java Concurrent包学习笔记(七):ConcurrentHashMap
(注意:以下讲解的ConcurrentHashMap是jdk 1.8的)
一、ConcurrentHashMap的数据结构
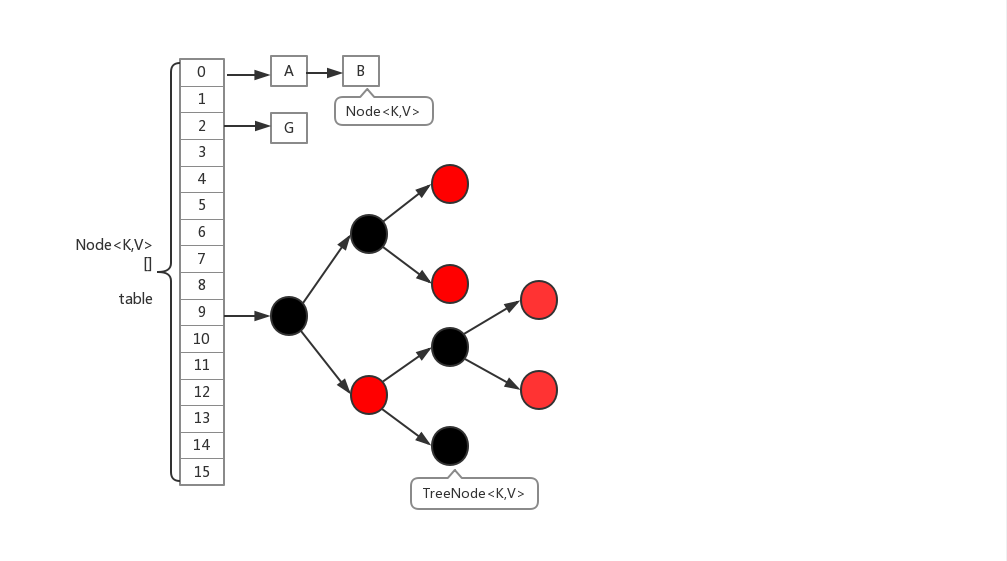
ConcurrentHashMap在1.8中的实现,相比于1.7的版本基本上全部都变掉了。
- 首先,取消了Segment分段锁的数据结构,取而代之的是数组+链表(红黑树)的结构。而对于锁的粒度,调整为对每个数组元素加锁(Node)。
- 然后是定位节点的hash算法被简化了,这样带来的弊端是Hash冲突会加剧。因此在链表节点数量大于8时,会将链表转化为红黑树进行存储。
- 用内置锁synchronized来代替重入锁ReentrantLock。
基本属性如下:
// node数组最大容量:2^30=1073741824 private static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30; // 默认初始值,必须是2的幕数 private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 16; //数组可能最大值,需要与toArray()相关方法关联 static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8; //并发级别,遗留下来的,为兼容以前的版本 private static final int DEFAULT_CONCURRENCY_LEVEL = 16; // 负载因子 private static final float LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f; // 链表转红黑树阀值,> 8 链表转换为红黑树 static final int TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8; //树转链表阀值,小于等于6(tranfer时,lc、hc=0两个计数器分别++记录原bin、新binTreeNode数量,<=UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD 则untreeify(lo)) static final int UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 6; static final int MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY = 64; private static final int MIN_TRANSFER_STRIDE = 16; private static int RESIZE_STAMP_BITS = 16; // 2^15-1,help resize的最大线程数 private static final int MAX_RESIZERS = (1 << (32 - RESIZE_STAMP_BITS)) - 1; // 32-16=16,sizeCtl中记录size大小的偏移量 private static final int RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT = 32 - RESIZE_STAMP_BITS; // forwarding nodes的hash值 static final int MOVED = -1; // 树根节点的hash值 static final int TREEBIN = -2; // ReservationNode的hash值 static final int RESERVED = -3; // 可用处理器数量 static final int NCPU = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors(); //存放node的数组 transient volatile Node<K,V>[] table; /*控制标识符,用来控制table的初始化和扩容的操作,不同的值有不同的含义 *当为负数时:-1代表正在初始化,-N代表有N-1个线程正在 进行扩容 *当为0时:代表当时的table还没有被初始化 *当为正数时:表示初始化或者下一次进行扩容的大小 private transient volatile int sizeCtl;
Node:
Node是ConcurrentHashMap存储结构的基本单元,继承于HashMap中的Entry,用于存储数据,Node数据结构很简单,就是一个链表,但是只允许对数据进行查找,不允许进行修改
static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> { //链表的数据结构 final int hash; final K key; //val和next都会在扩容时发生变化,所以加上volatile来保持可见性和禁止重排序 volatile V val; volatile Node<K,V> next; Node(int hash, K key, V val, Node<K,V> next) { this.hash = hash; this.key = key; this.val = val; this.next = next; } public final K getKey() { return key; } public final V getValue() { return val; } public final int hashCode() { return key.hashCode() ^ val.hashCode(); } public final String toString(){ return key + "=" + val; } //不允许更新value public final V setValue(V value) { throw new UnsupportedOperationException(); } public final boolean equals(Object o) { Object k, v, u; Map.Entry<?,?> e; return ((o instanceof Map.Entry) && (k = (e = (Map.Entry<?,?>)o).getKey()) != null && (v = e.getValue()) != null && (k == key || k.equals(key)) && (v == (u = val) || v.equals(u))); } //用于map中的get()方法,子类重写 Node<K,V> find(int h, Object k) { Node<K,V> e = this; if (k != null) { do { K ek; if (e.hash == h && ((ek = e.key) == k || (ek != null && k.equals(ek)))) return e; } while ((e = e.next) != null); } return null; } }
TreeNode
TreeNode继承与Node,但是数据结构换成了二叉树结构,它是红黑树的数据的存储结构,用于红黑树中存储数据,当链表的节点数大于8时会转换成红黑树的结构,他就是通过TreeNode作为存储结构代替Node来转换成黑红树
static final class TreeNode<K,V> extends Node<K,V> { //树形结构的属性定义 TreeNode<K,V> parent; // red-black tree links TreeNode<K,V> left; TreeNode<K,V> right; TreeNode<K,V> prev; // needed to unlink next upon deletion boolean red; //标志红黑树的红节点 TreeNode(int hash, K key, V val, Node<K,V> next, TreeNode<K,V> parent) { super(hash, key, val, next); this.parent = parent; } Node<K,V> find(int h, Object k) { return findTreeNode(h, k, null); } //根据key查找 从根节点开始找出相应的TreeNode, final TreeNode<K,V> findTreeNode(int h, Object k, Class<?> kc) { if (k != null) { TreeNode<K,V> p = this; do { int ph, dir; K pk; TreeNode<K,V> q; TreeNode<K,V> pl = p.left, pr = p.right; if ((ph = p.hash) > h) p = pl; else if (ph < h) p = pr; else if ((pk = p.key) == k || (pk != null && k.equals(pk))) return p; else if (pl == null) p = pr; else if (pr == null) p = pl; else if ((kc != null || (kc = comparableClassFor(k)) != null) && (dir = compareComparables(kc, k, pk)) != 0) p = (dir < 0) ? pl : pr; else if ((q = pr.findTreeNode(h, k, kc)) != null) return q; else p = pl; } while (p != null); } return null; } }
TreeBin
TreeBin从字面含义中可以理解为存储树形结构的容器,而树形结构就是指TreeNode,所以TreeBin就是封装TreeNode的容器,它提供转换黑红树的一些条件和锁的控制
static final class TreeBin<K,V> extends Node<K,V> { //指向TreeNode列表和根节点 TreeNode<K,V> root; volatile TreeNode<K,V> first; volatile Thread waiter; volatile int lockState; // 读写锁状态 static final int WRITER = 1; // 获取写锁的状态 static final int WAITER = 2; // 等待写锁的状态 static final int READER = 4; // 增加数据时读锁的状态 /** * 初始化红黑树 */ TreeBin(TreeNode<K,V> b) { super(TREEBIN, null, null, null); this.first = b; TreeNode<K,V> r = null; for (TreeNode<K,V> x = b, next; x != null; x = next) { next = (TreeNode<K,V>)x.next; x.left = x.right = null; if (r == null) { x.parent = null; x.red = false; r = x; } else { K k = x.key; int h = x.hash; Class<?> kc = null; for (TreeNode<K,V> p = r;;) { int dir, ph; K pk = p.key; if ((ph = p.hash) > h) dir = -1; else if (ph < h) dir = 1; else if ((kc == null && (kc = comparableClassFor(k)) == null) || (dir = compareComparables(kc, k, pk)) == 0) dir = tieBreakOrder(k, pk); TreeNode<K,V> xp = p; if ((p = (dir <= 0) ? p.left : p.right) == null) { x.parent = xp; if (dir <= 0) xp.left = x; else xp.right = x; r = balanceInsertion(r, x); break; } } } } this.root = r; assert checkInvariants(root); } ...... }
ForwardingNode:
临时节点(扩容时使用)
static final class ForwardingNode<K,V> extends Node<K,V> { final Node<K,V>[] nextTable; ForwardingNode(Node<K,V>[] tab) { super(MOVED, null, null, null); this.nextTable = tab; } Node<K,V> find(int h, Object k) { // loop to avoid arbitrarily deep recursion on forwarding nodes outer: for (Node<K,V>[] tab = nextTable;;) { Node<K,V> e; int n; if (k == null || tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0 || (e = tabAt(tab, (n - 1) & h)) == null) return null; for (;;) { int eh; K ek; if ((eh = e.hash) == h && ((ek = e.key) == k || (ek != null && k.equals(ek)))) return e; if (eh < 0) { if (e instanceof ForwardingNode) { tab = ((ForwardingNode<K,V>)e).nextTable; continue outer; } else return e.find(h, k); } if ((e = e.next) == null) return null; } } } }
构造函数:
public ConcurrentHashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor, int concurrencyLevel) { if (!(loadFactor > 0.0f) || initialCapacity < 0 || concurrencyLevel <= 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException(); if (initialCapacity < concurrencyLevel) // Use at least as many bins initialCapacity = concurrencyLevel; // as estimated threads long size = (long)(1.0 + (long)initialCapacity / loadFactor); int cap = (size >= (long)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ? MAXIMUM_CAPACITY : tableSizeFor((int)size); this.sizeCtl = cap; }
在创建ConcurrentHashMap时,并没有初始化table[]数组,只对Map容量,并发级别等做了赋值操作。
二、put方法
public V put(K key, V value) { return putVal(key, value, false); } final V putVal(K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) { if (key == null || value == null) throw new NullPointerException(); int hash = spread(key.hashCode()); int binCount = 0; for (Node<K,V>[] tab = table;;) { Node<K,V> f; int n, i, fh; if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)// 若table[]未创建,则初始化 tab = initTable(); else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i = (n - 1) & hash)) == null) {// table[i]后面无节点时,直接创建Node(无锁操作) if (casTabAt(tab, i, null, new Node<K,V>(hash, key, value, null))) break; // no lock when adding to empty bin } else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED)// 如果当前正在扩容,则帮助扩容并返回最新table[] tab = helpTransfer(tab, f); else {// 在链表或者红黑树中追加节点 V oldVal = null; synchronized (f) {// 这里并没有使用ReentrantLock,说明synchronized已经足够优化了 if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) { if (fh >= 0) {// 如果为链表结构 binCount = 1; for (Node<K,V> e = f;; ++binCount) { K ek; if (e.hash == hash && ((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek)))) {// 找到key,替换value oldVal = e.val; if (!onlyIfAbsent) e.val = value; break; } Node<K,V> pred = e; if ((e = e.next) == null) {// 在尾部插入Node pred.next = new Node<K,V>(hash, key, value, null); break; } } } else if (f instanceof TreeBin) {// 如果为红黑树 Node<K,V> p; binCount = 2; if ((p = ((TreeBin<K,V>)f).putTreeVal(hash, key, value)) != null) { oldVal = p.val; if (!onlyIfAbsent) p.val = value; } } } } if (binCount != 0) { if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD)// 到达阀值,变为红黑树结构 treeifyBin(tab, i); if (oldVal != null) return oldVal; break; } } } addCount(1L, binCount); return null; }
- 如果没有初始化就先调用initTable()方法来进行初始化过程
- 如果没有hash冲突就直接CAS插入
- 如果还在进行扩容操作就先进行扩容
- 如果存在hash冲突,就加锁来保证线程安全,这里有两种情况,一种是链表形式就直接遍历到尾端插入,一种是红黑树就按照红黑树结构插入,
- 最后一个如果该链表的数量大于阈值8,就要先转换成黑红树的结构,break再一次进入循环
- 如果添加成功就调用addCount()方法统计size,并且检查是否需要扩容
在并发处理中使用的是乐观锁,当有冲突的时候才进行并发处理。使用的是CAS机制Compare and Swap,可以参考:https://blog.csdn.net/ls5718/article/details/52563959
三、get方法
public V get(Object key) { Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> e, p; int n, eh; K ek; int h = spread(key.hashCode());// 定位到table[]中的i if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 && (e = tabAt(tab, (n - 1) & h)) != null) {// 若table[i]存在 if ((eh = e.hash) == h) {// 比较链表头部 if ((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek))) return e.val; } else if (eh < 0)// 若为红黑树,查找树 return (p = e.find(h, key)) != null ? p.val : null; while ((e = e.next) != null) {// 循环链表查找 if (e.hash == h && ((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek)))) return e.val; } } return null;// 未找到
}
- 首先定位到table[]中的i。
- 若table[i]存在,则继续查找。
- 首先比较链表头部,如果是则返回。
- 然后如果为红黑树,查找树。
- 最后再循环链表查找。
get操作上面并没有加锁。所以在多线程操作的过程中,并不能完全的保证一致性。这里和1.7当中类似,是弱一致性的体现。
get没有加锁的话,ConcurrentHashMap是如何保证读到的数据不是脏数据的呢?
get操作可以无锁是由于Node的元素val和指针next是用volatile修饰的,在多线程环境下线程A修改结点的val或者新增节点的时候是对线程B可见的。
- 总结下来:
- 第一:使用volatile关键字会强制将修改的值立即写入主存;
- 第二:使用volatile关键字的话,当线程2进行修改时,会导致线程1的工作内存中缓存变量的缓存行无效(反映到硬件层的话,就是CPU的L1或者L2缓存中对应的缓存行无效);
- 第三:由于线程1的工作内存中缓存变量的缓存行无效,所以线程1再次读取变量的值时会去主存读取。




