BFS_拓扑排序 使用图遍历思想也是OK的 虽然代码多了点
269. 火星词典
难度困难
现有一种使用英语字母的火星语言,这门语言的字母顺序与英语顺序不同。
给你一个字符串列表 words ,作为这门语言的词典,words 中的字符串已经 按这门新语言的字母顺序进行了排序 。
请你根据该词典还原出此语言中已知的字母顺序,并 按字母递增顺序 排列。若不存在合法字母顺序,返回 "" 。若存在多种可能的合法字母顺序,返回其中 任意一种 顺序即可。
字符串 s 字典顺序小于 字符串 t 有两种情况:
- 在第一个不同字母处,如果
s中的字母在这门外星语言的字母顺序中位于t中字母之前,那么s的字典顺序小于t。 - 如果前面
min(s.length, t.length)字母都相同,那么s.length < t.length时,s的字典顺序也小于t。
示例 1:
输入:words = ["wrt","wrf","er","ett","rftt"] 输出:"wertf"
示例 2:
输入:words = ["z","x"] 输出:"zx"
示例 3:
输入:words = ["z","x","z"] 输出:"" 解释:不存在合法字母顺序,因此返回"" 。
看看高手如何写拓扑排序!Solution2是我写的,solution1是高手的!果然比我的要简洁很多!
from collections import defaultdict
class Solution2:
def alienOrder(self, words) -> str:
n = len(words)
graph = defaultdict(list)
indegree = {}
for i in range(n):
for char in words[i]:
indegree[char] = 0
for i in range(1, n):
s, t = words[i-1], words[i]
for u, v in zip(s, t): # >>> a,b = "wrt","wrfzzzz"==>list(zip(a,b)) ==> [('w', 'w'), ('r', 'r'), ('t', 'f')]
if u != v:
graph[u].append(v)
indegree[v] += 1
break
else:
if len(s) > len(t): # a,b = ["abc","ab"] ==> return ""!!!
return ""
start_nodes = [node for node in indegree if indegree[node] == 0]
queue = collections.deque(start_nodes)
order = []
while queue:
node = queue.popleft()
order.append(node)
for neighbor in graph[node]:
indegree[neighbor] -= 1
if indegree[neighbor] == 0:
queue.append(neighbor)
orders = "".join(order)
return orders if len(orders) == len(indegree) else ""
class Solution:
def alienOrder(self, words) -> str:
g = defaultdict(list)
inDeg = {c: 0 for c in words[0]}
for i in range(1, len(words)):
s, t = words[i-1], words[i]
for c in t:
inDeg.setdefault(c, 0)
for u, v in zip(s, t): # >>> a,b = "wrt","wrfzzzz"==>list(zip(a,b)) ==> [('w', 'w'), ('r', 'r'), ('t', 'f')]
if u != v:
g[u].append(v)
inDeg[v] += 1
break
else:
if len(s) > len(t): # a,b = ["abc","ab"] ==> return ""!!!
return ""
q = [u for u, d in inDeg.items() if d == 0]
for u in q:
for v in g[u]:
inDeg[v] -= 1
if inDeg[v] == 0:
q.append(v)
return ''.join(q) if len(q) == len(inDeg) else ""
words = ["wrt","wrf","er","ett","rftt"]
print(Solution2().alienOrder(words))
127. 拓扑排序
中文
English
给定一个有向图,图节点的拓扑排序定义如下:
- 对于图中的每一条有向边
A -> B, 在拓扑排序中A一定在B之前. - 拓扑排序中的第一个节点可以是图中的任何一个没有其他节点指向它的节点.
针对给定的有向图找到任意一种拓扑排序的顺序.
样例
例如以下的图:
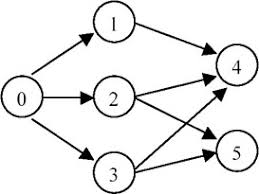
拓扑排序可以为:
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
[0, 2, 3, 1, 5, 4]
挑战
能否分别用BFS和DFS完成?
说明
注意事项
你可以假设图中至少存在一种拓扑排序
class Solution:
"""
@param graph: A list of Directed graph node
@return: Any topological order for the given graph.
"""
def topSort(self, graph):
node_to_indegree = self.get_indegree(graph)
# bfs
order = []
start_nodes = [n for n in graph if node_to_indegree[n] == 0]
queue = collections.deque(start_nodes)
while queue:
node = queue.popleft()
order.append(node)
for neighbor in node.neighbors:
node_to_indegree[neighbor] -= 1
if node_to_indegree[neighbor] == 0:
queue.append(neighbor)
return order
def get_indegree(self, graph):
node_to_indegree = {x: 0 for x in graph}
for node in graph:
for neighbor in node.neighbors:
node_to_indegree[neighbor] += 1
return node_to_indegree
\
from collections import deque
class Solution:
"""
@param: graph: A list of Directed graph node
@return: Any topological order for the given graph.
"""
def topSort(self, graph):
# write your code here
if not graph:
return []
def compute_indegres(graph):
ans = {}
for n in graph:
if n not in ans:
ans[n] = 0
for neighbor in n.neighbors:
ans[neighbor] = ans.get(neighbor, 0) + 1
return ans
def get_indegres0(indegrees):
return [n for n in indegrees if indegrees[n] == 0]
def sorted_nodes(init_nodes, indegrees):
ans = []
seen = set(init_nodes)
q = deque(init_nodes)
while q:
n = q.popleft()
ans.append(n)
for node in n.neighbors:
indegrees[node] -= 1
nodes0 = get_indegres0(indegrees)
for node in nodes0:
if node not in seen:
q.append(node)
seen.add(node)
return ans
indegrees = compute_indegres(graph)
init_nodes = get_indegres0(indegrees)
return sorted_nodes(init_nodes, indegrees)
=】



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号