Spring源码之springMVC
web.xml
它的作用是配置初始化信息,如web页面、servlet、servlet-mapping、filter、listener、启动加载级别等。
SpringMVC 通过servlet拦截所有的URL来达到控制的目的,所以它必须要有web.xml
比较关键的配置是:
-
contextConfigLocation 配置spring配置文件地址
-
DispatcherServlet 前端控制器
程序入口
ContextLoaderListener.initWebApplicationContext().createWebApplicationContext()
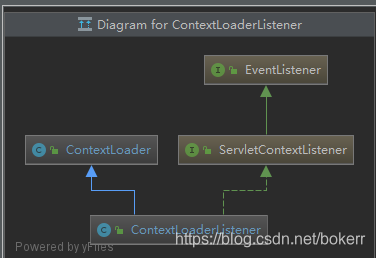
加载ApplicationContext 并注入Servlet容器
先判断contextClass 属性是否配置,否则加载默认的:XmlWebApplicationContext
protected Class<?> determineContextClass(ServletContext servletContext) {
String contextClassName = servletContext.getInitParameter(CONTEXT_CLASS_PARAM);
if (contextClassName != null) {
try {
return ClassUtils.forName(contextClassName, ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader());
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException(
"Failed to load custom context class [" + contextClassName + "]", ex);
}
}
else {
// 默认值:org.springframework.web.context.support.XmlWebApplicationContext 可继承它修改容器配置
contextClassName = defaultStrategies.getProperty(WebApplicationContext.class.getName());
try {
return ClassUtils.forName(contextClassName, ContextLoader.class.getClassLoader());
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException(
"Failed to load default context class [" + contextClassName + "]", ex);
}
}
}
ContextLoader 中的static 静态语句块可以知道加载的配置文件是: ContextLoader.properties
static {
// Load default strategy implementations from properties file.
// This is currently strictly internal and not meant to be customized
// by application developers.
try {
// DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PATH = ContextLoader.properties
ClassPathResource resource = new ClassPathResource(DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PATH, ContextLoader.class);
defaultStrategies = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource);
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Could not load 'ContextLoader.properties': " + ex.getMessage());
}
}
以上为容器加载阶段,详细细节之前章节已经讲述,不再赘述
ContextLoader 的 initWebApplicationContext 方法中,发现如下代码:
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, this.context);
servlet容器持有该引用
servlet
Servlet是按照servlet规范使用Java编写的程序,基于HTTP协议运行在服务器端,它的声明周期分为:初始化、运行、销毁。
初始化
- servlet容器加载servlet类,把它的.class字节码文件读取到内存中
- servlet容器创建一个ServletConfig对象,它包含该servlet的初始化配置信息
- servlet容器创建一个 servlet 对象
- servlet容器调用servlet对象的init() 方法进行初始化
运行阶段
- servlet容器接收到请求时,会根据请求创建一个servletRequest(请求信息) 对象和servletResponse(封装返回信息) 对象,
调用service方法并处理请求,通过servletResponse相应请求后销毁这两个对象。
销毁阶段
- Web应用终止,servlet容器调用servlet对象的destory方法,然后销毁servlet对象以及相关的 servletConfig对象。
DispatcherServlet
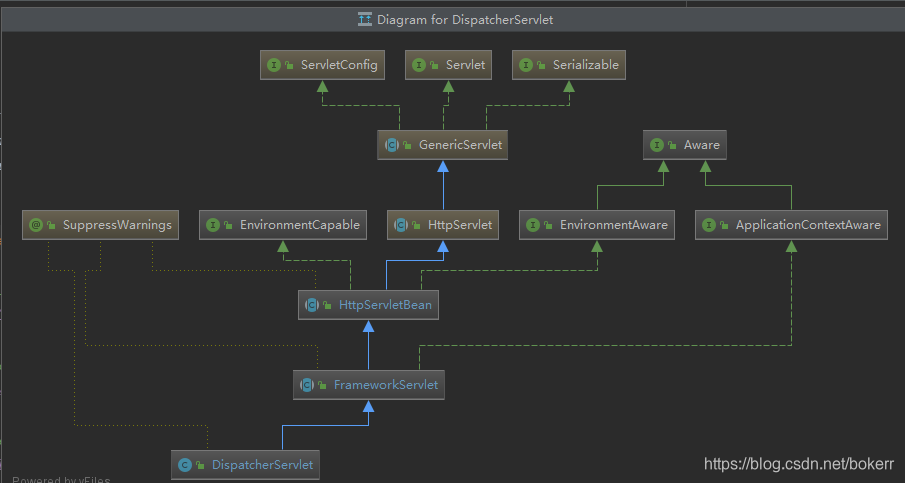
它是SpringMVC的核心, 是servlet的一个实现类
初始化
在它的父类HttpServletBean中找到了init方法的调用
该方法只是初始的配置信息加载
public final void init() throws ServletException {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Initializing servlet '" + getServletName() + "'");
}
// Set bean properties from init parameters.
// 解析 <init-param> 并验证
// requiredProperties 配置必须要的参数,否则抛出异常
PropertyValues pvs = new ServletConfigPropertyValues(getServletConfig(), this.requiredProperties);
if (!pvs.isEmpty()) {
try {
// servlet 转为 BeanWrapper 从而可以像spring那样 对 init-param 的值进行注入
BeanWrapper bw = PropertyAccessorFactory.forBeanPropertyAccess(this);
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = new ServletContextResourceLoader(getServletContext());
bw.registerCustomEditor(Resource.class, new ResourceEditor(resourceLoader, getEnvironment()));
initBeanWrapper(bw);// 钩子函数
bw.setPropertyValues(pvs, true);// 注册到自定义属性编辑器
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isErrorEnabled()) {
logger.error("Failed to set bean properties on servlet '" + getServletName() + "'", ex);
}
throw ex;
}
}
// Let subclasses do whatever initialization they like.
initServletBean();// 钩子函数
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Servlet '" + getServletName() + "' configured successfully");
}
}
继续,在父类 FrameworkServlet 中找到了钩子函数:initServletBean方法的具体实现:
有模板方法模式那味儿了,很遗憾这里还是准备工作
@Override
protected final void initServletBean() throws ServletException {
getServletContext().log("Initializing Spring FrameworkServlet '" + getServletName() + "'");
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("FrameworkServlet '" + getServletName() + "': initialization started");
}
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
// 对WebApplicationContext进一步初始化和补充
this.webApplicationContext = initWebApplicationContext();
initFrameworkServlet();
}
catch (ServletException | RuntimeException ex) {
logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex);
throw ex;
}
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
long elapsedTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;
logger.info("FrameworkServlet '" + getServletName() + "': initialization completed in " +
elapsedTime + " ms");
}
}
然后 initWebApplicationContext() 方法对容器进一步初始化和补充
protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() {// 对WebApplicationContext进一步初始化和补充
WebApplicationContext rootContext =
WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext());// 从 容器 servletContext 中获取
WebApplicationContext wac = null;
if (this.webApplicationContext != null) { // webApplicationContext 是否在构造函数中被注入 (未解析过) new DispatcherServlet()->.super(WebApplicationContext)
wac = this.webApplicationContext;
if (wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) wac;
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
cwac.setParent(rootContext);
}
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac);
}
}
}
if (wac == null) {
// WebApplicationContext 是否被 contextAttribute 属性注入
wac = findWebApplicationContext();
}
if (wac == null) {
// 既无构造器注入,也无contextAttribute属性注入,那么通过初始化的 WebApplicationContext 构造新的容器
wac = createWebApplicationContext(rootContext);
}
if (!this.refreshEventReceived) {
synchronized (this.onRefreshMonitor) {
onRefresh(wac);// 加载配置 钩子,由子类 DispatcherServlet 实现,用于 Spring Web功能的 相关解析器的初始化
}
}
if (this.publishContext) {
String attrName = getServletContextAttributeName();
getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName, wac);
}
return wac;
}
跟进 方法configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext() 发现了我们的老朋友 refresh() 方法,是不是很眼熟?
ApplicationContext 容器加载过程中 它近乎是一切的起点了,查看默认的容器类XmlWebApplicationContext 的类图不难证实这点
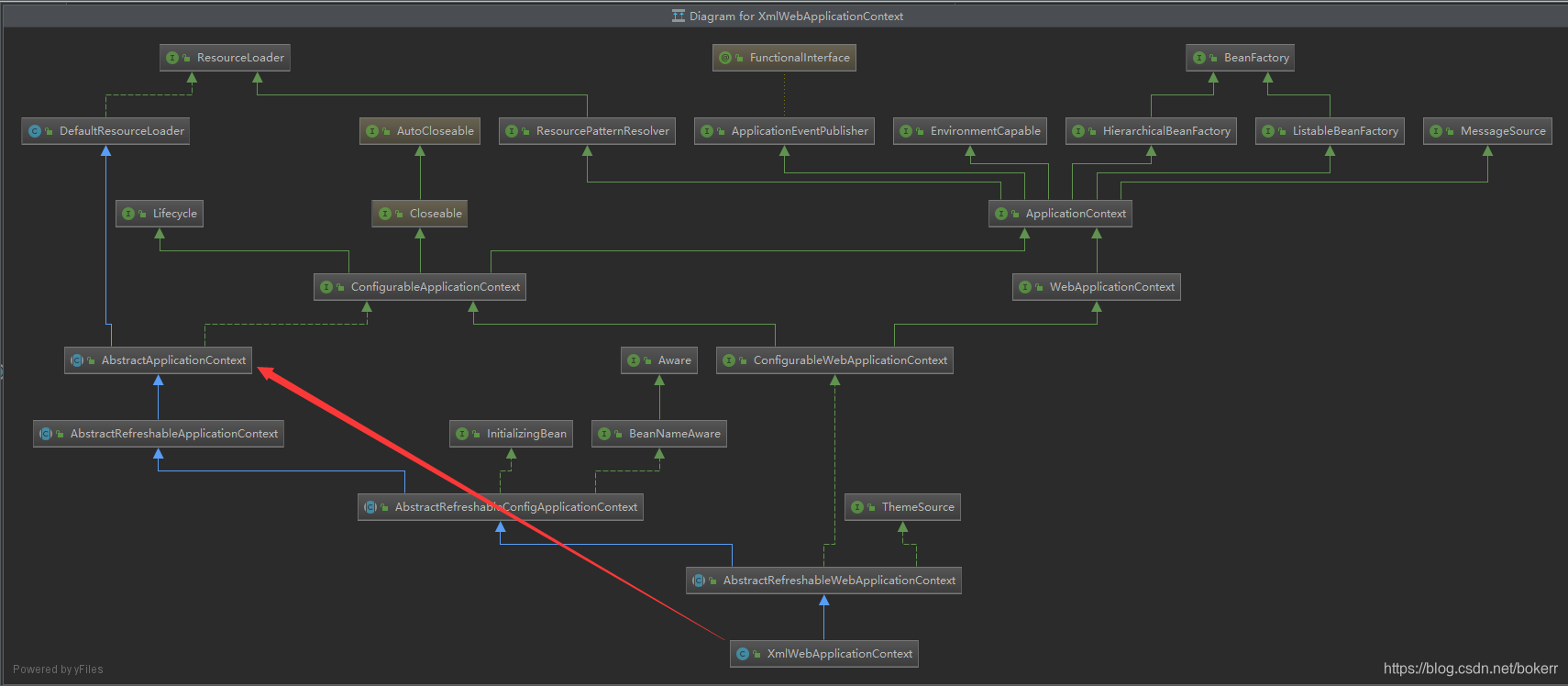
protected void configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac) {
...
......
.........
wac.refresh();// ConfigurableApplicationContext.refresh() <- AbstractApplicationContext.refresh() <- XmlWebApplicationContext
}
然后看initWebApplicationContext()方法内调用的,onRefresh()方法
FrameworkServlet 类中找到的onRefresh() 又是空方法,不解释,钩子函数它又来了,最后回到DispatcherServlet类,发现了该方法的具体定义:
该方法的主要功能是刷新Spring在Web功能实现中所必须使用的全局变量的初始化
从配置文件:DispatcherServlet.properties 可得知部分全局变量所使用的默认值
@Override
protected void onRefresh(ApplicationContext context) {// 用于 Spring Web功能的 相关解析器的初始化
initStrategies(context);
}
/**
* Initialize the strategy objects that this servlet uses.
* <p>May be overridden in subclasses in order to initialize further strategy objects.
*/
protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) {// 各个全局功能解析器初始化
initMultipartResolver(context);// 处理文件上传
initLocaleResolver(context);// 国际化配置? 基于:url session cookie 支持国际化
initThemeResolver(context);// Theme主题控制网页风格
// 可以有多个HandleMapping,根据优先级访问,直到获取到可用的Handle 为止 (Ordered 接口控制)
initHandlerMappings(context);// 处理客户端发起的Request请求,根据WebApplicationContext的配置来,回传给 DispatcherServler 对应的Controller
// DispatcherServlet 通过处理器映射(HandleMapping)配置,得到处理器(Handle),之后会轮询处理器(Handle)的<配适器模块>
// 并查找能够处理当前HTTP请求的处理器(Handle),的配适器实现(Adapter)
// org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.HttpRequestHandlerAdapter 对Http请求处理器进行配适 OtherClass <- HttpAdapter <- HttpHandle
// org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter 将Http请求配饰到一个Controller 的实现进行处理
// org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerAdapter 用于执行Controller方法的配适器,对注解方式的支持
initHandlerAdapters(context);// 配适器
initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context);// 异常处理
initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context);// 当Controller没有返回任何View对象或者逻辑视图名称,并在该方法中没有向response的输出流里面写任何数据,那么spring会使用约定方式提供一个逻辑视图名称。
// resolverViewName 方法 根据 viewName创建合适的View 实现
initViewResolvers(context);// Controller 计算结束后将结果封装到ModleAndView,DispatcherServlet 会根据ModleAndView 选择合适的视图进行渲染
initFlashMapManager(context);// SpringMVC Flash attributes 提供了属性存储功能,可够重定向时其它请求使用
}
DispatcherServlet 的逻辑处理
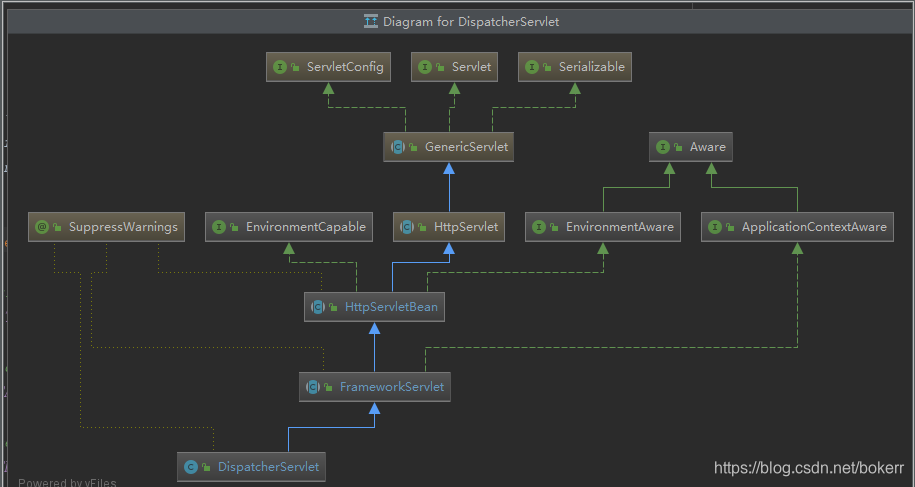
看 HttpServlet 类的结构 看关键的doGet和doPost,在FrameworkServlet类中找到了如下方法实现:
@Override
protected final void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
processRequest(request, response);
}
@Override
protected final void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
processRequest(request, response);
}
protected final void processRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
// 主要目的:提取请求参数,用于重定向
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
Throwable failureCause = null;
LocaleContext previousLocaleContext = LocaleContextHolder.getLocaleContext();// 为了后续请求能使用提取属性
LocaleContext localeContext = buildLocaleContext(request);
RequestAttributes previousAttributes = RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();// 为了后续请求能使用提取属性
ServletRequestAttributes requestAttributes = buildRequestAttributes(request, response, previousAttributes);
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
asyncManager.registerCallableInterceptor(FrameworkServlet.class.getName(), new RequestBindingInterceptor());
// 初始化
initContextHolders(request, localeContext, requestAttributes);
try {
// 准备工作 具体实现由 DispatcherServlet 提供
doService(request, response);
}
catch (ServletException | IOException ex) {
failureCause = ex;
throw ex;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
failureCause = ex;
}
finally {
resetContextHolders(request, previousLocaleContext, previousAttributes);// 设置提取的请求参数,用于重定向
if (requestAttributes != null) {
requestAttributes.requestCompleted();
}
publishRequestHandledEvent(request, response, startTime, failureCause);// 事件通知
}
}
忽略准备工作:doService().doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
如下为核心代码逻辑,之前提到的全部变量配置将登上舞台了
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;
// 当业务比较复杂时启用另一个线程
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);// 管理异步请求处理的中心类,通常不由应用程序类直接使用。
try {
ModelAndView mv = null;
Exception dispatchException = null;
try {
// 检查全局变量
// 如果请求类型为:multipartContent 将 HttpServletRequest 转为 MultipartHttpServletRequest (包装器 ? 策略模式)
processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);
multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request);// 检查原类型 包装 / 代理
// Determine handler for the current request.
// 根据URL 匹配
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);// 按优先级从各个HandleMapping 中获取Handle
if (mappedHandler == null) {
noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());// 根据handle 获取匹配的配适器 Adapter
String method = request.getMethod();
boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method);
if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) {// last-modified(缓存处理机制) 请求头处理 <最后修改时间>
long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());
// 未变化? 最后修改时间未变? 过滤重复请求???
if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) {
return;
}
}
// 调用拦截器的preHandle方法
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {
return;
}
// Actually invoke the handler.
// 激活Handle 并返回视图 (由配适器的 handle方法完成 )
// 查看配置文件DispatcherServlet.properties 可以知道 HandlerAdapter ha 的具体实现类,跟踪handle方法:
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return;
}
applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv);// 视图名称处理
// 调用所有拦截器的postHandle 方法,如果存在的话
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
dispatchException = ex;
}
catch (Throwable err) {
dispatchException = new NestedServletException("Handler dispatch failed", err);
}
processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
// 完成处理后,激活触发器
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex);
}
catch (Throwable err) {
// 完成处理后,激活触发器
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler,
new NestedServletException("Handler processing failed", err));
}
finally {
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
if (mappedHandler != null) {
mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response);
}
}
else {
if (multipartRequestParsed) {
cleanupMultipart(processedRequest);
}
}
}
}
查看配置文件 DispatcherServlet.properties 可以知道 HandlerAdapter ha 的具体实现类,跟踪handle方法:
org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerAdapter=org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.HttpRequestHandlerAdapter,
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter,
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerAdapter
org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerMapping=org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping,
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping
- getHandle()
AbstractHandlerMapping.getHandel().[ AbstractUrlHandlerMapping.getHandlerInternal() ]
根据请求url获取handel
protected Object getHandlerInternal(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
String lookupPath = getUrlPathHelper().getLookupPathForRequest(request);// 截取 url
Object handler = lookupHandler(lookupPath, request);// 根据 url 获取 handle
if (handler == null) {// 获取到的解析器为空
// We need to care for the default handler directly, since we need to
// expose the PATH_WITHIN_HANDLER_MAPPING_ATTRIBUTE for it as well.
Object rawHandler = null;
if ("/".equals(lookupPath)) {// 请求路径仅为根路径: 则使用RootHandle处理
rawHandler = getRootHandler();
}
if (rawHandler == null) {
rawHandler = getDefaultHandler();// 否则设置默认的 Handle
}
if (rawHandler != null) { // 默认 Handle 可能为空
// Bean name or resolved handler?
if (rawHandler instanceof String) { // 若查找的 Handle 类型为String 则为beanName 否则为 Handle 本身
String handlerName = (String) rawHandler;
rawHandler = obtainApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName);// 从容器中获取
}
validateHandler(rawHandler, request);// 校验钩子函数
// 初始化 Handle ??? HandlerExecutionChain 对 Handle 进行包装
handler = buildPathExposingHandler(rawHandler, lookupPath, lookupPath, null);
}
}
if (handler != null && logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Mapping [" + lookupPath + "] to " + handler);
}
else if (handler == null && logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No handler mapping found for [" + lookupPath + "]");
}
return handler;
}
2.getHandlerAdapter
根据handel获取配饰器Adapter
SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter.suport
public boolean supports(Object handler) {
return (handler instanceof Controller);
}
看到controller主要解析就完成了,剩下的事情就是处理请求,并绑定视图放回,以及当发生异常时对异常视图进行处理。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号