数据类型、约束条件
前言(创建表的完整语法)
语法: create table 表名( 字段名1 类型 (宽度) 约束条件, 字段名2 类型 (宽度) 约束条件, 字段名3 类型 (宽度) 约束条件 ) 注意: 1. 在同一张表中,字段名不能相同 2. 宽度和约束条件可选,字段名和类型必须有 3. 最后一个字段不能加逗号!
补充:
补充: 1. 宽度指的是对存储数据的限制 create table userinfo(name char); insert into userinfo values('jason'); ''' 1. 没有安全模式的数据库版本,是可以存放数据 但是只会存进去一个j (char默认存储一个字符) 2. 最新数据库版本直接报错,提示无法存储:Data too long for column 'name' at row 1 ''' 2. 约束条件初识>>>null 和not null create table t1(id int, name char not null); insert into t1 values(1, 'j'); # 正常存储 insert into t1 values(2, null); # 报错
总结(约束和类型的区别):
类型:限制字段必须以什么样的数据类型存储
约束条件:是在类型之外,添加一种额外的限制
数据类型
建表的时候,字段都有对应的数据类型
整型、浮点型、字符类型、日期类型、枚举和集合
整型
分类:TINYINT、SMALLINT、MEDIUMINT、INT、BIGINT
作用:存储年龄,等级,id,各种号码等
类型存储范围
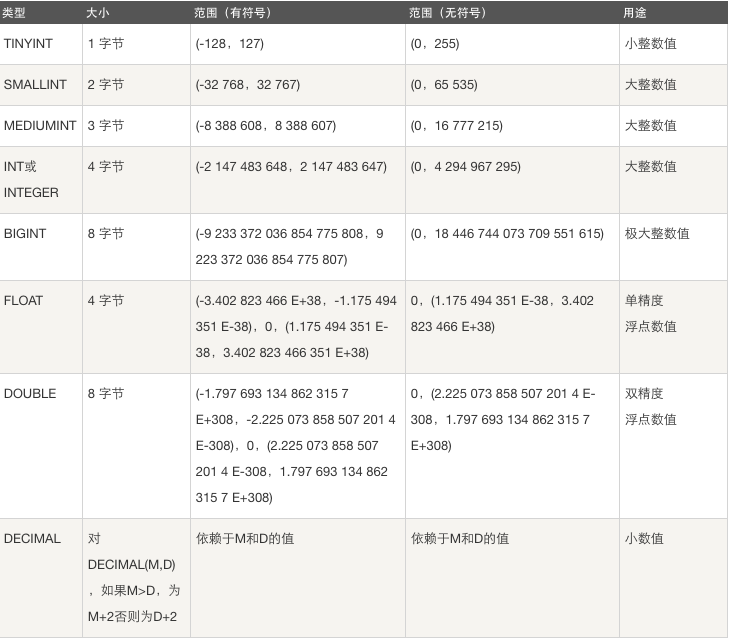
验证整型字段有无符号及范围(unsigned取消范围限制)

create table t1(x tinyint); insert into t1 values(128),(-129); select * from t1; '''执行结果: +------+ | x | +------+ | 127 | | -128 | +------+ ''' create table t2(x tinyint unsigned); insert into t2 values(-1),(256); select * from t2; '''执行结果 +------+ | x | +------+ | 0 | | 255 | +------+ ''' create table t3(x int unsigned); insert into t3 values(4294967296); select * from t3; '''执行结果: +------------+ | x | +------------+ | 4294967295 | | 4294967295 | +------------+ '''
疑问:类型后面的宽度能否改变字段存储的大小限制

create table t4(x int(8)); insert into t4 values(4294967296123); select * from t4; '''执行结果: +------------+ | x | +------------+ | 2147483647 | +------------+ ''' # 显示时,不够8位用0填充,如果超出8位则正常显示 create table t5(x int(8) unsigned zerofill); insert into t5 values(123); select * from t5; '''执行结果: +----------+ | x | +----------+ | 00000123 | +----------+ ''' # create table t6(id int(10) unsigned); # create table t7(id int(11));
强调
对于整型来说,数据类型后的宽度并不是存储限制,而是显示限制,
所以在创建表时,如果字段采用的是整型类型,完全无需指定显示宽度,
默认的显示宽度,足够显示完整当初存放的数据
严格模式补充
我们刚刚在上面设置了char,tinyint,存储数据时超过它们的最大存储长度,
发现数据也能正常存储进去,只是mysql帮我们自动截取了最大长度。
但在实际情况下,我们应该尽量减少数据库的操作,缓解数据库的压力,
让它仅仅只管理数据即可,这样的情况下就需要设置安全模式

show variables like "%mode%"; # 查看数据库配置中变量名包含mode的配置参数 +----------------------------------------+--------------------------------------+ | Variable_name | Value | +----------------------------------------+--------------------------------------+ | binlogging_impossible_mode | IGNORE_ERROR | | block_encryption_mode | aes-128-ecb | | gtid_mode | OFF | | innodb_autoinc_lock_mode | 1 | | innodb_strict_mode | OFF | | pseudo_slave_mode | OFF | | slave_exec_mode | STRICT | | sql_mode | NO_ENGINE_SUBSTITUTION | +----------------------------+---------------------------------------------------+ # 修改安全模式 set session # 只在当前操作界面有效 set global # 全局有效 set global sql_mode ='STRICT_TRANS_TABLES'; # 修改完之后退出当前客户端重新登陆即可
浮点型
分类:FLOAT、DOUBLE、decimal
应用场景:身高、体重。薪资
存储限制
字段限制特点(5,3) 前一位表示所有的位数,后一位表示小数个数 float(255,30) double(255,30) decimal(255,30)
精度验证

create table t9(x float(255,30)); create table t10(x double(255,30)); create table t11(x decimal(65,30)); insert into t9 values(1.111111111111111111111111111111); insert into t10 values(1.111111111111111111111111111111); insert into t11 values(1.111111111111111111111111111111); select * from t9; +---------------------------------------------------+ | x | +---------------------------------------------------+ | 1.111111164093017600000000000000 | +---------------------------------------------------+ select * from t10; +---------------------------------------------------+ | x | +---------------------------------------------------+ | 1.111111111111111111111111111111 | +---------------------------------------------------+ select * from t11; +---------------------------------------------------+ | x | +---------------------------------------------------+ | 1.111111111111111200000000000000 | +---------------------------------------------------+
字符类型
分类:char(定长)、varchar(变长)
作用:姓名,地址,描述类信息

create table t12(name char(4)); # 超出四个字符报错,不够四个字符空格补全 create table t13(name varchar(4)); # 超出四个字符报错,不够四个有几个就存几个 # 验证存储限制 insert into t12 values('hello'); insert into t13 values('hello'); select的结果一样: select * from t12; +------+ | name| +------+ | hell | +------+ select * from t13; +------+ | name| +------+ | hell | +------+ # 验证存储长度 insert into t12 values('a'); # 'a ' 空格补充的 insert into t13 values('a'); # 'a' select * from t12 +---------------------------+ | char_length(name) | +---------------------------+ | 1 | +------------------------ --+ select * from t13 # 无法查看真正的结果,看起来跟char的结果一样 select char_length(name) from t12 select char_length(name) from t13 # 仍然无法查看到真正的结果,看起来跟char的结果一样 """首先应该肯定的是在硬盘上存的绝对是真正的数据, 但显示的时候mysql会自动将末尾的空格去掉""" # 如果不想让mysql帮你做自动去除末尾空格的操作,需要再添加一个模式 set global sql_mode="strict_trans_tables,PAD_CHAR_TO_FULL_LENGTH"; # 退出客户端重新登陆 select char_length(x) from t12; #4 select char_length(y) from t13; #1 '''针对char类型,mysql在存储时会将数据用空格补全存放到硬盘中。 但是会在读出结果的时候自动取掉末尾的空格 '''
char 和varchar的区别

name char(5) # 缺点:浪费空间 # 优点:存取速度都快 egon alex lxx jxx txx name varchar(5) # 缺点:存取速度慢 # 优点:节省空间 1bytes+egon 1bytes+alex 1bytes+lxx 1bytes+jxx 1bytes+txx
时间类型
分类: data:2019-05-01 time:11:11:11 Datetime:2019-01-02 11:11:11 Year:2019

create table student( id int, name char(16), born_year year, birth date, study_time time, reg_time datetime ); insert into student values(1,'egon','2019','2019-05-09','11:11:00','2019-11-11 11:11:11'); select * from student; +------+--------+--------------+-------------+----------------+---------------------------------+ | id | name | born_year | birth | study_time | reg_time | +------+--------+--------------+-------------+----------------+---------------------------------+ | 1 | egon | 2019 | 2019-05-09 | 11:11:00 | 2019-11-11 11:11:11 | +------+--------+--------------+-------------+----------------+---------------------------------+
枚举和集合类型
分类:
枚举enum多选一
集合set多选多

create table user( id int, name char(16), gender enum('male','female','others') ); insert into user values(1,'jason','xxx'); # 报错 ERROR 1265 (01000): Data truncated for column 'gender' at row 1 insert into user values(2,'egon','female') # 正确! create table teacher( id int, name char(16), gender enum('male','female','others'), hobby set('read','sleep','sanna','dbj') ); insert into teacher values(1,'egon', 'male', 'read,sleep,dbj') # 集合也可以只存一个 select *from teacher; '''执行结果: +------+---------+-----------+--------------------+ | id | name | gender | hobby | +------+---------+-----------+--------------------+ | 1 | egon | male | read,sleep,dbj | +------+---------+-----------+--------------------+ '''
约束条件
PRIMARY KEY (PK) 标识该字段为该表的主键,可以唯一的标识记录
FOREIGN KEY (FK) 标识该字段为该表的外键
NOT NULL 标识该字段不能为空
UNIQUE KEY (UK) 标识该字段的值是唯一的
AUTO_INCREMENT 标识该字段的值自动增长(整数类型,而且为主键)
DEFAULT 为该字段设置默认值
UNSIGNED 无符号
ZEROFILL 使用0填充
not null+default

create table user2( id int, name char(16) ); insert into user2 values(1,null) # 可以修改 select * from user2; +------+--------+ | id | name | +------+--------+ | 1 | NULL | +------+--------+ alter table user modify name char(16) not null; select * from user2; +------+--------+ | id | name | +------+--------+ | 1 | | +------+--------+ insert into user(name,id) values(null,2); # 报错 插入数据可以在表名后面指定插入数据对应的字段 ERROR 1048 (23000): Column 'name' cannot be null create table student( id int, name char(16) not null, gender enum('male','female','others') default 'male' ) insert into student(id,name) values(1,'jason') # 成功 select id, name, gender from student2 where id=1; +------+---------+----------+ | id | name | gender | +------+---------+----------+ | 1 | jason | male | +------+---------+----------+
unique

# 单列唯一 create table user1( id int unique, name char(16) ); insert into user1 values(1,'jason'),(1,'egon'); # 成功 select * from users; +------+----------+ | id | name | +------+----------+ | 1 | jason | | 2 | tank | +------+----------+ insert into user1 values(1,'jason'),(2,'egon'); # 报错 ERROR 1062 (23000): Duplicate entry '1' for key 'id' # 多列唯一 create table server( id int, ip char(16), port int, unique(ip,port) ) insert into server values(1,'127.0.0.1',8080); insert into server values(2,'127.0.0.1',8080); # 报错(原因是联合唯一) ERROR 1062 (23000): Duplicate entry '127.0.0.1-8080' for key 'ip' insert into server values(1,'127.0.0.1',8081); # 不报错
primary key

# 单从约束角度来说primary key就等价于not null 加unique (补充: 除了约束之外,它还是innodb引擎组织数据的依据,提升查询效率) create table t20(id int primary key); desc t20; +-------+---------+------+-----+------------+-------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +-------+---------+------+-----+------------+-------+ | id | int(11) | NO | PRI | NULL | | +-------+---------+------+-----+------------+-------+ insert into t20 values(1),(2); # 没报错 insert into t20 values(1),(2); # 报错 ERROR 1062 (23000): Duplicate entry '1' for key 'PRIMARY'
primary key 注意事项

1. 一张表中必须有且只有一个主键,如果没有设置主键, 那么会从上往下搜索直到与发哦一个非空且唯一的字段,自动将其设置为主键 create table t21( id int, name char(16), age int not null unique, addr char(16) not null unique ) desc t21; +----------+--------------+------+-----+-----------+-------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +----------+--------------+------+-----+-----------+-------+ | id | int(11) | YES | | NULL | | | name | char(16) | YES | | NULL | | | age | int(11) | NO | PRI | NULL | | | addr | char(16) | NO | UNI | NULL | | +----------+--------------+------+-----+-----------+-------+ 2. 如果表里面没有指定任何的可以设置为主键的字段, 那么innodb会采用自己默认的一个隐藏字段作为主键, 隐藏意味着在查询的时候无法根据这个主键字段加速查询了 索引:类似于书的目录,没有主键就相当于一页一页翻着查 3. 一张表中通常都应该有一个id字段,并且通常将该id字段作成 主键
联合主键

# 多个字段联合起来作为表的一个主键,本质还是一个主键 create table server2(ip int, port char(16), addr char(16), primary key(ip, port)); desc server2; +-------+-------------+------+------+-----------+-------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +-------+-------------+------+------+-----------+-------+ | ip | int(11) | NO | PRI | 0 | | | port | char(16) | NO | PRI | | | | addr | char(16 ) | YES | | NULL | | +-------+--------------+------+-----+-----------+-------+
auto_increment

# 主键作为数据的编号,每次最好能自动递增 create table t40(id int auto_increment primary key, name char(16)); insert into t41(name) values('jason'),('tank'); select * from t41; +----+----------+ | id | name | +----+----------+ | 1 | jason | | 2 | tank | +----+----------+ # id字段自动从1开始递增 # 注意:auto_increment通常都是加在主键上,并且只能给设置为key的字段加
auto_increment 补充
delete from t41; 强调:上边这条命令确实可以将表里的所有记录都删除, 但是不会讲id充值为0, 所以该条命令根本是不是用来清空表的 delete是用来删除表中某些符合条件的记录 例如:delete from t41 where id > 10; 如果要清空表,使用 truncate t41; 作用:将整张表初始化,id重新开始从0记录




