C++两种方法实现栈(stack)
我们用一个问题来说。问题是这样的:
实现一个序列,该序列中包含n个栈Si (i = 1, 2, 3, ... , n),栈中存放的都是int类型的整数,并能够完成以下操作:
-
push(t, x) 将元素x加入到栈St中,并返回元素x,即入栈操作。
-
top(t) 显示栈St的最后一个元素。若栈为空,则什么都不做。
-
pop(t) 将栈St的最后一个元素删除,并返回最后一个元素,即出栈操作。若栈为空,则什么都不做。
(为了简单,没有对类分离,写在了一个文件里,有兴趣的小伙伴们可以尝试着将类分离开)
第一种方法:向量
由于向量直接提供了类似的 入栈和出栈函数,所以我想创建一个数组,数组中的元素是向量。每个向量就是一个栈。废话不多说,上代码:
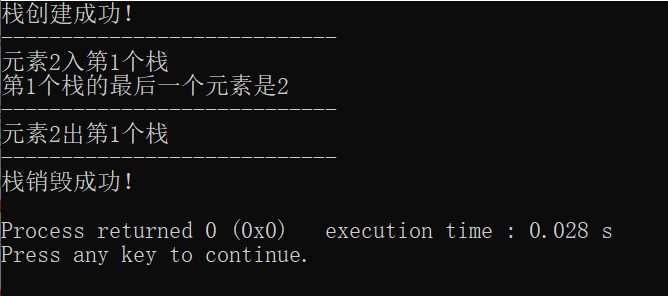
#include <iostream> #include <vector> using namespace std; class stackTest { public: stackTest(int n){ stacks = new vector<int>[n]; cout << "栈创建成功!" << endl; } ~stackTest(){ delete[] stacks; cout << "栈销毁成功!" << endl; } int push(int t, int x) { stacks[t-1].push_back(x); cout << "元素" << x << "入第" << t << "个栈" << endl; return x; } bool top(int t) { if (!stacks[t-1].empty()){ cout << "第" << t << "个栈的最后一个元素是" << stacks[t-1][stacks[t-1].size()-1] << endl; } return stacks[t-1].empty(); } int pop(int t) { int tmp = stacks[t-1][stacks[t-1].size()-1]; stacks[t-1].pop_back(); cout << "元素" << tmp << "出第" << t << "个栈" << endl; return tmp; } private: vector<int>* stacks; }; int main() { stackTest* s = new stackTest(2); cout << "----------------------------" << endl; s->push(1, 2); s->top(1); s->top(2); cout << "----------------------------" << endl; s->pop(1); s->top(1); cout << "----------------------------" << endl; delete s; return 0; }
运行结果:
第二种方法:结构体
用结构体实现栈,可以说是一般的方式了。代码如下:
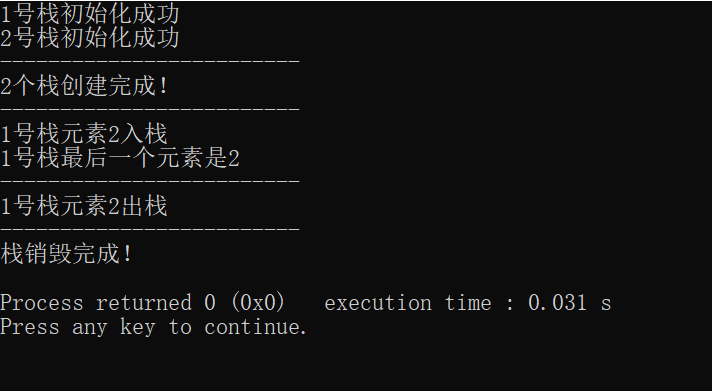
#include <iostream> using namespace std; const int STACKSIZE = 100; typedef struct{ int* base; int* top; int stack_size; }SqStack; bool initStack(SqStack& s) { s.base = new int[STACKSIZE]; if(!s.base){ cout << "初始化失败" << endl; return false; }else{ s.top = s.base; s.stack_size = STACKSIZE; cout << "初始化成功" << endl; return true; } } int pushStack(SqStack& s, int x) { if(s.top-s.base >= s.stack_size){ cout << "栈满,无法添加新元素" << endl; return -1; }else { *(s.top++) = x; return x; } } int popStack(SqStack& s){ if(s.top==s.base){ //cout << "栈为空" << endl; return -1; }else{ return *(--s.top); } } int topStack(SqStack& s) { if(s.top==s.base){ //cout << "栈为空" << endl; return -1; }else{ return *(s.top-1); } } class StackTest{ public: StackTest(int n){ stacks = new SqStack[n]; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){ cout << i+1 << "号栈"; initStack(stacks[i]); } cout << "-------------------------" << endl; cout << n << "个栈创建完成!" << endl; } ~StackTest(){ delete[] stacks; cout << "栈销毁完成!" << endl; } int push(int t, int x){ int tmp = pushStack(stacks[t-1], x); if(tmp != -1){ cout << t << "号栈元素" << tmp << "入栈" << endl;; } return tmp; } int pop(int t){ int tmp = popStack(stacks[t-1]); if(tmp != -1){ cout << t << "号栈元素" << tmp << "出栈" << endl;; } return tmp; } int top(int t){ int tmp = topStack(stacks[t-1]); if(tmp != -1){ cout << t << "号栈最后一个元素是" << tmp << endl;; } return tmp; } private: SqStack* stacks; }; int main() { StackTest* s = new StackTest(2); cout << "-------------------------" << endl; s->push(1, 2); s->top(1); s->top(2); cout << "-------------------------" << endl; s->pop(1); s->top(1); cout << "-------------------------" << endl; delete s; return 0; }
运行结果: