ES搜索排序,文档相关度评分介绍——Vector Space Model
Vector Space Model
The vector space model provides a way of comparing a multiterm query against a document. The output is a single score that represents how well the document matches the query. In order to do this, the model represents both the document and the query as vectors.
A vector is really just a one-dimensional array containing numbers, for example:
[1,2,5,22,3,8]
In the vector space model, each number in the vector is the weight of a term, as calculated with term frequency/inverse document frequency.
While TF/IDF is the default way of calculating term weights for the vector space model, it is not the only way. Other models like Okapi-BM25 exist and are available in Elasticsearch. TF/IDF is the default because it is a simple, efficient algorithm that produces high-quality search results and has stood the test of time.
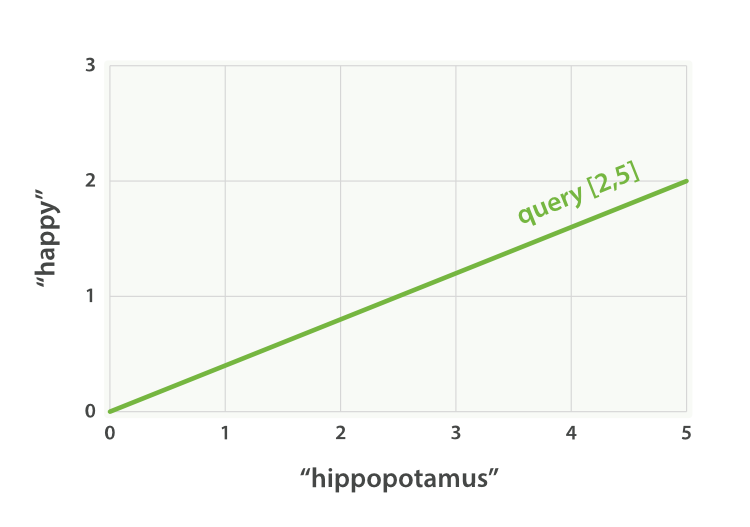
Imagine that we have a query for “happy hippopotamus.” A common word like happy will have a low weight, while an uncommon term like hippopotamus will have a high weight. Let’s assume that happyhas a weight of 2 and hippopotamus has a weight of 5. We can plot this simple two-dimensional vector—[2,5]—as a line on a graph starting at point (0,0) and ending at point (2,5), as shown inFigure 27, “A two-dimensional query vector for “happy hippopotamus” represented”.
Now, imagine we have three documents:
- I am happy in summer.
- After Christmas I’m a hippopotamus.
- The happy hippopotamus helped Harry.
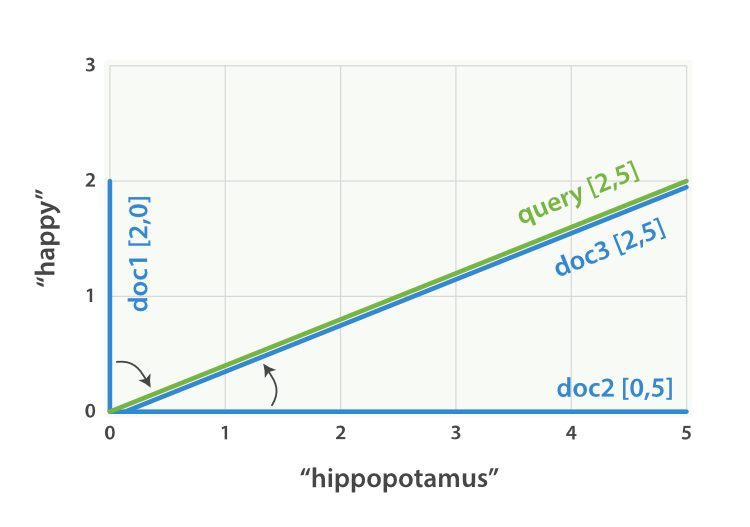
We can create a similar vector for each document, consisting of the weight of each query term—happy and hippopotamus—that appears in the document, and plot these vectors on the same graph, as shown in Figure 28, “Query and document vectors for “happy hippopotamus””:
- Document 1:
(happy,____________)—[2,0] - Document 2:
( ___ ,hippopotamus)—[0,5] - Document 3:
(happy,hippopotamus)—[2,5]
The nice thing about vectors is that they can be compared. By measuring the angle between the query vector and the document vector, it is possible to assign a relevance score to each document. The angle between document 1 and the query is large, so it is of low relevance. Document 2 is closer to the query, meaning that it is reasonably relevant, and document 3 is a perfect match.
In practice, only two-dimensional vectors (queries with two terms) can be plotted easily on a graph. Fortunately, linear algebra—the branch of mathematics that deals with vectors—provides tools to compare the angle between multidimensional vectors, which means that we can apply the same principles explained above to queries that consist of many terms.
You can read more about how to compare two vectors by using cosine similarity.
Now that we have talked about the theoretical basis of scoring, we can move on to see how scoring is implemented in Lucene.



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号