CF Round 432 C. Five Dimensional Points
题目链接:http://codeforces.com/contest/851/problem/C
题目大意:给出N个点,判断有多少个点是good的。对于一个点a来说,如果能从给出的N个点钟找到两个与a不同的点b,c并且 向量 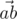 和
和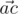 夹角是锐角,则说这个点是bad的,否则是good的。N < 1000
夹角是锐角,则说这个点是bad的,否则是good的。N < 1000
解题思路:首先会想到的是N3的算法,但是仔细考虑一下会发现,如果a是bad的,那么一次判断即可,否则a是good,那么b,c肯定都是bad。那么复杂度就可以大大降低了。
代码:
1 const int maxn = 1e3 + 5; 2 int n; 3 int a[maxn], b[maxn], c[maxn], d[maxn], e[maxn]; 4 bool sta[maxn]; 5 queue<int> q; 6 7 double cacu(int ab[], int ac[]){ 8 double ans = 0; 9 for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++){ 10 ans += ab[i] * ac[i]; 11 } 12 return ans; 13 } 14 void solve(){ 15 memset(sta, 0, sizeof(sta)); 16 int ans = 0; 17 for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){ 18 if(!sta[i]){ 19 bool flag = true; 20 sta[i] = true; 21 for(int j = 1; j <= n; j++){ 22 if(j == i) continue; 23 for(int k = 1; k <= n; k++){ 24 if(k == i || k == j) continue; 25 int ab[] = {a[j] - a[i], b[j] - b[i], c[j] - c[i], d[j] - d[i], e[j] - e[i]}; 26 int ac[] = {a[k] - a[i], b[k] - b[i], c[k] - c[i], d[k] - d[i], e[k] - e[i]}; 27 double tv1 = cacu(ab, ac), tv2 = cacu(ab, ab), tv3 = cacu(ac, ac); 28 double tmv = tv1 / sqrt(tv2) / sqrt(tv3); 29 tmv = acos(tmv); 30 if(tmv - PI / 2 < 0){ 31 flag = false; 32 break; 33 } 34 else{ 35 sta[j] = sta[k] = true; 36 } 37 } 38 if(!flag) break; 39 } 40 if(flag) { 41 ans++; 42 q.push(i); 43 } 44 } 45 } 46 printf("%d\n", ans); 47 while(!q.empty()){ 48 int u = q.front(); q.pop(); 49 printf("%d ", u); 50 } 51 } 52 int main(){ 53 scanf("%d", &n); 54 for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){ 55 scanf("%d %d %d %d %d", a + i, b + i, c + i, d + i, e + i); 56 } 57 solve(); 58 }
题目:
You are given set of n points in 5-dimensional space. The points are labeled from 1 to n. No two points coincide.
We will call point a bad if there are different points b and c, not equal to a, from the given set such that angle between vectors 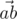 and
and 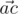 is acute (i.e. strictly less than
is acute (i.e. strictly less than 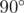 ). Otherwise, the point is called good.
). Otherwise, the point is called good.
The angle between vectors 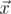 and
and 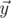 in 5-dimensional space is defined as
in 5-dimensional space is defined as 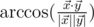 , where
, where 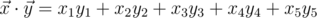 is the scalar product and
is the scalar product and 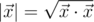 is length of
is length of 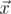 .
.
Given the list of points, print the indices of the good points in ascending order.
The first line of input contains a single integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 103) — the number of points.
The next n lines of input contain five integers ai, bi, ci, di, ei (|ai|, |bi|, |ci|, |di|, |ei| ≤ 103) — the coordinates of the i-th point. All points are distinct.
First, print a single integer k — the number of good points.
Then, print k integers, each on their own line — the indices of the good points in ascending order.
6
0 0 0 0 0
1 0 0 0 0
0 1 0 0 0
0 0 1 0 0
0 0 0 1 0
0 0 0 0 1
1
1
3
0 0 1 2 0
0 0 9 2 0
0 0 5 9 0
0
In the first sample, the first point forms exactly a 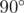 angle with all other pairs of points, so it is good.
angle with all other pairs of points, so it is good.
In the second sample, along the cd plane, we can see the points look as follows:
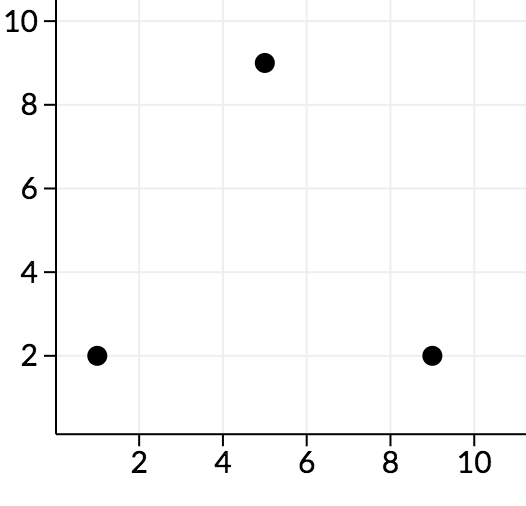
We can see that all angles here are acute, so no points are good.


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号