POJ - 1177 线段树
POJ - 1177 扫描线
这道题也算是一道扫描线的经典题目了。
只不过这道题是算周长,非常有意思的一道题。我们已经知道了,一般求面积并,是如何求的,现在我们要把扫描线进行改造一下,使得能算周长。
我们大致考虑一下图像上是如何实现的:
这样一个图我们要如何求他的面积?
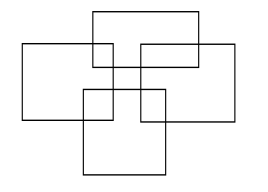
我们把轮廓画出来
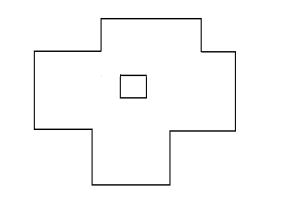
我们把扫描线画出来
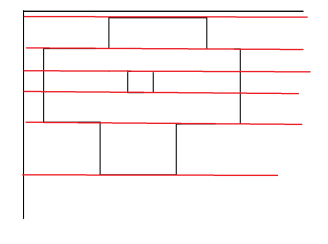
我们发现
从上到下我们竖直方向的长度,是每条线高度差*2*线段树的连续的段数目。
从上到下我们水平方向的长度,是横线的长度 = 现在这次总区间被覆盖的长度和上一次总区间被覆盖的长度之差的绝对值。
这样我们就找到解决的办法,维护就非常容易了,本题范围比较小,因此不用离散化,直接区间建树,节点维护4个值,
Len:区间内部被覆盖一次以上的长度
S:区间内被完全覆盖的次数
这个是常规操作。
然后维护区间内部,连续区间(每个之间是隔离的)的个数
然后两个lc,rc,代表区间左端点和右端点是否在连续区间内(合并区间的时候有用)
这样就行了。
然后考虑子节点往上pushup的情况,
首先区间被完全填满,那么len等于区间长度,lc,rc,num都是1。
如果到叶节点,都是0
否则,len,rc,lc,的长度由两个儿子节点提供,需要注意的是,num的情况是由两个儿子提供,如果左儿子的右边界和右儿子的左边界都是在连续的区间中,那么这个区间会被合成为1个区间,从而个数需要减1.
最后常规的操作即可。
#include<iostream> #include<algorithm> #include<stdio.h> #include<string.h> using namespace std; const int N = 5007; const int X = 20007; const int inf = 1<<29; inline int L(int r){return r<<1;}; inline int R(int r){return r<<1|1;}; inline int MID(int l,int r){return (l+r)>>1;}; struct Edge{ int l,r; int h; int f; }line[N*2]; struct node{ int l,r,len,s,num; //num这个区间有多少不连续的线段 bool lc,rc;//区间左右端点是否被覆盖 }tree[X<<2]; bool cmp(Edge a,Edge b) { return a.h<b.h; } void pushup(int root) { if (tree[root].s){ tree[root].len=tree[root].r-tree[root].l+1;//没有离散化 tree[root].rc=tree[root].lc=1; tree[root].num=1; }else if (tree[root].l == tree[root].r){ tree[root].len=0; tree[root].lc=tree[root].rc=0; tree[root].num=0; }else{ tree[root].len=tree[L(root)].len+tree[R(root)].len; tree[root].lc=tree[L(root)].lc; tree[root].rc=tree[R(root)].rc; tree[root].num=tree[L(root)].num+tree[R(root)].num-(tree[L(root)].rc && tree[R(root)].lc); } } void buildtree(int root,int l,int r){ tree[root].l=l; tree[root].r=r; tree[root].s=tree[root].len=0; tree[root].lc = tree[root].rc = tree[root].num = 0; if (l==r){ return ; } int mid = MID(l,r); buildtree(L(root),l,mid); buildtree(R(root),mid+1,r); } void update(int root,int ul,int ur,int v) { int l=tree[root].l; int r=tree[root].r; //cout<<root<<l<<" "<<r<<" "<<ul<<" "<<ur<<endl; if (ul==l && ur==r) { tree[root].s+=v; pushup(root); return; } int mid = MID(l,r); if (ur<=mid)update(L(root),ul,ur,v); else if(ul>mid)update(R(root),ul,ur,v); else{ update(L(root),ul,mid,v); update(R(root),mid+1,ur,v); } pushup(root); } int main(){ int n; while(scanf("%d",&n)!=EOF){ int x1,x2,y1,y2,mx=-inf,mn=inf; int tot=0; for (int i=0;i<n;i++){ scanf("%d%d%d%d",&x1,&y1,&x2,&y2); mx=max(mx,max(x1,x2)); mn=min(mn,min(x1,x2)); line[tot].l=x1; line[tot].r=x2; line[tot].h=y1; line[tot++].f=1; line[tot].l=x1; line[tot].r=x2; line[tot].h=y2; line[tot++].f=-1; } sort(line,line+tot,cmp); int ans=0; int last=0; buildtree(1,mn,mx-1); // cout<<"ss"<<endl; for (int i=0;i<tot;i++) { // cout<<line[0].l<<" "<<line[0].r<<endl; update(1,line[i].l,line[i].r-1,line[i].f); ans+=abs(tree[1].len-last); ans+=(line[i+1].h-line[i].h)*2*tree[1].num; last=tree[1].len; } printf("%d\n",ans); } return 0; }
usingnamespacestd; constint N = 5007; constint X = 20007; constint inf = 1<<29; inline int L(int r){return r<<1;}; inline int R(int r){return r<<1|1;}; inline int MID(int l,int r){return (l+r)>>1;}; struct Edge{ int l,r; int h; int f; }line[N*2]; struct node{ int l,r,len,s,num; //num这个区间有多少不连续的线段bool lc,rc;//区间左右端点是否被覆盖 }tree[X<<2]; bool cmp(Edge a,Edge b) { return a.h<b.h; } void pushup(int root) { if (tree[root].s){ tree[root].len=tree[root].r-tree[root].l+1;//没有离散化 tree[root].rc=tree[root].lc=1; tree[root].num=1; }elseif (tree[root].l == tree[root].r){ tree[root].len=0; tree[root].lc=tree[root].rc=0; tree[root].num=0; }else{ tree[root].len=tree[L(root)].len+tree[R(root)].len; tree[root].lc=tree[L(root)].lc; tree[root].rc=tree[R(root)].rc; tree[root].num=tree[L(root)].num+tree[R(root)].num-(tree[L(root)].rc && tree[R(root)].lc); } } void buildtree(int root,int l,int r){ tree[root].l=l; tree[root].r=r; tree[root].s=tree[root].len=0; tree[root].lc = tree[root].rc = tree[root].num = 0; if (l==r){ return ; } int mid = MID(l,r); buildtree(L(root),l,mid); buildtree(R(root),mid+1,r); } void update(int root,int ul,int ur,int v) { int l=tree[root].l; int r=tree[root].r; //cout<<root<<l<<" "<<r<<" "<<ul<<" "<<ur<<endl;if (ul==l && ur==r) { tree[root].s+=v; pushup(root); return; } int mid = MID(l,r); if (ur<=mid)update(L(root),ul,ur,v); elseif(ul>mid)update(R(root),ul,ur,v); else{ update(L(root),ul,mid,v); update(R(root),mid+1,ur,v); } pushup(root); } int main(){ int n; while(scanf("%d",&n)!=EOF){ int x1,x2,y1,y2,mx=-inf,mn=inf; int tot=0; for (int i=0;i<n;i++){ scanf("%d%d%d%d",&x1,&y1,&x2,&y2); mx=max(mx,max(x1,x2)); mn=min(mn,min(x1,x2)); line[tot].l=x1; line[tot].r=x2; line[tot].h=y1; line[tot++].f=1; line[tot].l=x1; line[tot].r=x2; line[tot].h=y2; line[tot++].f=-1; } sort(line,line+tot,cmp); int ans=0; int last=0; buildtree(1,mn,mx-1); // cout<<"ss"<<endl;for (int i=0;i<tot;i++) { // cout<<line[0].l<<" "<<line[0].r<<endl; update(1,line[i].l,line[i].r-1,line[i].f); ans+=abs(tree[1].len-last); ans+=(line[i+1].h-line[i].h)*2*tree[1].num; last=tree[1].len; } printf("%d\n",ans); } return0; }





