VAE demo
先看tflearn 官方的:
from __future__ import division, print_function, absolute_import
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scipy.stats import norm
import tensorflow as tf
import tflearn
# Data loading and preprocessing
import tflearn.datasets.mnist as mnist
X, Y, testX, testY = mnist.load_data(one_hot=True)
# Params
original_dim = 784 # MNIST images are 28x28 pixels
hidden_dim = 256
latent_dim = 2
# Building the encoder
encoder = tflearn.input_data(shape=[None, 784], name='input_images')
encoder = tflearn.fully_connected(encoder, hidden_dim, activation='relu')
z_mean = tflearn.fully_connected(encoder, latent_dim)
z_std = tflearn.fully_connected(encoder, latent_dim)
# Sampler: Normal (gaussian) random distribution
eps = tf.random_normal(tf.shape(z_std), dtype=tf.float32, mean=0., stddev=1.0,
name='epsilon')
z = z_mean + tf.exp(z_std / 2) * eps
# Building the decoder (with scope to re-use these layers later)
decoder = tflearn.fully_connected(z, hidden_dim, activation='relu',
scope='decoder_h')
decoder = tflearn.fully_connected(decoder, original_dim, activation='sigmoid',
scope='decoder_out')
# Define VAE Loss
def vae_loss(x_reconstructed, x_true):
# Reconstruction loss
encode_decode_loss = x_true * tf.log(1e-10 + x_reconstructed) \
+ (1 - x_true) * tf.log(1e-10 + 1 - x_reconstructed)
encode_decode_loss = -tf.reduce_sum(encode_decode_loss, 1)
# KL Divergence loss
kl_div_loss = 1 + z_std - tf.square(z_mean) - tf.exp(z_std)
kl_div_loss = -0.5 * tf.reduce_sum(kl_div_loss, 1)
return tf.reduce_mean(encode_decode_loss + kl_div_loss)
net = tflearn.regression(decoder, optimizer='rmsprop', learning_rate=0.001,
loss=vae_loss, metric=None, name='target_images')
# We will need 2 models, one for training that will learn the latent
# representation, and one that can take random normal noise as input and
# use the decoder part of the network to generate an image
# Train the VAE
training_model = tflearn.DNN(net, tensorboard_verbose=0)
training_model.fit({'input_images': X}, {'target_images': X}, n_epoch=100,
validation_set=(testX, testX), batch_size=256, run_id="vae")
# Build an image generator (re-using the decoding layers)
# Input data is a normal (gaussian) random distribution (with dim = latent_dim)
input_noise = tflearn.input_data(shape=[None, latent_dim], name='input_noise')
decoder = tflearn.fully_connected(input_noise, hidden_dim, activation='relu',
scope='decoder_h', reuse=True)
decoder = tflearn.fully_connected(decoder, original_dim, activation='sigmoid',
scope='decoder_out', reuse=True)
generator_model = tflearn.DNN(decoder, session=training_model.session)
# Building a manifold of generated digits
n = 25 # Figure row size
figure = np.zeros((28 * n, 28 * n))
# Random normal distributions to feed network with
x_axis = norm.ppf(np.linspace(0., 1., n))
y_axis = norm.ppf(np.linspace(0., 1., n))
for i, x in enumerate(x_axis):
for j, y in enumerate(y_axis):
samples = np.array([[x, y]])
x_reconstructed = generator_model.predict({'input_noise': samples})
digit = np.array(x_reconstructed[0]).reshape(28, 28)
figure[i * 28: (i + 1) * 28, j * 28: (j + 1) * 28] = digit
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
plt.imshow(figure, cmap='Greys_r')
plt.show()
再看:https://github.com/kiyomaro927/tflearn-vae/blob/master/source/test/one_dimension/vae.py
import tensorflow as tf
import tflearn
from dataset import Dataset, Datasets
import pickle
import sys
# loading data
try:
h_and_w = pickle.load(open('h_and_w.pkl', 'rb'))
trainX, trainY, testX, testY = h_and_w.load_data()
except:
print("No dataset was found.")
sys.exit(1)
# network parameters
input_dim = 1 # height data input
encoder_hidden_dim = 16
decoder_hidden_dim = 16
latent_dim = 2
# paths
TENSORBOARD_DIR='experiment/'
CHECKPOINT_PATH='out_models/'
# training parameters
n_epoch = 200
batch_size = 50
# encoder
def encode(input_x):
encoder = tflearn.fully_connected(input_x, encoder_hidden_dim, activation='relu')
mu_encoder = tflearn.fully_connected(encoder, latent_dim, activation='linear')
logvar_encoder = tflearn.fully_connected(encoder, latent_dim, activation='linear')
return mu_encoder, logvar_encoder
# decoder
def decode(z):
decoder = tflearn.fully_connected(z, decoder_hidden_dim, activation='relu')
x_hat = tflearn.fully_connected(decoder, input_dim, activation='linear')
return x_hat
# sampler
def sample(mu, logvar):
epsilon = tf.random_normal(tf.shape(logvar), dtype=tf.float32, name='epsilon')
std_encoder = tf.exp(tf.mul(0.5, logvar))
z = tf.add(mu, tf.mul(std_encoder, epsilon))
return z
# loss function(regularization)
def calculate_regularization_loss(mu, logvar):
kl_divergence = -0.5 * tf.reduce_sum(1 + logvar - tf.square(mu) - tf.exp(logvar), reduction_indices=1)
return kl_divergence
# loss function(reconstruction)
def calculate_reconstruction_loss(x_hat, input_x):
mse = tflearn.objectives.mean_square(x_hat, input_x)
return mse
# trainer
def define_trainer(target, optimizer):
trainop = tflearn.TrainOp(loss=target,
optimizer=optimizer,
batch_size=batch_size,
metric=None,
name='vae_trainer')
trainer = tflearn.Trainer(train_ops=trainop,
tensorboard_dir=TENSORBOARD_DIR,
tensorboard_verbose=3,
checkpoint_path=CHECKPOINT_PATH,
max_checkpoints=1)
return trainer
# flow of VAE training
def main():
input_x = tflearn.input_data(shape=(None, input_dim), name='input_x')
mu, logvar = encode(input_x)
z = sample(mu, logvar)
x_hat = decode(z)
regularization_loss = calculate_regularization_loss(mu, logvar)
reconstruction_loss = calculate_reconstruction_loss(x_hat, input_x)
target = tf.reduce_mean(tf.add(regularization_loss, reconstruction_loss))
optimizer = tflearn.optimizers.Adam()
optimizer = optimizer.get_tensor()
trainer = define_trainer(target, optimizer)
trainer.fit(feed_dicts={input_x: trainX}, val_feed_dicts={input_x: testX},
n_epoch=n_epoch,
show_metric=False,
snapshot_epoch=True,
shuffle_all=True,
run_id='VAE')
return 0
if __name__ == '__main__':
sys.exit(main())
keras的:https://gist.github.com/philipperemy/b8a7b7be344e447e7ee6625fe2fdd765
from __future__ import print_function
import os
import numpy as np
from keras.layers import RepeatVector
from keras.layers.core import Dropout
from keras.layers.recurrent import LSTM
from keras.models import Sequential
from keras.models import load_model
np.random.seed(123)
def prepare_sequences(x_train, window_length, random_indices):
full_sequence = x_train.flatten()
windows = []
outliers = []
for window_start in range(0, len(full_sequence) - window_length + 1):
window_end = window_start + window_length
window_range = range(window_start, window_end)
window = list(full_sequence[window_range])
contain_outlier = len(set(window_range).intersection(set(random_indices))) > 0
outliers.append(contain_outlier)
windows.append(window)
return np.expand_dims(np.array(windows), axis=2), outliers
def get_signal(size, outliers_size=0.01):
sig = np.expand_dims(np.random.normal(loc=0, scale=1, size=(size, 1)), axis=1)
if outliers_size < 1: # percentage.
outliers_size = int(size * outliers_size)
random_indices = np.random.choice(range(size), size=outliers_size, replace=False)
sig[random_indices] = np.random.randint(6, 9, 1)[0]
return sig, random_indices
def tp_fn_fp_tn(total, expected, actual):
tp = len(set(expected).intersection(set(actual)))
fn = len(set(expected) - set(actual))
fp = len(set(actual) - set(expected))
tn = len((total - set(expected)).intersection(total - set(actual)))
return tp, fn, fp, tn
def main():
window_length = 10
select_only_last_state = False
model_file = 'model.h5'
hidden_dim = 16
# no outliers.
signal_train, _ = get_signal(100000, outliers_size=0)
x_train, _ = prepare_sequences(signal_train, window_length, [])
# 1 percent are outliers.
signal_test, random_indices = get_signal(100000, outliers_size=0.01)
x_test, contain_outliers = prepare_sequences(signal_test, window_length, random_indices)
outlier_indices = np.where(contain_outliers)[0]
if os.path.isfile(model_file):
m = load_model(model_file)
else:
m = Sequential()
if select_only_last_state:
m.add(LSTM(hidden_dim, input_shape=(window_length, 1), return_sequences=False))
m.add(RepeatVector(window_length))
else:
m.add(LSTM(hidden_dim, input_shape=(window_length, 1), return_sequences=True))
m.add(Dropout(p=0.1))
m.add(LSTM(1, return_sequences=True, activation='linear'))
m.compile(loss='mse', optimizer='adam')
m.fit(x_train, x_train, batch_size=64, nb_epoch=5, validation_data=(x_test, x_test))
m.save(model_file)
pred_x_test = m.predict(x_test)
mae_of_predictions = np.squeeze(np.max(np.square(pred_x_test - x_test), axis=1))
mae_threshold = np.mean(mae_of_predictions) + np.std(mae_of_predictions) # can use a running mean instead.
actual = np.where(mae_of_predictions > mae_threshold)[0]
tp, fn, fp, tn = tp_fn_fp_tn(set(range(len(pred_x_test))), outlier_indices, actual)
precision = float(tp) / (tp + fp)
hit_rate = float(tp) / (tp + fn)
accuracy = float(tp + tn) / (tp + tn + fp + fn)
print('precision = {}, hit_rate = {}, accuracy = {}'.format(precision, hit_rate, accuracy))
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
再看看keras官方的:
from __future__ import absolute_import
from __future__ import division
from __future__ import print_function
from keras.layers import Lambda, Input, Dense
from keras.models import Model
from keras.datasets import mnist
from keras.losses import mse, binary_crossentropy
from keras.utils import plot_model
from keras import backend as K
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import argparse
import os
# reparameterization trick
# instead of sampling from Q(z|X), sample eps = N(0,I)
# z = z_mean + sqrt(var)*eps
def sampling(args):
"""Reparameterization trick by sampling fr an isotropic unit Gaussian.
# Arguments:
args (tensor): mean and log of variance of Q(z|X)
# Returns:
z (tensor): sampled latent vector
"""
z_mean, z_log_var = args
batch = K.shape(z_mean)[0]
dim = K.int_shape(z_mean)[1]
# by default, random_normal has mean=0 and std=1.0
epsilon = K.random_normal(shape=(batch, dim))
return z_mean + K.exp(0.5 * z_log_var) * epsilon
def plot_results(models,
data,
batch_size=128,
model_name="vae_mnist"):
"""Plots labels and MNIST digits as function of 2-dim latent vector
# Arguments:
models (tuple): encoder and decoder models
data (tuple): test data and label
batch_size (int): prediction batch size
model_name (string): which model is using this function
"""
encoder, decoder = models
x_test, y_test = data
os.makedirs(model_name, exist_ok=True)
filename = os.path.join(model_name, "vae_mean.png")
# display a 2D plot of the digit classes in the latent space
z_mean, _, _ = encoder.predict(x_test,
batch_size=batch_size)
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 10))
plt.scatter(z_mean[:, 0], z_mean[:, 1], c=y_test)
plt.colorbar()
plt.xlabel("z[0]")
plt.ylabel("z[1]")
plt.savefig(filename)
plt.show()
filename = os.path.join(model_name, "digits_over_latent.png")
# display a 30x30 2D manifold of digits
n = 30
digit_size = 28
figure = np.zeros((digit_size * n, digit_size * n))
# linearly spaced coordinates corresponding to the 2D plot
# of digit classes in the latent space
grid_x = np.linspace(-4, 4, n)
grid_y = np.linspace(-4, 4, n)[::-1]
for i, yi in enumerate(grid_y):
for j, xi in enumerate(grid_x):
z_sample = np.array([[xi, yi]])
x_decoded = decoder.predict(z_sample)
digit = x_decoded[0].reshape(digit_size, digit_size)
figure[i * digit_size: (i + 1) * digit_size,
j * digit_size: (j + 1) * digit_size] = digit
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
start_range = digit_size // 2
end_range = n * digit_size + start_range + 1
pixel_range = np.arange(start_range, end_range, digit_size)
sample_range_x = np.round(grid_x, 1)
sample_range_y = np.round(grid_y, 1)
plt.xticks(pixel_range, sample_range_x)
plt.yticks(pixel_range, sample_range_y)
plt.xlabel("z[0]")
plt.ylabel("z[1]")
plt.imshow(figure, cmap='Greys_r')
plt.savefig(filename)
plt.show()
# MNIST dataset
(x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = mnist.load_data()
image_size = x_train.shape[1]
original_dim = image_size * image_size
x_train = np.reshape(x_train, [-1, original_dim])
x_test = np.reshape(x_test, [-1, original_dim])
x_train = x_train.astype('float32') / 255
x_test = x_test.astype('float32') / 255
# network parameters
input_shape = (original_dim, )
intermediate_dim = 512
batch_size = 128
latent_dim = 2
epochs = 50
# VAE model = encoder + decoder
# build encoder model
inputs = Input(shape=input_shape, name='encoder_input')
x = Dense(intermediate_dim, activation='relu')(inputs)
z_mean = Dense(latent_dim, name='z_mean')(x)
z_log_var = Dense(latent_dim, name='z_log_var')(x)
# use reparameterization trick to push the sampling out as input
# note that "output_shape" isn't necessary with the TensorFlow backend
z = Lambda(sampling, output_shape=(latent_dim,), name='z')([z_mean, z_log_var])
# instantiate encoder model
encoder = Model(inputs, [z_mean, z_log_var, z], name='encoder')
encoder.summary()
plot_model(encoder, to_file='vae_mlp_encoder.png', show_shapes=True)
# build decoder model
latent_inputs = Input(shape=(latent_dim,), name='z_sampling')
x = Dense(intermediate_dim, activation='relu')(latent_inputs)
outputs = Dense(original_dim, activation='sigmoid')(x)
# instantiate decoder model
decoder = Model(latent_inputs, outputs, name='decoder')
decoder.summary()
plot_model(decoder, to_file='vae_mlp_decoder.png', show_shapes=True)
# instantiate VAE model
outputs = decoder(encoder(inputs)[2])
vae = Model(inputs, outputs, name='vae_mlp')
if __name__ == '__main__':
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
help_ = "Load h5 model trained weights"
parser.add_argument("-w", "--weights", help=help_)
help_ = "Use mse loss instead of binary cross entropy (default)"
parser.add_argument("-m",
"--mse",
help=help_, action='store_true')
args = parser.parse_args()
models = (encoder, decoder)
data = (x_test, y_test)
# VAE loss = mse_loss or xent_loss + kl_loss
if args.mse:
reconstruction_loss = mse(inputs, outputs)
else:
reconstruction_loss = binary_crossentropy(inputs,
outputs)
reconstruction_loss *= original_dim
kl_loss = 1 + z_log_var - K.square(z_mean) - K.exp(z_log_var)
kl_loss = K.sum(kl_loss, axis=-1)
kl_loss *= -0.5
vae_loss = K.mean(reconstruction_loss + kl_loss)
vae.add_loss(vae_loss)
vae.compile(optimizer='adam')
vae.summary()
plot_model(vae,
to_file='vae_mlp.png',
show_shapes=True)
if args.weights:
vae.load_weights(args.weights)
else:
# train the autoencoder
vae.fit(x_train,
epochs=epochs,
batch_size=batch_size,
validation_data=(x_test, None))
vae.save_weights('vae_mlp_mnist.h5')
plot_results(models,
data,
batch_size=batch_size,
model_name="vae_mlp")
上面介绍了VAE的原理,看起来很复杂,其实最终VAE也实现了跟AutoEncoder类似的作用,输入一个序列,得到一个隐变量(从隐变量的分布中采样得到),然后将隐变量重构成原始输入。不同的是,VAE学习到的是隐变量的分布(允许隐变量存在一定的噪声和随机性),因此可以具有类似正则化防止过拟合的作用。
以下的构建一个VAE模型的keras代码,修改自keras的example代码,具体参数参考了Dount论文:
def sampling(args):
"""Reparameterization trick by sampling fr an isotropic unit Gaussian.
# Arguments:
args (tensor): mean and log of variance of Q(z|X)
# Returns:
z (tensor): sampled latent vector
"""
z_mean, z_log_var = args
batch = K.shape(z_mean)[0]
dim = K.int_shape(z_mean)[1]
# by default, random_normal has mean=0 and std=1.0
epsilon = K.random_normal(shape=(batch, dim))
std_epsilon = 1e-4
return z_mean + (z_log_var + std_epsilon) * epsilon
input_shape = (seq_len,)
intermediate_dim = 100
latent_dim = latent_dim
# VAE model = encoder + decoder
# build encoder model
inputs = Input(shape=input_shape, name='encoder_input')
x = Dense(intermediate_dim, activation='relu', kernel_regularizer=regularizers.l2(0.001))(inputs)
x = Dense(intermediate_dim, activation='relu', kernel_regularizer=regularizers.l2(0.001))(x)
z_mean = Dense(latent_dim, name='z_mean')(x)
z_log_var = Dense(latent_dim, name='z_log_var', activation='softplus')(x)
# use reparameterization trick to push the sampling out as input
# note that "output_shape" isn't necessary with the TensorFlow backend
z = Lambda(sampling, output_shape=(latent_dim,), name='z')([z_mean, z_log_var])
# build decoder model
x = Dense(intermediate_dim, activation='relu', kernel_regularizer=regularizers.l2(0.001))(z)
x = Dense(intermediate_dim, activation='relu', kernel_regularizer=regularizers.l2(0.001))(x)
x_mean = Dense(seq_len, name='x_mean')(x)
x_log_var = Dense(seq_len, name='x_log_var', activation='softplus')(x)
outputs = Lambda(sampling, output_shape=(seq_len,), name='x')([x_mean, x_log_var])
vae = Model(inputs, outputs, name='vae_mlp')
# add loss
reconstruction_loss = mean_squared_error(inputs, outputs)
reconstruction_loss *= seq_len
kl_loss = 1 + z_log_var - K.square(z_mean) - K.exp(z_log_var)
kl_loss = K.sum(kl_loss, axis=-1)
kl_loss *= -0.5
vae_loss = K.mean(reconstruction_loss + kl_loss)
vae.add_loss(vae_loss)
vae.compile(optimizer='adam')
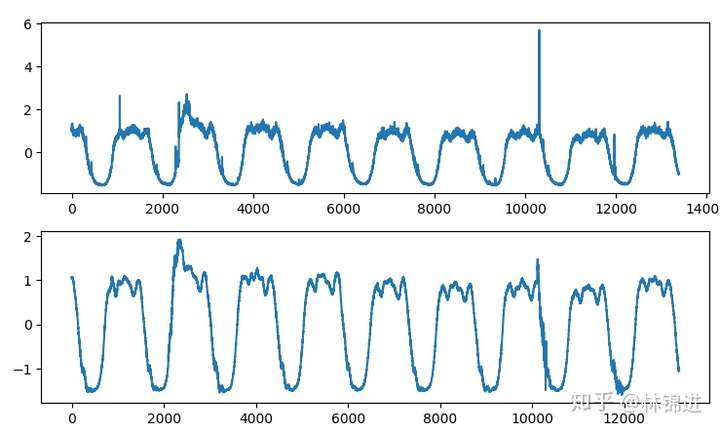
基于VAE的周期性KPI异常检测方法其实跟AutoEncoder基本一致,可以使用重构误差来判断异常,来下面是结果,上图是原始输入,下图是重构结果,我们能够看到VAE重构的结果比AutoEncoder的更好一些。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号