C语言指针的应用场景
C语言指针的应用场景
指针是C语言的精华和灵魂,不懂指针,基本等同于不会C语言。掌握指针,让学会C语言不再成为梦想而成为现实。
指针基本上有三大类:
- 指向数据的指针
- 指向函数的指针
- 泛型指针(
void *)
指针的应用场景可以分为以下10类:
- 1. 与函数相关的使用
- 1.1 在函数中用作输出型参数,产生副作用(更新被调用函数中的局部变量的值)
- 1.2 在函数中用作输出型参数,用于返回多个值
- 1.3 在函数中用作输入型参数,指向符合类型,避免传值的副作用(性能损耗)
- 1.4 用作函数返回值,返回一个左值
- 1.5 用于指向函数的函数指针,使用函数指针调用回调函数
- 2. 用于指向堆内存
- 3. 与`void`配合使用,用`void*`来表示一个泛型指针
- 4. 用于指向数组名(数组指针)
- 5. 用于指向字符串常量(字符串常量指针)
- 6. 在数据结构中,用作链式存储
1. 与函数相关的使用
1.1 在函数中用作输出型参数,产生副作用(更新被调用函数中的局部变量的值)
#include<stdio.h>
void demo(int *arr, int size, int *max){//计算数组最大值
*max = arr[0];
for(int i=1;i<size;i++){
if (arr[i] > *max)
*max=arr[i];
}
}
int main(){
int max, arr[5] = {12, 23, 34, 45, 54};
demo(arr, 5, &max);
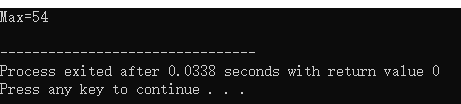
printf("Max=%d\n",max);
return 0;
}
结果:
1.2 在函数中用作输出型参数,用于返回多个值
#include<stdio.h>
#include<math.h>
int equationSolve(double a, double b, double c,double *x1, double *x2){
int delta = a*a - 4*a*c;
if(delta >= 0){
*x1 = (-b + sqrt(delta))/2*a;
*x2 = (-b - sqrt(delta))/2*a;
return 1;
}
else
return 0;
}
int main(void){
double x1, x2;
if(equationSolve(1,3,-14,&x1,&x2)){
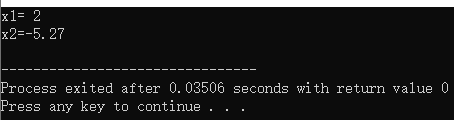
printf("x1=%2.f\nx2=%.2f\n", x1,x2);
}
else{
printf("无实根!\n");
}
return 0;
}
结果:
1.3 在函数中用作输入型参数,指向复合类型,避免传值的副作用(性能损耗)
#include<stdio.h>
typedef struct Inventory{
int sku;
char name[36];
char unit[12];
char suppler[48];
double price;
double stock;
}Inven;
void demo(const Inven *p){
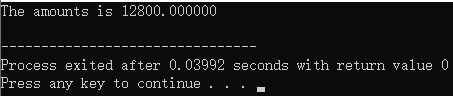
printf("The amounts is %f\n",p->price*(*p).stock);
}
int main(){
Inven inven = {123, "carban fibre","kg","uc",128, 100
};
demo(&inven);
return 0;
}
结果:
1.4 用作函数返回值,返回一个左值
#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void printIntArray(void** array, size_t length) {
printf("Array at %p\n", array);
while (length--) {
printf(" [%zu] at %p -> %p", length, array + length, *(array + length));
if (*(array + length)) {
printf(" -> %d", *(int*)*(array + length));
}
printf("\n");
}
}
void* getElement(void** array, size_t index) {
return *(array + index);
}
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
const size_t n = 5;
size_t i;
/* n element array */
void** test = malloc(sizeof(void*) * n);
i = n;
while (i--) {
*(test + i) = NULL;
}
/* Set element [1] */
int testData = 123;
printf("testData at %p -> %d\n", &testData, testData);
*(test + 1) = (void*)&testData;
printIntArray(test, n);
/* Prints 123, as expected */
printf("Array[1] = %d\n", *(int*)getElement(test, 1));
getchar();
return 0;
}
该实例报错(需纠正)
1.5 用于指向函数的函数指针,使用函数指针调用回调函数
//通用的冒泡排序函数的应用
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
template <class T>
void sort(T a[], int size, bool (*f)(T,T));
bool increaseInt(int x, int y){return x<y;
}
bool decreaseInt(int x, int y){return x>y;
}
bool increaseString(char *x, char *y){return strcmp(x, y)<0;}
bool decreaseString(char *x, char *y){return strcmp(x, y)>0;}
int main(){
int a[] = {3,1,4,2,5,8,6,7,0,9},i;
char *b[] = {"aaa", "bbb", "fff", "ttt","hhh", "ddd","ggg","www","rrr","vvv"};
sort(a, 10, increaseInt);
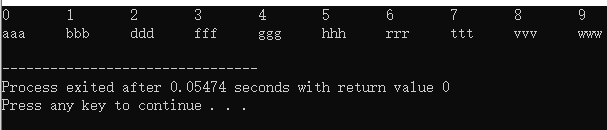
for(i = 0;i<10;++i) cout<<a[i]<<"\t";
cout<<endl;
sort(b, 10, increaseString);
for(i=0;i<10;i++) cout<<b[i]<<"\t";
cout<<endl;
while(1);
return 0;
}
// 通用的冒泡排序函数
template <class T>
void sort(T a[], int size, bool (*f)(T,T))
{
bool flag;
int i, j;
for (i = 1; i < size; ++i) {
flag = false;
for (j = 0; j <size - i; ++j) {
if (f(a[j+1], a[j])) {
T tmp = a[j];
a[j] = a[j+1];
a[j+1] = tmp;
flag = true;
}
}
if (!flag) break;
}
}
结果:
2. 用于指向堆内存
实质是通过库函数(malloc.h)返回void*指针
#include<stdio.h>
#include<malloc.h>
int** demo(int r, int c){
int **ap = (int**)malloc(sizeof(int*)*r);
for(int i=0;i<c;i++){
ap[i] = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*c);
}
return ap;
}
int main(){
int r = 3,c = 5;
int ** ap = demo(r, c);
int i, j;
for(i = 0;i<r;i++){
for(j=0;j<c;j++){
ap[i][j] = (i+1)*(j+1);
}
}
for(i=0;i<r;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<c;j++)
{
printf("%2d ",ap[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
结果:
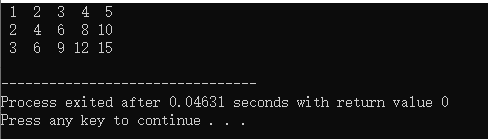
3. 与void配合使用,用void*来表示一个泛型指针
# include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
int swap2(void *x, void *y, int size){
void *tmp;
if((tmp=malloc(size)) == NULL)
return -1;
memcpy(tmp,x, size);
memcpy(x,y,size);
memcpy(y,tmp,size);
free(tmp);
return 0;
}
int main(){
int a = 3, b= 4;
swap2(&a, &b, sizeof(int));
printf("%d %d\n",a, b);
double c = 3, d = 4;
swap2(&c, &d, sizeof(double));
printf("%f %f\n", c, d);
return 0;
}
结果:
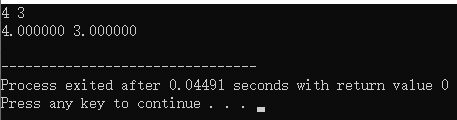
4. 用于指向数组名(数组指针)
#include<stdio.h>
void funcP(int *p, int r, int c){
for(int i=0;i<r*c;i++)
printf((i+1)%(r+1) ==0?"%2d\n":"%2d ",*p++);
printf("\n");
}
void funcAp(int (*p)[4], int r, int c){
for(int i=0;i<r;i++){
for(int j=0;j<c;j++)
printf("%2d ",*(*(p+i)+j));
printf("\n");
}
printf("\n");
}
void funcApp(int (*p)[3][4], int r, int c){
for(int i =0;i<r;i++){
for(int j=0;j<c;j++)
printf("%2d ",*(*(*p+i)+j));
printf("\n");
}
printf("\n");
}
int main(){
int arr[3][4] = {0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11};
int size = sizeof arr /sizeof *arr;
funcP((int*)arr,3,4);
funcAp(arr,3,4);
funcApp(&arr,3,4);
return 0;
}
结果:
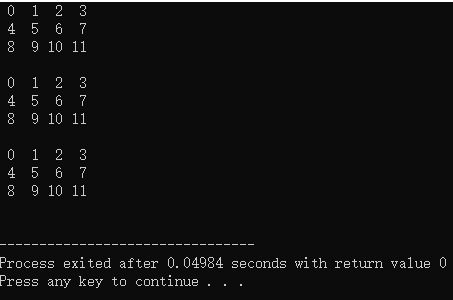
5. 用于指向一个字符串常量(字符串常量指针)
const char* demo(){
const char *sp = "hello";
return sp;
}
关于字符数组和字符指针可以如下图所示:

在字符指针数组,数组元素是一个字符指针,用于指向一个字符串常量,如:
char *pMonth[] = {"January", "February", "March", "April", "May", "June", "July", "August", "September", "October", "November", "December"};
char *week[10] = { "Mon","Tue","Wed","Thu","Fri","Sat","Sun"};
char* color[]={"红-red","橙-orange","黄-yellow","绿-green","青-cyan","蓝-blue","紫-purple"};
char *gans[10] = {"甲","乙","丙","丁","戊","己","庚","辛","壬","癸"};
char* zhis[12] = {"子","丑","寅","卯","辰","巳","午","未","申","酉","戌","亥"};
char* animals[12] = {"鼠","牛","虎","兔","龙","蛇","马","羊","猴","鸡","狗","猪"};
6. 在数据结构中,用作链式存储
#define ElementType int
typedef struct LNode{
ElementType data;
struct LNode *next;
}LNode, *LinkList;



