ffmpeg播放器实现详解 - 视频同步控制
ffplay是ffmpeg源码中一个自带的开源播放器实例,同时支持本地视频文件的播放以及在线流媒体播放,功能非常强大。
FFplay: FFplay is a very simple and portable media player using the FFmpeg libraries and the SDL library. It is mostly used as a testbed for the various FFmpeg APIs.
ffplay中的代码充分调用了ffmpeg中的函数库,因此,想学习ffmpeg的使用,或基于ffmpeg开发一个自己的播放器,ffplay都是一个很好的切入点。
由于ffmpeg本身的开发文档比较少,且ffplay播放器源码的实现相对复杂,除了基础的ffmpeg组件调用外,还包含视频帧的渲染、音频帧的播放、音视频同步策略及线程调度等问题。
因此,这里我们以ffmpeg官网推荐的一个ffplay播放器简化版本的开发例程为基础,在此基础上循序渐进由浅入深,最终探讨实现一个视频播放器的完整逻辑。
在上篇文章中,我们讨论了一个播放器的基础架构,梳理了组成播放器的基本组件及后台数据队列,并对代码结构进行了调整。本文在上篇文章的基础上,讨论音视频同步的相关内容,首先介绍与音视频同步相关的时间戳概念,然后介绍音视频同步涉及的原理及策略,最后重点讲述关键代码的实现过程。
公众号:断点实验室 音视频开发系列文章
ffmpeg源码编译环境搭建
ffplay源码编译
ffmpeg播放器实现详解 - 框架搭建
ffmpeg播放器实现详解 - 视频显示
ffmpeg播放器实现详解 - 音频播放
ffmpeg播放器实现详解 - 创建线程
ffmpeg播放器实现详解 - 视频同步控制
ffmpeg播放器实现详解 - 音频同步控制
ffmpeg播放器实现详解 - 快进快退控制
1、时间戳
时间戳的概念贯穿音视频开发始终,重要性不言而喻。时间戳告诉我们在什么时候,用多快的速度去播哪一帧,其中,DTS(decoding timestamp)告诉我们何时解码,PTS(presentation timestamp)告诉我们何时播放。
那么,为什么要有DTS和PTS?首先需要理解编码后的数据是如何存储的。
1.1 帧分组(Group of picture)
视频帧(这里主要以H.264编码为例)以序列为单位进行组织,一个序列是一段图像编码后的数据流,从关键帧I帧开始,包含了与组内I帧相关联的P帧和B帧,到下一个I帧结束,一个序列为一个帧组(group of picture),如下图所示。
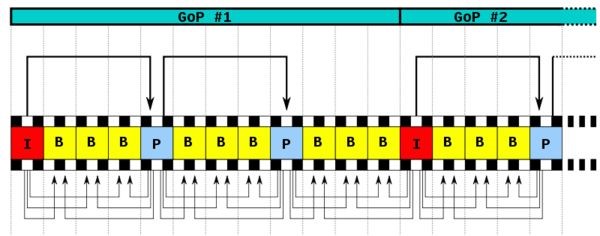
一个序列的长短,和序列呈现的视频内容有关。当前后帧视频画面变化较小时,一个序列可以很长,因为画面变化小意味着不需要太多的数据,即可对后续的画面进行描述,仅需提供首帧画面(I帧)及针对该画面的的变化内容(预测结果),即可恢复一个帧组的全部画面。
I帧具有以下特点:
- 解码时仅用I帧的数据就可重构完整图像,I帧不需要参考其他画面而生成
- I帧是P帧和B帧的参考帧(其质量直接影响到同组中以后各帧的质量)
- 在一组中只有一个I帧,I帧所占数据的信息量比较大
- I帧不需要考虑运动矢量
P帧为自己与帧组内的I帧或其他P帧的残差图编码形成,解码时需要用之前缓存的画面,叠加上本帧残差画面生成最终画面。
P帧具有以下特点:
- P帧是I帧后面相隔1~2帧的编码帧
- P帧采用运动补偿的方法传送它与前面的I或P帧的差值及运动矢量(预测误差)
- P帧属于前向预测的帧间编码,它只参考前面最靠近它的I帧或P帧
B帧是双向预测内插编码帧,B帧记录的是本帧与前后帧的差别,要解码B帧,不仅要取得之前的缓存画面,还要本帧之后的画面,通过前后画面与本帧数据的差异取得最终的画面。
B帧压缩率高,但因为解码时需要前后帧的共同配合,因此可能需要等待更长的解码时间,因为此时后面的帧可能还未接收或解析成功。因为B帧的这个特点,在一些实时性要求高的流媒体传输协议中,会要求编码器去除B帧数据编码,只保留I帧和P帧编码,保证解码的实时性要求。
B帧具有以下特点:
- B帧是双向预测编码帧,B帧是由前面的I或P帧和后面的P帧来进行预测的
- B帧传送的是它与前面的I或P帧和后面的P帧之间的预测误差及运动矢量
- B帧压缩比最高(可达到50倍的压缩率)
帧分组图中的箭头连线,反应了I/P/B帧之间的依赖关系,可以看出,P帧仅依赖I帧,B帧依赖它前后的I帧与P帧
1.2 PTS和DTS
我们继续在帧组概念基础上讨论时间戳,以下图为例,在帧组中因为有P/B帧的存在,使得视频帧的解码顺序和播放顺序存在不一致的情况,先解码的帧可能后播放,而后解码的帧也可能先播放。因此,我们采用解码时间戳DTS和显示时间戳PTS来解决解码时序与播放时序不一致的问题。

图中第一行为视频流的接收时序,其中每个帧都携带了DTS和PTS,ffmpeg会根据这些信息,将解码出来的音视频原始数据,按照最终显示的时序进行重组后,交给调用者显示播放。
这里需要提一下,图中的DTS与PTS值仅用来说明时间戳的工作原理,并不是一个真实的取值,在ffmpeg的返回值中,DTS与PTS的取值也是一个相对值,可以看作每帧图像在时间轴上的投影相对位置,并不直接对应现实世界中的绝对时间,因此,在音视频同步过程中,还需要对时间戳的值进行换算,才能得到每帧图像确切的播放时间。
2、视频同步策略分析
有了时间戳的基础,我们就能确定在什么时候,用多快的速度去播哪一帧了,这样就能完成整个视频的播放了吗?可能仍然不行,原因在于,即使我们能够得到每一个视频及音频帧的显示播放时间,并依次按照指定的时间播放,在理想情况下能够达到音视频同步的目的,但实际上,这种同步状态很难维持太长时间。
有太多的因素,如关键帧接收延迟,线程调度,每帧解码的时间不同等,影响着音视频的同步,在毫秒级别上,这种延迟会随着播放的进行被逐渐放大,进而完全失去同步。因此,我们需要一个机制,能够动态的调节每帧数据的播放,约束音视频帧间的时差,达到一种动态同步的结果。
既然要将原本不同步的音视频帧协调到一起,那么我们需要一个同步的基准,类似于弹钢琴时用到的节拍器一样,左右手都根据同一个节拍有条不紊的弹着。
类似的,在音视频同步中,也需要这样一个时间基准,有3种时间可以作为同步的时间基准,它们分别是系统时间,音频时间和视频时间。我们可选择将视频同步到音频上,将音频同步到视频上,或者将音视频都同步到系统时间上,每种方式的效果会有所不同。
本次内容先介绍将音频同步到视频上的方法,后续的内容会继续介绍其他两种同步方式,并给出最终的方案。
2.1 音频时间戳计算
既然我们选择以音频时间作为同步的时间基准,那么先来看看如何计算音频时间戳。音频时间戳的计算方式和视频时间戳有所差别,通常每个音频帧占用的缓存空间比较小,一般情况下会将多帧音频数据打包到一起发送,如通过rtp等流媒体协议,将多个aac音频帧打包到一起由推流端发送到接收端。
打包好的音频帧通过解封装解析到AVPacket后,会得到一个音频帧组,而这一组音频帧只对应一个时间戳(pkt->pts),这种情况下在解码后,就需要根据音频的采样频率,声道数以及每声道字节数等信息,来估算每个解码后音频采样数据对应的时间了。
另一方面,音频数据的播放是通过回调函数的方式,周期性的将一组音频数据送入声卡中播放的,回忆下我们之前在[ffmpeg播放器实现详解 - 音频播放]中讨论过的内容,每次送入声卡的缓存长度,和解码后音频数据的缓存长度是不一致的,因此需要根据每个packet对应的时间戳,以及采样频率,声道数等信息估算出每次送到声卡中缓存片段的时间值。
下面我们来看下具体的实现。首先看下在VideoState中新增的几个相关字段。
typedef struct VideoState {
...
//video/audio_clock save pts of last decoded frame/predicted pts of next decoded frame
double video_clock;//keep track of how much time has passed according to the video
double audio_clock;
double frame_timer;//视频播放到当前帧时的累计已播放时间
double frame_last_pts;//上一帧图像的显示时间戳,用于在video_refersh_timer中保存上一帧的pts值
double frame_last_delay;//上一帧图像的动态刷新延迟时间
} VideoState;// Since we only have one decoding thread, the Big Struct can be global in case we need it.
audio_clock & video_clock 分别用于追踪音频和视频播放时间的时间戳位置,后面会多次用到。我们在音频解码函数中,增加了时间戳相关的内容,并在解码函数返回前,根据pkt->pts及返回的数据长度,推算出这段音频数据相对于pkt->pts的时间,更新到音频时钟audio_clock上。
从下图中可以看到,解码函数,音频时钟获取函数,解码缓存及时间戳的关系。于此同时,随着解码缓存长度的递增,播放时间呈现出同比线性增长趋势。图中的红线可以看作由pcm采样数据还原出的音频信号。
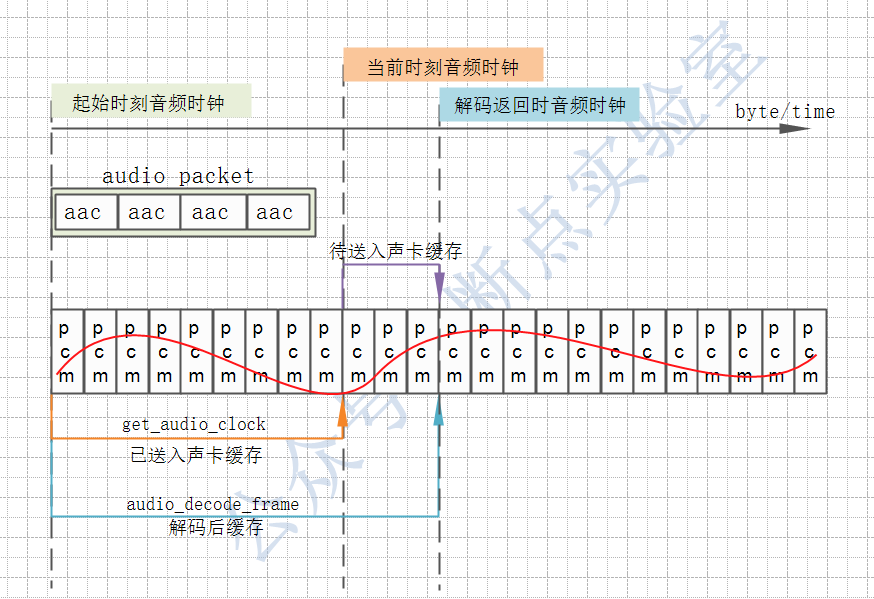
int audio_decode_frame(VideoState *is, double *pts_ptr) {
...
double pts;//音频播放时间戳
...
pts=is->audio_clock;//用每次更新的音频播放时间更新音频PTS
*pts_ptr=pts;
/*---------------------
* 当一个packet中包含多个音频帧时
* 通过[解码后音频原始数据长度]及[采样率]来推算一个packet中其他音频帧的播放时间戳pts
* 采样频率44.1kHz,量化位数16位,意味着每秒采集数据44.1k个,每个数据占2字节
--------------------*/
pcm_bytes=2*is->audio_st->codec->channels;//计算每组音频采样数据的字节数=每个声道音频采样字节数*声道数
/*----更新audio_clock---
* 一个pkt包含多个音频frame,同时一个pkt对应一个pts(pkt->pts)
* 因此,该pkt中包含的多个音频帧的时间戳由以下公式推断得出
* bytes_per_sec=pcm_bytes*is->audio_st->codec->sample_rate
* 从pkt中不断的解码,推断(一个pkt中)每帧数据的pts并累加到音频播放时钟
--------------------*/
is->audio_clock+=(double)data_size/(double)(pcm_bytes*is->audio_st->codec->sample_rate);
// We have data, return it and come back for more later
return data_size;//返回解码数据原始数据长度
}
...
// If update, update the audio clock w/pts
if (pkt->pts != AV_NOPTS_VALUE) {//检查音频播放时间戳
//获得一个新的packet的时候,更新audio_clock,用packet中的pts更新audio_clock(一个pkt对应一个pts)
is->audio_clock=pkt->pts*av_q2d(is->audio_st->time_base);//更新音频已经播的时间
}
}
}
下面是计算音频时间戳的代码,注释的已经很详细了,原理见上面的分析。
double get_audio_clock(VideoState *is) {
double pts=is->audio_clock;//Maintained in the audio thread,取得解码操作完成时的当前播放时间戳
//还未(送入声卡)播放的剩余原始音频数据长度,等于解码后的多帧原始音频数据长度-累计送入声卡的长度
int hw_buf_size=is->audio_buf_size-is->audio_buf_index;//计算当前音频解码数据缓存索引位置
int bytes_per_sec=0;//每秒的原始音频字节数
int pcm_bytes=is->audio_st->codec->channels*2;//每组原始音频数据字节数=声道数*每声道数据字节数
if (is->audio_st) {
bytes_per_sec=is->audio_st->codec->sample_rate*pcm_bytes;//计算每秒的原始音频字节数
}
if (bytes_per_sec) {//检查每秒的原始音频字节数是否有效
pts-=(double)hw_buf_size/bytes_per_sec;//根据送入声卡缓存的索引位置,往前倒推计算当前时刻的音频播放时间戳pts
}
return pts;//返回当前正在播放的音频时间戳
}
2.2 视频同步实现
有了音频时间戳,也就有了音视频同步的基准,下面我们来讨论下音视频同步的策略。
因为声音播放的速度通常恒定,试想下如果把一段一分钟的录音在半分钟内播放完,而且前快后慢,你听到的声音可能就不那么自然了。而视频的播放速度只要维持fps在25帧左右,多一帧或少一帧人眼一般感知不出来,因此,通过将视频同步到音频的方式,可以较好的达到音视频同步的效果,在视频播放超前于音频时,增加视频帧显示的时间,当视频播放滞后于音频时,减少视频帧显示时间,加速视频的刷新速度,通俗的解释就是面多了加水,水多了加面,这就是音视频同步的策略。
本次内容的代码仍以上一篇文章中的代码框架为基础,代码架构及运行时序见[ffmpeg播放器实现详解 - 创建线程]。
video_refresh_timer是视频同步的核心函数,上篇内容中的video_refresh_timer函数实现比较简单,仅以40ms的固定周期对画面进行刷新,本篇中的实现则复杂的多。下面将代码的核心部分贴出来,可以看到,这里比较当前帧与主时钟的时差,并用该时差与一个阈值进行比较,慢了delay设为0尽快显示,快了加倍延迟。
然后将每次计算出的实际延迟时间delay,即下一帧的刷新间隔时间更新到frame_timer上,并根据该值确定下一帧更新的绝对时间(delay本身是一个相对时间)。frame_timer本身是以系统时间为基准的,因此这里要减去此时的系统时间。
ffmpeg的时间戳和同步机制相对复杂,大家可以根据代码的注释,加入调试信息把程序跑一遍,体会其中的原理和细节。
void video_refresh_timer(void *userdata) {
...
// Update delay to sync to audio,取得声音播放时间戳(作为视频同步的参考时间)
if (is->av_sync_type != AV_SYNC_VIDEO_MASTER) {//检查主同步时钟源
ref_clock = get_master_clock(is);//根据主时钟来判断Video播放的快慢,以主时钟为基准时间
diff = vp->pts - ref_clock;//计算图像帧显示与主时钟的时间差
//根据时间差调整播放下一帧的延迟时间,以实现同步 Skip or repeat the frame,Take delay into account
sync_threshold = (delay > AV_SYNC_THRESHOLD) ? delay : AV_SYNC_THRESHOLD;
//判断音视频不同步条件,即[画面-声音]时间差&[画面-画面]时间差<10ms阈值,若>该阈值则为快进模式,不存在音视频同步问题
if (fabs(diff) < AV_NOSYNC_THRESHOLD) {
if (diff <= -sync_threshold) {//慢了delay设为0尽快显示
//下一帧画面显示的时间和当前的声音很近的话加快显示下一帧(即后面video_display显示完当前帧后开启定时器很快去显示下一帧
delay=0;
} else if (diff>=sync_threshold) {//快了加倍延迟
delay=2*delay;
}
}//如果diff(明显)大于AV_NOSYNC_THRESHOLD,即快进的模式了,画面跳动太大,不存在音视频同步的问题了
}
//更新视频播放到当前帧时的已播放时间值(所有图像帧动态播放累计时间值-真实值),frame_timer一直累加在播放过程中我们计算的延时
is->frame_timer+=delay;
//每次计算frame_timer与系统时间的差值(以系统时间为基准时间),将frame_timer与系统时间(绝对时间)相关联的目的
actual_delay=is->frame_timer-(av_gettime()/1000000.0);//Computer the REAL delay
if (actual_delay < 0.010) {//检查绝对时间范围
actual_delay = 0.010;// Really it should skip the picture instead
}
schedule_refresh(is,(int)(actual_delay*1000+0.5));//用绝对时间开定时器去动态显示刷新下一帧
...
}
3、源码编译验证
源码的编译方法和之前的例程完全相同,源码可采用如下Makefile脚本进行编译
tutorial05: tutorial05.c
gcc -o tutorial04 -g3 tutorial05.c -I${FFMPEG_INCLUDE} -I${SDL_INCLUDE} \
-L${FFMPEG_LIB} -lavutil -lavformat -lavcodec -lswscale -lswresample -lz -lm \
`sdl-config --cflags --libs`
clean:
rm -rf tutorial05
执行make命令开始编译,编译完成后,可在源码目录生成名为[tutorial05]的可执行文件。
与ffplay的使用方法类似,执行[tutorial05 url]命令,url可以选择本地视频文件,或媒体流地址。
./tutorial05 ./xxx.mp4
输入Ctrl+C结束程序运行
4、源码清单
源码在上篇内容基础上,主要增加了音频时间戳推算的代码,按照惯例,源码几乎每行都有注释,方便大家调试理解
// tutorial05.c
// A pedagogical video player that really works!
//
// This tutorial was written by Stephen Dranger (dranger@gmail.com).
//
// Code based on FFplay, Copyright (c) 2003 Fabrice Bellard,
// and a tutorial by Martin Bohme (boehme@inb.uni-luebeckREMOVETHIS.de)
// Tested on Gentoo, CVS version 5/01/07 compiled with GCC 4.1.1
//
//
// Updates tested on:
// Mac OS X 10.11.6
// Apple LLVM version 8.0.0 (clang-800.0.38)
//
// Use
//
// $ gcc -o tutorial05 tutorial05.c -lavutil -lavformat -lavcodec -lswscale -lz -lm `sdl-config --cflags --libs`
//
// to build (assuming libavutil/libavformat/libavcodec/libswscale are correctly installed your system).
//
// Run using
//
// $ tutorial05 myvideofile.mpg
//
// to play the video.
#include <libavcodec/avcodec.h>
#include <libavformat/avformat.h>
#include <libavformat/avio.h>
#include <libswscale/swscale.h>
#include <libavutil/avstring.h>
#include <libavutil/time.h>
#include <SDL.h>
#include <SDL_thread.h>
#ifdef __MINGW32__
#undef main // Prevents SDL from overriding main().
#endif
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
#define SDL_AUDIO_BUFFER_SIZE 1024
#define MAX_AUDIO_FRAME_SIZE 192000
#define MAX_AUDIOQ_SIZE (5 * 16 * 1024)
#define MAX_VIDEOQ_SIZE (5 * 256 * 1024)
#define AV_SYNC_THRESHOLD 0.01//前后两帧间的显示时间间隔的最小值0.01s
#define AV_NOSYNC_THRESHOLD 10.0//最小刷新间隔时间10ms
#define FF_ALLOC_EVENT (SDL_USEREVENT)
#define FF_REFRESH_EVENT (SDL_USEREVENT + 1)
#define FF_QUIT_EVENT (SDL_USEREVENT + 2)
#define VIDEO_PICTURE_QUEUE_SIZE 1
SDL_Surface *screen;//SDL绘图表面,A structure that contains a collection of pixels used in software blitting
uint64_t global_video_pkt_pts = AV_NOPTS_VALUE;
/*-------链表节点结构体--------
typedef struct AVPacketList {
AVPacket pkt;//链表数据
struct AVPacketList *next;//链表后继节点
} AVPacketList;
---------------------------*/
//编码数据包队列(链表)结构体
typedef struct PacketQueue {
AVPacketList *first_pkt, *last_pkt;//队列首尾节点指针
int nb_packets;//队列长度
int size;//保存编码数据的缓存长度,size=packet->size
SDL_mutex *qlock;//队列互斥量,保护队列数据
SDL_cond *qready;//队列就绪条件变量
} PacketQueue;
//图像帧结构体
typedef struct VideoPicture {
SDL_Overlay *bmp;//SDL画布overlay
int width, height;//Source height & width
int allocated;//是否分配内存空间,视频帧转换为SDL overlay标识
double pts;//当前图像帧的绝对显示时间戳
} VideoPicture;
typedef struct VideoState {
AVFormatContext *pFormatCtx;//保存文件容器封装信息及码流参数的结构体
AVPacket audio_pkt;//保存从队列中提取的数据包
AVFrame audio_frame;//保存从数据包中解码的音频数据
AVStream *video_st;//视频流信息结构体
AVStream *audio_st;//音频流信息结构体
struct SwsContext *sws_ctx;//描述转换器参数的结构体
AVIOContext *io_context;
PacketQueue videoq;//视频编码数据包队列(编码数据队列,以链表方式实现)
//解码后的图像帧队列(解码数据队列,以数组方式实现),渲染逻辑就会从pictq获取数据,同时解码逻辑又会往pictq写入数据
VideoPicture pictq[VIDEO_PICTURE_QUEUE_SIZE];
int pictq_size, pictq_rindex, pictq_windex;//队列长度,读/写位置索引
SDL_mutex *pictq_lock;//队列读写锁对象,保护图像帧队列数据
SDL_cond *pictq_ready;//队列就绪条件变量
PacketQueue audioq;//音频编码数据包队列(编码数据队列,以链表方式实现)
uint8_t audio_buf[(MAX_AUDIO_FRAME_SIZE*3)/2];//保存解码一个packet后的多帧原始音频数据(解码数据队列,以数组方式实现)
unsigned int audio_buf_size;//解码后的多帧音频数据长度
unsigned int audio_buf_index;//累计送入声卡的长度
uint8_t *audio_pkt_data;//编码数据缓存指针位置
int audio_pkt_size;//缓存中剩余的编码数据长度(是否已完成一个完整的pakcet包的解码,一个数据包中可能包含多个音频编码帧)
int audio_hw_buf_size;
int videoStream, audioStream;//音视频流类型标号
SDL_Thread *parse_tid;//编码数据包解析线程id
SDL_Thread *video_tid;//解码线程id
char filename[1024];//输入文件完整路径名
int quit;//全局退出进程标识,在界面上点了退出后,告诉线程退出
//video/audio_clock save pts of last decoded frame/predicted pts of next decoded frame
double video_clock;//keep track of how much time has passed according to the video
double audio_clock;
double frame_timer;//视频播放到当前帧时的累计已播放时间
double frame_last_pts;//上一帧图像的显示时间戳,用于在video_refersh_timer中保存上一帧的pts值
double frame_last_delay;//上一帧图像的动态刷新延迟时间
} VideoState;// Since we only have one decoding thread, the Big Struct can be global in case we need it.
VideoState *global_video_state;
//数据包队列初始化函数
void packet_queue_init(PacketQueue *q) {
memset(q, 0, sizeof(PacketQueue));//全零初始化队列结构体对象
q->qlock = SDL_CreateMutex();//创建互斥量对象
q->qready = SDL_CreateCond();//创建条件变量对象
}
//向队列中插入数据包
int packet_queue_put(PacketQueue *q, AVPacket *pkt) {
/*-------准备队列(链表)节点对象------*/
AVPacketList *pktlist=av_malloc(sizeof(AVPacketList));//在堆上创建链表节点对象
if (!pktlist) {//检查链表节点对象是否创建成功
return -1;
}
pktlist->pkt = *pkt;//将输入数据包赋值给新建链表节点对象中的数据包对象
pktlist->next = NULL;//链表后继指针为空
// if (av_packet_ref(pkt, pkt) < 0) {
// return -1;
// }
/*---------将新建节点插入队列-------*/
SDL_LockMutex(q->qlock);//队列互斥量加锁,保护队列数据
if (!q->last_pkt) {//检查队列尾节点是否存在(检查队列是否为空)
q->first_pkt = pktlist;//若不存在(队列尾空),则将当前节点作队列为首节点
}else {
q->last_pkt->next = pktlist;//若已存在尾节点,则将当前节点挂到尾节点的后继指针上,并作为新的尾节点
}
q->last_pkt = pktlist;//将当前节点作为新的尾节点
q->nb_packets++;//队列长度+1
q->size += pktlist->pkt.size;//更新队列编码数据的缓存长度
SDL_CondSignal(q->qready);//给等待线程发出消息,通知队列已就绪
SDL_UnlockMutex(q->qlock);//释放互斥量
return 0;
}
//从队列中提取数据包,并将提取的数据包出队列
static int packet_queue_get(PacketQueue *q, AVPacket *pkt, int block) {
AVPacketList *pktlist;//临时链表节点对象指针
int ret;//操作结果
SDL_LockMutex(q->qlock);//队列互斥量加锁,保护队列数据
for (;;) {
if (global_video_state->quit) {//检查退出进程标识
ret = -1;
break;
}//end for if
pktlist = q->first_pkt;//传递将队列首个数据包指针
if (pktlist) {//检查数据包是否为空(队列是否有数据)
q->first_pkt = pktlist->next;//队列首节点指针后移
if (!q->first_pkt) {//检查首节点的后继节点是否存在
q->last_pkt = NULL;//若不存在,则将尾节点指针置空
}
q->nb_packets--;//队列长度-1
q->size -= pktlist->pkt.size;//更新队列编码数据的缓存长度
*pkt = pktlist->pkt;//将队列首节点数据返回
av_free(pktlist);//清空临时节点数据(清空首节点数据,首节点出队列)
ret = 1;//操作成功
break;
} else if (!block) {
ret = 0;
break;
} else {//队列处于未就绪状态,此时通过SDL_CondWait函数等待qready就绪信号,并暂时对互斥量解锁
/*---------------------
* 等待队列就绪信号qready,并对互斥量暂时解锁
* 此时线程处于阻塞状态,并置于等待条件就绪的线程列表上
* 使得该线程只在临界区资源就绪后才被唤醒,而不至于线程被频繁切换
* 该函数返回时,互斥量再次被锁住,并执行后续操作
--------------------*/
SDL_CondWait(q->qready, q->qlock);//暂时解锁互斥量并将自己阻塞,等待临界区资源就绪(等待SDL_CondSignal发出临界区资源就绪的信号)
}
}
SDL_UnlockMutex(q->qlock);//释放互斥量
return ret;
}
//音频解码函数,从缓存队列中提取数据包、解码,并返回解码后的数据长度(对一个完整的packet解码,将解码数据写入audio_buf缓存,并返回多帧解码数据的总长度)
int audio_decode_frame(VideoState *is, double *pts_ptr) {
int coded_consumed_size, data_size=0,pcm_bytes;//每次消耗的编码数据长度[input](len1),输出原始音频数据的缓存长度[output],每组音频采样数据的字节数
AVPacket *pkt = &is->audio_pkt;//保存从队列中提取的数据包
double pts;//音频播放时间戳
for (;;) {
/*--2、从数据包pkt中不断的解码音频数据,直到剩余的编码数据长度<=0---*/
while (is->audio_pkt_size>0) {//检查缓存中剩余的编码数据长度(是否已完成一个完整的pakcet包的解码,一个数据包中可能包含多个音频编码帧)
int got_frame;//解码操作成功标识,成功返回非零值
//解码一帧音频数据,并返回消耗的编码数据长度
coded_consumed_size = avcodec_decode_audio4(is->audio_st->codec, &is->audio_frame, &got_frame, pkt);
if (coded_consumed_size < 0) {//检查是否执行了解码操作
// If error, skip frame.
is->audio_pkt_size = 0;//更新编码数据缓存长度
break;
}
if (got_frame) {//检查解码操作是否成功
//计算解码后音频原始数据长度[output]
data_size = av_samples_get_buffer_size(NULL, is->audio_st->codec->channels,
is->audio_frame.nb_samples, is->audio_st->codec->sample_fmt, 1);
memcpy(is->audio_buf, is->audio_frame.data[0], data_size);//将解码数据复制到输出缓存
}
is->audio_pkt_data += coded_consumed_size;//更新编码数据缓存指针位置
is->audio_pkt_size -= coded_consumed_size;//更新缓存中剩余的编码数据长度
if (data_size<=0) {//检查输出解码数据缓存长度
// No data yet, get more frames
continue;
}
pts=is->audio_clock;//用每次更新的音频播放时间更新音频PTS
*pts_ptr=pts;
/*---------------------
* 当一个packet中包含多个音频帧时
* 通过[解码后音频原始数据长度]及[采样率]来推算一个packet中其他音频帧的播放时间戳pts
* 采样频率44.1kHz,量化位数16位,意味着每秒采集数据44.1k个,每个数据占2字节
--------------------*/
pcm_bytes=2*is->audio_st->codec->channels;//计算每组音频采样数据的字节数=每个声道音频采样字节数*声道数
/*----更新audio_clock---
* 一个pkt包含多个音频frame,同时一个pkt对应一个pts(pkt->pts)
* 因此,该pkt中包含的多个音频帧的时间戳由以下公式推断得出
* bytes_per_sec=pcm_bytes*is->audio_st->codec->sample_rate
* 从pkt中不断的解码,推断(一个pkt中)每帧数据的pts并累加到音频播放时钟
--------------------*/
is->audio_clock+=(double)data_size/(double)(pcm_bytes*is->audio_st->codec->sample_rate);
// We have data, return it and come back for more later
return data_size;//返回解码数据原始数据长度
}
/*-----------------1、从缓存队列中提取数据包------------------*/
if (pkt->data) {//检查数据包是残留编码数据
av_packet_unref(pkt);//释放pkt中保存的编码数据
}
if (is->quit) {//检查退出进程标识
return -1;
}
// Next packet,从队列中提取数据包到pkt
if (packet_queue_get(&is->audioq, pkt, 1) < 0) {
return -1;
}
is->audio_pkt_data = pkt->data;//传递编码数据缓存指针
is->audio_pkt_size = pkt->size;//传递编码数据缓存长度
// If update, update the audio clock w/pts
if (pkt->pts != AV_NOPTS_VALUE) {//检查音频播放时间戳
//获得一个新的packet的时候,更新audio_clock,用packet中的pts更新audio_clock(一个pkt对应一个pts)
is->audio_clock=pkt->pts*av_q2d(is->audio_st->time_base);//更新音频已经播的时间
}
}
}
/*------Audio Callback-------
* 音频输出回调函数,系统通过该回调函数将解码后的pcm数据送入声卡播放,
* 系统通常一次会准备一组缓存pcm数据(减少低速系统i/o次数),通过该回调送入声卡,声卡根据音频pts依次播放pcm数据
* 待送入缓存的pcm数据完成播放后,再载入一组新的pcm缓存数据(每次音频输出缓存为空时,系统就调用此函数填充音频输出缓存,并送入声卡播放)
* When we begin playing audio, SDL will continually call this callback function
* and ask it to fill the audio buffer with a certain number of bytes
* The audio function callback takes the following parameters:
* stream: A pointer to the audio buffer to be filled,输出音频数据到声卡缓存
* len: The length (in bytes) of the audio buffer,缓存长度wanted_spec.samples=SDL_AUDIO_BUFFER_SIZE(1024)
--------------------------*/
void audio_callback(void *userdata, Uint8 *stream, int len) {
VideoState *is = (VideoState *) userdata;//传递用户数据
int wt_stream_len, audio_size;//每次送入声卡的数据长度,解码后的数据长度
double pts;//音频时间戳
while (len > 0) {//检查音频缓存的剩余长度
if (is->audio_buf_index >= is->audio_buf_size) {//检查是否需要执行解码操作
// We have already sent all our data; get more,从缓存队列中提取数据包、解码,并返回解码后的数据长度,audio_buf缓存中可能包含多帧解码后的音频数据
audio_size = audio_decode_frame(is, &pts);
if (audio_size < 0) {//检查解码操作是否成功
// If error, output silence.
is->audio_buf_size = 1024;
memset(is->audio_buf, 0, is->audio_buf_size);//全零重置缓冲区
} else {
is->audio_buf_size = audio_size;//返回packet中包含的原始音频数据长度(多帧)
}
is->audio_buf_index = 0;//初始化累计写入缓存长度
}//end for if
wt_stream_len = is->audio_buf_size - is->audio_buf_index;//计算解码缓存剩余长度
if (wt_stream_len > len) {//检查每次写入缓存的数据长度是否超过指定长度(1024)
wt_stream_len = len;//指定长度从解码的缓存中取数据
}
//每次从解码的缓存数据中以指定长度抽取数据并送入声卡传递给声卡
memcpy(stream, (uint8_t *)is->audio_buf + is->audio_buf_index, wt_stream_len);
len -= wt_stream_len;//更新解码音频缓存的剩余长度
stream += wt_stream_len;//更新缓存写入位置
is->audio_buf_index += wt_stream_len;//更新累计写入缓存数据长度
}//end for while
}
//视频(图像)帧渲染
void video_display(VideoState *is) {
SDL_Rect rect;//SDL矩形对象
VideoPicture *vp;//图像帧结构体指针
float aspect_ratio;//宽度/高度比
int w, h, x, y;//窗口尺寸及起始位置
vp = &is->pictq[is->pictq_rindex];//从图像帧队列(数组)中提取图像帧结构对象
if (vp->bmp) {//检查像素数据指针是否有效
if (is->video_st->codec->sample_aspect_ratio.num == 0) {
aspect_ratio = 0;
} else {
aspect_ratio = av_q2d(is->video_st->codec->sample_aspect_ratio) * is->video_st->codec->width / is->video_st->codec->height;
}
if (aspect_ratio <= 0.0) {
aspect_ratio = (float) is->video_st->codec->width / (float) is->video_st->codec->height;
}
h = screen->h;
w = ((int) rint(h * aspect_ratio)) & -3;
if (w > screen->w) {
w = screen->w;
h = ((int)rint(w / aspect_ratio)) & -3;
}
x = (screen->w - w) / 2;
y = (screen->h - h) / 2;
//设置矩形显示区域
rect.x = x;
rect.y = y;
rect.w = w;
rect.h = h;
SDL_DisplayYUVOverlay(vp->bmp, &rect);//图像渲染
}
}
//创建/重置图像帧,为图像帧分配内存空间
void alloc_picture(void *userdata) {
VideoState *is = (VideoState *) userdata;//传递用户数据
VideoPicture *vp=&is->pictq[is->pictq_windex];//从图像帧队列(数组)中提取图像帧结构对象
if (vp->bmp) {//检查图像帧是否已存在
// We already have one make another, bigger/smaller.
SDL_FreeYUVOverlay(vp->bmp);//释放当前overlay缓存
}
// Allocate a place to put our YUV image on that screen,根据指定尺寸及像素格式重新创建像素缓存区
vp->bmp = SDL_CreateYUVOverlay(is->video_st->codec->width, is->video_st->codec->height, SDL_YV12_OVERLAY, screen);
vp->width = is->video_st->codec->width;//设置图像帧宽度
vp->height = is->video_st->codec->height;//设置图像帧高度
SDL_LockMutex(is->pictq_lock);//锁定互斥量,保护画布的像素数据
vp->allocated = 1;//图像帧像素缓冲区已分配内存
SDL_CondSignal(is->pictq_ready);//给等待线程发出消息,通知队列已就绪
SDL_UnlockMutex(is->pictq_lock);//释放互斥量
}
/*---------------------------
* queue_picture:图像帧插入队列等待渲染
* @is:全局状态参数集
* @pFrame:保存图像解码数据的结构体
* @pts:当前图像帧的绝对显示时间戳
* 1、首先检查图像帧队列(数组)是否存在空间插入新的图像,若没有足够的空间插入图像则使当前线程休眠等待
* 2、在初始化的条件下,队列(数组)中VideoPicture的bmp对象(YUV overlay)尚未分配空间,通过FF_ALLOC_EVENT事件的方法调用alloc_picture分配空间
* 3、当队列(数组)中所有VideoPicture的bmp对象(YUV overlay)均已分配空间的情况下,直接跳过步骤2向bmp对象拷贝像素数据,像素数据在进行格式转换后执行拷贝操作
---------------------------*/
int queue_picture(VideoState *is, AVFrame *pFrame, double pts) {
/*-------1、检查队列是否有插入空间------*/
// Wait until we have space for a new pic
SDL_LockMutex(is->pictq_lock);//锁定互斥量,保护图像帧队列
while (is->pictq_size >= VIDEO_PICTURE_QUEUE_SIZE && !is->quit) {//检查队列当前长度
SDL_CondWait(is->pictq_ready, is->pictq_lock);//线程休眠等待pictq_ready信号
}
SDL_UnlockMutex(is->pictq_lock);//释放互斥量
if (is->quit) {//检查进程退出标识
return -1;
}
/*------2、初始化/重置YUV overlay------*/
// Windex is set to 0 initially.
VideoPicture *vp = &is->pictq[is->pictq_windex];//从图像帧队列中抽取图像帧对象
// Allocate or resize the buffer,检查YUV overlay是否已存在,否则初始化YUV overlay,分配像素缓存空间
if (!vp->bmp || vp->width != is->video_st->codec->width || vp->height != is->video_st->codec->height) {
SDL_Event event;//SDL事件对象
vp->allocated = 0;//图像帧未分配空间
// We have to do it in the main thread.
event.type = FF_ALLOC_EVENT;//指定分配图像帧内存事件
event.user.data1 = is;//传递用户数据
SDL_PushEvent(&event);//发送SDL事件
// Wait until we have a picture allocated.
SDL_LockMutex(is->pictq_lock);//锁定互斥量,保护图像帧队列
while (!vp->allocated && !is->quit) {//检查当前图像帧是否已初始化(为SDL overlay)
SDL_CondWait(is->pictq_ready, is->pictq_lock);//线程休眠等待alloc_picture发送pictq_ready信号唤醒当前线程
}
SDL_UnlockMutex(is->pictq_lock);//释放互斥量
if (is->quit) {//检查进程退出标识
return -1;
}
}
/*-------3、拷贝视频帧到YUV overlay------*/
// We have a place to put our picture on the queue.
// If we are skipping a frame, do we set this to null but still return vp->allocated = 1?
AVFrame pict;//临时保存转换后的图像帧像素,与队列中的元素相关联
if (vp->bmp) {//检查像素数据指针是否有效
SDL_LockYUVOverlay(vp->bmp);//locks the overlay for direct access to pixel data,原子操作,保护像素缓冲区,避免非法修改
// Point pict at the queue.
pict.data[0] = vp->bmp->pixels[0];//将转码后的图像与画布的像素缓冲器关联
pict.data[1] = vp->bmp->pixels[2];
pict.data[2] = vp->bmp->pixels[1];
pict.linesize[0] = vp->bmp->pitches[0];//将转码后的图像扫描行长度与画布像素缓冲区的扫描行长度相关联
pict.linesize[1] = vp->bmp->pitches[2];//linesize-Size, in bytes, of the data for each picture/channel plane
pict.linesize[2] = vp->bmp->pitches[1];//For audio, only linesize[0] may be set
// Convert the image into YUV format that SDL uses,将解码后的图像帧转换为AV_PIX_FMT_YUV420P格式,并拷贝到图像帧队列
sws_scale(is->sws_ctx, (uint8_t const * const *) pFrame->data, pFrame->linesize, 0, is->video_st->codec->height, pict.data, pict.linesize);
SDL_UnlockYUVOverlay(vp->bmp);//Unlocks a previously locked overlay. An overlay must be unlocked before it can be displayed
vp->pts = pts;//传递当前图像帧的绝对显示时间戳
// Now we inform our display thread that we have a pic ready.
if (++is->pictq_windex == VIDEO_PICTURE_QUEUE_SIZE) {//更新并检查当前图像帧队列写入位置
is->pictq_windex = 0;//重置图像帧队列写入位置
}
SDL_LockMutex(is->pictq_lock);//锁定队列读写锁,保护队列数据
is->pictq_size++;//更新图像帧队列长度
SDL_UnlockMutex(is->pictq_lock);//释放队列读写锁
}
return 0;
}
//修改FFmpeg内部退出回调对应的函数
int decode_interrupt_cb(void *opaque) {
return (global_video_state && global_video_state->quit);
}
/*---------------------------
* parse_thread:编码数据包解析线程函数(从视频文件中解析出音视频编码数据单元,一个AVPacket的data通常对应一个NAL)
* 1、直接识别文件格式和间接识别媒体格式
* 2、打开解码器并启动解码线程
* 3、分离音视频媒体包并挂接到相应队列
---------------------------*/
int parse_thread(void *arg) {
VideoState *is = (VideoState *) arg;//传递用户参数
global_video_state = is;//传递全局状态参量结构体
AVFormatContext *pFormatCtx = NULL;//保存文件容器封装信息及码流参数的结构体
AVPacket pkt, *packet = &pkt;//在栈上创建临时数据包对象并关联指针
// Find the first video/audio stream.
is->videoStream=-1;//视频流类型标号初始化为-1
is->audioStream=-1;//音频流类型标号初始化为-1
int video_index = -1;//视频流类型标号初始化为-1
int audio_index = -1;//音频流类型标号初始化为-1
int i;//循环变量
AVDictionary *io_dict = NULL;
AVIOInterruptCB callback;
// Will interrupt blocking functions if we quit!
callback.callback = decode_interrupt_cb;
callback.opaque = is;
if (avio_open2(&is->io_context, is->filename, 0, &callback, &io_dict)) {
fprintf(stderr, "Unable to open I/O for %s\n", is->filename);
return -1;
}
// Open video file,打开视频文件,取得文件容器的封装信息及码流参数
if (avformat_open_input(&pFormatCtx, is->filename, NULL, NULL) != 0) {
return -1; // Couldn't open file.
}
is->pFormatCtx = pFormatCtx;//传递文件容器封装信息及码流参数
// Retrieve stream information,取得文件中保存的码流信息
if (avformat_find_stream_info(pFormatCtx, NULL) < 0) {
return -1; // Couldn't find stream information.
}
// Dump information about file onto standard error,打印pFormatCtx中的码流信息
av_dump_format(pFormatCtx, 0, is->filename, 0);
// Find the first video stream.
for (i = 0; i < pFormatCtx->nb_streams; i++) {//遍历文件中包含的所有流媒体类型(视频流、音频流、字幕流等)
if (pFormatCtx->streams[i]->codec->codec_type==AVMEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO && video_index < 0) {//若文件中包含有视频流
video_index=i;//用视频流类型的标号修改标识,使之不为-1
}
if (pFormatCtx->streams[i]->codec->codec_type==AVMEDIA_TYPE_AUDIO && audio_index < 0) {//若文件中包含有音频流
audio_index=i;//用音频流类型的标号修改标识,使之不为-1
}
}
if (audio_index >= 0) {//检查文件中是否存在音频流
stream_component_open(is, audio_index);//根据指定类型打开音频流
}
if (video_index >= 0) {//检查文件中是否存在视频流
stream_component_open(is, video_index);//根据指定类型打开视频流
}
if (is->videoStream < 0 || is->audioStream < 0) {//检查文件中是否存在音视频流
fprintf(stderr, "%s: could not open codecs\n", is->filename);
goto fail;
}
// Main decode loop.
for (;;) {
if (is->quit) {//检查退出进程标识
break;
}
// Seek stuff goes here,检查音视频编码数据包队列长度是否溢出
if (is->audioq.size > MAX_AUDIOQ_SIZE ||
is->videoq.size > MAX_VIDEOQ_SIZE) {
SDL_Delay(10);
continue;
}
//从文件中依次读取每个图像编码数据包,并存储在AVPacket数据结构中
if (av_read_frame(is->pFormatCtx, packet) < 0) {
if (is->pFormatCtx->pb->error == 0) {
SDL_Delay(100); // No error; wait for user input.
continue;
} else {
break;
}
}
// Is this a packet from the video stream?
if (packet->stream_index == is->videoStream) {//检查数据包是否为视频类型
packet_queue_put(&is->videoq, packet);//向队列中插入数据包
} else if (packet->stream_index == is->audioStream) {//检查数据包是否为音频类型
packet_queue_put(&is->audioq, packet);//向队列中插入数据包
} else {//检查数据包是否为字幕类型
av_packet_unref(packet);//释放packet中保存的(字幕)编码数据
}
}
// All done - wait for it.
while (!is->quit) {
SDL_Delay(100);
}
fail://异常处理
{
SDL_Event event;//SDL事件对象
event.type = FF_QUIT_EVENT;//指定退出事件类型
event.user.data1 = is;//传递用户数据
SDL_PushEvent(&event);//将该事件对象压入SDL后台事件队列
}
return 0;
}
/*---------------------------
* 更新内部视频播放计时器(记录视频已经播时间(video_clock))
* @is:全局状态参数集
* @src_frame:当前(输入的)(待更新的)图像帧对象
* @pts:当前图像帧的显示时间戳
* update the PTS to be in sync
---------------------------*/
double synchronize_video(VideoState *is, AVFrame *src_frame, double pts) {
/*----------检查显示时间戳----------*/
if (pts != 0) {//检查显示时间戳是否有效
// If we have pts, set video clock to it.
is->video_clock = pts;//用显示时间戳更新已播放时间
} else {//若获取不到显示时间戳
// If we aren't given a pts, set it to the clock.
pts = is->video_clock;//用已播放时间更新显示时间戳
}
/*--------更新视频已经播时间--------*/
// Update the video clock,若该帧要重复显示(取决于repeat_pict),则全局视频播放时序video_clock应加上重复显示的数量*帧率
double frame_delay = av_q2d(is->video_st->codec->time_base);//该帧显示完将要花费的时间
// If we are repeating a frame, adjust clock accordingly,若存在重复帧,则在正常播放的前后两帧图像间安排渲染重复帧
frame_delay += src_frame->repeat_pict*(frame_delay*0.5);//计算渲染重复帧的时值(类似于音符时值)
is->video_clock += frame_delay;//更新视频播放时间
// printf("repeat_pict=%d \n",src_frame->repeat_pict);
return pts;//此时返回的值即为下一帧将要开始显示的时间戳
}
//视频解码线程函数
int decode_thread(void *arg) {
VideoState *is=(VideoState*)arg;//传递用户数据
AVPacket pkt, *packet=&pkt;//在栈上创建临时数据包对象并关联指针
int frameFinished;//解码操作是否成功标识,解码帧结束标志frameFinished
// Allocate video frame,为解码后的视频信息结构体分配空间并完成初始化操作(结构体中的图像缓存按照下面两步手动安装)
AVFrame *pFrame = av_frame_alloc();
double pts;//当前桢在整个视频中的(绝对)时间位置
for (;;) {
if (packet_queue_get(&is->videoq,packet,1)<0) {//从队列中提取数据包到packet,并将提取的数据包出队列
// Means we quit getting packets
break;
}
pts = 0;//(绝对)显示时间戳初始化
// global_video_pkt_pts = packet->pts;// Save global pts to be stored in pFrame in first call.
/*-------------------------
* Decode video frame,从封装视频文件中解码完整的一帧数据,并将frameFinished设置为true
* 可能无法通过只解码一个packet就获得一个完整的视频帧frame,可能需要读取多个packet才行,avcodec_decode_video2()会在解码到完整的一帧时设置frameFinished为真
* avcodec_decode_video2会按照dts指定的顺序解码,然后按照正确的显示顺序输出图像帧,并附带图像帧的pts
* 若解码顺序与显示顺序存在不一致,则avcodec_decode_video2会先对当前帧进行缓存(此时frameFinished=0),然后按照正确的顺序输出图像帧
* The decoder bufferers a few frames for multithreaded efficiency
* It is also absolutely required to delay decoding in the case of B frames
* where the decode order may not be the same as the display order.
* Takes input raw video data from frame and writes the next output packet,
* if available, to avpkt. The output packet does not necessarily contain data for the most recent frame,
* as encoders can delay and reorder input frames internally as needed.
-------------------------*/
avcodec_decode_video2(is->video_st->codec, pFrame, &frameFinished, packet);
//取得编码数据包中的显示时间戳PTS(int64_t),并暂时保存在pts(double)中
// if (packet->dts==AV_NOPTS_VALUE && pFrame->opaque && *(uint64_t*)pFrame->opaque!=AV_NOPTS_VALUE) {
// pts = *(uint64_t *)pFrame->opaque;
// } else if (packet->dts != AV_NOPTS_VALUE) {
// pts = packet->dts;
// } else {
// pts = 0;
// }
pts=av_frame_get_best_effort_timestamp(pFrame);//取得编码数据包中的图像帧显示序号PTS(int64_t),并暂时保存在pts(double)中
/*-------------------------
* 在解码线程函数中计算当前图像帧的显示时间戳
* 1、取得编码数据包中的图像帧显示序号PTS(int64_t),并暂时保存在pts(double)中
* 2、根据PTS*time_base来计算当前桢在整个视频中的显示时间戳,即PTS*(1/framerate)
* av_q2d把AVRatioal结构转换成double的函数,
* 用于计算视频源每个图像帧显示的间隔时间(1/framerate),即返回(time_base->num/time_base->den)
-------------------------*/
//根据pts=PTS*time_base={numerator=1,denominator=25}计算当前桢在整个视频中的显示时间戳
pts*=av_q2d(is->video_st->time_base);//time_base为AVRational有理数结构体{num=1,den=25},记录了视频源每个图像帧显示的间隔时间
// Did we get a video frame,检查是否解码出完整一帧图像
if (frameFinished) {
pts = synchronize_video(is, pFrame, pts);//检查当前帧的显示时间戳pts并更新内部视频播放计时器(记录视频已经播时间(video_clock))
if (queue_picture(is, pFrame, pts) < 0) {//将解码完成的图像帧添加到图像帧队列,并记录图像帧的绝对显示时间戳pts
break;
}
}
av_packet_unref(packet);//释放pkt中保存的编码数据
}
av_free(pFrame);//清除pFrame中的内存空间
return 0;
}
// These are called whenever we allocate a frame buffer. We use this to store the global_pts in a frame at the time it is allocated.
int our_get_buffer(struct AVCodecContext *c, AVFrame *pic, int flags) {
int ret = avcodec_default_get_buffer2(c, pic, 0);
uint64_t *pts = av_malloc(sizeof(uint64_t));
*pts = global_video_pkt_pts;
pic->opaque = pts;
return ret;
}
//根据指定类型打开流,找到对应的解码器、创建对应的音频配置、保存关键信息到 VideoState、启动音频和视频线程
int stream_component_open(VideoState *is, int stream_index) {
AVFormatContext *pFormatCtx = is->pFormatCtx;//传递文件容器的封装信息及码流参数
AVCodecContext *codecCtx = NULL;//解码器上下文对象,解码器依赖的相关环境、状态、资源以及参数集的接口指针
AVCodec *codec = NULL;//保存编解码器信息的结构体,提供编码与解码的公共接口,可以看作是编码器与解码器的一个全局变量
SDL_AudioSpec wanted_spec, spec;//wanted_spec是进程请求SDL库的音频参数,spec是SDL库返回给进程它能支持的音频参数,如果请求超过SDL支持返回,则返回最相近参数
AVDictionary *optionsDict = NULL;
//检查输入的流类型是否在合理范围内
if (stream_index<0 || stream_index>=pFormatCtx->nb_streams) {
return -1;
}
// Get a pointer to the codec context for the video stream.
codecCtx = pFormatCtx->streams[stream_index]->codec;//取得解码器上下文
if (codecCtx->codec_type == AVMEDIA_TYPE_AUDIO) {//检查解码器类型是否为音频解码器
// Set audio settings from codec info,SDL_AudioSpec a structure that contains the audio output format
// 创建SDL_AudioSpec结构体,设置音频播放参数
wanted_spec.freq = codecCtx->sample_rate;//采样频率 DSP frequency -- samples per second
wanted_spec.format = AUDIO_S16SYS;//采样格式 Audio data format
wanted_spec.channels = codecCtx->channels;//声道数 Number of channels: 1 mono, 2 stereo
wanted_spec.silence = 0;//无输出时是否静音
//默认每次读音频缓存的大小,推荐值为 512~8192,ffplay使用的是1024 specifies a unit of audio data refers to the size of the audio buffer in sample frames
wanted_spec.samples = SDL_AUDIO_BUFFER_SIZE;
wanted_spec.callback = audio_callback;//设置读取音频数据的回调接口函数 the function to call when the audio device needs more data
wanted_spec.userdata = is;//传递用户数据
/*---------------------------
* 以指定参数打开音频设备,并返回与指定参数最为接近的参数,该参数为设备实际支持的音频参数
* Opens the audio device with the desired parameters(wanted_spec)
* return another specs we actually be using
* and not guaranteed to get what we asked for
--------------------------*/
if (SDL_OpenAudio(&wanted_spec, &spec) < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "SDL_OpenAudio: %s\n", SDL_GetError());
return -1;
}
is->audio_hw_buf_size = spec.size;
}
/*-----------------------
* Find the decoder for the video stream,根据视频流对应的解码器上下文查找对应的解码器,返回对应的解码器(信息结构体)
* The stream's information about the codec is in what we call the "codec context.
* This contains all the information about the codec that the stream is using
-----------------------*/
codec = avcodec_find_decoder(codecCtx->codec_id);
if (!codec || (avcodec_open2(codecCtx, codec, &optionsDict) < 0)) {
fprintf(stderr, "Unsupported codec!\n");
return -1;
}
//检查解码器类型
switch (codecCtx->codec_type) {
case AVMEDIA_TYPE_AUDIO://音频解码器
is->audioStream = stream_index;//音频流类型标号初始化
is->audio_st = pFormatCtx->streams[stream_index];
is->audio_buf_size = 0;//解码后的多帧音频数据长度
is->audio_buf_index = 0;//累计送入声卡的长度
memset(&is->audio_pkt, 0, sizeof(is->audio_pkt));
packet_queue_init(&is->audioq);//音频数据包队列初始化
SDL_PauseAudio(0);//audio callback starts running again,开启音频设备,如果这时候没有获得数据那么它就静音
break;
case AVMEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO://视频解码器
is->videoStream = stream_index;//视频流类型标号初始化
is->video_st = pFormatCtx->streams[stream_index];
//以系统时间为基准,初始化播放到当前帧的已播放时间值,该值为真实时间值、动态时间值、绝对时间值
is->frame_timer=(double)av_gettime()/1000000.0;
is->frame_last_delay = 40e-3;//初始化上一帧图像的动态刷新延迟时间
packet_queue_init(&is->videoq);//视频数据包队列初始化
is->video_tid = SDL_CreateThread(decode_thread, is);//创建解码线程
// Initialize SWS context for software scaling,设置图像转换像素格式为AV_PIX_FMT_YUV420P
is->sws_ctx = sws_getContext(is->video_st->codec->width, is->video_st->codec->height,
is->video_st->codec->pix_fmt, is->video_st->codec->width, is->video_st->codec->height, AV_PIX_FMT_YUV420P, SWS_BILINEAR, NULL, NULL, NULL);
// codecCtx->get_buffer2=our_get_buffer;
break;
default:
break;
}
return 0;
}
/*------取得当前播放音频数据的pts------
* 音视频同步的原理是根据音频的pts来控制视频的播放
* 也就是说在视频解码一帧后,是否显示以及显示多长时间,是通过该帧的PTS与同时正在播放的音频的PTS比较而来的
* 如果音频的PTS较大,则视频准备完毕立即刷新,否则等待
*
* 因为pcm数据采用audio_callback回调方式进行播放
* 对于音频播放我们只能得到写入回调函数前缓存音频帧的pts,而无法得到当前播放帧的pts(需要采用当前播放音频帧的pts作为参考时钟)
* 考虑到音频的大小与播放时间成正比(相同采样率),那么当前时刻正在播放的音频帧pts(位于回调函数缓存中)
* 就可以根据已送入声卡的pcm数据长度、缓存中剩余pcm数据长度,缓存长度及采样率进行推算了
--------------------------------*/
double get_audio_clock(VideoState *is) {
double pts=is->audio_clock;//Maintained in the audio thread,取得解码操作完成时的当前播放时间戳
//还未(送入声卡)播放的剩余原始音频数据长度,等于解码后的多帧原始音频数据长度-累计送入声卡的长度
int hw_buf_size=is->audio_buf_size-is->audio_buf_index;//计算当前音频解码数据缓存索引位置
int bytes_per_sec=0;//每秒的原始音频字节数
int pcm_bytes=is->audio_st->codec->channels*2;//每组原始音频数据字节数=声道数*每声道数据字节数
if (is->audio_st) {
bytes_per_sec=is->audio_st->codec->sample_rate*pcm_bytes;//计算每秒的原始音频字节数
}
if (bytes_per_sec) {//检查每秒的原始音频字节数
pts-=(double)hw_buf_size/bytes_per_sec;//根据送入声卡缓存的索引位置,往前倒推计算当前时刻的音频播放时间戳pts
}
return pts;//返回当前正在播放的音频时间戳
}
//定时器触发的回调函数
static Uint32 sdl_refresh_timer_cb(Uint32 interval, void *opaque) {
SDL_Event event;//SDL事件对象
event.type = FF_REFRESH_EVENT;//视频显示刷新事件
event.user.data1 = opaque;//传递用户数据
SDL_PushEvent(&event);//发送事件
return 0; // 0 means stop timer
}
/*---------------------------
* Schedule a video refresh in 'delay' ms.
* 设置一下帧播放的延迟
* 告诉系统在指定的延时后来推送一个FF_REFRESH_EVENT事件,起到类似于节拍器的作用
* 这个事件将在事件队列里触发sdl_refresh_timer_cb函数的调用
* @delay用于在图像帧的解码顺序与渲染顺序不一致的情况下,调节下一帧的渲染时机
* 从而尽可能的使所有图像帧按照固定的帧率渲染刷新
--------------------------*/
static void schedule_refresh(VideoState *is, int delay) {
SDL_AddTimer(delay, sdl_refresh_timer_cb, is);//在指定的时间(ms)后回调用户指定的函数
}
/*---------------------------
* 显示刷新函数(FF_REFRESH_EVENT响应函数)
* 将视频同步到音频上(声音是连续播放的,因此用画面去同步声音),计算下一帧的延迟时间
* 使用当前帧的PTS和上一帧的PTS差来估计播放下一帧的延迟时间,并根据video的播放速度来调整这个延迟时间
---------------------------*/
void video_refresh_timer(void *userdata) {
VideoState *is=(VideoState*)userdata;//传递用户数据
VideoPicture *vp;//图像帧对象
//delay-前后帧间的显示时间间隔,diff-图像帧显示与音频帧播放间的时间差
//sync_threshold-前后帧间的最小时间差,actual_delay-当前帧-下已帧的显示时间间隔(动态时间、真实时间、绝对时间)
double delay,diff,sync_threshold,actual_delay,ref_clock;//ref_clock-音频时间戳
if (is->video_st) {//检查全局状态参数集中的视频流信息结构体是否有效(是否已加载视频文件)
if (is->pictq_size == 0) {//检查图像帧队列中是否有等待显示刷新的图像
schedule_refresh(is, 1);//若队列为空,则发送显示刷新事件并再次进入video_refresh_timer函数
} else {
vp = &is->pictq[is->pictq_rindex];//从显示队列中取得等待显示的图像帧
//计算当前帧和前一帧显示(pts)的间隔时间(显示时间戳的差值)
delay = vp->pts - is->frame_last_pts;//The pts from last time,前后帧间的时间差
if (delay <= 0 || delay >= 1.0) {//检查时间间隔是否在合理范围
// If incorrect delay, use previous one
delay = is->frame_last_delay;//沿用之前的动态刷新间隔时间
}
// Save for next time
is->frame_last_delay = delay;//保存上一帧图像的动态刷新延迟时间
is->frame_last_pts = vp->pts;//保存上一帧图像的显示时间戳
// Update delay to sync to audio,取得声音播放时间戳(作为视频同步的参考时间)
ref_clock=get_audio_clock(is);//根据Audio clock来判断Video播放的快慢,获取当前播放声音的时间戳
//也就是说在diff这段时间中声音是匀速发生的,但是在delay这段时间frame的显示可能就会有快慢的区别
diff=vp->pts-ref_clock;//计算图像帧显示与音频帧播放间的时间差
//根据时间差调整播放下一帧的延迟时间,以实现同步 Skip or repeat the frame,Take delay into account
sync_threshold=(delay>AV_SYNC_THRESHOLD) ? delay : AV_SYNC_THRESHOLD;//比较前后两帧间的显示时间间隔与最小时间间隔
//判断音视频不同步条件,即音视频间的时间差 & 前后帧间的时间差<10ms阈值,若>该阈值则为快进模式,不存在音视频同步问题
if (fabs(diff)<AV_NOSYNC_THRESHOLD) {
if (diff<=-sync_threshold) {//比较前一帧&当前帧[画面-声音]间的时间间隔与前一帧 & 当前帧[画面-画面]间的时间间隔,慢了,delay设为0
//下一帧画面显示的时间和当前的声音很近的话加快显示下一帧(即后面video_display显示完当前帧后开启定时器很快去显示下一帧
delay=0;
} else if (diff>=sync_threshold) {//比较两帧画面间的显示时间与两帧画面间声音的播放时间,快了,加倍delay
delay=2*delay;
}
}//如果diff(明显)大于AV_NOSYNC_THRESHOLD,即快进的模式了,画面跳动太大,不存在音视频同步的问题了
//更新视频播放到当前帧时的已播放时间值(所有图像帧动态播放累计时间值-真实值),frame_timer一直累加在播放过程中我们计算的延时
is->frame_timer+=delay;
//每次计算frame_timer与系统时间的差值(以系统时间为基准时间),将frame_timer与系统时间(绝对时间)相关联的目的
actual_delay=is->frame_timer-(av_gettime()/1000000.0);//Computer the REAL delay
if (actual_delay < 0.010) {//检查绝对时间范围
actual_delay = 0.010;// Really it should skip the picture instead
}
schedule_refresh(is,(int)(actual_delay*1000+0.5));//用绝对时间开定时器去动态显示刷新下一帧
video_display(is);//刷新当前图像,Show the picture
// Update queue for next picture!
if (++is->pictq_rindex == VIDEO_PICTURE_QUEUE_SIZE) {//更新图像帧队列读索引位置
is->pictq_rindex = 0;//若读索引抵达队列尾,则重置读索引位置
}
SDL_LockMutex(is->pictq_lock);//锁定互斥量,保护画布的像素数据
is->pictq_size--;//更新图像帧队列长度
SDL_CondSignal(is->pictq_ready);//发送队列就绪信号
SDL_UnlockMutex(is->pictq_lock);//释放互斥量
}
} else {//若视频信息获取失败,则经过指定延时(100ms)后重新尝试刷新视图
schedule_refresh(is, 100);
}
}
//入口函数,初始化SDL库,注册SDL消息事件,启动文件解析线程,进入消息循环
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
if (argc<2) {//检查输入参数个数是否正确
fprintf(stderr, "Usage: test <file>\n");
exit(1);
}
av_register_all();// Register all formats and codecs,注册所有多媒体格式及编解码器
VideoState *is=av_mallocz(sizeof(VideoState));//创建全局状态对象
av_strlcpy(is->filename, argv[1], 1024);//复制视频文件路径名
is->pictq_lock = SDL_CreateMutex();//创建编码数据包队列互斥锁对象
is->pictq_ready = SDL_CreateCond();//创建编码数据包队列就绪条件对象
//SDL_Init initialize the Event Handling, File I/O, and Threading subsystems,初始化SDL
if (SDL_Init(SDL_INIT_VIDEO | SDL_INIT_AUDIO | SDL_INIT_TIMER)) {
fprintf(stderr, "Could not initialize SDL - %s\n", SDL_GetError());//initialize the video audio & timer subsystem
exit(1);
}
// Make a screen to put our video,在SDL2.0中SDL_SetVideoMode及SDL_Overlay已经弃用,改为SDL_CreateWindow及SDL_CreateRenderer创建窗口及着色器
#ifndef __DARWIN__
screen = SDL_SetVideoMode(640, 480, 0, 0);//创建SDL窗口及绘图表面,并指定图像尺寸及像素格式
#else
screen = SDL_SetVideoMode(640, 480, 24, 0);//创建SDL窗口及绘图表面,并指定图像尺寸及像素格式
#endif
if (!screen) {//检查SDL(绘图表面)窗口是否创建成功(SDL用绘图表面对象操作窗口)
fprintf(stderr, "SDL: could not set video mode - exiting\n");
exit(1);
}
schedule_refresh(is, 40);//在指定的时间(40ms)后回调用户指定的函数,进行图像帧的显示更新
is->parse_tid = SDL_CreateThread(parse_thread, is);//创建编码数据包解析线程
if (!is->parse_tid) {//检查线程是否创建成功
av_free(is);
return -1;
}
/*-----------------------
* SDL事件(消息)循环
* 播放器通过消息循环机制,不断循环往复的触发(驱动)图像帧渲染操作,完成整个视频文件的渲染
* 整个过程类似于按照指定节拍弹奏钢琴,消息循环机制保证了视频按照固定的节拍(6/8)播放
* 因为存在解码顺序与渲染顺序不一致的情况(解码B帧的情况),视频同步机制保证了在图像在解码后都尽量按照固定节拍播放
* 在每次的消息响应函数video_refresh_timer中,重新计算下一帧的显示时间
* 并通过schedule_refresh指定时间(类似于节拍器作用),触发下一轮的图像帧显示
-----------------------*/
SDL_Event event;//SDL事件(消息)对象
for (;;) {
SDL_WaitEvent(&event);//Use this function to wait indefinitely for the next available event,主线程阻塞,等待事件到来
switch (event.type) {//事件到来后唤醒主线程后,检查事件类型,执行相应操作
case FF_QUIT_EVENT:
case SDL_QUIT://退出进程事件
is->quit = 1;
// If the video has finished playing, then both the picture and audio queues are waiting for more data.
// Make them stop waiting and terminate normally..
SDL_CondSignal(is->audioq.qready);//发出队列就绪信号避免死锁
SDL_CondSignal(is->videoq.qready);
SDL_Quit();
exit(0);
break;
case FF_ALLOC_EVENT://分配overlay事件
alloc_picture(event.user.data1);//分配overlay事件响应函数
break;
case FF_REFRESH_EVENT://视频显示刷新事件
video_refresh_timer(event.user.data1);//视频显示刷新事件响应函数
break;
default:
break;
}
}
return 0;
}
// 著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
// 公众号:断点实验室
// 扫描二维码,关注更多优质原创,内容包括:音视频开发、图像处理、网络、
// Linux,Windows、Android、嵌入式开发等




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号