一 对象封装
package main
import "fmt"
type Phone0 struct {
number string
color string
}
func (p Phone0) Dial() {
fmt.Printf("Dail from %s ; color is %s\n", p.number, p.color)
}
func (p *Phone0) Init(number string, color string) {
p.number = number
p.color = color
}
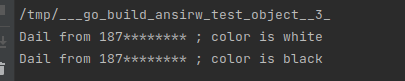
func main(){
p := Phone0{}
p.Init("187********", "white")
p.Dial()
p.color = "black"
p.Dial()
}
二 继承
package main
import "fmt"
type Phone1 struct {
number string
}
func (p *Phone1) Init(number string) {
p.number = number
}
func (p Phone1) Dial() {
fmt.Printf("Dail from %s \n", p.number)
}
type Xiaomi struct {
Phone1
dtype string
}
func (x *Xiaomi) Init(number string, dtype string) {
x.Phone1.Init(number)
x.dtype = dtype
}
func (x Xiaomi) DialXiaomi() {
fmt.Printf("Dail from %s, type is %s \n", x.number, x.dtype)
}
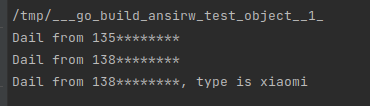
func main() {
p := Phone1{}
p.Init("135********")
p.Dial()
e := Xiaomi{}
e.Init("138********", "xiaomi")
e.Dial()
e.DialXiaomi()
}
三 多态
package main
import "fmt"
type PhoneIf interface {
Dial()
Feature()
}
type Apple struct {
apple_feature string
}
func (apple *Apple) Dial() {
fmt.Println("Dial from Iphone")
}
func (apple *Apple) Feature() {
fmt.Println("Iphone feature")
}
type Huawei struct {
huawei_feature string
}
func (huawei *Huawei) Dial() {
fmt.Println("Dial from Huawei")
}
func (huawei *Huawei) Feature() {
fmt.Println("Huawei feature")
}
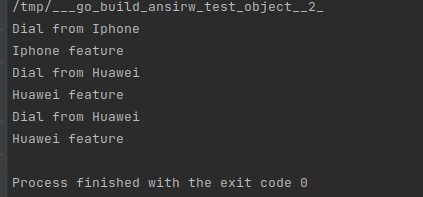
func main() {
var phone PhoneIf
phone = &Apple{}
phone.Dial()
phone.Feature()
phone = &Huawei{}
phone.Dial()
phone.Feature()
phone2 := &Huawei{}
phone2.Dial()
phone2.Feature()
}
四 补充说明
- go中的public就是名称首字母大小写,大写为public,假如一中的 p.color = "black" 用在不同的包将出错, 此时需要将coler改成Color
- 二和三中的 func内 struct和 interface 用* 和不用* 都行, 一般要操作成员变量的时候,用* 更妥,更有效读取和变更成员变量的值







