不能同时调用构造方法
public Student() {
// 默认隐藏,调用父类的无参构造
super(); // 用来调用父类的构造器,必须要写在子类构造器的第一行
System.out.println("Student无参执行了");
}
private String name = "xiaoming";
public void test(String name) {
System.out.println(name); // xiaoli
System.out.println(this.name); // xiaoming
System.out.println(super.name); // xiaohong
}
public void print() {
System.out.println("Student");
}
public void testPrint() {
print(); // Student
this.print(); // Student
super.print(); // Person
}
}
方法重写
package com.oop;
import com.oop.demo07.A;
import com.oop.demo07.B;
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 静态方法:方法的调用只和左边,即定义的数据类型有关 eg: test()
// 非静态方法:子类会重写父类的方法 eg: print()
A a = new A();
a.test(); // A=>test()
a.print(); // A=>print()
// 父类的引用指向子类
B b = new A();
b.test(); // B=>test()
b.print(); // A=>print()
}
}
package com.oop.demo07;
public class A extends B{
public static void test() {
System.out.println("A=>test()");
}
// @Override 重写
// 重写时方法名必须相同,参数列表必须相同
@Override // 注解:有功能的注释
public void print() {
System.out.println("A=>print()");
}
}
package com.oop.demo07;
// 重写:方法重写,与属性无关
public class B {
public static void test() {
System.out.println("B=>test()");
}
public void print() {
System.out.println("B=>print()");
}
}
多态
package com.oop;
import com.oop.demo08.Person;
import com.oop.demo08.Student;
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 一个对象的实际类型是确定的
// new Person();
// new Student();
// 可以指向的引用类型就不确定:父类的引用可以指向子类
Student s1 = new Student(); // Student可以调用自己的或者继承父类的方法
Person s2 = new Student(); // Person可以指向子类,但不能调用子类独有的方法
Object s3 = new Student();
// 对象能执行哪些方法,主要看对象的左边类型
s1.sleep(); // sleeping 子类调用父类方法
s2.sleep(); // sleeping
s1.run(); // run 子类重写父类方法
s2.run(); // run
s1.eat(); // eat
/* s2.eat(); // error */
((Student) s2).eat(); // eat 强制类型转换
}
}
package com.oop.demo08;
public class Person {
// 多态是方法的多态,属性没有多态
// 多态存在条件:继承关系,方法重写,父类引用指向子类对象 eg: Person s1 = new Student();
public void run() {
System.out.println("running");
}
public void sleep() {
System.out.println("sleeping");
}
}
package com.oop.demo08;
public class Student extends Person{
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("run");
}
public void eat() {
System.out.println("eat");
}
}
instanceof和类型转换
package com.oop;
import com.oop.demo09.Person;
import com.oop.demo09.Student;
import com.oop.demo09.Teacher;
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// instanceof
// Object => String
// Object => Person => Teacher
// Object => Person => Student
Object object = new Student();
System.out.println(object instanceof Student); // true
System.out.println(object instanceof Person); // true
System.out.println(object instanceof Object); // true
System.out.println(object instanceof Teacher); // false
System.out.println(object instanceof String); // false
System.out.println("===============================");
Person person = new Student();
System.out.println(person instanceof Student); // true
System.out.println(person instanceof Person); // true
System.out.println(person instanceof Object); // true
System.out.println(person instanceof Teacher); // false
// System.out.println(person instanceof String); // error Person和String同级
System.out.println("===============================");
Student student = new Student();
System.out.println(student instanceof Student); // true
System.out.println(student instanceof Person); // true
System.out.println(student instanceof Object); // true
// System.out.println(student instanceof Teacher); // error
// System.out.println(student instanceof String); // error
System.out.println("===============================");
// 类型转换
// 父类转换子类(高转低,强制转换)
Person obj = new Student();
// 将 obj 强制转换为 Student类型
Student stu = (Student) obj;
stu.go(); // go
// 子类转换父类(高转低)
Student stu2 = new Student();
stu2.go();
Person per = stu;
// 子类转换父类可能会丢失一些自己本来的方法
// per.go(); // error
}
}
package com.oop.demo09;
public class Person {
public void run() {
System.out.println("running");
}
}
package com.oop.demo09;
public class Student extends Person{
public void go() {
System.out.println("go");
}
}
package com.oop.demo09;
public class Teacher extends Person{
}
static
package com.oop.demo10;
// final修饰的类,没有子类不能被继承
public final class Person {
{
// 匿名代码块
// 用处:赋初始值
System.out.println("匿名代码块");
}
static {
// 静态代码块
// 只执行一次
System.out.println("静态代码块");
}
public Person() {
System.out.println("构造方法");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person person1 = new Person();
// 静态代码块
// 匿名代码块
// 构造方法
System.out.println("=======================");
Person person2 = new Person();
// 匿名代码块
// 构造方法
}
}
package com.oop.demo10;
// static
public class Student /* extends Person // error */{
private static int age = 10; // 静态变量
private double score = 59.9; // 非静态变量
public void run() {
System.out.println("run");
}
public static void go() {
System.out.println("go");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student s1 = new Student();
System.out.println(Student.age); // 静态变量可以直接通过类名调用
// System.out.println(Student.score); // error
System.out.println(s1.age);
System.out.println(s1.score);
// run(); // error
s1.run();
new Student().run();
go();
Student.go();
}
}
package com.oop.demo10;
// 静态导入包
import static java.lang.Math.random;
import static java.lang.Math.PI;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(Math.random()); // 返回随机数
// 静态导入包之后,可以直接调用
System.out.println(random());
System.out.println(PI);
}
}
抽象类
package com.oop.demo11;
// abstract 抽象类
// 不能new抽象类,只能通过子类去实现
public abstract class Action {
// 约束
// 抽象方法,只有方法名字,没有方法实现
public abstract void doSth();
// 抽象类中可以写普通方法
// 抽象方法必须写在抽象类中
public void talk() {
}
}
package com.oop.demo11;
// 继承了抽象类的子类,必须要实现抽象类的方法,除非子类也是抽象类
public class A extends Action{
@Override
public void doSth() {
}
}
接口
package com.oop.demo12;
// 接口不能实例化
public interface UserService {
// 接口中所有定义的方法都是抽象的 public abstract
void add(String name);
void delete(String name);
void update(String name);
void query(String name);
// 接口中所有定义的变量都是静态常量 public static final
int AGE = 99;
}
package com.oop.demo12;
public interface TimeService {
void timer();
}
package com.oop.demo12;
// 类 可以实现接口 implements
// 实现接口的类,就需要重写接口中的方法
// 接口可以“多继承”
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService, TimeService{
@Override
public void add(String name) {
}
@Override
public void delete(String name) {
}
@Override
public void update(String name) {
}
@Override
public void query(String name) {
}
@Override
public void timer() {
}
}
内部类
package com.oop;
import com.oop.demo13.Outer;
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Outer outer = new Outer();
outer.out(); // 这是外部类的方法
outer.getIn(); // 这是内部类的方法
// 通过外部类实例化内部类
Outer.Inner inner = outer.new Inner();
inner.in(); // 这是内部类的方法
inner.getID(); // 99
inner.getOut(); // 这是外部类的方法
}
}
package com.oop.demo13;
// 外部类
public class Outer {
private int id = 99;
public void out() {
System.out.println("这是外部类的方法");
}
// 获取内部类的方法
public void getIn() {
new Inner().in();
}
// 内部类
public class Inner {
public void in() {
System.out.println("这是内部类的方法");
}
// 获取外部类的私有属性
public void getID() {
System.out.println(id);
}
// 获取外部类的方法
public void getOut() {
out();
}
}
// 静态内部类
public static class InnerStatic {
public void getID() {
// System.out.println(id); // error 静态内部类不能直接访问外部类变量
}
}
// 局部内部类
public void method() {
class Inner {
public void in() {
}
}
}
//
}
// 一个java类中可以有多个class类,但是只能有一个public class类
class A {
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
package com.oop.demo13;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 无命名初始化类
// 好处:不能将实例保存到变量中
new Apple().eat(); // 1
new UserService() {
@Override
public void hello() {
}
};
}
}
class Apple {
public void eat() {
System.out.println("1");
}
}
interface UserService {
void hello();
}
异常
Errorpackage com.exception;
package com.exception;
public class Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// new Demo01().a(); // java.lang.StackOverflowError
// System.out.println(11 / 0); // java.lang.ArithmeticException
}
public void a() {
b();
}
public void b() {
a();
}
}
捕获和抛出异常
package com.exception;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 1;
int b = 0;
// Ctrl + Alt + T
// 捕获多个异常要从小到大
try { // try监控区域
System.out.println(a/b);
}catch (ArithmeticException e) { // 捕获异常
System.out.println("程序出现异常,变量不能为0");
}catch (Error e){
System.out.println("Error");
}catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Exception");
}catch (Throwable t){
System.out.println("Throwable");
}finally { // 处理善后
System.out.println("finally");
}
new Test().test(1, 0);
}
// 假设这个方法中,处理不了这个异常,可以直接在方法上抛出异常
public void test(int a,int b) throws ArithmeticException{
if (b == 0) {
throw new ArithmeticException(); // 主动抛出异常,一般用在方法中
}
}
}
自定义异常
package com.exception.demo02;
// 自定义异常类
public class MyException extends Exception{
// 传递数字大于10
private int detail;
public MyException(int a) {
this.detail = a;
}
// toString 异常的打印信息
@Override
public String toString() {
return "MyException{" +
"detail=" + detail +
'}';
}
}
package com.exception.demo02;
public class Test {
// 可能会存在异常的方法
static void test(int a) throws MyException{
System.out.println("传递的参数为:" + a);
if (a > 10) {
throw new MyException(a); // 抛出
}
System.out.println("OK");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
test(1);
}catch (MyException e) {
System.out.println("MyException=>" + e);
}
try {
test(11);
}catch (MyException e) {
System.out.println("MyException=>" + e);
}
}
}
本文作者:伏月廿柒
本文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/by0627/p/16191286.html
版权声明:本作品采用知识共享署名-非商业性使用-禁止演绎 2.5 中国大陆许可协议进行许可。





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步