函数式编程,方法引用,Java双冒号(::)示例详解
第一部分
方法引用,又称双冒号(::),是简化的lambda表达式,主要使用形式包括四种:
方法引用的形式(Kinds of Method References)
| 类型 | Kind | Example |
| 指向静态方法的引用 | Reference to a static method | ContainingClass::staticMethodName |
| 指向特定对象实例方法的引用 | Reference to an instance method of a particular object | containingObject::instanceMethodName |
| 指向特定类型任意对象实例方法的引用 | Reference to an instance method of an arbitrary object of a particular type | ContainingType::methodName |
| 指向构造函数的引用 | Reference to a constructor | ClassName::new |
考虑以下例子:
Person类
1 import java.time.LocalDate; 2 3 public class Person { 4 5 public enum Sex { 6 MALE, FEMALE 7 } 8 9 String name; 10 LocalDate birthday; 11 Sex gender; 12 String emailAddress; 13 14 public Person(String name, LocalDate birthday, Sex gender) { 15 this.name = name; 16 this.birthday = birthday; 17 this.gender = gender; 18 } 19 20 public int getAge() { 21 int age = LocalDate.now().minusYears(birthday.getYear()).minusDays(birthday.getDayOfYear()).getYear(); 22 return age; 23 } 24 25 public LocalDate getBirthday() { 26 return birthday; 27 } 28 29 public static int compareByAge(Person a, Person b) { 30 return a.birthday.compareTo(b.birthday); 31 } 32 }
如果对Person数组排序,可通过下面这种方式,先声明一个类,然后实例化。
①实例化类的写法:
1 List<Person> roster = Arrays.asList(); 2 3 Person[] rosterAsArray = roster.toArray(new Person[roster.size()]); 4 5 class PersonAgeComparator implements Comparator<Person> { 6 public int compare(Person a, Person b) { 7 return a.getBirthday().compareTo(b.getBirthday()); 8 } 9 } 10 11 Arrays.sort(rosterAsArray, new PersonAgeComparator());
静态方法sort的方法签名:
1 static <T> void sort(T[] a, Comparator<? super T> c)
Comparator是一个函数式接口
1 @FunctionalInterface 2 public interface Comparator<T> { 3 4 int compare(T o1, T o2); 5 }
②可以通过lambda表达式,替换创建一个类:
返回值为compare的方法体
1 Arrays.sort(rosterAsArray, 2 (Person a, Person b) -> { 3 return a.getBirthday().compareTo(b.getBirthday()); 4 } 5 );
③单独的表达式,可以去掉return和大括号,写法为:
1 Arrays.sort(rosterAsArray, (Person a, Person b) -> a.getBirthday().compareTo(b.getBirthday()));
④参数类型可以自动推断,可以去掉参数类型:
1 Arrays.sort(rosterAsArray, (a, b) -> a.getBirthday().compareTo(b.getBirthday()));
⑤方法引用可以使代码进一步简洁:
1 Arrays.sort(rosterAsArray, Person::compareByAge);
下面示例演示4种类型
1)指向静态方法的引用
1 Arrays.sort(rosterAsArray, Person::compareByAge);
2)指向类实例方法的引用
1 String[] stringArray = { "Barbara", "James", "Mary", "John", "Patricia", "Robert", "Michael", "Linda" };
2 Arrays.sort(stringArray, String::compareToIgnoreCase);
3)指向特定类型任意对象实例方法的引用
1 class ComparisonProvider { 2 public int compareByName(Person a, Person b) { 3 return a.getName().compareTo(b.getName()); 4 } 5 6 public int compareByAge(Person a, Person b) { 7 return a.getBirthday().compareTo(b.getBirthday()); 8 } 9 } 10 ComparisonProvider myComparisonProvider = new ComparisonProvider(); 11 Arrays.sort(rosterAsArray, myComparisonProvider::compareByName);
4)指向构造函数的引用
有如下方法,将一个集合转为另外一个集合
1 public static <T, SOURCE extends Collection<T>, DEST extends Collection<T>> 2 DEST transferElements( 3 SOURCE sourceCollection, 4 Supplier<DEST> collectionFactory) { 5 6 DEST result = collectionFactory.get(); 7 for (T t : sourceCollection) { 8 result.add(t); 9 } 10 return result; 11 }
转换如下:
1 Set<Person> rosterSetLambda = transferElements(roster, () -> { return new HashSet<>(); });
简洁写法如下:
1 Set<Person> rosterSet = transferElements(roster, HashSet::new);
上述代码隐藏了泛型:
1 Set<Person> rosterSet = transferElements(roster, HashSet<Person>::new);
以上参考自:https://docs.oracle.com/javase/tutorial/java/javaOO/methodreferences.html
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 分割线 - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
第二部分
下面结合方法引用对应的(内置)函数式接口,通过代码示例,详细解说。
双冒号(::)和 箭头函数(->)一并展示如下:
如:HashMap::new 等同于 ( ) -> new HashMap()
熟悉方法引用对应的函数式接口很重要,因为它是方法的参数。熟悉了它,可以结合Java高级特性(泛型、反射等)写出抽象可复用的函数式代码。
1 import java.util.ArrayList; 2 import java.util.Arrays; 3 import java.util.LinkedList; 4 import java.util.List; 5 import java.util.function.BiConsumer; 6 import java.util.function.BiFunction; 7 import java.util.function.Consumer; 8 import java.util.function.Function; 9 import java.util.function.Supplier; 10 import java.util.stream.Collectors; 11 12 public class Test { 13 14 // 实例对象引用实例方法 15 Supplier<String> supplier1 = "lowerCase"::toUpperCase; 16 Supplier<String> supplier1_1 = () -> "lowerCase".toUpperCase(); 17 18 // 类引用(无参)构造函数 19 Supplier<String> supplier2 = String::new; 20 Supplier<String> supplier2_1 = () -> new String(); 21 22 // 类引用(有参)构造函数 23 Function<String, String> function1 = String::new; 24 Function<String, String> function1_1 = (String str) -> new String(str); 25 26 // 类引用实例方法,入参为传入实例对象,入参、出参同类型 27 Function<String, String> function2 = String::toUpperCase; 28 Function<String, String> function2_1 = (String str) -> str.toUpperCase(); 29 30 // Predicate<T>可理解为特殊的Function<T, Boolean> 31 32 Person person = new Person(); 33 // 须为无参静态方法 34 Supplier<Boolean> supplierBln = Person::isTest; 35 Supplier<Boolean> supplierBln_1 = () -> Person.isTest(); 36 37 // 实例对象调用实例方法 38 Supplier<String> supplierStr = person::getName; 39 Supplier<String> supplierStr_1 = () -> person.getName(); 40 41 // 无参构造函数 42 Supplier<Person> supplierPerson = Person::new; 43 Supplier<Person> supplierPerson_1 = () -> new Person(); 44 45 // 有参构造函数 46 BiFunction<String, String, Person> biFunction = Person::new; 47 BiFunction<String, String, Person> biFunction_1 = (name, gender) -> new Person(name, gender); 48 49 // 类名调用set方法,特定场景下,可取代反射 50 BiConsumer<Person, String> biConsumer = Person::setName; 51 52 // 类名调用实例方法,入参为传入实例对象 53 Function<Person, Person> functionP = Person::toOpposite; 54 Function<Person, Person> functionP_1 = person -> person.toOpposite(); 55 56 Consumer<String> consumer = System.out::println; 57 Consumer<String> consumer_1 = (String str) -> System.out.println(str);; 58 59 public static void main(String[] args) { 60 List<String> list = Arrays.asList("1", "2", "3"); 61 boolean bl = list.stream().anyMatch("1"::equals); 62 List<String> retval = list.stream().collect(Collectors.toCollection(LinkedList::new)); 63 64 List<Person> persons = Arrays.asList(new Person(10, "Jack", "M")); 65 Person person = new Person(20, "Lily", "F"); 66 persons.stream().filter(Person::isMale).filter(person::isUnder).collect(Collectors.toCollection(ArrayList::new)); 67 } 68 }
Person类代码如下:
1 public class Person { 2 int age; 3 String name; 4 String gender; 5 6 public Person() { 7 } 8 9 public Person(String name) { 10 this.name = name; 11 } 12 13 public Person(String name, String gender) { 14 this.name = name; 15 this.gender = gender; 16 } 17 18 public Person(int age, String name, String gender) { 19 this.age = age; 20 this.name = name; 21 this.gender = gender; 22 } 23 24 public String getName() { 25 return name; 26 } 27 28 public void setName(String name) { 29 this.name = name; 30 } 31 32 public Person toOpposite() { 33 if (gender.charAt(0) == 'M') 34 gender = "F"; 35 else 36 gender = "M"; 37 return this; 38 } 39 40 public static boolean isTest() { 41 return true; 42 } 43 44 public boolean isUnder(Person person) { 45 return person.age > this.age; 46 } 47 48 public boolean isMale() { 49 return gender.equals("M"); 50 } 51 }
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 分割线 - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
第三部分
扩展至自定义的函数式接口
下面结合Elasticsearch,进一步实例讲解
指向类静态方法的引用
NodesUsageResponse节点使用响应,50行使用了方法引用

泛型方法,入参为函数Reader<V>
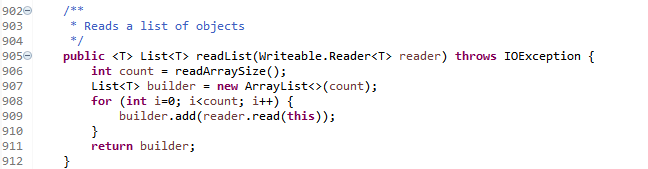
函数式接口Reader<V>,定义了方法reader(StreamInput in):
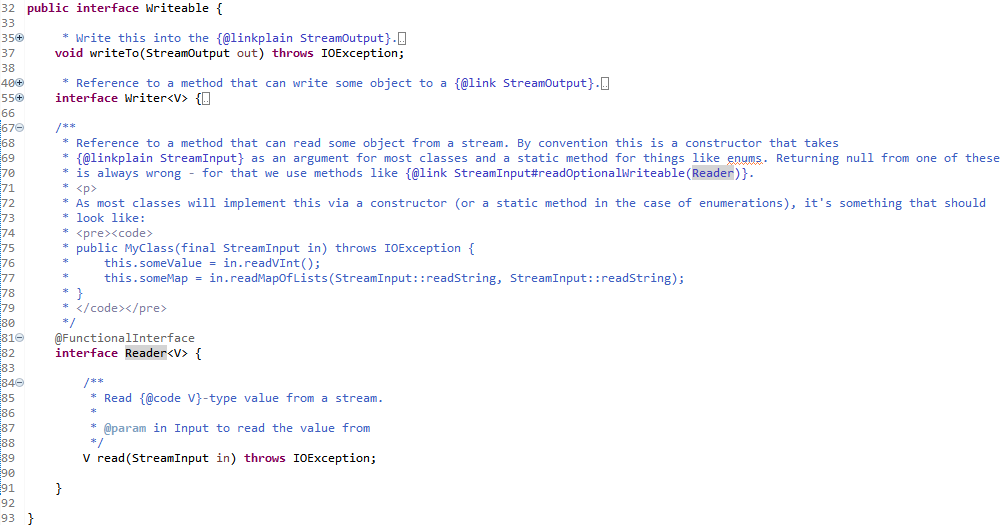
reader.read(this)实际调用函数是

第三种类型
指向特定类型任意对象实例方法的引用(Reference to an Instance Method of an Arbitrary Object of a Particular Type)
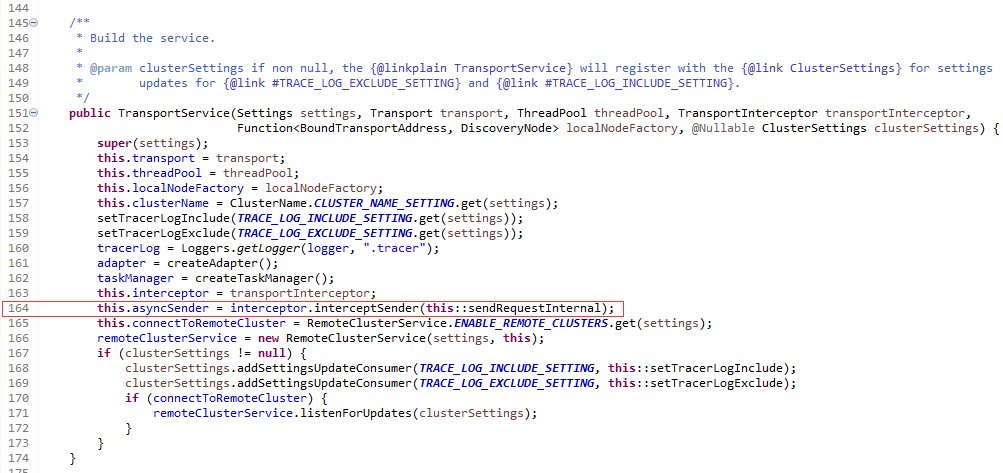
TransportService传输服务,构造函数164行使用了方法引用
成员变量asyncSender和interceptor
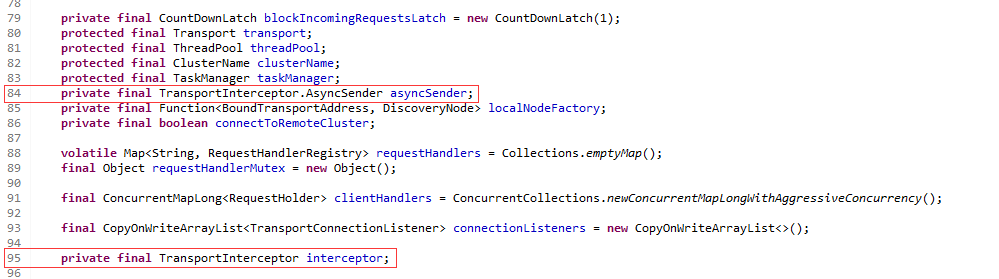
作用为请求发送拦截器接口TrsnsportInterceptor,调用的为49行,返回AsyncSender函数式接口,57行为函数式接口定义。
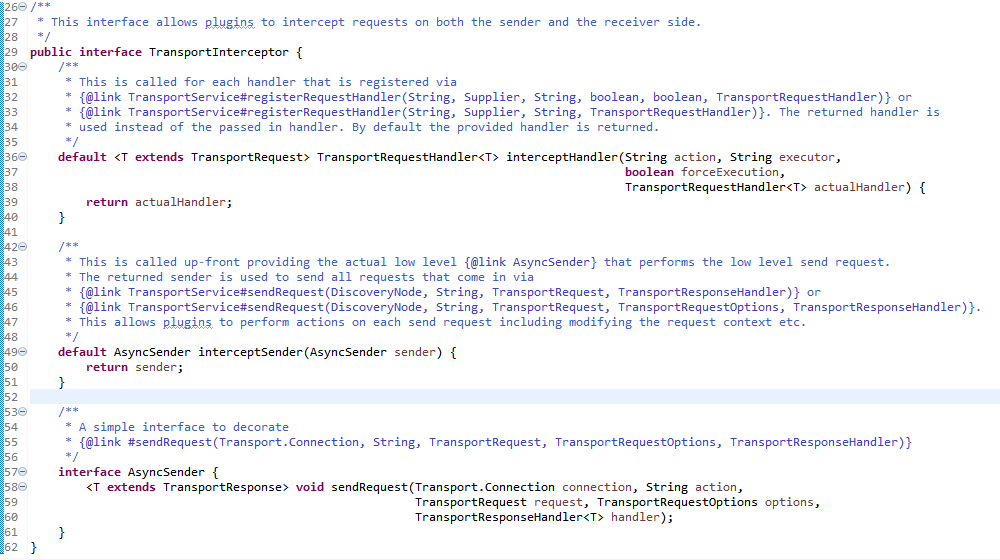
TransportService构造函数,使用了类实例方法sendRequestInternal
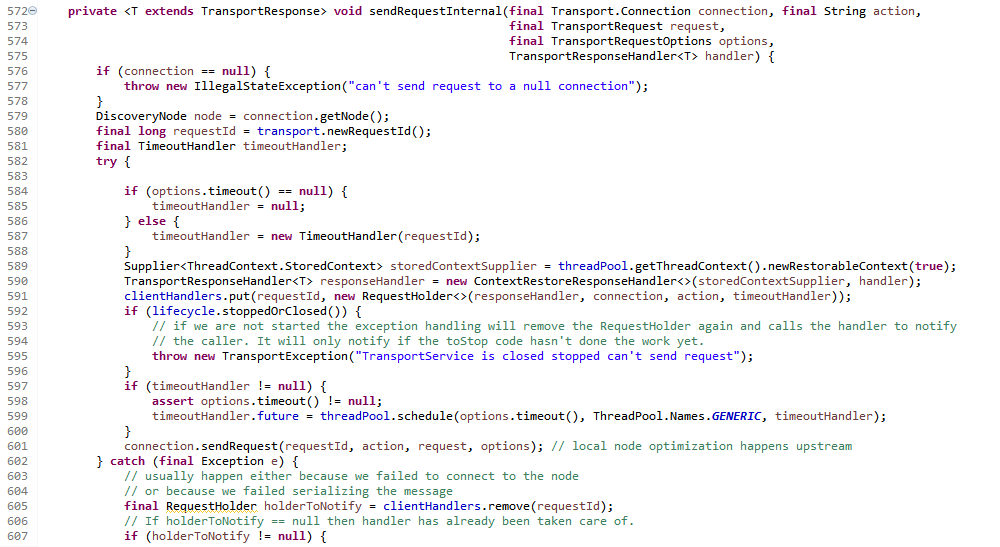
方法sendRequestInternal的方法参数列表、返回值类型和接口TransportInterceptor中的函数是接口AsyncSender一致。
第四种类型
指向构造函数的应用
构造函数,以67行为例
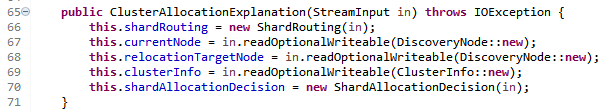
泛型方法 StreamInput # readOptionalWriteable
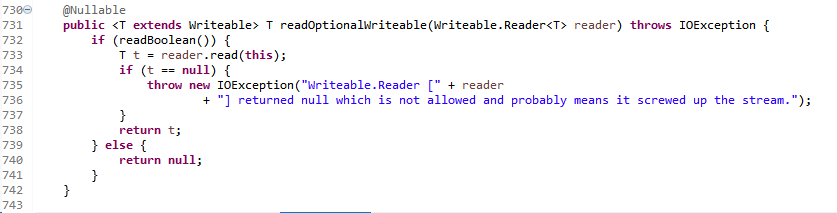
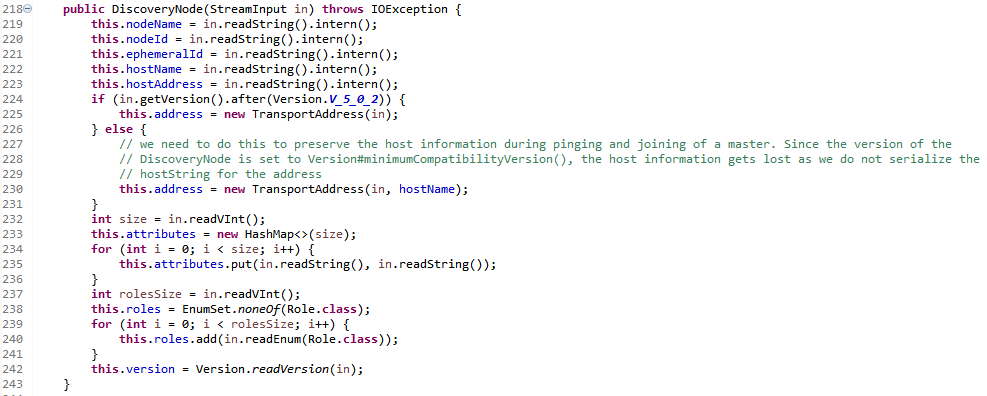
方法引用DiscoveryNode::new,实际调用构造函数如下



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号