struts2---访问WEB
一:在Action中,可以通过以下方式访问WEB的HttpSession,HttpServletRequest,HttpServletResponse等资源
与Servlet API解耦的访问方式
通过 import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext;
通过实现XxxAware接口;
特点:只能访问有限的servlet API对象。有限的方法(读取请求参数,读写域对象的属性,使session失效)
在主页面中调用action到struts.xml文件中然后找到Action类。在Action类中处理完后到struts.xml,然后找到相对性的jsp页面。展示信息
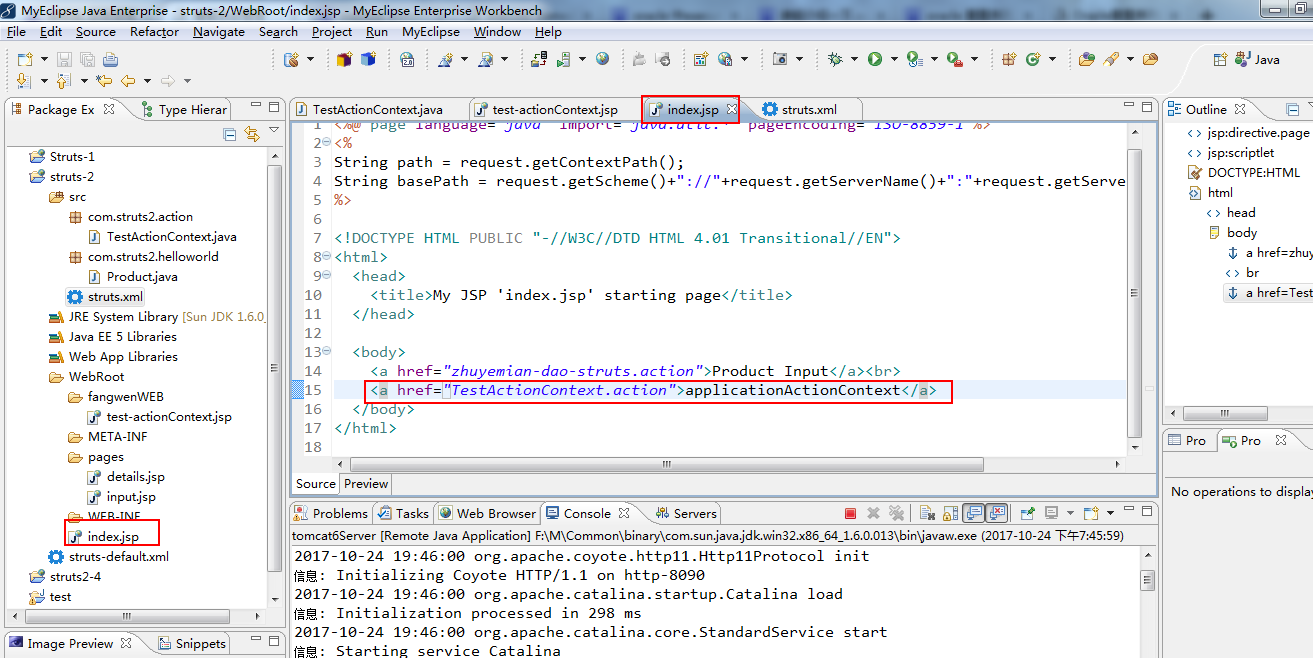
在struts.xml中找到Java类。
package com.struts2.action;
import java.util.Map;
import org.apache.struts2.dispatcher.SessionMap;
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext;
public class TestActionContext {
public String execute(){
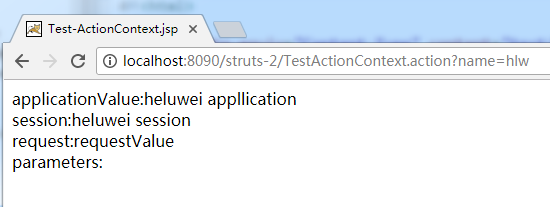
//一:application
//1:获取ActionContext对象。 ActionContext是Action的上下文对象。可以从中获取到当前Action需要的一切信息。
ActionContext actionContext=ActionContext.getContext();
//2:获取application对应的MAP。
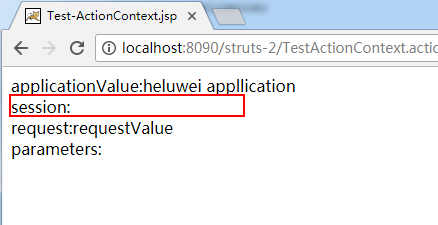
Map<String,Object> applicationMap =actionContext.getApplication();
applicationMap.put("applicationMapKey", "heluwei appllication");
//二:session
Map<String,Object> sessionMap=actionContext.getSession();
sessionMap.put("sessionKey", "heluwei session");
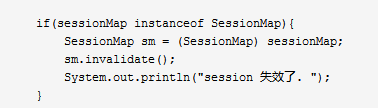
if(sessionMap instanceof SessionMap){
SessionMap sm = (SessionMap) sessionMap;
sm.invalidate();
System.out.println("session 失效了. ");
}
//3. request*
//ActionContext 中并没有提供 getRequest 方法来获取 request 对应的 Map
//需要手工调用 get() 方法, 传入 request 字符串来获取.
Map<String, Object> requestMap = (Map<String, Object>) actionContext.get("request");
requestMap.put("requestKey", "requestValue");
//4. 获取请求参数对应的 Map, 并获取指定的参数值.
//键: 请求参数的名字, 值: 请求参数的值对应的字符串数组
//注意: 1. getParameters 的返回值为在 Map<String, Object>, 而不是 Map<String, String[]>
// 2. parameters 这个 Map 只能读, 不能写入数据, 如果写入, 但不出错, 但也不起作用!
Map<String, Object> parameters = actionContext.getParameters();
System.out.println(((String[])parameters.get("name"))[0]);
parameters.put("age", 100);
return "success";
}
}
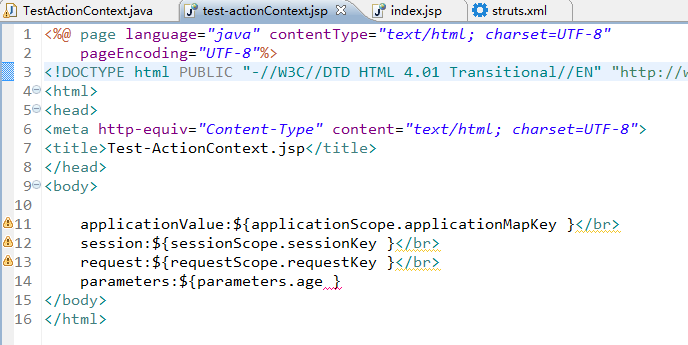
在页面上显示信息:
二:实现XxxAware接口
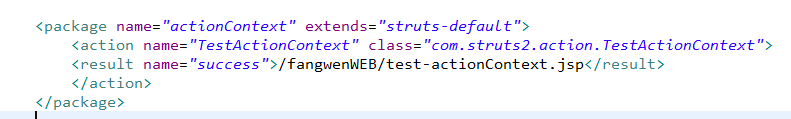
<package name="actionContext" extends="struts-default"> <action name="TestActionContext" class="com.struts2.action.TestActionContext"> <result name="success">/fangwenWEB/test-actionContext.jsp</result> </action> <action name="TestAware" class="com.struts2.action.TestAware"> <result name="success">/fangwenWEB/test-Aware.jsp</result> </action> </package>
package com.struts2.action; import java.util.Map; import org.apache.struts2.interceptor.ApplicationAware; public class TestAware implements ApplicationAware{ public String execute() { application.put("applicationkey2", "Aware applicationValue"); return "success"; } private Map<String,Object> application; public void setApplication(Map<String, Object> application) { this.application=application; } }
application Map注入到set方法中。然后定义一个application成员变量。

》session对应的Map实际上是SessionMap类型。强转后调用invalidate()方法。可使session失效。
二:耦合的方式
就是多了一个Servlet。
》调用 org.apache.struts2.ServletActionContext;
package com.struts2.action; import javax.servlet.ServletContext; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpSession; import org.apache.struts2.ServletActionContext; public class TestServletActionContext { public String execute(){ HttpServletRequest request=ServletActionContext.getRequest(); HttpSession session=request.getSession(); ServletContext context=ServletActionContext.getServletContext(); return "success"; } }
》实现ServletXxxAware接口
package com.struts2.action; import javax.servlet.ServletContext; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import org.apache.struts2.interceptor.ServletRequestAware; import org.apache.struts2.util.ServletContextAware; public class TestServletAware implements ServletRequestAware,ServletContextAware{ public String execute(){ return "success"; } private ServletContext context; public void setServletContext(ServletContext context) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub this.context=context; } public void setServletRequest(HttpServletRequest request) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub } }




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号