codeforces 572(Div2)A、B、C、D1、D2、E
Cdoeforces 572(Div2)A、B、C、D1、D2、E
传送门:https://codeforces.com/contest/1189
A.题意:
给你一串长为n的字符串,要求你将其切割为若干个good 的子串,一个子串如果其中0和1的个数不相等,那么这个子串是good子串,输出最少切割后的子串个数和切割后的结果
题解:
最多只用切1次,因为一个串中0和1的个数只有相等和不相等两种情况,如果串中0和1的个数不相等那么就不用切割,否则随便拿头或者拿尾即可
代码:
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <deque>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <cmath>
#include <ctime>
#include <bitset>
#include <cstdio>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<LL, LL> pLL;
typedef pair<LL, int> pLi;
typedef pair<int, LL> pil;;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
typedef unsigned long long uLL;
#define ls rt<<1
#define rs rt<<1|1
#define lson l,mid,rt<<1
#define rson mid+1,r,rt<<1|1
#define bug printf("*********\n")
#define FIN freopen("input.txt","r",stdin);
#define FON freopen("output.txt","w+",stdout);
#define IO ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0)
#define debug1(x) cout<<"["<<#x<<" "<<(x)<<"]\n"
#define debug2(x,y) cout<<"["<<#x<<" "<<(x)<<" "<<#y<<" "<<(y)<<"]\n"
#define debug3(x,y,z) cout<<"["<<#x<<" "<<(x)<<" "<<#y<<" "<<(y)<<" "<<#z<<" "<<z<<"]\n"
const double eps = 1e-8;
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
const int maxn = 3e5 + 5;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const LL INFLL = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f;
struct EDGE {
int v, nxt;
} edge[maxn << 1];
int head[maxn], tot;
void add_edge(int u, int v) {
edge[tot].v = v, edge[tot].nxt = head[u], head[u] = tot++;
}
int main() {
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
FIN
#endif
int n;
string str;
cin >> n >> str;
int cnt1 = 0, cnt0 = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if(str[i] == '0') {
cnt0++;
} else {
cnt1++;
}
}
if(cnt1 != cnt0) {
cout << 1 << endl;
cout << str << endl;
} else {
cout << 2 << endl;
cout << str.substr(0, n - 1) << " ";
cout << str.substr(n - 1, 1) << endl;
}
return 0;
}
B题意:
给你n个数,要求你将其排成一个数环,要求第i个数小于第i-1、第i+1个数之和,构造出来
题解:
排序后,形成一个环,我们贪心的构造一下,我们取max,sec,th三个最大的数,构成一个环,那么max是放在sec和th之间时,他们三个如果符合条件,那么形成的环里面,按排序顺序输出的时候,i-1项都为三项中的最大项,即一定满足条件
代码:
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <deque>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <cmath>
#include <ctime>
#include <bitset>
#include <cstdio>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<LL, LL> pLL;
typedef pair<LL, int> pLi;
typedef pair<int, LL> pil;;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
typedef unsigned long long uLL;
#define ls rt<<1
#define rs rt<<1|1
#define lson l,mid,rt<<1
#define rson mid+1,r,rt<<1|1
#define bug printf("*********\n")
#define FIN freopen("input.txt","r",stdin);
#define FON freopen("output.txt","w+",stdout);
#define IO ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0)
#define debug1(x) cout<<"["<<#x<<" "<<(x)<<"]\n"
#define debug2(x,y) cout<<"["<<#x<<" "<<(x)<<" "<<#y<<" "<<(y)<<"]\n"
#define debug3(x,y,z) cout<<"["<<#x<<" "<<(x)<<" "<<#y<<" "<<(y)<<" "<<#z<<" "<<z<<"]\n"
const double eps = 1e-8;
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
const int maxn = 3e5 + 5;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const LL INFLL = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f;
struct EDGE {
int v, nxt;
} edge[maxn << 1];
int head[maxn], tot;
void add_edge(int u, int v) {
edge[tot].v = v, edge[tot].nxt = head[u], head[u] = tot++;
}
int a[maxn];
int main() {
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
FIN
#endif
int n;
scanf("%d", &n);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
}
sort(a + 1, a + n + 1);
if(a[n - 1] + a[n - 2] <= a[n]) {
printf("NO\n");
} else {
printf("YES\n");
printf("%d %d %d ", a[n - 2], a[n], a[n - 1]);
for(int i = n - 3; i >= 1; i--) {
printf("%d%c", a[i], i == 1 ? '\n' : ' ');
}
}
return 0;
}
C题意:
现在有n个数字,n满足2的幂次,现在要你将每两项结合起来,形成新数列,再将新数列的每两项结合起来,形成一个新数列,依次递推,最后只剩下一项时停止,当结合时,然后两项之和大于10就模10,并且得到一个贡献,现在有m次询问,询问数列[l,r]区间的贡献是多少
题解:
因为是和超过10就有一个贡献,所以区间和有多少个10那么就有多少贡献。。。。
emmm思维题
代码:
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <deque>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <cmath>
#include <ctime>
#include <bitset>
#include <cstdio>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<LL, LL> pLL;
typedef pair<LL, int> pLi;
typedef pair<int, LL> pil;;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
typedef unsigned long long uLL;
#define ls rt<<1
#define rs rt<<1|1
#define lson l,mid,rt<<1
#define rson mid+1,r,rt<<1|1
#define bug printf("*********\n")
#define FIN freopen("input.txt","r",stdin);
#define FON freopen("output.txt","w+",stdout);
#define IO ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0)
#define debug1(x) cout<<"["<<#x<<" "<<(x)<<"]\n"
#define debug2(x,y) cout<<"["<<#x<<" "<<(x)<<" "<<#y<<" "<<(y)<<"]\n"
#define debug3(x,y,z) cout<<"["<<#x<<" "<<(x)<<" "<<#y<<" "<<(y)<<" "<<#z<<" "<<z<<"]\n"
const double eps = 1e-8;
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
const int maxn = 3e5 + 5;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const LL INFLL = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f;
struct EDGE {
int v, nxt;
} edge[maxn << 1];
int head[maxn], tot;
void add_edge(int u, int v) {
edge[tot].v = v, edge[tot].nxt = head[u], head[u] = tot++;
}
int n;
int a[maxn];
int sum[maxn];
int main() {
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
FIN
#endif
scanf("%d", &n);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
sum[i] = sum[i - 1] + a[i];
}
int m;
scanf("%d", &m);
while(m--) {
int l, r;
scanf("%d%d", &l, &r);
printf("%d\n", (sum[r] - sum[l - 1]) / 10);
}
}
D1题意:
给你一颗树,边权任意,你每次可以选择任意两个叶子节点在路径上add一个任意的实数边权,问你是否可以形成边权的任意组合
题解:
拿这个图来举例
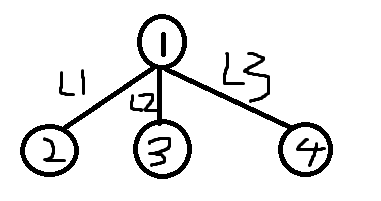
我要想得到(L1,L2,L3)(x,0,0)这种组合,那么我只需要在2,3的路径上添加x/2,2,4的路径上添加上x/2,3,4的路径上添加上-x/2,就可以得到这种组合了。
即如果图中有度数为1的点若干个,度大于等于3的点若干个,我就可以组合出任意组合来
即,如果我的点的度数为2,就会导致false
所以判断一下度数就好了
代码:
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <deque>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <cmath>
#include <ctime>
#include <bitset>
#include <cstdio>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<LL, LL> pLL;
typedef pair<LL, int> pLi;
typedef pair<int, LL> pil;;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
typedef unsigned long long uLL;
#define ls rt<<1
#define rs rt<<1|1
#define lson l,mid,rt<<1
#define rson mid+1,r,rt<<1|1
#define bug printf("*********\n")
#define FIN freopen("input.txt","r",stdin);
#define FON freopen("output.txt","w+",stdout);
#define IO ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0)
#define debug1(x) cout<<"["<<#x<<" "<<(x)<<"]\n"
#define debug2(x,y) cout<<"["<<#x<<" "<<(x)<<" "<<#y<<" "<<(y)<<"]\n"
#define debug3(x,y,z) cout<<"["<<#x<<" "<<(x)<<" "<<#y<<" "<<(y)<<" "<<#z<<" "<<z<<"]\n"
const double eps = 1e-8;
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
const int maxn = 3e5 + 5;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const LL INFLL = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f;
struct EDGE {
int v, nxt;
} edge[maxn << 1];
int head[maxn], tot;
void add_edge(int u, int v) {
edge[tot].v = v, edge[tot].nxt = head[u], head[u] = tot++;
}
int degree[maxn];
int main() {
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
FIN
#endif
memset(head, -1, sizeof(head));
tot = 0;
int n;
scanf("%d", &n);
for(int i = 1, u, v; i < n; i++) {
scanf("%d%d", &u, &v);
degree[u]++;
degree[v]++;
}
bool flag = true;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if(degree[i] == 2) {
flag = false;
}
}
if(flag) {
printf("YES\n");
} else {
printf("NO\n");
}
return 0;
}
D2题意:
和D1题意差不多
给你一颗树,但是现在给你了要求的边权,问你怎么样构造才能构造出这样的边权
题解:
要求的路径上有四种情况
1.两个端点u,v都是叶子节点
2.u在叶子节点,v不在
3.v在叶子节点,u不在
4.u,v都不在叶子结点
2和3情况一样
那么我们可以这样来讨论
对于第一种情况,改变u,v这两点上的路径边权即可
对于第二、三种情况,我们可以找出,一个非叶子节点v的两个叶子节点(因为是一颗完全二叉树,一定可以向下找出两个叶子节点,这个可以dfs一下实现),假设找到的两个叶子节点是点a和点b,那么我们可以u->a加上val/2
u->b加上val/2,最后a->b减去val/2即可
对于第四种情况同理,我们可以找到u的两个叶子节点a,b,v的两个叶子节点c,d,然后和刚才的方法一样,
a ->c加上val / 2,然后b -> d去加上val / 2,最后,a ->b减去val / 2,以及c -> d去减去val / 2即可。
代码:
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <deque>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <cmath>
#include <ctime>
#include <bitset>
#include <cstdio>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<LL, LL> pLL;
typedef pair<LL, int> pLi;
typedef pair<int, LL> pil;;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
typedef unsigned long long uLL;
#define ls rt<<1
#define rs rt<<1|1
#define lson l,mid,rt<<1
#define rson mid+1,r,rt<<1|1
#define bug printf("*********\n")
#define FIN freopen("input.txt","r",stdin);
#define FON freopen("output.txt","w+",stdout);
#define IO ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0)
#define debug1(x) cout<<"["<<#x<<" "<<(x)<<"]\n"
#define debug2(x,y) cout<<"["<<#x<<" "<<(x)<<" "<<#y<<" "<<(y)<<"]\n"
#define debug3(x,y,z) cout<<"["<<#x<<" "<<(x)<<" "<<#y<<" "<<(y)<<" "<<#z<<" "<<z<<"]\n"
const double eps = 1e-8;
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
const int maxn = 3e5 + 5;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const LL INFLL = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f;
struct EDGE {
int v, w, nxt;
} edge[maxn << 1];
int head[maxn], tot;
void add_edge(int u, int v, int w) {
edge[tot].v = v, edge[tot].w = w; edge[tot].nxt = head[u], head[u] = tot++;
}
int degree[maxn];
// strcut Path{
// int u, v, w;
// P() {};
// P(int _u, int _v, int _w) {
// u = _u, v = _v, w = _w;
// }
// } path[maxn];
pair<pair<int, int>, int> path[maxn];
inline int dfs(int u, int fa) {
if(degree[u] == 1) return u;
else {
for(int i = head[u], v; ~i; i = edge[i].nxt) {
v = edge[i].v;
if(v == fa) continue;
else return dfs(v, u);
}
}
return u;
}
vector<pair<pair<int, int>, int>> ans;
int main() {
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
FIN
#endif
memset(head, -1, sizeof(head));
tot = 0;
int n;
scanf("%d", &n);
for(int i = 1, u, v, w; i < n; i++) {
scanf("%d%d%d", &u, &v,&w);
add_edge(u, v, w);
add_edge(v, u, w);
degree[u]++;
degree[v]++;
path[i] = make_pair(make_pair(u, v), w);
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if(degree[i] == 2) {
printf("NO\n");
return 0;
}
}
printf("YES\n");
for(int i = 1, u, v; i < n; i++) {
tie (u, v) = path[i].first; //u、v就是path[i]的u、v
pair<int, int> UU = {-1, -1};
for(int j = head[u], tv; ~j; j = edge[j].nxt) {
tv = edge[j].v;
if(tv == v) continue;
int tmp = dfs(tv, u);
if(UU.first == -1) UU.first = tmp;
else if(UU.second == -1) {
UU.second = tmp;
break;
}
}
pair<int, int> VV = {-1, -1};
for(int j = head[v], tu; ~j; j = edge[j].nxt) {
tu = edge[j].v;
if(tu == u) continue;
int tmp = dfs(tu, v);
if(VV.first == -1) VV.first = tmp;
else if(VV.second == -1) {
VV.second = tmp;
break;
}
}
if(degree[u] == 1) UU = {u, u};
if(degree[v] == 1) VV = {v, v};
int real = path[i].second / 2;
ans.push_back(make_pair(make_pair(UU.first, VV.first), real));
ans.push_back(make_pair(make_pair(UU.second, VV.second), real));
if(UU.first != UU.second) ans.push_back(make_pair(make_pair(UU.first, UU.second), -real));
if(VV.first != VV.second) ans.push_back(make_pair(make_pair(VV.first, VV.second), -real));
}
printf("%d\n", (int)ans.size());
for(int i = 0; i < ans.size(); i++) printf("%d %d %d\n", ans[i].first.first, ans[i].first.second, ans[i].second);
return 0;
}
E题意:
给你n,p,k,要你求有多少对数,满足
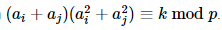
题解:
公式推导如下:
所以得到\(a_i^4-ka_i\%p\)的个数,组合一下即可
代码:
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <deque>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <cmath>
#include <ctime>
#include <bitset>
#include <cstdio>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<LL, LL> pLL;
typedef pair<LL, int> pLi;
typedef pair<int, LL> pil;;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
typedef unsigned long long uLL;
#define ls rt<<1
#define rs rt<<1|1
#define lson l,mid,rt<<1
#define rson mid+1,r,rt<<1|1
#define bug printf("*********\n")
#define FIN freopen("input.txt","r",stdin);
#define FON freopen("output.txt","w+",stdout);
#define IO ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0)
#define debug1(x) cout<<"["<<#x<<" "<<(x)<<"]\n"
#define debug2(x,y) cout<<"["<<#x<<" "<<(x)<<" "<<#y<<" "<<(y)<<"]\n"
#define debug3(x,y,z) cout<<"["<<#x<<" "<<(x)<<" "<<#y<<" "<<(y)<<" "<<#z<<" "<<z<<"]\n"
const double eps = 1e-8;
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
const int maxn = 3e5 + 5;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const LL INFLL = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f;
struct EDGE {
int v, nxt;
} edge[maxn << 1];
int head[maxn], tot;
void add_edge(int u, int v) {
edge[tot].v = v, edge[tot].nxt = head[u], head[u] = tot++;
}
map<int, int> mp;
LL a[maxn];
int main() {
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
FIN
#endif
int n, k, p;
scanf("%d%d%d", &n, &p, &k);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
scanf("%lld", &a[i]);
LL t = ((a[i] * a[i] % p * a[i] % p * a[i] % p) % p + p - (k * a[i]) % p + p) % p;
mp[t]++;
}
LL ans = 0;
map<int, int>::iterator it;
for(it = mp.begin(); it != mp.end(); it++) {
int val = it->first;
int sz = it->second;
// debug2(val, sz);
ans += sz * (sz - 1) / 2;
}
printf("%lld\n", ans);
return 0;
}


