Spring ---helloworld
1:创建一个HelloWorld的类
1 package com.spring.helloworld; 2 3 public class HelloWorld { 4 private String name; 5 6 public void setName(String name) { 7 System.out.println("helloWorld的set方法"); 8 this.name = name; 9 } 10 public void hello(){ 11 System.out.println("helloworld:"+name); 12 } 13 public HelloWorld() { 14 System.out.println("helloWorld的构造器"); 15 } 16 }
2:正常使用 HelloWorld类:
1 HelloWorld helloWorld=new HelloWorld(); 2 helloWorld.setName("beijing"); 3 helloWorld.hello();
3:使用Spring容器IOC:
把2中的创建对象。传入属性都交给Spring来管理
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <bean id="helloWorld" class="com.spring.helloworld.HelloWorld"> <property name="name" value="aa"></property> </bean> </beans>
id:就相当于是HelloWorld这个类的引用。如果不写。访问的时候直接写类的全类名也是可以的。
4:使用IOC容器
//1:创建IOC容器
//ApplicationContext是一个接口。代表IOC容器
//ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 是ApplicationContext接口下ConfigurableApplicationContext接口下的一个实现类。用来加载配置文件。
ApplicationContext act=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); //2:从IOC中获得Bean实例 有id HelloWorld helloWorld=(HelloWorld) act.getBean("helloWorld");
//3:没有id
HelloWorld helloWorld2=(HelloWorld) act.getBean("com.spring.helloworld.HelloWorld");
helloWorld.hello();
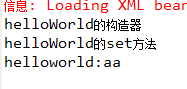
说明容器创建的时候先去调用构造器。然后调用set方法。
一:构造器注入的方式:
1 package com.spring.helloworld; 2 3 public class Student { 4 private String name; 5 private String age; 6 private Integer sal; 7 public Student(String name, String age, Integer sal) { 8 super(); 9 this.name = name; 10 this.age = age; 11 this.sal = sal; 12 } 13 @Override 14 public String toString() { 15 return "Student [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + ", sal=" + sal + "]"; 16 } 17 18 }
写配置文件:
<bean id="student" class="com.spring.helloworld.Student">
<constructor-arg value="lu" type="java.lang.String"/>
<constructor-arg value="19" type="java.lang.String"/>
<constructor-arg value="99" type="java.lang.Integer"/>
</bean>
后面加上type 就是为了去和构造器中的字段一一对应。
然后从IOC容器中得到创建的Student对象。
Student student=(Student) act.getBean("student");
System.out.println(student);
****特殊字符: 用<![CDATA[ ]]>
<constructor-arg type="java.lang.String">
<value><![CDATA[<19>]]></value>
</constructor-arg>
二:set注入
package com.spring.helloworld; public class Car { private String company; private String brand; private int maxSpeed; public void setCompany(String company) { this.company = company; } public void setBrand(String brand) { this.brand = brand; } public void setMaxSpeed(int maxSpeed) { this.maxSpeed = maxSpeed; } @Override public String toString() { return "Car [company=" + company + ", brand=" + brand + ", maxSpeed=" + maxSpeed + "]"; } }
XML文件配置:
1 <bean id="car" class="com.spring.helloworld.Car"> 2 <property name="company" value="Audi"/> 3 <property name="brand" value="shanghai"/> 4 <property name="maxSpeed" value="420"/> 5 </bean>
三:构造器注入。Car对象作为Student的一个属性。如何注入?
package com.spring.helloworld; public class Student { private String name; private String age; private Car car; public Student(String name, String age, Car car) { super(); this.name = name; this.age = age; this.car = car; } @Override public String toString() { return "Student [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + ", car=" + car + "]"; } }
XML配置文件:
1):ref元素指向一个Car的id。
<bean id="car" class="com.spring.helloworld.Car"> <property name="company" value="Audi"/> <property name="brand" value="shanghai"/> <property name="maxSpeed" value="420"/> </bean> <bean id="student" class="com.spring.helloworld.Student"> <constructor-arg> <value>lu</value> </constructor-arg> <constructor-arg> <value>19</value> </constructor-arg> <constructor-arg ref="car"/> </bean>
2):内部Bean。
<bean id="student" class="com.spring.helloworld.Student"> <constructor-arg> <value>lu</value> </constructor-arg> <constructor-arg> <value>19</value> </constructor-arg> <constructor-arg> <bean class="com.spring.helloworld.Car"> <property name="company" value="Audi"/> <property name="brand" value="shanghai"/> <property name="maxSpeed" value="420"/> </bean> </constructor-arg> </bean>
四:list集合set注入
1 <bean id="car" class="com.spring.helloworld.Car"> 2 <property name="company" value="Audi"></property> 3 <property name="brand" value="shanghai"></property> 4 <property name="maxSpeed" value="420"></property> 5 </bean> 6 <bean id="car2" class="com.spring.helloworld.Car"> 7 <property name="company" value="Audi2"></property> 8 <property name="brand" value="shanghai"></property> 9 <property name="maxSpeed" value="430"></property> 10 </bean> 11 <bean id="car3" class="com.spring.helloworld.Car"> 12 <property name="company" value="Audi3"></property> 13 <property name="brand" value="shanghai"></property> 14 <property name="maxSpeed" value="440"></property> 15 </bean> 16 <bean id="student" class="com.spring.helloworld.Student"> 17 <constructor-arg> 18 <value>lu</value> 19 </constructor-arg> 20 <constructor-arg> 21 <value>19</value> 22 </constructor-arg> 23 <property name="cars"> 24 <list> 25 <ref bean="car"/> 26 <ref bean="car2"/> 27 <ref bean="car3"/> 28 </list> 29 </property> 30 </bean>
五:Map集合
set注入:
private Map<String,Car> cars; public void setCars(Map<String, Car> cars) { this.cars = cars; }
<property name="cars">
<map>
<entry key="AA" value-ref="car"></entry>
<entry key="BB" value-ref="car2"></entry>
</map>
</property>
构造器注入:
<constructor-arg>
<map>
<entry key="AA" value-ref="car"></entry>
<entry key="BB" value-ref="car2"></entry>
</map>
</constructor-arg>
六:使用p:命名空间 只能是SET注入(这种方法不能是构造器注入)
1 <bean id="car" class="com.spring.helloworld.Car" p:company="Audi" p:brand="shanghai" p:maxSpeed="450"></bean>
car作为Student的一个属性。
<bean id="student" class="com.spring.helloworld.Student" p:name="lu" p:age="19" p:cars-ref="car" />
p:cars-ref="car" 跟的是对应的car的id中的值
使用p标签的时候先要在配置文件中加上要使用的标签
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
七:自动装配
<bean id="cars" class="com.spring.helloworld.Car" p:company="Audi" p:brand="shanghai" p:maxSpeed="450"></bean>
<bean id="student" class="com.spring.helloworld.Student"
p:name="lu" p:age="19" autowire="byName"
/>
Car中的id对应的是Student中的属性名。
<bean id="a" class="com.spring.helloworld.Car" p:company="Audi" p:brand="shanghai" p:maxSpeed="450"></bean> <bean id="student" class="com.spring.helloworld.Student" p:name="lu" p:age="19" autowire="byType" />
byType:根据bean的类型和当前bean的属性的类型进行自动装配。若IOC容器中有1个以上的类型匹配的bean,则抛异常
八:bean的作用域
1:scope="singleton"
<bean id="car" class="com.spring.helloworld.Car" p:company="Audi" p:brand="shanghai" p:maxSpeed="450" />
默认是单例的。
Car car=(Car) act.getBean("car");
Car car2=(Car) act.getBean("car");
System.out.println(car==car2);
public Car() { System.out.println("构造器"); }

说明car和car2是同一个对象。在创建IOC容器的时候就已经创建bean了。
2:scope="prototype"
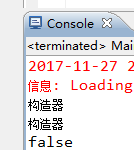
在创建IOC容器的时候没有创建。每请求一次。创建一个。car和car2不是同一个对象。protorype:原型的。每次请求的都是新的bean。
九:导入外部资源文件
jdbc.user=luwei jdbc.password=123456 jdbc.driverClass=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver jdbc.jdbcUrl=jdbc:mysql:///luwei jdbc.initPoolSize=5 jdbc.maxPoolSize=10
<!-- 导入外部的资源文件 -->
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:db.properties"/>
<!-- 配置数据源 -->
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource">
<property name="user" value="${jdbc.user}"></property>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"></property>
<property name="driverClass" value="${jdbc.driverClass}"></property>
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="${jdbc.jdbcUrl}"></property>
<property name="initialPoolSize" value="${jdbc.initPoolSize}"></property>
<property name="maxPoolSize" value="${jdbc.maxPoolSize}"></property>
</bean>




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号