1. vue.js的快速入门使用
1.1 vue.js库的下载
vue.js是目前前端web开发最流行的工具库,由尤雨溪在2014年2月发布的。
另外几个常见的工具库:react.js /angular.js
官方网站:
中文:https://cn.vuejs.org/
英文:https://vuejs.org/
官方文档:https://cn.vuejs.org/v2/guide/
vue.js目前有1.x、2.x和3.x 版本,我们学习2.x版本的。
1.2 vue.js库的基本使用
在github下载:
在官网下载地址: https://cn.vuejs.org/v2/guide/installation.html
vue的引入类似于jQuery,开发中可以使用开发版本vue-x.x.x.js,产品上线要换成vue.min.js。
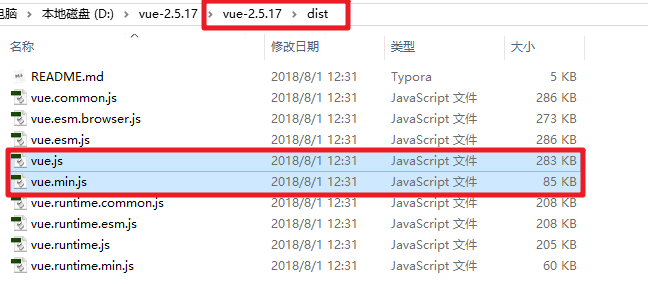
下图是github网站下载的vue.js目录
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
window.onload = function(){
// vue.js的代码开始于一个Vue对象。所以每次操作数据都要声明Vue对象开始。
var vm = new Vue({
el:'#app', // 设置当前vue对象要控制的标签范围。
data:{ // data是将要展示到HTML标签元素中的数据。
message: 'hello world!',
}
});
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<!-- {{ message }} 表示把vue对象里面data属性中的对应数据输出到页面中 -->
<!-- 在双标签中显示数据要通过{{ }}来完成 -->
<p>{{ message }}</p>
</div>
</body>
</html>
|
总结:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
1. vue的使用要从创建Vue对象开始
var vm = new Vue();
2. 创建vue对象的时候,需要传递参数,是json对象,json对象对象必须至少有两个属性成员
var vm = new Vue({
el:"#app",
data: {
数据变量:"变量值",
数据变量:"变量值",
数据变量:"变量值",
},
});
el:设置vue可以操作的html内容范围,值一般就是css的id选择器。
data: 保存vue.js中要显示到html页面的数据。
3. vue.js要控制器的内容外围,必须先通过id来设置。
<div id="app">
<h1>{{message}}</h1>
<p>{{message}}</p>
</div>
|
1.3 vue.js的M-V-VM思想
MVVM 是Model-View-ViewModel 的缩写,它是一种基于前端开发的架构模式。
Model 指代的就是vue对象的data属性里面的数据。这里的数据要显示到页面中。
View 指代的就是vue中数据要显示的HTML页面,在vue中,也称之为“视图模板” 。
ViewModel 指代的是vue.js中我们编写代码时的vm对象了,它是vue.js的核心,负责连接 View 和 Model,保证视图和数据的一致性,所以前面代码中,data里面的数据被显示中p标签中就是vm对象自动完成的。

编写代码,让我们更加清晰的了解MVVM:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
|
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="js/vue.min.js"></script>
<script>
window.onload = function(){
// 创建vm对象
var vm = new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
name:"大标题",
age:16,
},
})
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<!-- 在双标签中显示数据要通过{{ }}来完成 -->
<h1>{{name}}</h1>
<p>{{age}}</p>
<!-- 在表单输入框中显示数据要使用v-model来完成,模板语法的时候,我们会详细学习 -->
<input type="text" v-model="name">
</div>
</body>
</html>
|
在浏览器中可以在 console.log通过 vm对象可以直接访问el和data属性,甚至可以访问data里面的数据
1
2
3
4
|
console.log(vm.$el) # #box vm对象可以控制的范围
console.log(vm.$data); # vm对象要显示到页面中的数据
console.log(vm.$data.message); # 访问data里面的数据
console.log(vm.message);# 这个 message就是data里面声明的数据,也可以使用 vm.变量名显示其他数据,message只是举例.
|
总结:
1. 如果要输出data里面的数据作为普通标签的内容,需要使用{{ }}
用法:
vue对象的data属性:
data:{
name:"小明",
}
标签元素:
<h1>{{ name }}</h1>
2. 如果要输出data里面的数据作为表单元素的值,需要使用vue.js提供的元素属性v-model
用法:
vue对象的data属性:
data:{
name:"小明",
}
表单元素:
<input v-model="name">
使用v-model把data里面的数据显示到表单元素以后,一旦用户修改表单元素的值,则data里面对应数据的值也会随之发生改变,甚至,页面中凡是使用了这个数据都会发生变化。
1.4 显示数据
- 在双标签中显示数据要通过{{ }}来完成数据显示
- 在表单输入框中显示数据要使用v-model来完成数据显示
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="js/vue.min.js"></script>
<script>
window.onload = function(){
var vm = new Vue({
el:"#app",
data:{
str1: "hello",
num: 20,
url1: "http://www.baidu.com",
url2: "http://www.taobao.com"
}
})
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<p>{{ str1 }}</p>
<p>{{ str1.split("").reverse().join("") }}</p>
<p>num和num2中比较大的数是:{{ num>num2? num:num2 }}</p>
<input type="text" v-model="name">
</body>
</html>
|
双花括号仅用输出文本内容,如果要输出html代码,则不能使用这个.要使用v-html来输出. v-html必须在html标签里面作为属性写出来.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div class="app">
<h1>{{title}}</h1>
<h3>{{url1}}</h3>
{{img}}<br>
<span v-html="img"></span>
</div>
<script>
let vm = new Vue({
el:".app",
data:{
title:"我的vue",
url1:"我的收获地址",
img:'<img src="images/shendan.png">',
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
|
总结:
1. 可以在普通标签中使用{{ }} 或者 v-html 来输出data里面的数据
<h1>{{message}}</h1>
2. 可以在表单标签中使用v-model属性来输出data里面的数据,同时还可以修改data里面的数据
<input type="text" v-model="username">
在输出内容到普通标签的使用{{ }}
v-model或者v-html等vue提供的属性,或者 {{}} 都支持js代码。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
<h1>{{str1.split("").reverse().join("")}}</h1>
<!-- 3.2 支持js的运算符-->
<h1>{{num1+3}}</h1>
<!-- 3.3 js还有一种运算符,三元运算符,类似于python里面的三元表达式
三元运算符的语法:
判断条件 ? 条件为true : 条件为false的结果
python 三元表达式[三目运算符]的语法:
a if 条件 else b
-->
<h1>num1和num2之间进行比较,最大值:{{ num2>num1?num2:num1 }}</h1>
|
例子:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
|
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Vue的快速使用</title>
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<p>{{url}}</p>
<div>{{text}}</div>
<div v-html="text"></div>
<input v-model="url">
<div>num是{{num%2==0?'偶数':'奇数'}}</div>
<div>num的下一个数字:{{num-0+1}}</div>
<input type="text" v-model="num">
<div>{{message.split("").reverse().join("")}}</div>
<input type="text" v-model="message.split('').reverse().join('')">
</div>
<script>
var vm = new Vue({
el:"#app", // 设置vue对象控制的标签范围
data:{ // vue要操作的数据
url:"http://www.luffycity.com",
text:"<h1>大标题</h1>",
num: 100,
message:"abcdef",
},
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
|
2. 常用指令
指令 (Directives) 是带有“v-”前缀的特殊属性。每一个指令在vue中都有固定的作用。
在vue中,提供了很多指令,常用的有:v-if、v-model、v-for等等。
指令会在vm对象的data属性的数据发生变化时,会同时改变元素中的其控制的内容或属性。
因为vue的历史版本原因,所以有一部分指令都有两种写法:
vue1.x写法 vue2.x的写法
v-html ----> {{ 普通文本 }} # vue2.x 也支持v-html,输出html代码的内容
v-bind:属性名 ----> :属性
v-on:事件名 ----> @事件名
2.1 操作属性
格式:
<标签名 :标签属性="data属性"></标签名>
1
2
3
|
<p :title="str1">{{ str1 }}</p> <!-- 也可以使用v-html显示双标签的内容,{{ }} 是简写 -->
<a :href="url2">淘宝</a>
<a v-bind:href="url1">百度</a> <!-- v-bind是vue1.x版本的写法 -->
|
显示wifi密码效果:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="index">
<img :src="url" :alt="title"><br>
<input :type="type" placeholder="请输入wifi密码"> <button @click="type='text'">显示密码</button>
</div>
<script>
let vm = new Vue({
el:"#index",
data:{
url:"https://www.luffycity.com/static/img/head-logo.a7cedf3.svg",
title:"路飞学成",
type:"password"
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
|
2.2 事件绑定
有两种事件操作的写法,@事件名 和 v-on:事件名
1
2
|
<button v-on:click="num++">按钮</button> <!-- v-on 是vue1.x版本的写法 -->
<button @click="num+=5">按钮2</button>
|
总结:
1. 使用@事件名来进行事件的绑定
语法:
<h1 @click="num++">{{num}}</h1>
2. 绑定的事件的事件名,全部都是js的事件名:
@submit ---> onsubmit
@focus ---> onfocus
....
例如:完成商城购物车中的商品增加减少数量
步骤:
- 给vue对象添加操作数据的方法
- 在标签中使用指令调用操作数据的方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
|
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="box">
<button @click="++num">+</button>
<input type="text" v-model="num">
<button @click="sub">-</button>
</div>
<script>
let vm = new Vue({
el:"#box",
data:{
num:0,
},
methods:{
sub(){
if(this.num<=1){
this.num=0;
}else{
this.num--;
}
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
<!--#box>(button+input+button) tab键-->
|
2.3 操作样式
2.3.1 控制标签class类名
格式:
<h1 :class="值">元素</h1> 值可以是字符串、对象、对象名、数组
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
|
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
<style>
.box1{
color: red;
border: 1px solid #000;
}
.box2{
background-color: orange;
font-size: 32px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="box">
<!--- 添加class类名,值是一个对象
{
class类1:布尔值变量1,
class类2:布尔值变量2,
}
-->
<p :class="{box1:myclass1}">一个段落</p>
<p @click="myclass3=!myclass3" :class="{box1:myclass2,box2:myclass3}">一个段落</p>
</div>
<script>
let vm1=new Vue({
el:"#box",
data:{
myclass1:false, // 布尔值变量如果是false,则不会添加对象的属性名作为样式
myclass2:true, // 布尔值变量如果是true,则不会添加对象的属性名作为样式
myclass3:false,
},
})
</script>
<!-- 上面的代码可以:class的值保存到data里面的一个变量,然后使用该变量作为:class的值 -->
<style>
.box4{
background-color: red;
}
.box5{
color: green;
}
</style>
<div id="app">
<button @click="mycls.box4=!mycls.box4">改变背景</button>
<button @click="mycls.box5=!mycls.box5">改变字体颜色</button>
<p :class="mycls">第二个段落</p>
</div>
<script>
let vm2 = new Vue({
el:"#app",
data:{
mycls:{
box4:false,
box5:true
},
}
})
</script>
<!-- 批量给元素增加多个class样式类 -->
<style>
.box6{
background-color: red;
}
.box7{
color: green;
}
.box8{
border: 1px solid yellow;
}
</style>
<div id="app2">
<p :class="[mycls1,mycls2]">第三个段落</p>
</div>
<script>
let vm3 = new Vue({
el:"#app2",
data:{
mycls1:{
box6:true,
box7:true,
},
mycls2:{
box8:true,
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
|
代码执行效果:

总结:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
1. 给元素绑定class类名,最常用的就是第二种。
vue对象的data数据:
data:{
myObj:{
complete:true,
uncomplete:false,
}
}
html元素:
<div class="box" :class="myObj">2222</div>
最终浏览器效果:
<div class="box complete">2222</div>
|
2.3.2 控制标签style样式
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
|
格式1:值是json对象,对象写在元素的:style属性中
标签元素:
<div :style="{color: activeColor, fontSize: fontSize + 'px' }"></div>
data数据如下:
data: {
activeColor: 'red',
fontSize: 30
}
格式2:值是对象变量名,对象在data中进行声明
标签元素:
<div v-bind:style="styleObject"></div>
data数据如下:
data: {
styleObject: {
color: 'red',
fontSize: '13px'
}
}
格式3:值是数组
标签元素:
<div v-bind:style="[style1, style2]"></div>
data数据如下:
data: {
style1:{
color:"red"
},
style2:{
background:"yellow",
fontSize: "21px"
}
}
|
2.3.2 实例-vue版本选项卡
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
|
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
#card{
width: 500px;
height: 350px;
}
.title{
height:50px;
}
.title span{
width: 100px;
height: 50px;
background-color:#ccc;
display: inline-block;
line-height: 50px; /* 设置行和当前元素的高度相等,就可以让文本内容上下居中 */
text-align:center;
}
.content .list{
width: 500px;
height: 300px;
background-color: yellow;
display: none;
}
.content .active{
display: block;
}
.title .current{
background-color: yellow;
}
</style>
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="card">
<div class="title">
<span @click="num=0" :class="num==0?'current':''">国内新闻</span>
<span @click="num=1" :class="num==1?'current':''">国际新闻</span>
<span @click="num=2" :class="num==2?'current':''">银河新闻</span>
<!--<span>{{num}}</span>-->
</div>
<div class="content">
<div class="list" :class="num==0?'active':''">国内新闻列表</div>
<div class="list" :class="num==1?'active':''">国际新闻列表</div>
<div class="list" :class="num==2?'active':''">银河新闻列表</div>
</div>
</div>
<script>
// 思路:
// 当用户点击标题栏的按钮[span]时,显示对应索引下标的内容块[.list]
// 代码实现:
var card = new Vue({
el:"#card",
data:{
num:0,
},
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
|
代码运行效果:

2.4 条件渲染指令
vue中提供了两个指令可以用于判断是否要显示元素,分别是v-if和v-show。
2.4.1 v-if
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
标签元素:
<!-- vue对象最终会把条件的结果变成布尔值 -->
<h1 v-if="ok">Yes</h1>
data数据:
data:{
ok:false // true则是显示,false是隐藏
}
|
2.4.2 v-else
v-else指令来表示 v-if 的“else 块”,v-else 元素必须紧跟在带 v-if 或者 v-else-if 的元素的后面,否则它将不会被识别。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
标签元素:
<h1 v-if="ok">Yes</h1>
<h1 v-else>No</h1>
data数据:
data:{
ok:false // true则是显示,false是隐藏
}
|
2.4.3 v-else-if
可以出现多个v-else-if语句,但是v-else-if之前必须有一个v-if开头。后面可以跟着v-else,也可以没有。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
标签元素:
<h1 v-if="num==1">num的值为1</h1>
<h1 v-else-if="num==2">num的值为2</h1>
<h1 v-else>num的值是{{num}}</h1>
data数据:
data:{
num:2
}
|
2.4.4 v-show
用法和v-if大致一样,区别在于2点:
- v-show后面不能v-else或者v-else-if
- v-show隐藏元素时,使用的是display:none来隐藏的,而v-if是直接从HTML文档中移除元素[ DOM操作中的remove ]
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
标签元素:
<h1 v-show="ok">Hello!</h1>
data数据:
data:{
ok:false // true则是显示,false是隐藏
}
|
2.5 列表渲染指令
在vue中,可以通过v-for指令可以将一组数据渲染到页面中,数据可以是数组或者对象。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
|
数据是数组:
<ul>
<!--i是列表的每一个元素-->
<li v-for="book in book_list">{{book.title}}</li>
</ul>
<ul>
<!--i是列表的每一个元素,j是每个元素的下标-->
<li v-for="(book, index) in book_list">第{{ index+1}}本图书:{{book.title}}</li>
</ul>
<script>
var vm1 = new Vue({
el:"#app",
data:{
book_list:[
{"id":1,"title":"图书名称1","price":200},
{"id":2,"title":"图书名称2","price":200},
{"id":3,"title":"图书名称3","price":200},
{"id":4,"title":"图书名称4","price":200},
]
}
})
</script>
数据是对象:
<ul>
<!--i是每一个value值-->
<li v-for="value in book">{{value}}</li>
</ul>
<ul>
<!--i是每一个value值,j是每一个键名-->
<li v-for="attr, value in book">{{attr}}:{{value}}</li>
</ul>
<script>
var vm1 = new Vue({
el:"#app",
data:{
book: {
// "attr":"value"
"id":11,
"title":"图书名称1",
"price":200
},
},
})
</script>
|
练习:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
goods:[
{"name":"python入门","price":150},
{"name":"python进阶","price":100},
{"name":"python高级","price":75},
{"name":"python研究","price":60},
{"name":"python放弃","price":110},
]
# 把上面的数据采用table表格输出到页面,价格大于60的数据需要添加背景色橙色[orange]
|
3. Vue对象提供的属性功能
3.1 过滤器
过滤器,就是vue允许开发者自定义的文本格式化函数,可以使用在两个地方:输出内容和操作数据中。
定义过滤器的方式有两种。
3.1.1 使用Vue.filter()进行全局定义
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
Vue.filter("RMB1", function(v){
//就是来格式化(处理)v这个数据的
if(v==0){
return v
}
return v+"元"
})
|
3.1.2 在vue对象中通过filters属性来定义
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
var vm = new Vue({
el:"#app",
data:{},
filters:{
RMB2:function(value){
if(value==''){
return;
}else{
return '¥ '+value;
}
}
}
});
|
3.4 计算和侦听属性
3.4.1 计算属性
我们之前学习过字符串反转,如果直接把反转的代码写在元素中,则会使得其他同事在开发时时不易发现数据被调整了,所以vue提供了一个计算属性(computed),可以让我们把调整data数据的代码存在在该属性中。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
|
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="js/vue.min.js"></script>
<script>
window.onload = function(){
var vm = new Vue({
el:"#app",
data:{
str1: "abcdefgh"
},
computed:{ //计算属性:里面的函数都必须有返回值
strRevs: function(){
var ret = this.str1.split("").reverse().join("");
return ret
}
}
});
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<p>{{ str1 }}</p>
<p>{{ strRevs }}</p>
</div>
</body>
</html>
|
3.4.2 监听属性
侦听属性,可以帮助我们侦听data某个数据的变化,从而做相应的自定义操作。
侦听属性是一个对象,它的键是要监听的对象或者变量,值一般是函数,当侦听的data数据发生变化时,会自定执行的对应函数,这个函数在被调用时,vue会传入两个形参,第一个是变化前的数据值,第二个是变化后的数据值。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
|
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="js/vue.min.js"></script>
<script>
window.onload = function(){
var vm = new Vue({
el:"#app",
data:{
num:20
},
watch:{
num:function(newval,oldval){
//num发生变化的时候,要执行的代码
console.log("num已经发生了变化!");
}
}
})
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<p>{{ num }}</p>
<button @click="num++">按钮</button>
</div>
</body>
</html>
|
3.5 vue对象的生命周期
每个Vue对象在创建时都要经过一系列的初始化过程。在这个过程中Vue.js会自动运行一些叫做生命周期的的钩子函数,我们可以使用这些函数,在对象创建的不同阶段加上我们需要的代码,实现特定的功能。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
|
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="js/vue.min.js"></script>
<script>
window.onload = function(){
var vm = new Vue({
el:"#app",
data:{
num:0
},
beforeCreate:function(){
console.log("beforeCreate,vm对象尚未创建,num="+ this.num); //undefined
this.name=10; // 此时没有this对象呢,所以设置的name无效,被在创建对象的时候被覆盖为0
},
created:function(){
console.log("created,vm对象创建完成,设置好了要控制的元素范围,num="+this.num ); // 0
this.num = 20;
},
beforeMount:function(){
console.log( this.$el.innerHTML ); // <p>{{num}}</p>
console.log("beforeMount,vm对象尚未把data数据显示到页面中,num="+this.num ); // 20
this.num = 30;
},
mounted:function(){
console.log( this.$el.innerHTML ); // <p>30</p>
console.log("mounted,vm对象已经把data数据显示到页面中,num="+this.num); // 30
},
beforeUpdate:function(){
// this.$el 就是我们上面的el属性了,$el表示当前vue.js所控制的元素#app
console.log( this.$el.innerHTML ); // <p>30</p>
console.log("beforeUpdate,vm对象尚未把更新后的data数据显示到页面中,num="+this.num); // beforeUpdate----31
},
updated:function(){
console.log( this.$el.innerHTML ); // <p>31</p>
console.log("updated,vm对象已经把过呢更新后的data数据显示到页面中,num=" + this.num ); // updated----31
},
});
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<p>{{num}}</p>
<button @click="num++">按钮</button>
</div>
</body>
</html>
|
总结:
在vue使用的过程中,如果要初始化操作,把初始化操作的代码放在 mounted 中执行。
mounted阶段就是在vm对象已经把data数据实现到页面以后。一般页面初始化使用。例如,用户访问页面加载成功以后,就要执行的ajax请求。
另一个就是created,这个阶段就是在 vue对象创建以后,把ajax请求后端数据的代码放进 created
3.2 阻止事件冒泡和刷新页面
使用.stop和.prevent
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
|
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
.box1{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background: #ccc;
}
.box2{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background: pink;
}
</style>
<script src="js/vue.min.js"></script>
<script>
window.onload = function(){
var vm = new Vue({
el:"#app",
data:{}
})
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<div class="box1" @click="alert('box1')">
<div class="box2" @click.stop.prevent="alert('box2')"></div> <!-- @click.stop来阻止事件冒泡 -->
</div>
<form action="#">
<input type="text">
<input type="submit">
<input type="submit" value="提交02" @click.prevent=""> <!-- @click.prevent来阻止表单提交 -->
</form>
</div>
</body>
</html>
|
3.3 综合案例-todolist
我的计划列表
html代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
|
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>todolist</title>
<style type="text/css">
.list_con{
width:600px;
margin:50px auto 0;
}
.inputtxt{
width:550px;
height:30px;
border:1px solid #ccc;
padding:0px;
text-indent:10px;
}
.inputbtn{
width:40px;
height:32px;
padding:0px;
border:1px solid #ccc;
}
.list{
margin:0;
padding:0;
list-style:none;
margin-top:20px;
}
.list li{
height:40px;
line-height:40px;
border-bottom:1px solid #ccc;
}
.list li span{
float:left;
}
.list li a{
float:right;
text-decoration:none;
margin:0 10px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="list_con">
<h2>To do list</h2>
<input type="text" name="" id="txt1" class="inputtxt">
<input type="button" name="" value="增加" id="btn1" class="inputbtn">
<ul id="list" class="list">
<!-- javascript:; # 阻止a标签跳转 -->
<li>
<span>学习html</span>
<a href="javascript:;" class="up"> ↑ </a>
<a href="javascript:;" class="down"> ↓ </a>
<a href="javascript:;" class="del">删除</a>
</li>
<li><span>学习css</span><a href="javascript:;" class="up"> ↑ </a><a href="javascript:;" class="down"> ↓ </a><a href="javascript:;" class="del">删除</a></li>
<li><span>学习javascript</span><a href="javascript:;" class="up"> ↑ </a><a href="javascript:;" class="down"> ↓ </a><a href="javascript:;" class="del">删除</a></li>
</ul>
</div>
</body>
</html>
|
特效实现效果:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
|
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>todolist</title>
<style type="text/css">
.list_con{
width:600px;
margin:50px auto 0;
}
.inputtxt{
width:550px;
height:30px;
border:1px solid #ccc;
padding:0px;
text-indent:10px;
}
.inputbtn{
width:40px;
height:32px;
padding:0px;
border:1px solid #ccc;
}
.list{
margin:0;
padding:0;
list-style:none;
margin-top:20px;
}
.list li{
height:40px;
line-height:40px;
border-bottom:1px solid #ccc;
}
.list li span{
float:left;
}
.list li a{
float:right;
text-decoration:none;
margin:0 10px;
}
</style>
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="todolist" class="list_con">
<h2>To do list</h2>
<input type="text" v-model="message" class="inputtxt">
<input type="button" @click="addItem" value="增加" class="inputbtn">
<ul id="list" class="list">
<li v-for="item,key in dolist">
<span>{{item}}</span>
<a @click="upItem(key)" class="up" > ↑ </a>
<a @click="downItem(key)" class="down"> ↓ </a>
<a @click="delItem(key)" class="del">删除</a>
</li>
</ul>
</div>
<script>
// 计划列表代码
let vm = new Vue({
el:"#todolist",
data:{
message:"",
dolist:[
"学习html",
"学习css",
"学习javascript",
]
},
methods:{
addItem(){
if(this.messsage==""){
return false;
}
this.dolist.push(this.message);
this.message = ""
},
delItem(key){
// 删除和替换
// 参数1: 开始下表
// 参数2: 元素长度,如果不填默认删除到最后
// 参数3: 表示使用当前参数替换已经删除内容的位置
this.dolist.splice(key, 1);
},
upItem(key){
if(key==0){
return false;
}
// 向上移动
let result = this.dolist.splice(key,1);
this.dolist.splice(key-1,0,result[0]);
},
downItem(key){
// 向下移动
let result = this.dolist.splice(key, 1);
console.log(result);
this.dolist.splice(key+1,0,result[0]);
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
|
4. 通过axios实现数据请求
vue.js默认没有提供ajax功能的。
所以使用vue的时候,一般都会使用axios的插件来实现ajax与后端服务器的数据交互。
注意,axios本质上就是javascript的ajax封装,所以会被同源策略限制。
下载地址:
https://unpkg.com/axios@0.18.0/dist/axios.js
https://unpkg.com/axios@0.18.0/dist/axios.min.js
axios提供发送请求的常用方法有两个:axios.get() 和 axios.post() 。
增 post
删 delete
改 put修改整个数据的所有字段/patch修改数据的单个字段
查 get
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
|
// 发送get请求
// 参数1: 必填,字符串,请求的数据接口的url地址,例如请求地址:http://www.baidu.com?id=200
// 参数2:可选,json对象,要提供给数据接口的参数
// 参数3:可选,json对象,请求头信息
axios.get('服务器的资源地址',{
params:{ // get参数
参数名:'参数值', // id: 200,
},
header:{ // 请求头
}
}).then(function (response) { // 请求成功以后的回调函数
console.log("请求成功");
console.log(response.data); // 获取服务端提供的数据
}).catch(function (error) { // 请求失败以后的回调函数[如果then里面代码有错误,也会执行这里的代码]
console.log("请求失败");
console.log(error.response); // 获取错误信息
});
// 发送post请求,参数和使用和axios.get()一样。
// 参数1: 必填,字符串,请求的数据接口的url地址
// 参数2:必填,json对象,要提供给数据接口的参数,如果没有参数,则必须使用{}
// 参数3:可选,json对象,请求头信息
axios.put('服务器的资源地址',{
username: 'xiaoming',
password: '123456'
},{
responseData:"json",
})
.then(function (response) { // 请求成功以后的回调函数
console.log(response);
})
.catch(function (error) { // 请求失败以后的回调函数
console.log(error);
});
// b'firstName=Fred&lastName=Flintstone'
|
4.1 json
json是 JavaScript Object Notation 的首字母缩写,单词的意思是javascript对象表示法,这里说的json指的是类似于javascript对象的一种数据格式。
json的作用:在不同的系统平台,或不同编程语言之间传递数据。
4.1.1 json数据的语法
json数据对象类似于JavaScript中的对象,但是它的键对应的值里面是没有函数方法的,值可以是普通变量,不支持undefined,值还可以是数组或者json对象。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
// 原生的js的json对象
var obj = {
age:10,
sex: '女',
work:function(){
return "好好学习",
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
// json数据的对象格式,json数据格式,是没有方法的,只有属性:
{
"name":"tom",
"age":18
}
// json数据的数组格式:
["tom",18,"programmer"]
|
复杂的json格式数据可以包含对象和数组的写法。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
{
"name":"小明",
"age":200,
"is_delete": false,
"fav":["code","eat","swim","read"],
"son":{
"name":"小小明",
"age":100,
"lve":["code","eat"]
}
}
// 数组结构也可以作为json传输数据。
|
json数据可以保存在.json文件中,一般里面就只有一个json对象。
总结:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
1. json文件的后缀是.json
2. json文件一般保存一个单一的json数据
3. json数据的属性不能是方法或者undefined,属性值只能:数值[整数,小数,布尔值]、字符串、json和数组
4. json数据只使用双引号、每一个属性成员之间使用逗号隔开,并且最后一个成员没有逗号。
{
"name":"小明",
"age":200,
"fav":["code","eat","swim","read"],
"son":{
"name":"小小明",
"age":100
}
}
|
工具:postman可以用于测试开发的数据接口。
4.1.2 js中提供的json数据转换方法
javascript提供了一个JSON对象来操作json数据的数据转换.
| 方法 | 参数 | 返回值 | 描述 |
|---|
| stringify |
json对象 |
字符串 |
json对象转成字符串 |
| parse |
字符串 |
json对象 |
字符串格式的json数据转成json对象 |
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
|
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
// json语法
let humen = {
"username":"xiaohui",
"password":"1234567",
"age":20
};
console.log(humen);
console.log(typeof humen);
// JSON对象提供对json格式数据的转换功能
// stringify(json对象) # 用于把json转换成字符串
let result = JSON.stringify(humen);
console.log(result);
console.log(typeof result);
// parse(字符串类型的json数据) # 用于把字符串转成json对象
let json_str = '{"password":"1123","age":20,"name":"xiaobai"}';
console.log(json_str)
console.log(typeof json_str)
let json_obj = JSON.parse(json_str);
console.log(json_obj);
console.log(typeof json_obj)
console.log(json_obj.age)
</script>
</body>
</html>
|
4.2 ajax
ajax,一般中文称之为:“阿贾克斯”,是英文 “Async Javascript And Xml”的简写,译作:异步js和xml数据传输数据。
ajax的作用: ajax可以让js代替浏览器向后端程序发送http请求,与后端通信,在用户不知道的情况下操作数据和信息,从而实现页面局部刷新数据/无刷新更新数据。
所以开发中ajax是很常用的技术,主要用于操作后端提供的数据接口,从而实现网站的前后端分离。
ajax技术的原理是实例化js的XMLHttpRequest对象,使用此对象提供的内置方法就可以与后端进行数据通信。
{
"name":"晓明",
"age": 12
}
<xml version="1.0">
<name>晓明</name>
<age>12</age>
</xml>
4.2.1 数据接口
数据接口,也叫api接口,表示后端提供操作数据/功能的url地址给客户端使用。
客户端通过发起请求向服务端提供的url地址申请操作数据【操作一般:增删查改】
同时在工作中,大部分数据接口都不是手写,而是通过函数库/框架来生成。
4.2.3 ajax的使用
ajax的使用必须与服务端程序配合使用,但是目前我们先学习ajax的使用,所以暂时先不涉及到服务端python代码的编写。因此,我们可以使用别人写好的数据接口进行调用。
jQuery将ajax封装成了一个函数$.ajax(),我们可以直接用这个函数来执行ajax请求。
编写代码获取接口提供的数据:
jQ版本
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
|
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="js/jquery-1.12.4.js"></script>
<script>
$(function(){
$("#btn").on("click",function(){
$.ajax({
// 后端程序的url地址
url: 'http://wthrcdn.etouch.cn/weather_mini',
// 也可以使用method,提交数据的方式,默认是'GET',常用的还有'POST'
type: 'get',
dataType: 'json', // 返回的数据格式,常用的有是'json','html',"jsonp"
data:{ // 设置发送给服务器的数据,如果是get请求,也可以写在url地址的?后面
"city":'北京'
}
})
.done(function(resp) { // 请求成功以后的操作
console.log(resp);
})
.fail(function(error) { // 请求失败以后的操作
console.log(error);
});
});
})
</script>
</head>
<body>
<button id="btn">点击获取数据</button>
</body>
</html>
|
vue版本:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
|
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
<script src="js/axios.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<input type="text" v-model="city">
<button @click="get_weather">点击获取天气</button>
</div>
<script>
let vm = new Vue({
el:"#app",
data:{
city:"",
},
methods:{
get_weather(){
// http://wthrcdn.etouch.cn/weather_mini?city=城市名称
axios.get("http://wthrcdn.etouch.cn/weather_mini?city="+this.city)
.then(response=>{
console.log(response);
}).catch(error=>{
console.log(error.response)
});
// 上面的参数写法,也可以是下面这种格式:
// axios.get("http://wthrcdn.etouch.cn/weather_mini",{
// // get请求的附带参数
// params:{
// "city":"广州",
// }
// }).then(response=>{
// console.log(response.data); // 获取接口数据
// }).catch(error=>{
// console.log(error.response); // 获取错误信息
// })
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
|
4.2.4 同源策略
同源策略,是浏览器为了保护用户信息安全的一种安全机制。所谓的同源就是指代通信的两个地址(例如服务端接口地址与浏览器客户端页面地址)之间比较,是否协议、域名(IP)和端口相同。不同源的客户端脚本[javascript]在没有明确授权的情况下,没有权限读写对方信息。
ajax本质上还是javascript,是运行在浏览器中的脚本语言,所以会被受到浏览器的同源策略所限制。
前端地址:http://www.oldboy.cn/index.html | 是否同源 | 原因 |
|---|
http://www.oldboy.cn/user/login.html |
是 |
协议、域名、端口相同 |
http://www.oldboy.cn/about.html |
是 |
协议、域名、端口相同 |
https://www.oldboy.cn/user/login.html |
否 |
协议不同 ( https和http ) |
http:/www.oldboy.cn:5000/user/login.html |
否 |
端口 不同( 5000和80) |
http://bbs.oldboy.cn/user/login.html |
否 |
域名不同 ( bbs和www ) |
同源策略针对ajax的拦截,代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
|
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
<script src="js/axios.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<button @click="get_music">点击获取天气</button>
</div>
<script>
let vm = new Vue({
el:"#app",
data:{},
methods:{
get_music(){
axios.get("http://tingapi.ting.baidu.com/v1/restserver/ting?method=baidu.ting.search.catalogSug&query=我的中国心")
.then(response=>{
console.log(response);
}).catch(error=>{
console.log(error.response)
});
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
|
上面代码运行错误如下:
Access to XMLHttpRequest at 'http://tingapi.ting.baidu.com/v1/restserver/ting?method=baidu.ting.search.catalogSug&query=%E6%88%91%E7%9A%84%E4%B8%AD%E5%9B%BD%E5%BF%83' from origin 'http://localhost:63342' has been blocked by CORS policy: No 'Access-Control-Allow-Origin' header is present on the requested resource.
上面错误,关键词:Access-Control-Allow-Origin
只要出现这个关键词,就是访问受限。出现同源策略的拦截问题。
4.2.5 ajax跨域(跨源)方案之CORS
ajax跨域(跨源)方案:后端授权[CORS],jsonp,服务端代理
CORS是一个W3C标准,全称是"跨域资源共享",它允许浏览器向跨源的后端服务器发出ajax请求,从而克服了AJAX只能同源使用的限制。
实现CORS主要依靠后端服务器中响应数据中设置响应头信息返回的。
django的视图
def post(request):
response = new Response()
response .set_header(“Access-Control-Allow-Origin”,“http://localhost:63342”)
return response;
// 在响应行信息里面设置以下内容:
Access-Control-Allow-Origin: ajax所在的域名地址
Access-Control-Allow-Origin: www.oldboy.cn # 表示只允许www.oldboy.cn域名的客户端的ajax跨域访问
// * 表示任意源,表示允许任意源下的客户端的ajax都可以访问当前服务端信息
Access-Control-Allow-Origin: *
总结:
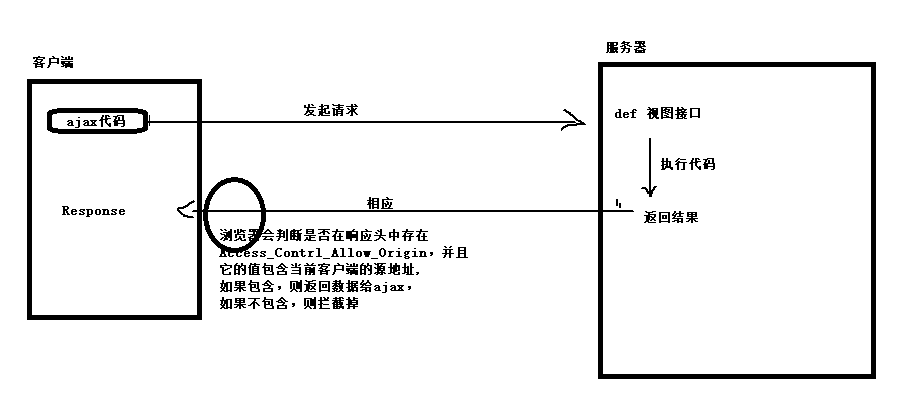
0. 同源策略:浏览器的一种保护用户数据的一种安全机制。
浏览器会限制ajax不能跨源访问其他源的数据地址。
同源:判断两个通信的地址之间,是否协议,域名[IP],端口一致。
ajax: http://127.0.0.1/index.html
api数据接口: http://localhost/index
这两个是同源么?不是同源的。是否同源的判断依据不会根据电脑来判断,而是通过协议、域名、端口的字符串是否来判断。
1. ajax默认情况下会受到同源策略的影响,一旦受到影响会报错误如下:
No 'Access-Control-Allow-Origin' header is present on the requested resource
2. 解决ajax只能同源访问数据接口的方式:
1. CORS,跨域资源共享,在服务端的响应行中设置:
Access-Control-Allow-Origin: 允许访问的域名地址
2. jsonp
3. 是否服务端代理
思路:通过python来请求对应的服务器接口,获取到数据以后,
5. 组件化开发
5.1 组件[component]
组件(Component)是自定义封装的功能。在前端开发过程中,经常出现多个网页的功能是重复的,而且很多不同的页面之间,也存在同样的功能。
而在网页中实现一个功能,需要使用html定义功能的内容结构,使用css声明功能的外观样式,还要使用js来定义功能的特效,因此就产生了把一个功能相关的[HTML、css和javascript]代码封装在一起组成一个整体的代码块封装模式,我们称之为“组件”。
所以,组件就是一个html网页中的功能,一般就是一个标签,标签中有自己的html内容结构,css样式和js特效。
这样,前端人员就可以在组件化开发时,只需要书写一次代码,随处引入即可使用。
vue的组件有两种:默认组件[全局组件] 和 单文件组件
5.1.1 默认组件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
|
<div id="app">
<addnum></addnum>
<addnum></addnum>
<addnum></addnum>
<addnum></addnum>
<addnum></addnum>
</div>
<script>
Vue.component("addnum",{
template:'<div><input type="text" v-model="num"><button @click="num+=1">点击</button></div>',
data: function(){
// 写在这里的数据只有当前组件可以使用
return {
num:1,
}
}
});
var vm = new Vue({
el:"#app",
// 这里写的数据是全局公用的,整个文件共享
data:{
}
})
</script>
|
6. Vue自动化工具(Vue-cli)
前面学习了普通组件以后,接下来我们继续学习单文件组件则需要提前先安装准备一些组件开发工具。否则无法使用和学习单文件组件。
一般情况下,单文件组件,我们运行在 自动化工具vue-CLI中,可以帮我们编译单文件组件。所以我们需要在系统中先搭建vue-CLI工具,
官网:https://cli.vuejs.org/zh/
Vue CLI 需要 Node.js 8.9 或更高版本 (推荐 8.11.0+)。你可以使用 nvm 或 nvm-windows在同一台电脑中管理多个 Node 版本。
nvm工具的下载和安装: https://www.jianshu.com/p/d0e0935b150a
https://www.jianshu.com/p/622ad36ee020
安装记录:
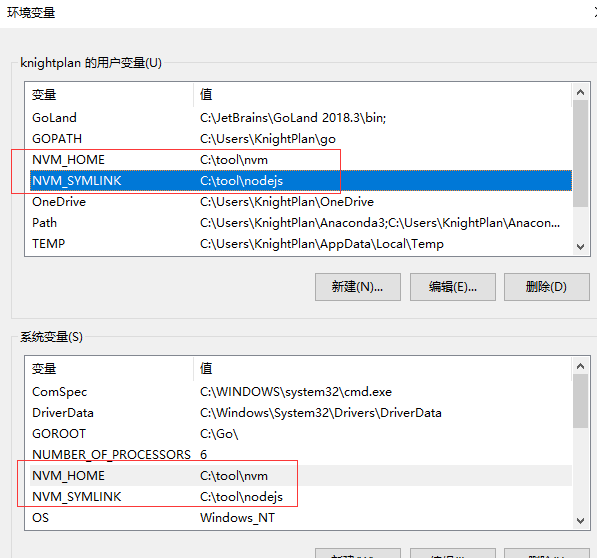
打开:https://github.com/coreybutler/nvm-windows/releases
安装完成以后,先查看环境变量是否设置好了.
常用的nvm命令
nvm list # 列出目前在nvm里面安装的所有node版本 nvm install node版本号 # 安装指定版本的node.js nvm uninstall node版本号 # 卸载指定版本的node.js nvm use node版本号 # 切换当前使用的node.js版本
如果使用nvm工具,则直接可以不用自己手动下载,如果使用nvm下载安装 node的npm比较慢的时候,可以修改nvm的配置文件(在安装根目录下)
# settings.txt
root: C:\tool\nvm [这里的目录地址是安装nvm时自己设置的地址,要根据实际修改]
path: C:\tool\nodejs
arch: 64
proxy: none
node_mirror: http://npm.taobao.org/mirrors/node/
npm_mirror: https://npm.taobao.org/mirrors/npm/
6.1 安装node.js
Node.js是一个新的后端(后台)语言,它的语法和JavaScript类似,所以可以说它是属于前端的后端语言,后端语言和前端语言的区别:
- 运行环境:后端语言一般运行在服务器端,前端语言运行在客户端的浏览器上
- 功能:后端语言可以操作文件,可以读写数据库,前端语言不能操作文件,不能读写数据库。
我们一般安装LTS(长线支持版本 Long-Time Support):
下载地址:https://nodejs.org/en/download/【上面已经安装了nvm,那么这里不用手动安装了】
node.js的版本有两大分支:
官方发布的node.js版本:0.xx.xx 这种版本号就是官方发布的版本
社区发布的node.js版本:xx.xx.x 就是社区开发的版本
Node.js如果安装成功,可以查看Node.js的版本,在终端输入如下命令:
node -v
6.2 npm
在安装node.js完成后,在node.js中会同时帮我们安装一个npm包管理器npm。我们可以借助npm命令来安装node.js的包。这个工具相当于python的pip管理器。
npm install -g 包名 # 安装模块 -g表示全局安装,如果没有-g,则表示在当前项目安装
npm list # 查看当前目录下已安装的node包
npm view 包名 engines # 查看包所依赖的Node的版本
npm outdated # 检查包是否已经过时,命令会列出所有已过时的包
npm update 包名 # 更新node包
npm uninstall 包名 # 卸载node包
npm 命令 -h # 查看指定命令的帮助文档
6.3 安装Vue-cli
npm install -g vue-cli
如果安装速度过慢,一直超时,可以考虑切换npm镜像源:http://npm.taobao.org/
6.4 使用Vue-CLI初始化创建前端项目
6.4.1 生成项目目录
使用vue自动化工具可以快速搭建单页应用项目目录。
该工具为现代化的前端开发工作流提供了开箱即用的构建配置。只需几分钟即可创建并启动一个带热重载、保存时静态检查以及可用于生产环境的构建配置的项目:
// 生成一个基于 webpack 模板的新项目
vue init webpack 项目目录名
例如:
vue init webpack myproject
// 启动开发服务器 ctrl+c 停止服务
cd myproject
npm run dev # 运行这个命令就可以启动node提供的测试http服务器
运行了上面代码以后,终端下会出现以下效果提示:
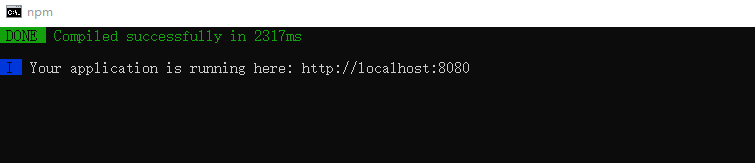
那么访问:http://localhost:8080/

6.4.2 项目目录结构
src 主开发目录,要开发的单文件组件全部在这个目录下的components目录下
static 静态资源目录,所有的css,js文件放在这个文件夹
dist项目打包发布文件夹,最后要上线单文件项目文件都在这个文件夹中[后面打包项目,让项目中的vue组件经过编译变成js 代码以后,dist就出现了]
node_modules目录是node的包目录,
config是配置目录,
build是项目打包时依赖的目录
src/router 路由,后面需要我们在使用Router路由的时候,自己声明.
6.4.3 项目执行流程图
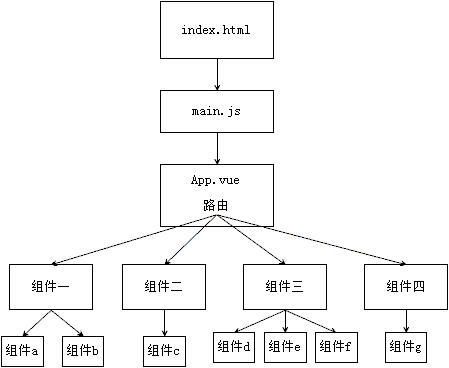
整个项目是一个主文件index.html,index.html中会引入src文件夹中的main.js,main.js中会导入顶级单文件组件App.vue,App.vue中会通过组件嵌套或者路由来引用components文件夹中的其他单文件组件。
7. 单文件组件的使用
组件有两种:普通组件、单文件组件
普通组件的缺点:
- html代码是作为js的字符串进行编写,所以组装和开发的时候不易理解,而且没有高亮效果。
- 普通组件用在小项目中非常合适,但是复杂的大项目中,如果把更多的组件放在html文件中,那么维护成本就会变得非常昂贵。
- 普通组件只是整合了js和html,但是css代码被剥离出去了。使用的时候的时候不好处理。
将一个组件相关的html结构,css样式,以及交互的JavaScript代码从html文件中剥离出来,合成一个文件,这种文件就是单文件组件,相当于一个组件具有了结构、表现和行为的完整功能,方便组件之间随意组合以及组件的重用,这种文件的扩展名为“.vue”,比如:“Home.vue”。
-
创建组件
在组件中编辑三个标签,编写视图、vm对象和css样式代码。
7.1 template 编写html代码的地方
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
<template>
<div id="Home">
<span @click="num--" class="sub">-</span>
<input type="text" size="1" v-model="num">
<span @click="num++" class="add">+</span>
</div>
</template>
|
7.2 script编写vue.js代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
<script>
export default {
name:"Home",
data: function(){
return {
num:0,
}
}
}
</script>
|
7.3 style编写当前组件的样式代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
<style scoped>
.sub,.add{
border: 1px solid red;
padding: 4px 7px;
}
</style>
|
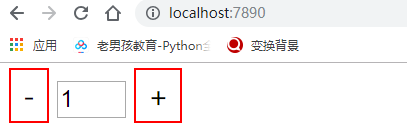
7.4 完成案例-点击加减数字
创建Homes.vue
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
<template>
<div class="add_num">
<span @click="num++">+</span>
<input type="text" size="2" v-model="num">
<span @click="num--">-</span>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default{
name:"AddNum",
data: function(){
return {
num: 0,
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.add_num{
font-size: 32px;
}
</style>
|
在App.vue组件中调用上面的组件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
<template>
<div id="Home">
<span @click="num--" class="sub">-</span>
<input type="text" size="1" v-model="num">
<span @click="num++" class="add">+</span>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name:"Home",
data: function(){
return {
num:0,
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.sub,.add{
border: 1px solid red;
padding: 4px 7px;
}
</style>
|
在开发vue项目之前,需要手动把 App.vue的HelloWorld组件代码以及默认的css样式,清楚。
上面的代码效果:
7.4 组件的嵌套
有时候开发vue项目时,页面也可以算是一个大组件,同时页面也可以分成多个子组件.
因为,产生了父组件调用子组件的情况.
例如,我们可以声明一个组件,作为父组件
在components/创建一个保存子组件的目录HomeSon
在HomeSon目录下,可以创建当前页面的子组件,例如,是Menu.vue
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
// 组件中代码必须写在同一个标签中
<template>
<div id="menu">
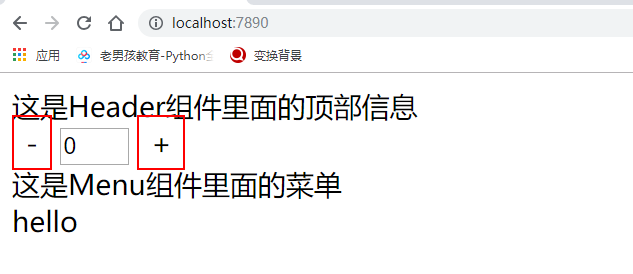
<span>{{msg}}</span>
<div>hello</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name:"Menu",
data: function(){
return {
msg:"这是Menu组件里面的菜单",
}
}
}
</script>
|
然后,在父组件中调用上面声明的子组件。
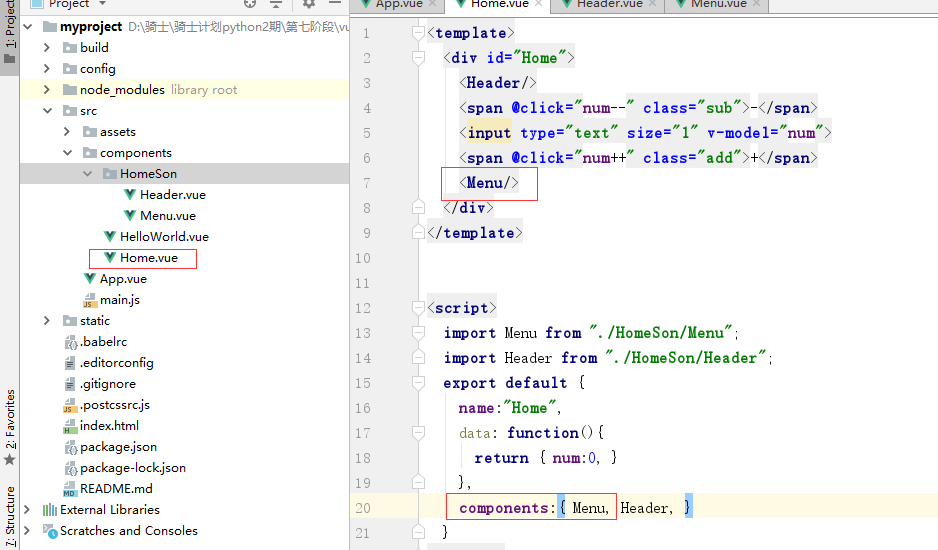
最后,父组件被App.vue调用.就可以看到页面效果.
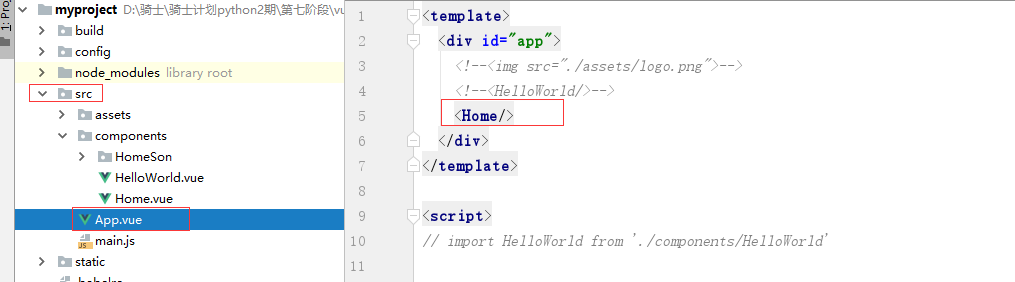
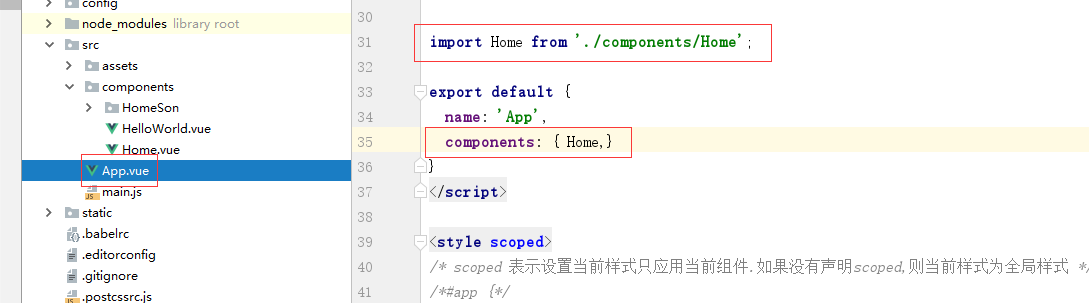
效果:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
|
<template>
<div id="Home">
<span @click="num--" class="sub">-</span>
<input type="text" size="1" v-model="num">
<span @click="num++" class="add">+</span>
<Menu/>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Menu from "./HomeSon/Menu";
export default {
name:"Home",
data: function(){
return {
num:0,
}
},
components:{Menu}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.sub,.add{
border: 1px solid red;
padding: 4px 7px;
}
</style>
|
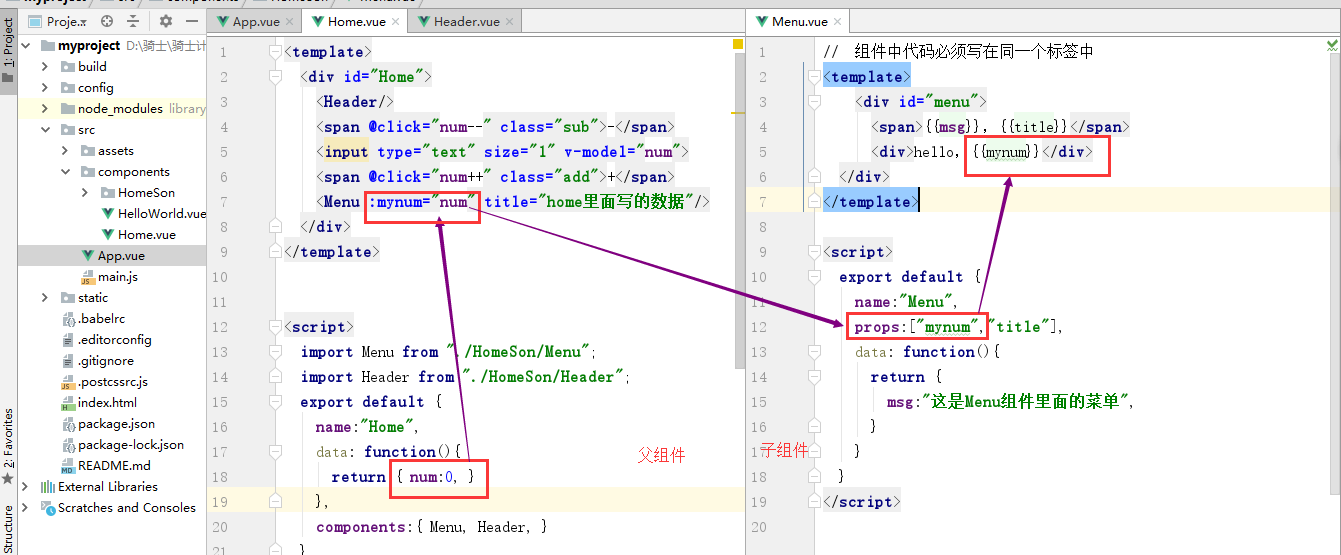
7.5 传递数据
父组件的数据传递给子组件
例如,我们希望把父组件的数据传递给子组件.
可以通过props属性来进行数据传递.
传递数据三个步骤:
-
在父组件中,调用子组件的组名处,使用属性值的方式往下传递数据
1
2
3
4
5
|
<Menu :mynum="num" title="home里面写的数据"/>
# 上面表示在父组件调用Menu子组件的时候传递了2个数据:
如果要传递变量[变量可以各种类型的数据],属性名左边必须加上冒号:,同时,属性名是自定义的,会在子组件中使用。
如果要传递普通字符串数据,则不需要加上冒号:
|
-
在子组件中接受上面父组件传递的数据,需要在vm组件对象中,使用props属性类接受。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
<script>
export default {
name:"Menu",
props:["mynum","title"],
data: function(){
return {
msg:"这是Menu组件里面的菜单",
}
}
}
</script>
// 上面 props属性中表示接受了两个数据。
|
-
在子组件中的template中使用父组件传递过来的数据.
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
<template>
<div id="menu">
<span>{{msg}},{{title}}</span>
<div>hello,{{mynum}}</div>
</div>
</template>
|
效果:
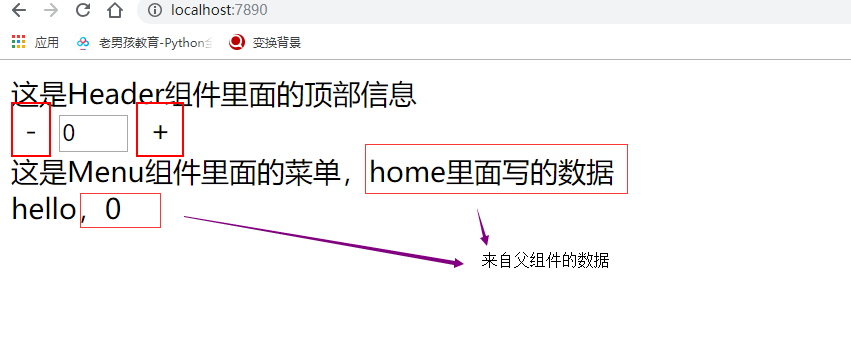
步骤流程:
使用父组件传递数据给子组件时, 注意一下几点:
-
传递数据是变量,则需要在属性左边添加冒号.
传递数据是变量,这种数据称之为"动态数据传递"
传递数据不是变量,这种数据称之为"静态数据传递"
-
父组件中修改了数据,在子组件中会被同步修改,但是,子组件中的数据修改了,是不是影响到父组件中的数据.
这种情况,在开发时,也被称为"单向数据流"
子组件传递数据给父组件
-
在子组件中,通过this.$emit()来调用父组件中定义的事件.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
|
<template>
<div>
<p>Post的子组件</p>
<p>data={{data}}</p>
<p>fnum={{fnum}}</p>
<div><input type="text" v-model="fnum"></div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "PostSon",
// 父组件传递数据给子组件: 1. 在父组件中调用子组件的组件名称标签上面声明属性和传递值,2. 在子组件中通过props进行接收
props:["data","fnum"], // 接受父组件中传递过来的数据
// 子组件传递数据给父组件[事件的方式进行传递]:
watch:{
fnum(){
console.log(this.fnum);
// this.$emit("父元素的自定义事件","要传递的数据"); // 通过this.$emit()方法,子组件可以把数据传递给父组件
this.$emit("postparentdata",this.fnum);
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
|
-
父组件中声明一个和子组件中this.$emit("自定义事件名称")对应的事件属性。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
<template>
<div>
<h1>num={{num}}</h1>
<Son data="我是父组件里面的内容" :fnum="num" @postparentdata="getsondata"></Son>
</div>
</template>
|
-
父组件中,声明一个自定义方法,在事件被调用时,执行的。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
<script>
import Son from "./PostSon"
export default {
name: "Post",
data(){
return {
num: 100,
}
},
components:{
Son:Son,
},
methods:{
getsondata(message){
console.log("父组件"+message);
this.num = message;
}
}
}
</script>
|
作业:
- 使用组件化开发,完成之前的选项卡练习功能
- 使用组件化开发,完成之前的todolist功能
- 使用组件化开发,完成table表格的增删查改作业,数据使用本地存储进行保存
8. 在组件中使用axios获取数据
默认情况下,我们的项目中并没有对axios包的支持,所以我们需要下载安装。
在项目根目录中使用 npm安装包
npm install axios
接着在main.js文件中,导入axios并把axios对象 挂载到vue属性中多为一个子对象,这样我们才能在组件中使用。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
// The Vue build version to load with the `import` command
// (runtime-only or standalone) has been set in webpack.base.conf with an alias.
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App' // 这里表示从别的目录下导入 单文件组件
import axios from 'axios'; // 从node_modules目录中导入包
Vue.config.productionTip = false
Vue.prototype.$axios = axios; // 把对象挂载vue中
/* eslint-disable no-new */
new Vue({
el: '#app',
components: { App },
template: '<App/>'
});
|
8.1 在组建中使用axios获取数据
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
<script>
export default{
。。。
methods:{
get_data:function(){
// 使用axios请求数据
this.$axios.get("http://wthrcdn.etouch.cn/weather_mini?city=深圳").then((response)=>{
console.log(response);
}).catch(error=>{
console.log(error);
})
}
}
}
</script>
|
效果:

使用的时候,因为本质上来说,我们还是原来的axios,所以也会收到同源策略的影响。
9. 安装路由vue-router
官方文档:https://router.vuejs.org/zh/
9.1 下载安装路由组件
npm i vue-router -S
npm install vue-router --save
9.2 配置路由
9.2.1 初始化路由对象
在src目录下创建routes路由目录,在router目录下创建index.js路由文件
index.js路由文件中,编写初始化路由对象的代码 .
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
// 1. 引入vue和vue-router组件核心对象,并在vue中通过use注册vue-router组件
import Vue from "vue";
import Router from "vue-router";
Vue.use(Router);
// 2. 暴露vue-router对象,并在vue-router里面编写路由,提供给main.js调用
export default new Router({
// 设置路由模式为‘history’,去掉默认的#
mode: "history",
routes:[
// 路由列表
]
})
|
9.2.2 注册路由信息
打开main.js文件,把router路由规则对象注册到vue中,代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
// The Vue build version to load with the `import` command
// (runtime-only or standalone) has been set in webpack.base.conf with an alias.
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App'
import router from './router/index';
Vue.config.productionTip = false
/* eslint-disable no-new */
new Vue({
el: '#app',
router,
components: { App },
template: '<App/>'
});
|
9.2.3 在视图中显示路由对应的内容
在App.vue组件中,添加显示路由对应的内容。代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
<template>
<div id="app">
<!-- 标签名必须是这个rouer-view -->
<router-view/>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'App',
components: {
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
|
注意:如果在vue创建项目的时候,设置安装vue-router,则项目会自动帮我们生成上面的router目录和index.js里面的代码,以及自动到main.js里面注册路由对象。
9.3 路由对象提供的操作
在我们安装注册了vue-router组件吗以后,vue-router在vue项目中会帮我们在全局范围内所有组件里面创建2个对象给我们使用:
this.$router,可用于在js代码中进行页面跳转。this.$route,可用于获取地址栏上面的url参数。
9.3.1 页面跳转
在vue-router提供的操作中, 进行页面跳转有2种方式:
-
使用<router-link to="url地址">来跳转
-
在<script>中使用this.$router.push(url地址)来跳转
在<script>中还可以使用this.$router.go(整数),表示跳转返回上一页或者上几页,下一个或者下几页
9.3.1.1 router-link标签
例如,我们就可以在Home.vue组件中,使用router-link跳转到User.vue组件中。
routes/index.js,代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
|
// 1. 引入vue和vue-router组件核心对象,并在vue中通过use注册vue-router组件
import Vue from "vue";
import Router from "vue-router";
Vue.use(Router); // Router是类
// 2. 暴露vue-router对象,并在vue-router里面编写路由,提供给main.js调用
// 导入组件
// import 组件名 from "../components/组件名"
import Home from "../components/Home";
import User from "../components/User";
export default new Router({
mode:"history", // 路由地址的显示模式: 默认hash,表示地址栏上面出现#
routes:[
// {
// name:"路由名称[对应组件的name值,将来用于跳转页面]",
// path: "访问url路径",
// component: 组件名
// },
{
name:"Home",
path: "/",
component: Home
},{
name:"User",
path: "/user",
component: User
},
],
});
// vue-router除了可以进行组件和url地址的绑定以外,还可以
// 进行不同组件的页面跳转,
|
Home.vue代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
|
<template>
<div>
首页页面组件
<a href="/user">个人中心</a>
<!-- router-link标签,本质上就是a标签,只是由vue-router进行加工处理
可以显示局部页面刷新,不会重新加载内容,进行ajax跳转
-->
<router-link to="/user">个人中心</router-link>
<router-link :to="url">个人中心</router-link>
<router-link :to="{name:'User'}">个人中心</router-link>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "Home",
data(){
return {
url: "/user",
}
},
methods:{
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
|
![1581908101280]()
9.3.1.2 this.$router.push()跳转
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
|
<template>
<div>
首页页面组件
<a href="/user">个人中心</a>
<!-- router-link标签,本质上就是a标签,只是由vue-router进行加工处理
可以显示局部页面刷新,不会重新加载内容,进行ajax跳转
-->
<router-link to="/user">个人中心</router-link>
<router-link :to="url">个人中心</router-link>
<router-link :to="{name:'User'}">个人中心</router-link>
<button @click="jump">个人中心</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "Home",
data(){
return {
url: "/user",
}
},
methods:{
jump(){
// 开发中可以先进行权限,登录之类的判断,然后再进行跳转
// this.$router.back(); // 返回上一页,本质上就是 location.back()
// this.$router.go(-1); // 返回上一页,本质上就是 location.go()
// this.$router.forward(); // 跳转到下一页,本质上就是 location.forward()
//this.$router.push("/user"); // 跳转到站内的制定地址页面中,本质上就是 location.href
// 注意,this.$router.push() 不能跳转到其他网站。如果真的要跳转外站,则使用location.href="站外地址,记得加上http://协议"
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
|
9.3.2 参数传递
vue-router提供了this.$route,可以让我们接受来自其他页面的附带参数。参数有2种:
-
查询字符串(query string),就是地址栏上面?号后面的参数,
例如:http://localhost:8008/user?name=xiaoming&pwd=123,这里name=xiaoming&pwd=123就是查询字符串参数。
-
路由参数(router params),就是地址栏上面路由路径的一部分,
例如:http://localhost:8080/user/300/xiaoming,此时,300属于路由路径的一部分,这个300就是路由参数.,当然,xiaoming,或者user也可以理解是路由参数,就是看我们的页面中是否需要接收而已。
9.3.2.1 获取查询字符串
- 必须先有一个页面跳转发送参数。例如,在Home组件中跳转到User组件中,需要传递name和pwd查询字符串。
Home.vue代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
|
<template>
<div>
首页页面组件
<!-- <a href="/user">个人中心</a>
<!– router-link标签,本质上就是a标签,只是由vue-router进行加工处理
可以显示局部页面刷新,不会重新加载内容,进行ajax跳转
–>
<router-link to="/user">个人中心</router-link>
<router-link :to="url">个人中心</router-link>
<router-link :to="{name:'User'}">个人中心</router-link>
<button @click="jump">个人中心</button>-->
<router-link :to="`/user?name=${name}&pwd=${pwd}`">查询字符串参数</router-link>
<router-link :to="'/user?name='+name+'&pwd='+pwd">查询字符串参数</router-link>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "Home",
data(){
return {
name: "xiaoming",
pwd: "123",
url: "/user",
}
},
methods:{
jump(){
// 开发中可以先进行权限,登录之类的判断,然后再进行跳转
// this.$router.back(); // 返回上一页,本质上就是 location.back()
// this.$router.go(-1); // 返回上一页,本质上就是 location.go()
// this.$router.forward(); // 跳转到下一页,本质上就是 location.forward()
this.$router.push("/user"); // 跳转到站内的制定地址页面中,本质上就是 location.href
// 注意,this.$router.push 不能跳转到其他网站。如果真的要跳转外站,则使用location.href="站外地址,记得加上http://协议"
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
|
- 可以下一个页面中,这里代表的就是User组件,接收来自Home组件的参数。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
<template>
<div>
用户中心页面组件
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "User",
created() {
// 接收地址栏上面的参数
// this.$route是vue-router提供的一个用于接收地址参数的对象。
// 经过main.js里面注册router对象以后,
// 将来在所有的子组件中,可以通过this.$route来获取参数或者通过this.$router跳转页面
// 查询字符串参数
// query是this.$route里面的一个数组,this.$route会自动收集地址栏上所有的参数保存到query里面
// let name = this.$route.query.name;
// let pwd = this.$route.query.pwd;
// console.log(`name=${name}&pwd=${pwd}`); // ``里面,${}圈住的内容会被js当成变量来解析
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
|
9.3.2.2. 获取路由参数
例如:我们用户的界面都是一样的,但是每一个用户来到自己的页面中,显示的内容肯定都是不一样的,此时,我们需要使用不同的路径来区分不同的用户。这时候,可以在路由路径中使用路由参数表示不同用户的id
例如:我们就需要设置一个route/index.js中路由信息里面,哪一段路由属于路由参数。
src/routes/index.js设置路由参数。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
|
// 1. 引入vue和vue-router组件核心对象,并在vue中通过use注册vue-router组件
import Vue from "vue";
import Router from "vue-router";
Vue.use(Router); // Router是类
// 2. 暴露vue-router对象,并在vue-router里面编写路由,提供给main.js调用
// 导入组件
// import 组件名 from "../components/组件名"
import Home from "../components/Home";
import User from "../components/User";
export default new Router({
mode:"history", // 路由地址的显示模式: 默认hash,表示地址栏上面出现#
routes:[
// {
// name:"路由名称[对应组件的name值,将来用于跳转页面]",
// path: "访问url路径",
// component: 组件名
// },
{
name:"Home",
path: "/",
component: Home
},{
name:"User",
path: "/user/:id/img-:img_id",
component: User
},
],
});
// vue-router除了可以进行组件和url地址的绑定以外,还可以
// 进行不同组件的页面跳转,
|
然后我们就是在Home中如果需要转到User里面。
Home.vue代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
|
<template>
<div>
首页页面组件
<!-- <a href="/user">个人中心</a>
<!– router-link标签,本质上就是a标签,只是由vue-router进行加工处理
可以显示局部页面刷新,不会重新加载内容,进行ajax跳转
–>
<router-link to="/user">个人中心</router-link>
<router-link :to="url">个人中心</router-link>
<router-link :to="{name:'User'}">个人中心</router-link>
<button @click="jump">个人中心</button>-->
<!-- <router-link :to="`/user?name=${name}&pwd=${pwd}`">查询字符串参数</router-link>-->
<!-- <router-link :to="'/user?name='+name+'&pwd='+pwd">查询字符串参数</router-link>-->
<router-link to="/user/100/img-10086">路由参数</router-link>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "Home",
data(){
return {
name: "xiaoming",
pwd: "123",
url: "/user",
}
},
methods:{
jump(){
// 开发中可以先进行权限,登录之类的判断,然后再进行跳转
// this.$router.back(); // 返回上一页,本质上就是 location.back()
// this.$router.go(-1); // 返回上一页,本质上就是 location.go()
// this.$router.forward(); // 跳转到下一页,本质上就是 location.forward()
this.$router.push("/user"); // 跳转到站内的制定地址页面中,本质上就是 location.href
// 注意,this.$router.push 不能跳转到其他网站。如果真的要跳转外站,则使用location.href="站外地址,记得加上http://协议"
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
|
User.vue,组件中可以通过this.$route.params接收路由参数。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
|
<template>
<div>
用户中心页面组件
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "User",
created() {
// 接收地址栏上面的参数
// this.$route是vue-router提供的一个用于接收地址参数的对象。
// 经过main.js里面注册router对象以后,
// 将来在所有的子组件中,可以通过this.$route来获取参数或者通过this.$router跳转页面
// 查询字符串参数
// query是this.$route里面的一个数组,this.$route会自动收集地址栏上所有的参数保存到query里面
// let name = this.$route.query.name;
// let pwd = this.$route.query.pwd;
// console.log(`name=${name}&pwd=${pwd}`); // ``里面,${}圈住的内容会被js当成变量来解析
// 路由参数
// params是this.$route里面的一个数组,this.$route会自动收集路由列表中已经标记为路由参数所有内容保存到params中
let id = this.$route.params.id;
console.log(id);
let img_id = this.$route.params.img_id;
console.log(`img_id = ${img_id}`);
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
|





















 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号