SSD5_STL简介及在IDE中使用命令行参数
STL = Standard Template Library,标准模板库,STL的目的是标准化组件,这样就不用重新开发,可以使用现成的组件。STL现在是C++的一部分,因此不用额外安装什么。
在C++标准中,STL被组织为下面的13个头文件:<algorithm>、<deque>、<functional>、<iterator>、<vector>、<list>、<map>、<memory>、<numeric>、<queue>、<set>、<stack>和<utility>。
我们现在用到的不多,下面就介绍一下常用的吧
容器vector
说明
构造:
方法:
#include <iostream> #include <vector> using namespace std; typedef vector<int> INTVECTOR;//自定义类型INTVECTOR //测试vector容器的功能 void main(void) { //vec1对象初始为空 INTVECTOR vec1; //vec2对象最初有10个值为6的元素 INTVECTOR vec2(10,6); //vec3对象最初有3个值为6的元素,拷贝构造 INTVECTOR vec3(vec2.begin(),vec2.begin()+3); //声明一个名为i的双向迭代器 INTVECTOR::iterator i; //从前向后显示vec1中的数据 cout<<"vec1.begin()--vec1.end():"<<endl; for (i =vec1.begin(); i !=vec1.end(); ++i) cout << *i << " "; cout << endl; //从前向后显示vec2中的数据 cout<<"vec2.begin()--vec2.end():"<<endl; for (i =vec2.begin(); i !=vec2.end(); ++i) cout << *i << " "; cout << endl; //从前向后显示vec3中的数据 cout<<"vec3.begin()--vec3.end():"<<endl; for (i =vec3.begin(); i !=vec3.end(); ++i) cout << *i << " "; cout << endl; //测试添加和插入成员函数,vector不支持从前插入 vec1.push_back(2);//从后面添加一个成员 vec1.push_back(4); [1] //从vec1第一的位置开始插入vec3的所有成员 vec1.insert(vec1.begin(),vec3.begin(),vec3.end()); cout<<"after push() and insert() now the vec1 is:" <<endl; for (i =vec1.begin(); i !=vec1.end(); ++i) cout << *i << " "; cout << endl; //测试赋值成员函数 vec2.assign(8,1); // 重新给vec2赋值,8个成员的初始值都为1 cout<<"vec2.assign(8,1):" <<endl; for (i =vec2.begin(); i !=vec2.end(); ++i) cout << *i << " "; cout << endl; //测试引用类函数 cout<<"vec1.front()="<<vec1.front()<<endl;//vec1第零个成员 cout<<"vec1.back()="<<vec1.back()<<endl;//vec1的最后一个成员 cout<<"vec1. at(4)="<<vec1. at(4)<<endl;//vec1的第五个成员 cout<<"vec1[4]="<<vec1[4]<<endl; //测试移出和删除 vec1.pop_back();//将最后一个成员移出vec1 vec1.erase(vec1.begin()+1,vec1.end()-2);//删除成员 cout<<"vec1.pop_back() and vec1.erase():" <<endl; for (i =vec1.begin(); i !=vec1.end(); ++i) cout << *i << " "; cout << endl; //显示序列的状态信息 cout<<"vec1.size(): "<<vec1.size()<<endl;//打印成员个数 cout<<"vec1.empty(): "<<vec1.empty()<<endl;//判断vec1是否为空,空则返回1,不空返回0 }
看链表list
1.list构造函数
list<int> L0; // 空链表
list<int> L1(9); // 建一个含个默认值是的元素的链表
list<int> L2(5,1); // 建一个含个元素的链表,值都是
list<int> L3(L2); // 建一个L2的copy链表
list<int> L4(L0.begin(), L0.end());//建一个含L0一个区域的元素
2. assign()分配值,有两个重载
L1.assign(4,3); // L1(3,3,3,3)
L1.assign(++list1.beging(), list2.end()); // L1(2,3)
3.operator= 赋值重载运算符
L1 = list1; // L1(1,2,3)
4. front()返回第一个元素的引用
int nRet = list1.front() // nRet = 1
5. back()返回最后一元素的引用
int nRet = list1.back() // nRet = 3
6. begin()返回第一个元素的指针(iterator)
it = list1.begin(); // *it = 1
7. end()返回最后一个元素的下一位置的指针(list为空时end()=begin())
it = list1.end();
--it; // *it = 3
8.rbegin()返回链表最后一元素的后向指针(reverse_iterator or const)
list<int>::reverse_iterator it = list1.rbegin(); // *it = 3
9. rend()返回链表第一元素的下一位置的后向指针
list<int>::reverse_iterator it = list1.rend(); // *(--riter) = 1
10.push_back()增加一元素到链表尾
list1.push_back(4) // list1(1,2,3,4)
11. push_front()增加一元素到链表头
list1.push_front(4) // list1(4,1,2,3)
12. pop_back()删除链表尾的一个元素
list1.pop_back() // list1(1,2)
13.pop_front()删除链表头的一元素
list1.pop_front() // list1(2,3)
14.clear()删除所有元素
list1.clear(); // list1空了,list1.size() =0
15.erase()删除一个元素或一个区域的元素(两个重载函数)
list1.erase(list1.begin()); // list1(2,3)
list1.erase(++list1.begin(),list1.end()); // list1(1)
16. remove()删除链表中匹配值的元素(匹配元素全部删除)
list对象L1(4,3,5,1,4)
L1.remove(4); // L1(3,5,1);
17.remove_if()删除条件满足的元素(遍历一次链表),参数为自定义的回调函数
// 小于2的值删除
bool myFun(const int& value) { return (value < 2); }
list1.remove_if(myFun); // list1(3)
18.empty()判断是否链表为空
bool bRet = L1.empty(); //若L1为空,bRet = true,否则bRet = false。
19.max_size()返回链表最大可能长度
list<int>::size_type nMax = list1.max_size();// nMax = 1073741823
20.size()返回链表中元素个数
list<int>::size_type nRet = list1.size(); // nRet = 3
21.resize()重新定义链表长度(两重载函数)
list1.resize(5) // list1 (1,2,3,0,0)用默认值填补
list1.resize(5,4) // list1 (1,2,3,4,4)用指定值填补
22.reverse()反转链表:
list1.reverse(); // list1(3,2,1)
23.sort()对链表排序,默认升序(可自定义回调函数)
list对象L1(4,3,5,1,4)
L1.sort(); // L1(1,3,4,4,5)
L1.sort(greater<int>()); // L1(5,4,4,3,1)
再看栈stack
主要有一下几个函数:
empty
语法: bool empty();
如当前堆栈为空,empty() 函数 返回 true 否则返回false.
pop
语法: void pop();
pop() 函数移除堆栈中最顶层元素。
size
语法: size_type size();
size() 函数返当前堆栈中的元素数目。
top
语法: TYPE &top();
top() 函数返回对栈顶元素的引用.
可以通过它访问stack中的每个元素:
i = s.size();
while(i--)
printf("%lf\n",*(&s.top()-i));
//栈 stack支持 empty() size() top() push() pop() #include <stack> #include <vector> #include <list> #include <cstdio> using namespace std; int main() { //可以使用list或vector作为栈的容器,默认是使用deque的。 stack<int, list<int>> a; stack<int, vector<int>> b; int i; //压入数据 for (i = 0; i < 10; i++) { a.push(i); b.push(i); } //栈的大小 printf("%d %d\n", a.size(), b.size()); //取栈项数据并将数据弹出栈 while (!a.empty()) { printf("%d ", a.top()); a.pop(); } putchar('\n'); while (!b.empty()) { printf("%d ", b.top()); b.pop(); } putchar('\n'); return 0; }
#include<iostream> #include<stack> using namespace std; int main(){ stack<int>mys; mys.push(5); mys.push(3); mys.push(8); mys.push(4); mys.push(1); mys.push(2); mys.push(7); while(!mys.empty()){ cout<<mys.top()<<" "; mys.pop(); } cout<<endl; return 0; }
最后是队列queue
queue的基本操作有:
入队,如例:q.push(x); 将x接到队列的末端。
出队,如例:q.pop(); 弹出队列的第一个元素,注意,并不会返回被弹出元素的值。
访问队首元素,如例:q.front(),即最早被压入队列的元素。
访问队尾元素,如例:q.back(),即最后被压入队列的元素。
判断队列空,如例:q.empty(),当队列空时,返回true。
访问队列中的元素个数,如例:q.size()
#include <iostream> #include <queue> using namespace std; class T { public: int x, y, z; T(int a, int b, int c):x(a), y(b), z(c) { } }; bool operator < (const T &t1, const T &t2) { return t1.z < t2.z; // 按照z的顺序来决定t1和t2的顺序 } main() { priority_queue<T> q; q.push(T(4,4,3)); q.push(T(2,2,5)); q.push(T(1,5,4)); q.push(T(3,3,6)); while (!q.empty()) { T t = q.top(); q.pop(); cout << t.x << " " << t.y << " " << t.z << endl; } return 1; }
介绍一下如何在IDE中使用命令行参数
VC++ 6.0
在工作窗口按下Alt+F7进入设置面板
选择选项卡“调试”,程序变量

Eclipse CDT
选择Run As->Run Configurations
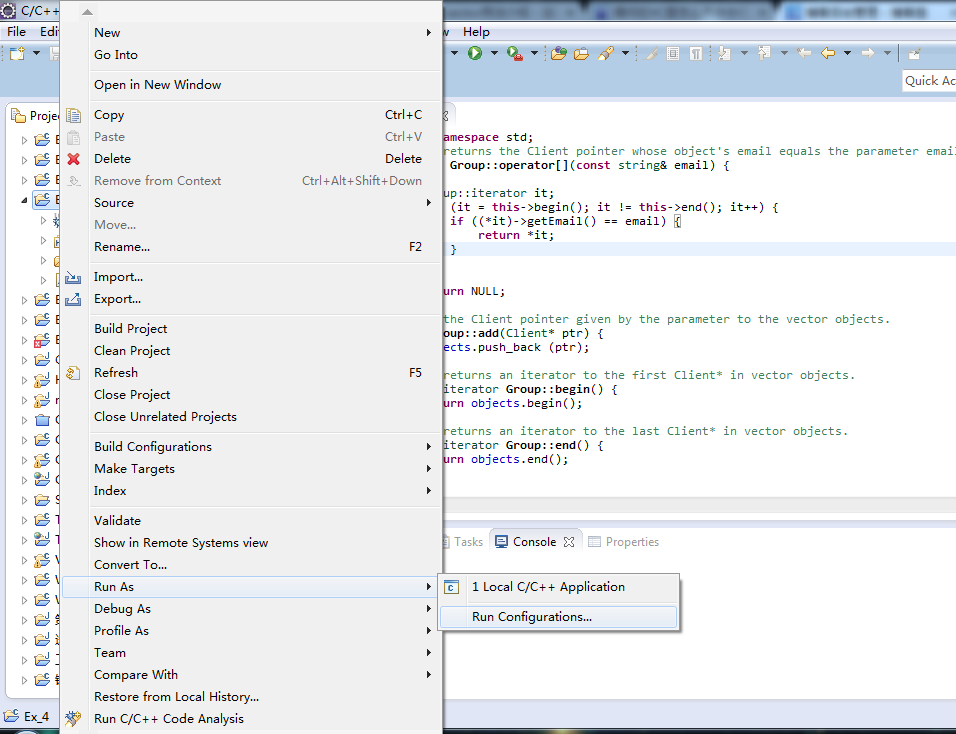
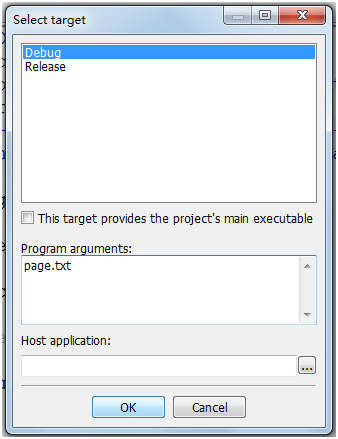
选择Arguments

CodeBlocks
选择 Project->Set programs' arguments...

添加参数
欢迎交流!!!!共同进步。。。

