pyecharts模块
pyecharts简介
官网链接:http://pyecharts.org/#/
pyecharts 是一个用于生成 Echarts 图表的类库。Echarts 是百度开源的一个数据可视化 JS 库。用 Echarts 生成的图可视化效果非常好,pyecharts 是为了与 Python 进行对接,方便在 Python 中直接使用数据生成图。
pyecharts 用于 web 绘图,有较多的绘图种类,且代码量比较少。它是基于一个 Echarts 的库噶欧辰的,而Echarts 是百度开源的一个可视化 JavaScript 库。
pyecharts 可以将图片保存为多种格式,但需要插件,否则只能保存为 html 格式。安装 pyecharts 可以用:
pip install pyecharts
安装图片保存插件可用:
pip install pyecharts-snapshot
以及:
npm install -g phantomjs-prebuilt
柱状图
from pyecharts.charts import Bar from pyecharts import options as opts bar = Bar() bar.add_xaxis(['毛衣','寸衫',"领带",'裤子',"风衣","高跟鞋","袜子"]) bar.add_yaxis('商家A',[114,55,27,101,125,27,105]) bar.add_yaxis('商家B',[57,134,101,22,69,90,129]) bar.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="某商场销售情况",subtitle='A和B公司'), toolbox_opts=opts.ToolboxOpts(is_show=True)) bar.set_series_opts(label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(position="top")) bar.render_notebook() # 在 notebook 中展示 # bar.render(r"D:\桌面\snapshot.html") 生成 html 文件

bar = Bar() bar.add_xaxis(['毛衣','寸衫',"领带",'裤子',"风衣","高跟鞋","袜子"]) bar.add_yaxis('商家A',[114,55,27,101,125,27,105]) bar.add_yaxis('商家B',[57,134,101,22,69,90,129]) bar.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="某商场销售情况",subtitle='A和B公司'), toolbox_opts=opts.ToolboxOpts(is_show=True)) bar.set_series_opts(label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(position="right")) bar.reversal_axis() bar.render_notebook()

饼状图
普通饼图
from pyecharts.charts import Pie from pyecharts import options as opts L1 = ["教授","副教授","讲师","助教","其他"] num = [20,30,10,12,8] c = Pie() c.add("",[list(z) for z in zip(L1,num)]) c.set_global_opts(title_opts = opts.TitleOpts(title="Pie-职称比例"), toolbox_opts = opts.ToolboxOpts(is_show=True)) c.set_series_opts(label_opts = opts.LabelOpts(formatter="{b}:{c}")) c.render_notebook()

环形图
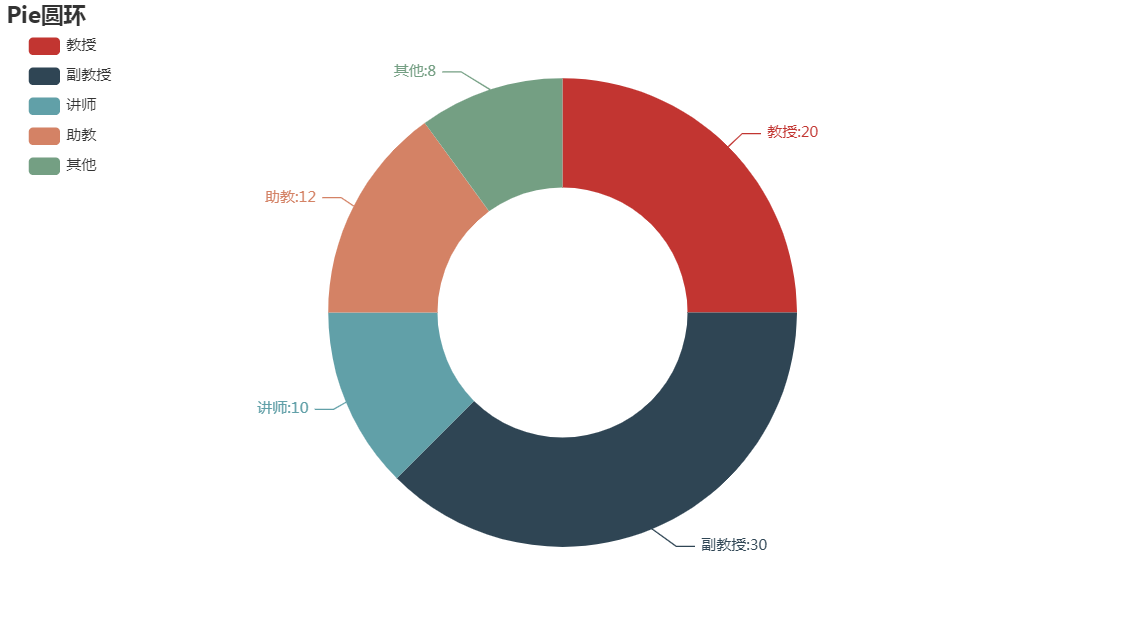
from pyecharts.charts import Pie from pyecharts import options as opts c = Pie() L1 = ["教授","副教授","讲师","助教","其他"] num = [20,30,10,12,8] c.add("",[list(z) for z in zip(L1,num)],radius=["40%","75%"]) c.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title='Pie圆环'), legend_opts=opts.LegendOpts(orient='vertical',pos_top='5%',pos_left="2%")) c.set_series_opts(label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(formatter="{b}:{c}")) c.render_notebook()

玫瑰图
from pyecharts.charts import Pie from pyecharts import options as opts c = Pie() L1 = ["教授","副教授","讲师","助教","其他"] num = [20,30,10,12,8] c.add("",[list(z) for z in zip(L1,num)],radius=["40%","75%"],rosetype="area") c.set_global_opts(title_opts = opts.TitleOpts(title="玫瑰图"),toolbox_opts = opts.ToolboxOpts(is_show=True), legend_opts=opts.LegendOpts(orient='vertical',pos_top="5%",pos_left="2%")) c.set_series_opts(label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(formatter='{b}:{c}')) c.render_notebook()

散点图
from pyecharts.charts import Scatter from pyecharts import options as opts s = Scatter() week = ['Mon','Thur','Wed','Tues','Fri','Sar','Sun'] s.add_xaxis(week) s.add_yaxis('商家A',[11,22,33,44,55,66,77]) s.add_yaxis('商家B',[0,10,20,30,40,50,60]) s.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title='散点图'), toolbox_opts = opts.ToolboxOpts(is_show=True), legend_opts = opts.LegendOpts(orient='vertical',pos_top='5%',pos_left="2%")) s.set_series_opts(label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(position='top')) s.render_notebook()

多图绘制
# 如果要在一张图中绘制两幅图,需要用到 网格: from pyecharts import options as opts from pyecharts.charts import Bar,Line,Grid A = ["小米","三星","华为","苹果","魅族","VIVO","OPPO"] CA = [100,125,87,90,78,98,118] B = ["草莓","芒果","葡萄","雪梨","西瓜","柠檬","车厘子"] CB = [78,95,120,102,88,108,98] bar = Bar() bar.add_xaxis(A) bar.add_yaxis("商家A",CA) bar.add_yaxis("商家B",CB) bar.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="多图绘制")) bar.render_notebook() line = Line() line.add_xaxis(B) line.add_yaxis("商家A",CA) line.add_yaxis("商家B",CB) line.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="2图",pos_top="48%"), legend_opts=opts.LegendOpts(pos_top="48%")) line.render_notebook() grid = Grid() grid.add(bar,grid_opts=opts.GridOpts(pos_bottom="60%")) grid.add(line,grid_opts=opts.GridOpts(pos_top="60%")) grid.render_notebook()

桑基图
一般用于分析原因,流量等: import pandas as pd from pyecharts import options as opts from pyecharts.charts import Sankey df = pd.DataFrame({'性别':['男','男','男','女','女','女'], "熬夜原因":['打游戏','看剧','加班','打游戏','看剧','加班'], '人数':[40,20,40,8,25,36]}) display(df) def transForm(df): nodes = [] links = [] for i in range(2): values = df.iloc[:,i].unique() for value in values: dic = {} dic['name']=value nodes.append(dic) for i in df.values: dic = {} dic['source'] = i[0] dic['target'] = i[1] dic['value'] = i[2] links.append(dic) return nodes,links nodes,links = transForm(df) print(nodes) print(links) sankey = Sankey() sankey.add("桑基图",nodes,links, linestyle_opt = opts.LineStyleOpts(opacity=0.2,curve=0.5,color="source"), label_opts = opts.LabelOpts(position='right')) sankey.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title='桑基图示例')) sankey.render_notebook()

词云
from pyecharts import options as opts from pyecharts.charts import Page,WordCloud from pyecharts.globals import SymbolType words = [ ("牛肉面",7800),("黄河",6181),("《读者》",4386),("水晶饺子",3055),("雨燕中学",4244),("碣石文化广场",2055), ("玄武山",8067),("华工",1868),("十一孔",3483),("宋瘄寮",1122),("石洲",980),("红白",1111),("Beautyleg",3000), ("Winnie",6666),("toxic_妲己",2222),("绯月樱",4444) ] c = WordCloud() c.add("",words,word_size_range=[10,70]) c.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="词云")) c.render_notebook()



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号