mysql的查询以及索引和存储引擎
一.mysql的查询
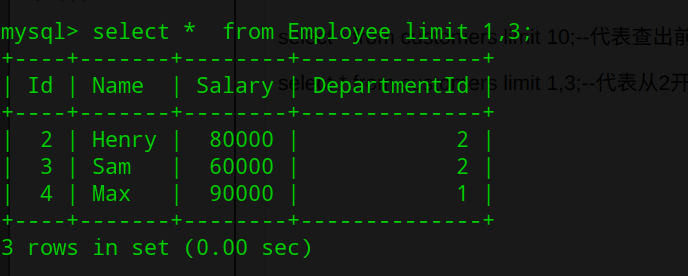
1.limit查询用法
select * from Employee limit 10;--代表查出前10条数据,1-10
select * from Employee limit 1,3;--代表从2开始查询三条,即id 为2,3,4的数据
2.in 查询用法
select * from Employee where name in ('Henry','Max');

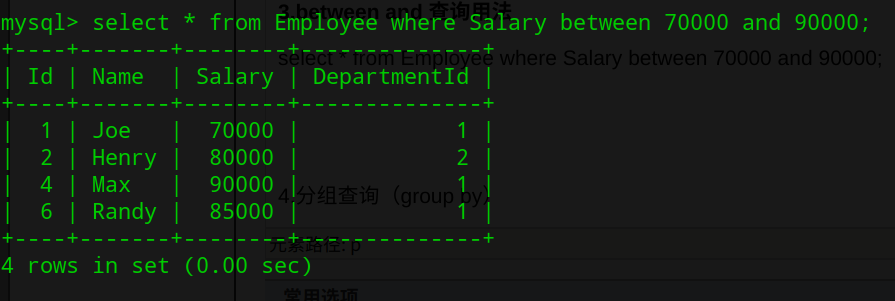
3.between and 查询用法
select * from Employee where Salary between 70000 and 90000;
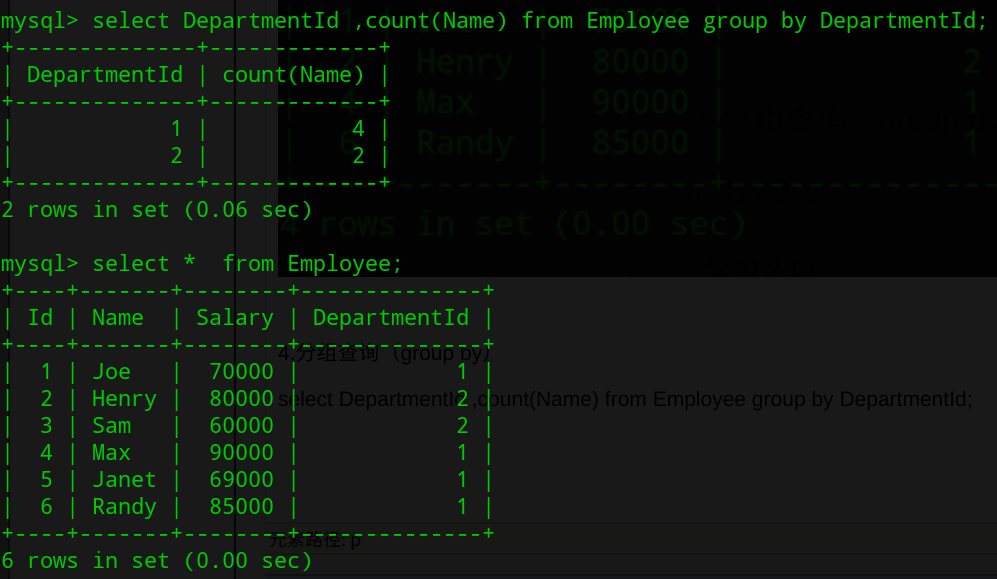
4.分组查询(group by)
select DepartmentId ,count(Name) from Employee group by DepartmentId;
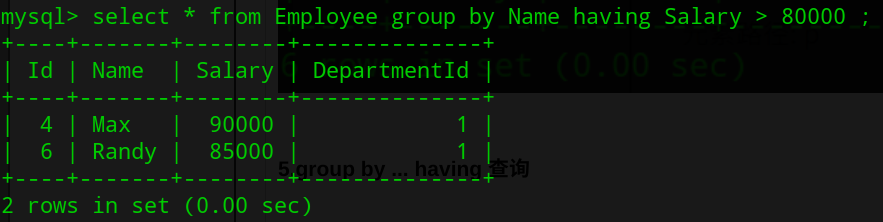
5.group by ... having 查询
select * from Employee group by Name having Salary > 80000;
6.max查询用法
Employee 表包含所有员工信息,每个员工有其对应的 Id, salary 和 department Id。
+----+-------+--------+--------------+
| Id | Name | Salary | DepartmentId |
+----+-------+--------+--------------+
| 1 | Joe | 70000 | 1 |
| 2 | Henry | 80000 | 2 |
| 3 | Sam | 60000 | 2 |
| 4 | Max | 90000 | 1 |
+----+-------+--------+--------------+
Department 表包含公司所有部门的信息。
+----+----------+
| Id | Name |
+----+----------+
| 1 | IT |
| 2 | Sales |
+----+----------+
编写一个 SQL 查询,找出每个部门工资最高的员工。例如,根据上述给定的表格,Max 在 IT 部门有最高工资,Henry 在 Sales 部门有最高工资。
+------------+----------+--------+
| Department | Employee | Salary |
+------------+----------+--------+
| IT | Max | 90000 |
| Sales | Henry | 80000 |
+------------+----------+--------+
解法1:
select b.Name as Department,a.Name as Employee, max(Salary) as Salary
from Employee a , Department b
where a.DepartmentId = b.Id
group by Department;
解法2:
select b.Name as Department,a.Name as Employee, max(Salary) as Salary
from Employee a inner join Department b
on a.DepartmentId = b.Id
group by Department;
7.left join (左连接,以左表为主)
8.right join(右连接,以右表为主)
9.inner join (2表取交集)
10.union (查询结果去重)
11.union all (查询结果不去重)
12.排序 order by
13.模糊查询 like '% %'
14.取top3的查询
Employee 表包含所有员工信息,每个员工有其对应的 Id, salary 和 department Id 。
+----+-------+--------+--------------+
| Id | Name | Salary | DepartmentId |
+----+-------+--------+--------------+
| 1 | Joe | 70000 | 1 |
| 2 | Henry | 80000 | 2 |
| 3 | Sam | 60000 | 2 |
| 4 | Max | 90000 | 1 |
| 5 | Janet | 69000 | 1 |
| 6 | Randy | 85000 | 1 |
+----+-------+--------+--------------+
Department 表包含公司所有部门的信息。
+----+----------+
| Id | Name |
+----+----------+
| 1 | IT |
| 2 | Sales |
+----+----------+
编写一个 SQL 查询,找出每个部门工资前三高的员工。例如,根据上述给定的表格,查询结果应返回:
+------------+----------+--------+
| Department | Employee | Salary |
+------------+----------+--------+
| IT | Max | 90000 |
| IT | Randy | 85000 |
| IT | Joe | 70000 |
| Sales | Henry | 80000 |
| Sales | Sam | 60000 |
+------------+----------+--------+笨解法:
(select c.Department,c.Employee,c.Salary
from
(select b.Name as Department,a.Name as Employee, a.Salary
from Employee a
left join Department b
on a.DepartmentId = b.Id)c
where c.Department='IT' order by c.Salary desc limit 3)
union all
(select c.Department,c.Employee,c.Salary
from
(select b.Name as Department,a.Name as Employee, a.Salary
from Employee a
left join Department b
on a.DepartmentId = b.Id)c
where c.Department='Sales' order by c.Salary desc limit 3);
二.索引
1.索引的分类和创建
普通,无限制,index
唯一,必须唯一,unique index,可以有空值
主键,特殊的唯一索引,不允许有空值
组合,多个字段上
全文,full text ,一般用的少
一般用唯一和主键比较多
create table t(id int not null ,title char(10), index titile_index(10));
alter table t add index id_index (id);
drop index id_index;
create index d_index on t(id);
三.慢查询
1.打开慢查询配置
修改此文件:vim /etc/mysql/mysql.conf.d/mysqld.cnf
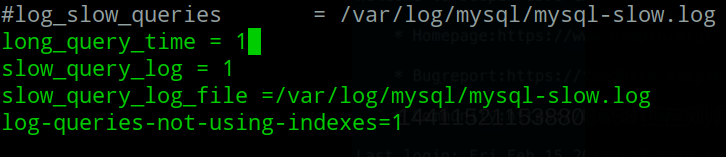
long_query_time =1 :指sql查询时间超过1s的
slow_query_log =1 :指慢查询开启
slow_query_log_file :指慢查询的日志路径
log-queries-not-using-indexes=1:指未创建索引的查询
之后;service mysql restart(重启mysql服务)
查看慢查询是否已开启:
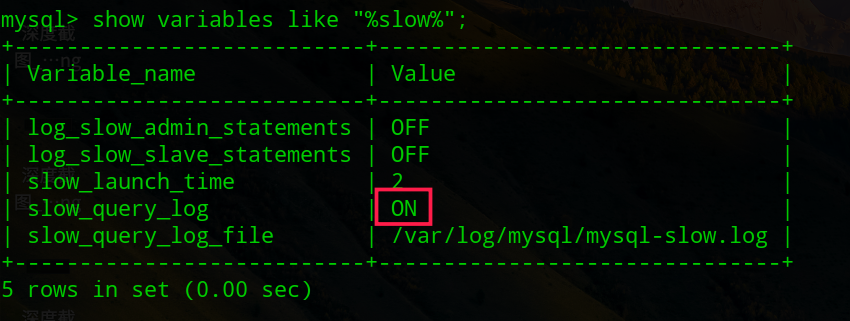
2.查看慢查询的日志
方法1.vim /var/log/mysql/mysql-slow.log
方法2.在此路径:cd /var/log/mysql 下执行 mysqldumpslow mysql-slow.log
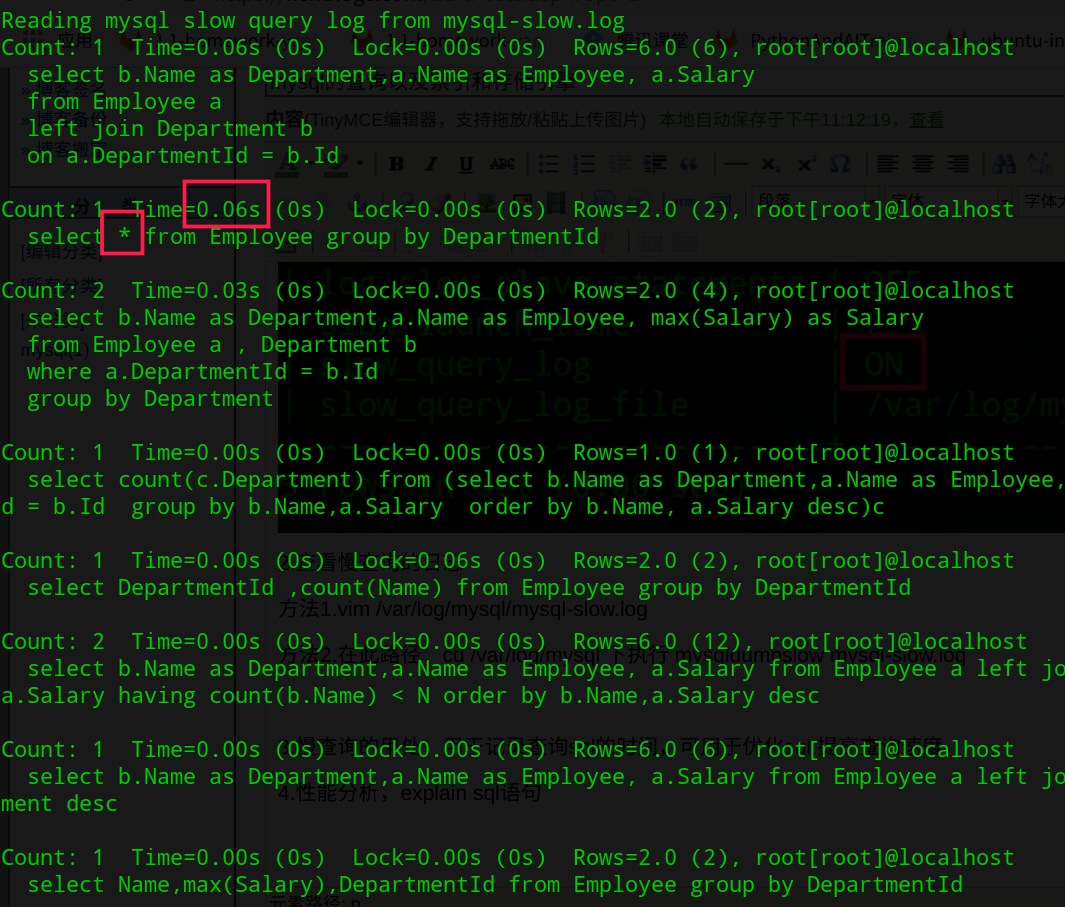
3.慢查询的用处:用于记录查询sql的时间,可用于优化sql,提高查询速度
4.性能分析,explain sql语句
四.存储引擎
MyISAM
它不支持事务,也不支持外键,尤其是访问速度快,对事务完整性没有要求或者以SELECT、INSERT为主的应用基本都可以使用这个引擎来创建表。
每个MyISAM在磁盘上存储成3个文件,其中文件名和表名都相同,但是扩展名分别为:
.frm(存储表定义)
.MYD(MYData,存储数据)
.MYI(MYIndex,存储索引)
InnoDB
支持事务,查询速度相对于MyISAM慢,每个MyISAM在磁盘上存储成3个文件,其中文件名和表名都相同,但是扩展名分别为:
.frm(存储表定义)
.ibd(存储数据和索引)
索引和数据储存在一个区域,类似于超市分区,水果,蔬菜,肉类等,所以查询速度没那么快
锁:
MyISAM:支持表级锁
InnoDB:支持行级锁 --InnoDB支持并发量大





