什么?这么精髓的View的Measure流程源码全解析,你确定不看看?
前言
Android开发中我们平时接触最多的是各种View, View是一个比较大的体系,包含了绘制流程、事件分发、各种动画、自定义View 等等。前几天我写了一篇事件分发源码解析的文章, 今天我们来探索一下绘制流程中有点难懂的测量流程。
基础知识准备
测量涉及到的相关类和方法:
- MeasureSpec: 中文翻译测量规格,包含了两部分:SpecMode(测量模式)、SpecSize(对应测量模式下的规格大小)。它是由32位int值表示的,高两位代表SpecMode,低30位代表SpecSize
- measure(): 测量的入口方法,里面调用了onMeasure方法
- onMeasure(): 暴露给开发者可以自定义测量规则,不重写的话默认走的都是View的onMeasure方法
现在我们从View的onMeasure方法聊起来吧~~~
View的onMeasure源码解析
为了方便大家理解先给大家上三段常见的代码:
①View的width和height都是wrap_content
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<FrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:padding="16dp">
<View
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center"
android:background="@color/red" />
</FrameLayout>
②View的width和height都是match_parent
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<FrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:padding="16dp">
<View
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_gravity="center"
android:background="@color/red" />
</FrameLayout>
③View的width和height都是100dp
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<FrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:padding="16dp">
<View
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:layout_gravity="center"
android:background="@color/red" />
</FrameLayout>
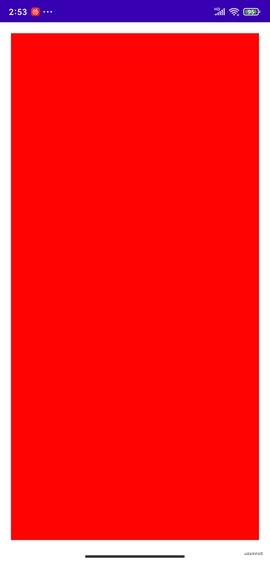
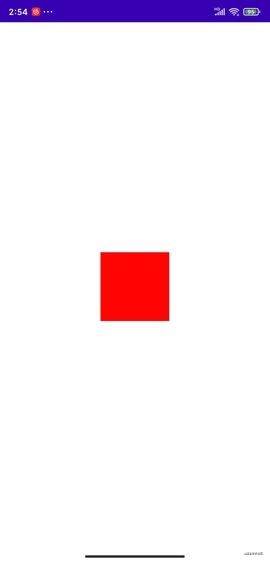
上面三段代码展示效果如下:
场景①和②:
场景③:
简单描述下上面出现的情况:
- 当view的宽高设置成match_parent和wrap_content的时候,显示的大小和父view的大小一致
- 当view的宽高设置成固定值(xxdp)的时候,显示的大小就是我们设置的固定值大小
如果你已经对上面结果感觉毫无疑问而且心里已经知其所以然了,后面的内容可以不用看了。点个赞就可以走了。。。
等等。。开个玩笑。。怎么就当真了呢。。哈哈哈。。废话不多说,走,我们点进去源码瞅瞅。
View.onMeasure
//View.java
public final void measure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
...
//1
onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
...
}
上述代码①处代码调用了view的onMeasure方法,先不聊widthMeasureSpec和heightMeasureSpec的由来,这个后面补上。接着我们看View的onMeasure方法:
//View.java
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
//1
setMeasuredDimension(
getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumWidth(),widthMeasureSpec),//4
getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumHeight(), heightMeasureSpec)//4
);
}
//2
protected final void setMeasuredDimension(int measuredWidth, int measuredHeight) {
...
setMeasuredDimensionRaw(measuredWidth, measuredHeight);
}
//3
private void setMeasuredDimensionRaw(int measuredWidth, int measuredHeight) {
mMeasuredWidth = measuredWidth;
mMeasuredHeight = measuredHeight;
mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_MEASURED_DIMENSION_SET;
}
//返回background(Drawable)的minWidth、mMinWidth(android_minWitdh)较大值
protected int getSuggestedMinimumWidth() {
return (mBackground == null) ? mMinWidth : max(mMinWidth,mBackground.getMinimumWidth());
}
//返回background(Drawable)的minHeight、mMinHeight(android_minHeight)较大值
protected int getSuggestedMinimumHeight() {
return (mBackground == null) ? mMinHeight :
max(mMinHeight, mBackground.getMinimumHeight());
}
//4
public static int getDefaultSize(int size, int measureSpec) {
int result = size;
int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec);
int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec);
switch (specMode) {
//5
case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED:
result = size;
break;
//6
case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:
case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:
result = specSize;
break;
}
return result;
}
上述代码略微多一点,但是方法都比较简单,下面我们一一介绍下:
- 标注①②③处的调用链:onMeasure-->setMeasuredDimension-->setMeasuredDimensionRaw 走到方法③setMeasuredDimensionRaw处,view的测量流程就结束了,同时赋值了mMeasuredWidth 和mMeasuredHeight,这个时候我们就可以通过getMeasuredWidth()和getMeasuredHeight() 拿到宽高值了
- 方法②setMeasuredDimension处又调用了方法④getDefaultSize
- 方法④getDefaultSize里面大致逻辑是:
- 如果传入的measureSpec的MeasureSpec.Mode的值是MeasureSpec.AT_MOST或者MeasureSpec.EXACTLY 则返回specSize。
- 如果传入的measureSpec的MeasureSpec.Mode的值是MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED 则返回size(getSuggestedMinimumWidth()、getSuggestedMinimumHeight())。
现在我们的疑惑点就在于方法①onMeasure的参数是从哪里来的
那么下面我们就瞅瞅FrameLayout相关测量源码
FrameLayout的onMeasure源码解析
在讲FrameLayout的onMeasure前,我们先默认一个事实,这个FrameLayout是Activity的根View,它会被添加到DecorView上,DecorView实际上也是一个FramLayout,下面的源码解释了DecorView的MeasureSpec的由来:
//ViewRootImpl.java
private void performTraversals() {
...
//获取DecorView的MeasureSpec
int childWidthMeasureSpec = getRootMeasureSpec(mWidth, lp.width);
int childHeightMeasureSpec = getRootMeasureSpec(mHeight, lp.height);
//测量入口
performMeasure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
...
//layout入口
performLayout(lp, mWidth, mHeight);
...
//draw入口
performDraw();
...
}
private static int getRootMeasureSpec(int windowSize, int rootDimension) {
int measureSpec;
switch (rootDimension) {
case ViewGroup.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT:
// Window can't resize. Force root view to be windowSize.
//默认DecorView的measureSpec是:size=windowSize mode是EXACTLY
measureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(windowSize, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
break;
case ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT:
// Window can resize. Set max size for root view.
measureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(windowSize, MeasureSpec.AT_MOST);
break;
default:
// Window wants to be an exact size. Force root view to be that size.
measureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(rootDimension,MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
break;
}
return measureSpec;
}
private void performMeasure(int childWidthMeasureSpec, int childHeightMeasureSpec) {
if (mView == null) {
return;
}
...
//mView即为DecorView
mView.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
...
}
从上面的代码得知:DecorView的measureSpec是size=windowSize比如(1920px 1080px) mode=EXACTLY, 然后由于Activity根FramLayout的width和height都是match_parent, 所以 FrameLayout measureSpec和DecorView的measureSpec是一致的, 接下来我们看FrameLayout的onMeasure源码:
//FrameLayout.java
//这里的widthMeasureSpec的size 手机屏幕宽度 mode是EXACTLY
//heightMeasureSpec的size是手机屏幕高度-状态栏高度 mode是EXACTLY
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
...
int maxHeight = 0;
int maxWidth = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
final View child = getChildAt(i);
if (mMeasureAllChildren || child.getVisibility() != GONE) {
//1
measureChildWithMargins(child, widthMeasureSpec, 0, heightMeasureSpec, 0);
final LayoutParams lp = (LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
maxWidth = Math.max(maxWidth,
child.getMeasuredWidth() + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin);
maxHeight = Math.max(maxHeight,
child.getMeasuredHeight() + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin);
...
}
}
...
//2
setMeasuredDimension(resolveSizeAndState(maxWidth, widthMeasureSpec, childState),
resolveSizeAndState(maxHeight, heightMeasureSpec,
childState << MEASURED_HEIGHT_STATE_SHIFT));
}
//ViewGroup.java
//3
protected void measureChildWithMargins(View child, int parentWidthMeasureSpec,
int widthUsed, int parentHeightMeasureSpec, int heightUsed) {
final MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
//4
final int childWidthMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentWidthMeasureSpec,
mPaddingLeft + mPaddingRight + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin
+ widthUsed, lp.width);
//5
final int childHeightMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentHeightMeasureSpec,
mPaddingTop + mPaddingBottom + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin
+ heightUsed, lp.height);
//6
child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
}
//7
public static int getChildMeasureSpec(int spec, int padding, int childDimension) {
//measureSpec的mode
int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(spec);
//measureSpec的size
int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(spec);
int size = Math.max(0, specSize - padding);
int resultSize = 0;
int resultMode = 0;
switch (specMode) {
case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:
if (childDimension >= 0) {//child的宽高值是固定值比如40dp
resultSize = childDimension;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
//child的lp.width是match_parent
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
//child的lp.width是wrap_content
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
}
break;
case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:
if (childDimension >= 0) {//child的宽高值是固定值比如40dp
resultSize = childDimension;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
//此时 child的match_parent 和 wrap_content 返回的MeasureSpec 一模一样
//mode都是AT_MOST
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
}
break;
case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED:
if (childDimension >= 0) {
//child的宽高值是固定值比如40dp
resultSize = childDimension;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
//此时 child的match_parent 和 wrap_content 返回的MeasureSpec 一模一样
//mode都是AT_MOST
resultSize = View.sUseZeroUnspecifiedMeasureSpec ? 0 : size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
resultSize = View.sUseZeroUnspecifiedMeasureSpec ? 0 : size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED;
}
break;
}
return MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(resultSize, resultMode);
}
//View.java
//8
public static int resolveSizeAndState(int size, int measureSpec, int childMeasuredState){
final int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec);
final int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec);
final int result;
switch (specMode) {
case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST://对应了wrap_content
//如果子view的size大于measureSpec的size返回specSize 不能大于父类传递进来的specSize
if (specSize < size) {
result = specSize | MEASURED_STATE_TOO_SMALL;
} else {//如果子view的size小于specSize 则返回子view的size
result = size;
}
break;
//EXACTLY模式(一般对应固定值或match_parent) 返回measureSpec的specSize
case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:
result = specSize;
break;
case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED://未设置特定测量模式 返回传入的size
default:
result = size;
}
return result | (childMeasuredState & MEASURED_STATE_MASK);
}
上面的源代码有点多,不着急,我们一个一个来介绍:
-
注释①处我们遍历child,挨个调用方法③measureChildWithMargins()
-
方法③measureChildWithMargins内部 注释④⑤都是调用了方法⑦getChildMeasureSpec
-
方法⑦getChildMeasureSpec比较核心我们详细介绍:
- 首先我们看方法⑦getChildMeasureSpec的参数是measureSpec(即刚才我们提到的decorView的measureSpec)、padding、childDimension(child在xml里面写的width和height), childDimension的取值有三个:固定值xxdp match_parent wrap_content
- 方法⑦getChildMeasureSpec返回了child的measureSpec其计算规则如下图:
![]()
-
注释⑥处调用了child.measure 走入了我们前面讲的view的测量流程, 到这文章前面我们提到三种情景就可以解释通了:
- view的宽高为match_parent或者wrap_content, FrameLayout计算得出子view的MeasureSpec(size=specSize mode=EXATLY或者AT_MOST),但是走到子View里面的测量流程的时候对于EXACTLY和AT_MOST一视同仁取得都是specSize。
- view的值为固定值时,FrameLayout计算得出子view的MeasureSpec(size=childDimension mode=EXATLY),注意这里measureSpec的specSize是childDimension
-
所有子view测量完后,我们计算并保存了maxWidth 和maxHeight, 然后就到了注释②处的setMeasuredDimension方法,然后通过注释⑧resolveSizeAndState方法及参数measureSpec和childMaxSize计算出了FramLayout的width和height,FramLayout测量也就算结束了。注释⑧resolveSizeAndState方法里面的注释我已经标注的很明白了,就不详细介绍了
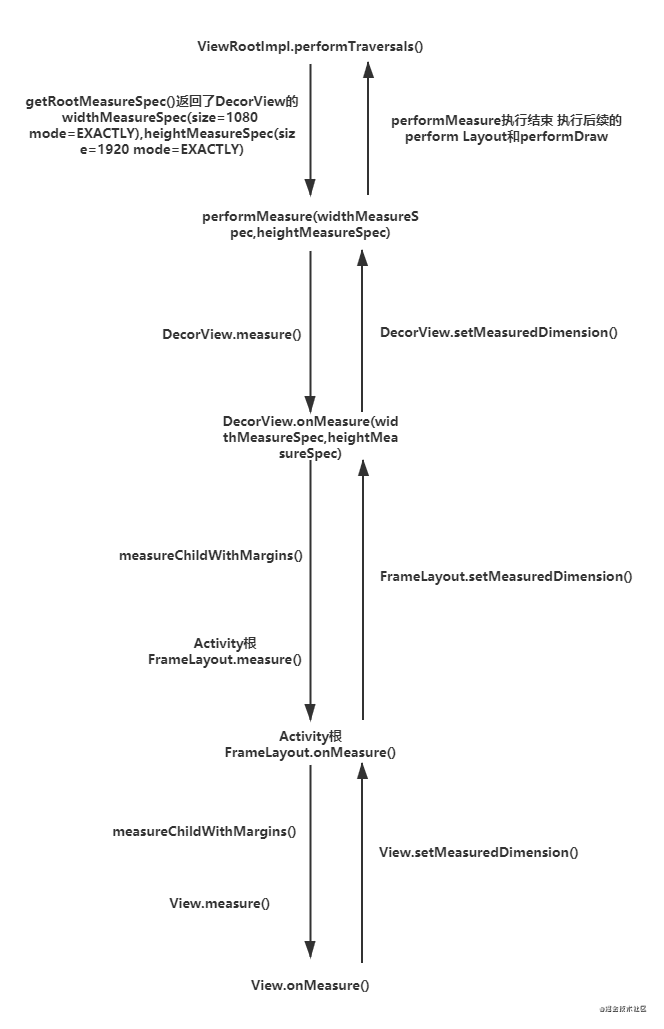
通过上面的流程分析,我们基本把测量流程梳理了一遍,其流程图如下:
总结
-
如果View/ViewGroup并没有重写onMeasure的话,match_parent 和wrap_content表现出来的效果是一样的,都是取得parentMeasureSpec的size ,所以如果想表现成wrap_content的效果,我们需要重写onMeasure方法来定义自己的测量规则,比如:①如果TextView的wrap_content需要生效的话我们可以在AT_MOST模式下,将TextView的宽高设置成文字的矩形大小②如果ImageView的wrap_content需要生效的话我们可以在AT_MOST模式下,将Image的宽高设置成图片的原始大小
-
常规测量模式下,我们的子view是不可能比父View还大,这个时候我们会产生一个疑问:如果我们希望子view/ViewGroup可以超出父view该如何做,答案是UNSPECIFIED,推荐阅读类是NestedScrollView
-
setMeasuredDimension方法是一个view测量的终点方法,其赋值了mMeasureWidth和mMeasureHeight
-
自定义ViewGroup并继承自ViewGroup的时候,如果不重写onMeasure就会导致子view根本没测量,一般我们可以通过调用measureChildren()来测量子view或者自己定义测量规则
推荐阅读
架构师学习笔记
耗时268天,7大模块、2983页58万字,Android开发核心知识笔记!
Java基础、计算机网络、系统
史上最全!押题率90%的 Android 中高级工程师面试复习大纲及真题答案整理(上篇)
Android基础夯实99题,点这里
史上最全!押题率90%的 Android 中高级工程师面试复习大纲及真题答案整理(中篇)
Android高级面试题(上)
史上最全!押题率90%的 Android 中高级工程师面试复习大纲及真题答案整理(下篇)
Android高级面试题(下)
史上最全!押题率90%的 Android 中高级工程师面试复习大纲及真题答案整理(终章)



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号