第64课.c++中的异常处理(上)
1.c++异常处理
c++内置了异常处理的语法:try...catch...
try语句处理正常代码逻辑
catch语句处理异常情况
try语句中的异常由对应的catch语句处理(注意一个try语句块只能捕获一个异常给catch)
try
{
double r = divider(1, 0); // divider产生异常时,会抛出异常到当前这个位置。
// try语句块对异常进行捕捉,捕捉到异常时,会把异常抛给catch语句块执行
}
catch(...)
{
cout << "Divided by zero..." << endl;
}
c++通过throw语句抛出异常信息
double divide(double a, double b)
{
const double delta = 0.0000000000000001;
double ret = 0;
if( !((-delta < b) && (b > delta )) )
{
return ret = a / b;
}
else
{
throw 0; // 产生除0异常, 并把这个异常抛出
}
return ret;
}
2.c++异常处理分析
throw抛出的异常必须被catch处理。
a.当前函数能够处理异常,程序继续往下执行。
b.当前函数无法处理异常,则函数停止执行,并返回。
未被处理的异常会顺着函数调用栈传播,直到被处理为止,否则程序将停止执行

eg:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
double divide(double a, double b)
{
const double delta = 0.000000000000001;
double ret = 0;
if( !((-delta < b) && (delta > b)) )
{
ret = a / b;
}
{
throw 0;
}
return ret;
}
int main()
{
try
{
double r = divide(1, 0);
cout << "r = " << r << endl;
}
catch(...)
{
cout << "Divide by zero..." << endl;
}
return 0;
}
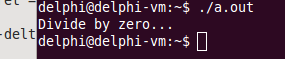
注意:这里执行完catch后就继续往下执行了,不会返回之前throw的地方,因为之前的程序已经被终止了
3.异常处理的匹配规则
a.同一个try语句可以跟上多个catch语句
b.catch语句可以定义具体处理的异常类型
c.不同类型的异常有不同的catch语句负责处理
d.try语句中可以抛出任何类型的异常
e.catch(...)用于处理所有类型的异常
f.任何异常都只能被捕获(catch)一次
异常抛出后,自上而下、严格匹配(不能进行任何类型转换)每个catch语句处理的类型
eg:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
void Demo1()
{
try
{
throw 'c';
throw 1;
}
catch(char c)
{
cout << "catch(char c)" << endl;
}
catch(int i)
{
cout << "catch(int i)" << endl;
}
catch(short di)
{
cout << "catch(short di)" << endl;
}
catch(double dwi)
{
cout << "catch(double dwi)" << endl;
}
catch(...)
{
cout << "catch(...)" << endl;
}
}
void Demo2()
{
throw "D.T.Software"; // 注意这里类型为const char*,而不是string
}
void Demo3()
{
throw string("D.T.Software"); // 注意这里类型为string
}
int main()
{
Demo1();
try
{
Demo2();
}
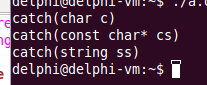
catch(char c)
{
cout << "catch(char c)" << endl;
}
catch(char* s)
{
cout << "catch(char* s)" << endl;
}
catch(const char* cs)
{
cout << "catch(const char* cs)" << endl;
}
catch(string ss)
{
cout << "catch(string ss)" << endl;
}
try
{
Demo3();
}
catch(char c)
{
cout << "catch(char c)" << endl;
}
catch(char* s)
{
cout << "catch(char* s)" << endl;
}
catch(const char* cs)
{
cout << "catch(const char* cs)" << endl;
}
catch(string ss)
{
cout << "catch(string ss)" << endl;
}
return 0;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号