重新认识Android
首先我们来看下源码中源于Activity的定义:
- public class Activity extends ContextThemeWrapper
- implements LayoutInflater.Factory2,
- Window.Callback, KeyEvent.Callback,
- OnCreateContextMenuListener, ComponentCallbacks2 {
- ...
- }
下面我们来详细分析每一部分的具体意义:
extends ContextThemeWrapper表示Activity本质上是一个ContextThemeWrapper,而ContextThemeWrapper具体是什么呢?看ContextThemeWrapper在源码中的定义:
- public class ContextThemeWrapper extends ContextWrapper {
- ...
- }
可见ContextThemeWrapper是一个ContextWrapper,继续往下看:
- public class ContextWrapper extends Context {
- Context mBase;
- ...
- }
ContextWrapper本质上是一个Context,context 的定义如下:
- public abstract class Context {
- ...
- }
整体结构如下图所示(图引用自:http://blog.csdn.net/qinjuning/article/details/7310620):
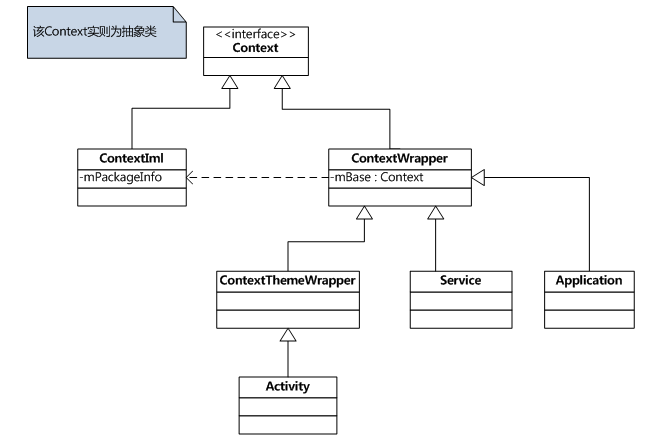
Context是一个抽象类,因此可以知道Activity其实就是一个Context,并实现了一些接口,如何理解Context呢?
Context 俗称上下文,在很多对象定义中我们都用到了Context,例如ImageViewimageView = new ImageView(this); 这里的this就是当前Activity所在的Context,源码中对Context的解释如下:
Interface to global information about anapplication environment. This is an abstract class whose implementation isprovided by the Android system. It allows access to application-specificresources and classes, as well as up-calls for application-level operationssuch as launching activities, broadcasting and receiving intents, etc.
Context只是一个接口,真正实现Context功能的是ContexImpl类,为了了解Context具体有什么作用,我们先来了解下Context中定义了哪些接口:
- public abstract ComponentNamestartService(Intent service);
- public abstract boolean stopService(Intentservice);
- public abstract void startActivity(Intentintent);
- public abstract void sendBroadcast(Intentintent);
- public abstract Intent registerReceiver(BroadcastReceiverreceiver, IntentFilter filter);
- public abstract Resources getResources();
以上是Context众多接口中的一个片段,看着接口是不是很熟悉?其实我们经常用到的一些函数其实都是在Context中定义的,因此Context可以被认为是用来封装一下通用功能的一个类,当然这个类不仅仅是针对Activity,最常见的service也是继承自Context,以及一大堆类都继承自Context,具体可参考:http://developer.android.com/reference/android/content/Context.html,关于Context的具体介绍可参考:http://blog.csdn.net/qinjuning/article/details/7310620
ContextWrapper仅仅是对Context的简单封装,如果要对Context修改,我们只需要修改ContextWrapper,而不需要对通用的Context进行修改,ContextWrapper的目的仅此而已。而ContextThemeWrapper只是在ContextWrapper的基础上加入了Theme相关的一些内容,对于Activity来说需要处理一些Theme相关的东西,但是对于Service来说只需继承ContextWrapper,因为Service不需要处理Theme相关的内容。
分析完extends部分,我们再来看下implements部分,extends决定了Activity的本质,implements部分可以认为是对Activity的扩展。
- LayoutInflater.Factory:通过LayoutInflater来inflate一个layout时的回调接口
- Window.Callback: Activity 靠这个接口才有机会对消息进行处理,这部分涉及到消息的传递,以后将专门介绍。
- ComponentCallbacks2:定义了内存管理的接口,内存过低时的回调和处理处理接口
- KeyEvent.Callback:键盘事件响应的回调接口,例如onKeyDown()等
- OnCreateContextMenuListener:上下文菜单显示事件的监听接口,通过实现该方法来处理上下文菜单显示时的一些操作
通过以上分析,我们大概了解了Activity具体是什么了,这对以后理解Activity应该能带来一定的帮助。

Examples of android:scaleType attribute.
Top row (l-r) center, centerCrop,centerInside.
Bottom row (l-r): fitCenter, fitStart, fitEnd, fitXY.
- VuDroid (Based on MuPDF) Review on Open-App
- APV (based on MuPDF)
- PDF-Annotation (Based on APV, MuPDF) appears to be the only OS app with annotation abilities, and they're not confirmed to work.
- Android PDF Viewer (Based on Sun's pdf-renderer)
- eBookDroid (Based on VuDroid, MuPDF))
- DroidReader (Based on MuPDF)
- APDFViewer (Based on Poppler, xpdf)
- iPDF View (Based on APV, MuPDF)
- Perfect Viewer plugin
ActionBar




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号