视觉SLAM 十四讲——3D-2D:PnP求解——BA
PnP问题的求解方法有很多,例如,用3对点估计位姿的P3P、直接线性变换法(DLT),EPnP(Efficient PnP),UPnP等;
非线性优化的方式,构建最小二乘问题并迭代进行求解,即万金油式的Bundle Adjustment。
本节组要介绍BA,并给出示例。
主要内容
1. 概念
线性方法:先求解相机位姿,再求空间点位置
非线性优化方法:把相机位姿和空间点位置都看成优化变量,两者一起优化,通用的求解方式(PnP,ICP问题)。
在PnP问题中,Bundle Adjustment 问题是一个最小化重投影误差(Reprojection Error)的问题。
2. BA求解 (P163-165)
1)重投影误差公式表示
![]()
其中,![]() 为第i个特征点的像素坐标,
为第i个特征点的像素坐标,![]() 为特征位置坐标。
为特征位置坐标。
2)线性化
求解每个误差项关于优化变量的导数:
![]()
其中,
优化变量为:李代数se(3)的扰动量,特征点的空间位置P
量测输入为:像素坐标点 ![]()
2.1) 误差变化量对位姿扰动量的导数(2×6的雅克比矩阵):

其中,需要注意:
a) 观测值-预测值,保留一阶导数前面的负号,
预测值-观测值,去掉负号。
b) 雅克比矩阵对应的se(3)中:平移在前,旋转在后,
如果旋转在前,平移在后,需要将矩阵的前三列与后三列对调。
2.2) 误差变化量对特征点位置的导数(2×3的雅克比矩阵):
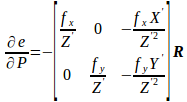
注:矩阵前面的负号,关系到残差的方向。
3. 应用
BA是一种通用的做法,可以不限于两幅图像,可以放入多幅图像的位姿和特征点进行优化,甚至可以把整个SLAM放进来。
当然,规模先对比较大,主要在后端使用。
在前段,主要考虑局部相机位姿和特征点的小型BA问题,希望对他进行实时求解和优化。
4. 代码注意的点
1) VertexSE3Expmap 顶点的定义:
模板参数: 6维的李代数,优化变量的类型为:SE3Quat(类的内部使用了四元数加位移向量来存储位姿,但同时也支持李代数上的运算)
位姿定点的增量更新实现函数:oplusImpl (其中实现了李代数的指数映射)
/** * \brief SE3 Vertex parameterized internally with a transformation matrix and externally with its exponential map */ class G2O_TYPES_SBA_API VertexSE3Expmap : public BaseVertex<6, SE3Quat>{ public: EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW VertexSE3Expmap(); bool read(std::istream& is); bool write(std::ostream& os) const; virtual void setToOriginImpl() { _estimate = SE3Quat(); } virtual void oplusImpl(const double* update_) { Eigen::Map<const Vector6d> update(update_); setEstimate(SE3Quat::exp(update)*estimate()); } };
2)VertexSBAPointXYZ 顶点的定义
模板参数:3维的向量表示特征点的位置,类型为Vector3D
特征点位置顶点的更新函数:增量相加
class G2O_TYPES_SBA_API VertexSBAPointXYZ : public BaseVertex<3, Vector3D> { public: EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW VertexSBAPointXYZ(); virtual bool read(std::istream& is); virtual bool write(std::ostream& os) const; virtual void setToOriginImpl() { _estimate.fill(0.); } virtual void oplusImpl(const double* update) { Eigen::Map<const Vector3D> v(update); _estimate += v; } };
3) EdgeProjectXYZ2UV 边的定义:
3.1)模板参数定义:2维的量测信息,Vector2D,两个顶点类型 VertexSBAPointXYZ 以及 VertexSE3Expmap;
3.2) 残差计算函数 computeError:
先从该边连接的两个顶点中获取当前的位姿和特征点位置信息(更新到最近一次的信息);
其次,获取该边连接的参数信息,即相机的内参信息;
最后,根据量测输入计算残差信息(map:将特征点位置根据当前位姿转化到相机坐标系;cam_map:将相机坐标系的点(归一化)通过内参K转化到像素坐标点)
3.3) 投影方程的误差计算(量测方程线性化):linearizeOplus的实现
class G2O_TYPES_SBA_API EdgeProjectXYZ2UV : public BaseBinaryEdge<2, Vector2D, VertexSBAPointXYZ, VertexSE3Expmap>{ public: EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW; EdgeProjectXYZ2UV(); bool read(std::istream& is); bool write(std::ostream& os) const; void computeError() { const VertexSE3Expmap* v1 = static_cast<const VertexSE3Expmap*>(_vertices[1]); const VertexSBAPointXYZ* v2 = static_cast<const VertexSBAPointXYZ*>(_vertices[0]); const CameraParameters * cam = static_cast<const CameraParameters *>(parameter(0)); Vector2D obs(_measurement); _error = obs-cam->cam_map(v1->estimate().map(v2->estimate())); } virtual void linearizeOplus(); CameraParameters * _cam; };
4) 量测方程线性化(分别对位姿和特征点位置求导):linearizeOplus
4.1) 特征点位置的求导结果:_jacobianOplusXi
4.2)位姿的求导结果:_jacobianOplusXj (与上面的公式稍有差别,李代数中定义旋转在前)
4.3)g2o的相机里,用f 统一描述 fx 和 fy。
void EdgeProjectXYZ2UV::linearizeOplus() { VertexSE3Expmap * vj = static_cast<VertexSE3Expmap *>(_vertices[1]); SE3Quat T(vj->estimate()); VertexSBAPointXYZ* vi = static_cast<VertexSBAPointXYZ*>(_vertices[0]); Vector3D xyz = vi->estimate(); Vector3D xyz_trans = T.map(xyz); double x = xyz_trans[0]; double y = xyz_trans[1]; double z = xyz_trans[2]; double z_2 = z*z; const CameraParameters * cam = static_cast<const CameraParameters *>(parameter(0)); Matrix<double,2,3,Eigen::ColMajor> tmp; tmp(0,0) = cam->focal_length; tmp(0,1) = 0; tmp(0,2) = -x/z*cam->focal_length; tmp(1,0) = 0; tmp(1,1) = cam->focal_length; tmp(1,2) = -y/z*cam->focal_length; _jacobianOplusXi = -1./z * tmp * T.rotation().toRotationMatrix(); _jacobianOplusXj(0,0) = x*y/z_2 *cam->focal_length; _jacobianOplusXj(0,1) = -(1+(x*x/z_2)) *cam->focal_length; _jacobianOplusXj(0,2) = y/z *cam->focal_length; _jacobianOplusXj(0,3) = -1./z *cam->focal_length; _jacobianOplusXj(0,4) = 0; _jacobianOplusXj(0,5) = x/z_2 *cam->focal_length; _jacobianOplusXj(1,0) = (1+y*y/z_2) *cam->focal_length; _jacobianOplusXj(1,1) = -x*y/z_2 *cam->focal_length; _jacobianOplusXj(1,2) = -x/z *cam->focal_length; _jacobianOplusXj(1,3) = 0; _jacobianOplusXj(1,4) = -1./z *cam->focal_length; _jacobianOplusXj(1,5) = y/z_2 *cam->focal_length; }
5)g2o初始化
5.1) BlockSolver 模板参数初始化(顶点的维度信息)
typedef g2o::BlockSolver< g2o::BlockSolverTraits<6,3> > Block; // pose 维度为 6, landmark 维度为 3
5.2)初始化中设置线性求解器(求解方法)
6) 增加边信息(位姿和特征点位置)
7) 增加参数信息:相机的内存
8) 增加边:
先设置ID,其次设置该边连接的顶点信息,设置量测信息,设置连接的参数信息,
9) 启动优化
参考链接
《视觉SLAM十四讲精品总结》7:VO—— 3D-2D:PnP+BA
代码
#include <iostream> #include <opencv2/core/core.hpp> #include <opencv2/features2d/features2d.hpp> #include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp> #include <opencv2/calib3d/calib3d.hpp> #include <Eigen/Core> #include <Eigen/Geometry> #include <g2o/core/base_vertex.h> #include <g2o/core/base_unary_edge.h> #include <g2o/core/block_solver.h> #include <g2o/core/optimization_algorithm_levenberg.h> #include <g2o/solvers/csparse/linear_solver_csparse.h> #include <g2o/types/sba/types_six_dof_expmap.h> #include <chrono> using namespace std; using namespace cv; void find_feature_matches ( const Mat& img_1, const Mat& img_2, std::vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints_1, std::vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints_2, std::vector< DMatch >& matches ); // 像素坐标转相机归一化坐标 Point2d pixel2cam ( const Point2d& p, const Mat& K ); void bundleAdjustment ( const vector<Point3f> points_3d, const vector<Point2f> points_2d, const Mat& K, Mat& R, Mat& t ); int main ( int argc, char** argv ) { if ( argc != 5 ) { cout<<"usage: pose_estimation_3d2d img1 img2 depth1 depth2"<<endl; return 1; } //-- 读取图像 Mat img_1 = imread ( argv[1], CV_LOAD_IMAGE_COLOR ); Mat img_2 = imread ( argv[2], CV_LOAD_IMAGE_COLOR ); vector<KeyPoint> keypoints_1, keypoints_2; vector<DMatch> matches; find_feature_matches ( img_1, img_2, keypoints_1, keypoints_2, matches ); cout<<"一共找到了"<<matches.size() <<"组匹配点"<<endl; // 建立3D点 Mat d1 = imread ( argv[3], CV_LOAD_IMAGE_UNCHANGED ); // 深度图为16位无符号数,单通道图像 Mat K = ( Mat_<double> ( 3,3 ) << 520.9, 0, 325.1, 0, 521.0, 249.7, 0, 0, 1 ); vector<Point3f> pts_3d; vector<Point2f> pts_2d; for ( DMatch m:matches ) { ushort d = d1.ptr<unsigned short> (int ( keypoints_1[m.queryIdx].pt.y )) [ int ( keypoints_1[m.queryIdx].pt.x ) ]; if ( d == 0 ) // bad depth continue; float dd = d/5000.0; Point2d p1 = pixel2cam ( keypoints_1[m.queryIdx].pt, K ); pts_3d.push_back ( Point3f ( p1.x*dd, p1.y*dd, dd ) ); pts_2d.push_back ( keypoints_2[m.trainIdx].pt ); } cout<<"3d-2d pairs: "<<pts_3d.size() <<endl; Mat r, t; solvePnP ( pts_3d, pts_2d, K, Mat(), r, t, false, SOLVEPNP_EPNP); // 调用OpenCV 的 PnP 求解,可选择EPNP,DLS等方法 Mat R; cv::Rodrigues ( r, R ); // r为旋转向量形式,用Rodrigues公式转换为矩阵 cout<<"R="<<endl<<R<<endl; cout<<"t="<<endl<<t<<endl; cout<<"calling bundle adjustment"<<endl; bundleAdjustment ( pts_3d, pts_2d, K, R, t ); } void find_feature_matches ( const Mat& img_1, const Mat& img_2, std::vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints_1, std::vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints_2, std::vector< DMatch >& matches ) { //-- 初始化 Mat descriptors_1, descriptors_2; // used in OpenCV3 Ptr<FeatureDetector> detector = ORB::create(); Ptr<DescriptorExtractor> descriptor = ORB::create(); // use this if you are in OpenCV2 // Ptr<FeatureDetector> detector = FeatureDetector::create ( "ORB" ); // Ptr<DescriptorExtractor> descriptor = DescriptorExtractor::create ( "ORB" ); Ptr<DescriptorMatcher> matcher = DescriptorMatcher::create ( "BruteForce-Hamming" ); //-- 第一步:检测 Oriented FAST 角点位置 detector->detect ( img_1,keypoints_1 ); detector->detect ( img_2,keypoints_2 ); //-- 第二步:根据角点位置计算 BRIEF 描述子 descriptor->compute ( img_1, keypoints_1, descriptors_1 ); descriptor->compute ( img_2, keypoints_2, descriptors_2 ); //-- 第三步:对两幅图像中的BRIEF描述子进行匹配,使用 Hamming 距离 vector<DMatch> match; // BFMatcher matcher ( NORM_HAMMING ); matcher->match ( descriptors_1, descriptors_2, match ); //-- 第四步:匹配点对筛选 double min_dist=10000, max_dist=0; //找出所有匹配之间的最小距离和最大距离, 即是最相似的和最不相似的两组点之间的距离 for ( int i = 0; i < descriptors_1.rows; i++ ) { double dist = match[i].distance; if ( dist < min_dist ) min_dist = dist; if ( dist > max_dist ) max_dist = dist; } printf ( "-- Max dist : %f \n", max_dist ); printf ( "-- Min dist : %f \n", min_dist ); //当描述子之间的距离大于两倍的最小距离时,即认为匹配有误.但有时候最小距离会非常小,设置一个经验值30作为下限. for ( int i = 0; i < descriptors_1.rows; i++ ) { if ( match[i].distance <= max ( 2*min_dist, 30.0 ) ) { matches.push_back ( match[i] ); } } } Point2d pixel2cam ( const Point2d& p, const Mat& K ) { return Point2d ( ( p.x - K.at<double> ( 0,2 ) ) / K.at<double> ( 0,0 ), ( p.y - K.at<double> ( 1,2 ) ) / K.at<double> ( 1,1 ) ); } void bundleAdjustment ( const vector< Point3f > points_3d, const vector< Point2f > points_2d, const Mat& K, Mat& R, Mat& t ) { // 初始化g2o typedef g2o::BlockSolver< g2o::BlockSolverTraits<6,3> > Block; // pose 维度为 6, landmark 维度为 3 Block::LinearSolverType* linearSolver = new g2o::LinearSolverCSparse<Block::PoseMatrixType>(); // 线性方程求解器 Block* solver_ptr = new Block ( linearSolver ); // 矩阵块求解器 g2o::OptimizationAlgorithmLevenberg* solver = new g2o::OptimizationAlgorithmLevenberg ( solver_ptr ); g2o::SparseOptimizer optimizer; optimizer.setAlgorithm ( solver ); // vertex g2o::VertexSE3Expmap* pose = new g2o::VertexSE3Expmap(); // camera pose Eigen::Matrix3d R_mat; R_mat << R.at<double> ( 0,0 ), R.at<double> ( 0,1 ), R.at<double> ( 0,2 ), R.at<double> ( 1,0 ), R.at<double> ( 1,1 ), R.at<double> ( 1,2 ), R.at<double> ( 2,0 ), R.at<double> ( 2,1 ), R.at<double> ( 2,2 ); pose->setId ( 0 ); pose->setEstimate ( g2o::SE3Quat ( R_mat, Eigen::Vector3d ( t.at<double> ( 0,0 ), t.at<double> ( 1,0 ), t.at<double> ( 2,0 ) ) ) ); optimizer.addVertex ( pose ); int index = 1; for ( const Point3f p:points_3d ) // landmarks { g2o::VertexSBAPointXYZ* point = new g2o::VertexSBAPointXYZ(); point->setId ( index++ ); point->setEstimate ( Eigen::Vector3d ( p.x, p.y, p.z ) ); point->setMarginalized ( true ); // g2o 中必须设置 marg 参见第十讲内容 optimizer.addVertex ( point ); } // parameter: camera intrinsics g2o::CameraParameters* camera = new g2o::CameraParameters ( K.at<double> ( 0,0 ), Eigen::Vector2d ( K.at<double> ( 0,2 ), K.at<double> ( 1,2 ) ), 0 ); camera->setId ( 0 ); optimizer.addParameter ( camera ); // edges index = 1; for ( const Point2f p:points_2d ) { g2o::EdgeProjectXYZ2UV* edge = new g2o::EdgeProjectXYZ2UV(); edge->setId ( index ); edge->setVertex ( 0, dynamic_cast<g2o::VertexSBAPointXYZ*> ( optimizer.vertex ( index ) ) ); edge->setVertex ( 1, pose ); edge->setMeasurement ( Eigen::Vector2d ( p.x, p.y ) ); edge->setParameterId ( 0,0 ); edge->setInformation ( Eigen::Matrix2d::Identity() ); optimizer.addEdge ( edge ); index++; } chrono::steady_clock::time_point t1 = chrono::steady_clock::now(); optimizer.setVerbose ( true ); optimizer.initializeOptimization(); optimizer.optimize ( 100 ); chrono::steady_clock::time_point t2 = chrono::steady_clock::now(); chrono::duration<double> time_used = chrono::duration_cast<chrono::duration<double>> ( t2-t1 ); cout<<"optimization costs time: "<<time_used.count() <<" seconds."<<endl; cout<<endl<<"after optimization:"<<endl; cout<<"T="<<endl<<Eigen::Isometry3d ( pose->estimate() ).matrix() <<endl; }
结果及分析
calling bundle adjustment iteration= 0 chi2= 0.001139 time= 0.00024794 cumTime= 0.00024794 edges= 75 schur= 1 lambda= 78.084078 levenbergIter= 1 iteration= 1 chi2= 0.000000 time= 8.4022e-05 cumTime= 0.000331962 edges= 75 schur= 1 lambda= 52.056052 levenbergIter= 1 iteration= 2 chi2= 0.000000 time= 7.3859e-05 cumTime= 0.000405821 edges= 75 schur= 1 lambda= 34.704035 levenbergIter= 1 iteration= 3 chi2= 0.000000 time= 7.2104e-05 cumTime= 0.000477925 edges= 75 schur= 1 lambda= 23.136023 levenbergIter= 1 iteration= 4 chi2= 0.000000 time= 7.1545e-05 cumTime= 0.00054947 edges= 75 schur= 1 lambda= 15.424015 levenbergIter= 1 iteration= 5 chi2= 0.000000 time= 7.1754e-05 cumTime= 0.000621224 edges= 75 schur= 1 lambda= 10.282677 levenbergIter= 1 iteration= 6 chi2= 0.000000 time= 7.1703e-05 cumTime= 0.000692927 edges= 75 schur= 1 lambda= 6.855118 levenbergIter= 1 iteration= 7 chi2= 0.000000 time= 7.1395e-05 cumTime= 0.000764322 edges= 75 schur= 1 lambda= 4.570079 levenbergIter= 1 iteration= 8 chi2= 0.000000 time= 7.2222e-05 cumTime= 0.000836544 edges= 75 schur= 1 lambda= 9.140157 levenbergIter= 1 optimization costs time: 0.00163647 seconds. after optimization: T= 0.997848 -0.0510879 0.0410952 -0.128454 0.0499059 0.998324 0.0292911 -0.0103276 -0.0425228 -0.0271772 0.998726 0.0590494 0 0 0 1
相比PnP的结果,在小数点第三位会有区别。(主要原因是将位姿和特征点统一放进去一起进行最优化估计)



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号