【MySQL】覆盖索引和回表
- 先来了解一下两大类索引
- 聚簇索引(也称聚集索引,主键索引等)
- 普通索引(也成非聚簇索引,二级索引等)
- 聚簇索引
- 如果表设置了主键,则主键就是聚簇索引
- 如果表没有主键,则会默认第一个NOT NULL,且唯一(UNIQUE)的列作为聚簇索引
- 以上都没有,则会默认创建一个隐藏的row_id作为聚簇索引
InnoDB的聚簇索引的叶子节点存储的是行记录(其实是页结构,一个页包含多行数据),InnoDB必须要有至少一个聚簇索引。
由此可见,使用聚簇索引查询会很快,因为可以直接定位到行记录。
- 普通索引
普通索引也叫二级索引,除聚簇索引外的索引,即非聚簇索引。
InnoDB的普通索引叶子节点存储的是主键(聚簇索引)的值,而MyISAM的普通索引存储的是记录指针。
请看如下示例:
- 建表
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `user`( -> `id` INT UNSIGNED AUTO_INCREMENT, -> `name` VARCHAR(60), -> `age` TINYINT(4), -> PRIMARY KEY (id), -> INDEX idx_age (age) -> )ENGINE=innodb charset=utf8mb4;
# id 字段是聚簇索引,age 字段是普通索引(二级索引)
- 随便加几个数据
insert into user(name,age) values('张三',30); insert into user(name,age) values('李四',20); insert into user(name,age) values('王五',40); insert into user(name,age) values('刘八',10);
mysql> select * from user; +----+------+-----+ | id | name | age | +----+------+-----+ | 1 | 张三 | 30 | | 2 | 李四 | 20 | | 3 | 王五 | 40 | | 4 | 刘八 | 10 | +----+------+-----+ 4 rows in set (0.06 sec)
- 索引存储结构
id 是主键,所以是聚簇索引,其叶子节点存储的是对应行记录的数据

age 是普通索引(二级索引),非聚簇索引,其叶子节点存储的是聚簇索引的的值
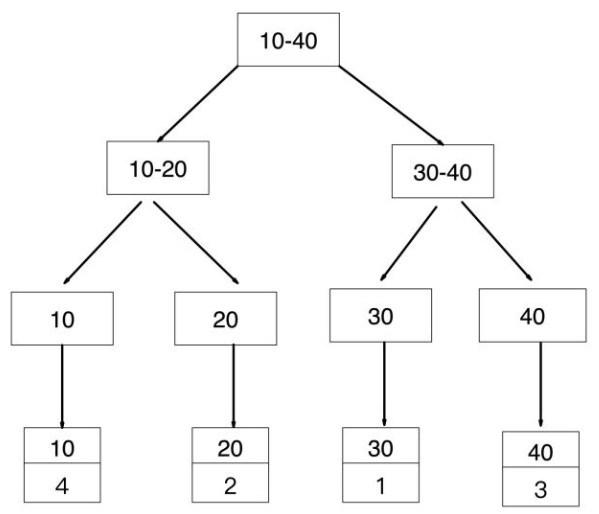
如果查询条件为主键(聚簇索引),则只需扫描一次B+树即可通过聚簇索引定位到要查找的行记录数据。 如:select * from user where id = 1;
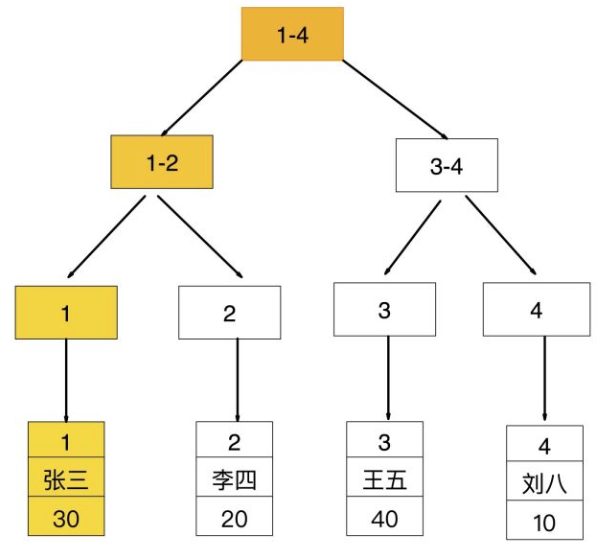
如果查询条件为普通索引(非聚簇索引),需要扫描两次B+树,第一次扫描通过普通索引定位到聚簇索引的值,然后第二次扫描通过聚簇索引的值定位到要查找的行记录数据。
如:select * from user where age = 30;
1》先通过普通索引【age=30】定位到主键值 【id=1】
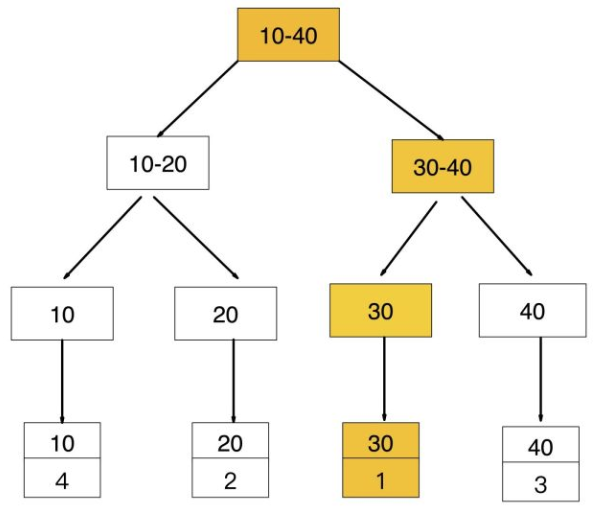
2》在通过聚集索引【id=1】定位到行记录数据
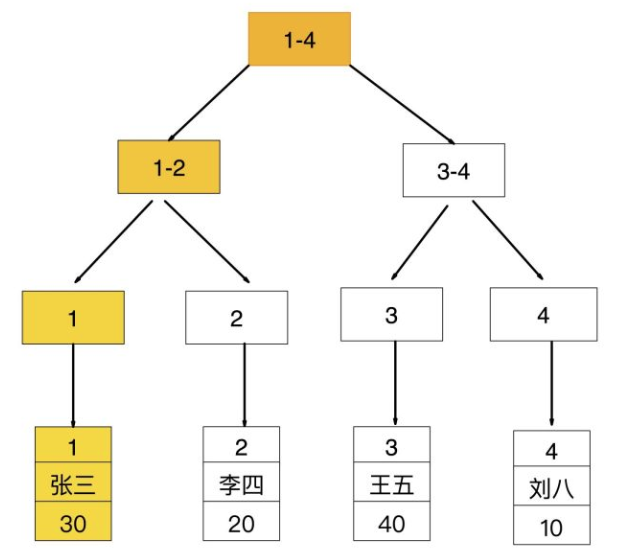
- 回表查询
先通过普通索引的值定位到聚簇索引值,在通过聚簇索引的值定位到行记录数据,要通过扫描两次索引B+树,它的性能较扫描一次较低
- 索引覆盖
只需在一颗索引树上就能获取SQL所需的所有列数据,无需回表,速度更快。 例如:select id,age from user where age = 10;
- 如何实现覆盖索引
常见的方法是:将被查询的字段,建立到联合索引里去(若查询有where条件,同时where条件字段也必须为索引字段)。
1》如实现:select id,age from user where age = 10;
explain分析:因为age是普通索引,使用到了age索引,通过一次扫描B+树即可查询到相应的结果,这样就实现了覆盖索引
此时的Extra列的【Using Index】表示进行了聚簇索引
mysql> explain select id,age from user where age = 10; +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+---------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+---------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | user | NULL | ref | idx_age | idx_age | 2 | const | 1 | 100.00 | Using index | +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+---------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------------+ 1 row in set (0.07 sec)
2》如实现:select id,age,name from user where age = 10;
explain分析:age是普通索引,但name列不在索引树上,所以通过age索引在查询到id和age的值后,需要进行回表再查询name的值。
此时的Extra列的NULL表示进行了回表查询
mysql> explain select id,age,name from user where age = 10; +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+---------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+---------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | user | NULL | ref | idx_age | idx_age | 2 | const | 1 | 100.00 | NULL | +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+---------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+ 1 row in set (0.05 sec)
explain 使用方式如下:EXPLAIN +SQL语句 如:EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM t1
- 为了实现索引覆盖,需要建组合索引idx_age_name(age,name)
mysql> drop index idx_age on user;
mysql> create index idx_age_name on user(`age`,`name`);
我们再次EXPLAIN分析一次:
mysql> explain select id,age,name from user where age = 10; +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+--------------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+--------------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | user | NULL | ref | idx_age_name | idx_age_name | 2 | const | 1 | 100.00 | Using index | +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+--------------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------------+ 1 row in set (0.05 sec)
#可见Extra的值为【Using Index】,表示使用的覆盖索引
哪些场景适合使用索引覆盖来优化SQL:
- 全表count查询优化
mysql> explain select count(age) from user; +----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+--------------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+--------------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | user | NULL | index | NULL | idx_age_name | 245 | NULL | 4 | 100.00 | Using index | +----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+--------------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+ 1 row in set (0.06 sec)
- 分页查询
mysql> explain select id,age,name from user order by age limit 100,2; +----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+--------------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+--------------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | user | NULL | index | NULL | idx_age_name | 245 | NULL | 4 | 100.00 | Using index | +----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+--------------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+ 1 row in set (0.06 sec)
学而不思则罔 思而不学则殆 !


