Shiro 认证流程详解
1. 认证
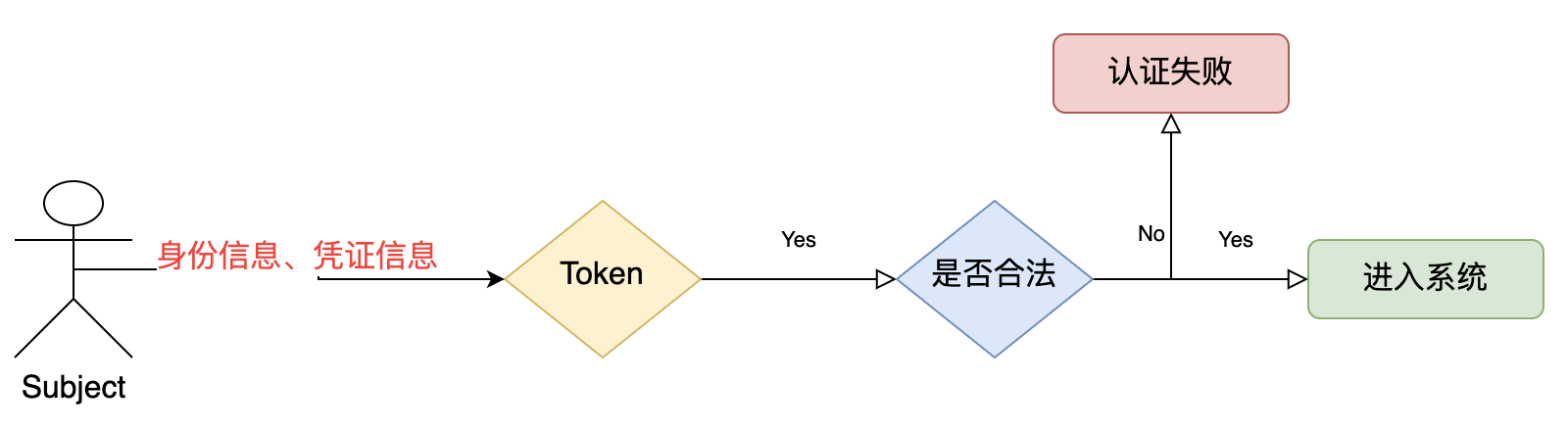
身份认证,就是判断一个用户是否为合法用户的处理过程。最常用的简单身份认证方式是系统通过核对用户输入的用户名口令,看其是否与系统中存储的该用户的用户名和口令一致,来判断用户身份是否正确。
2. Shiro 中认证的关键对象
- Subject 主体:访问系统的用户,主体可以是用户、程序等等,进行认证的都称为主体;
- Principal 身份信息:是主体(Subject)进行身份认证的标识,标识必须具有唯一性,如用户名、手机号、邮箱地址等,一个主体可以有多个身份,但是必须有一个主身份(Primary Principal)
- Credential 凭证信息:是只有主体自己知道的安全信息,如密码、证书等。
3. 认证流程
4. 认证开发
4.1 模拟数据库中已存储用户信息【创建 shiro.ini 文件】
[users] wangwu=123 zhangsan=123456 lisi=789
4.2 开发认证代码
public class TestAuthenticator { public static void main(String[] args) { // 1. 创建安全管理器 DefaultSecurityManager securityManager = new DefaultSecurityManager(); // 2. 给安全管理器设置 realm 【Realm 需要获取用户认证的数据源信息】 securityManager.setRealm(new IniRealm("classpath:shiro.ini")); // 3. SecurityUtils 设置安全管理器 SecurityUtils.setSecurityManager(securityManager); // 4. 获取关键对象 Subject 主体 Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject(); // 5. 创建令牌 UsernamePasswordToken token = new UsernamePasswordToken("wangwu", "123"); // 用户认证 try { System.out.println("认证状态: " + subject.isAuthenticated()); subject.login(token); System.out.println("认证状态: " + subject.isAuthenticated()); } catch (UnknownAccountException e) { e.printStackTrace(); System.out.println("认证失败: 用户名不存在~"); } catch (IncorrectCredentialsException e) { e.printStackTrace(); System.out.println("认证失败: 密码错误~"); } } }
-
-
LockedAccountException(帐号被锁定)
-
ExcessiveAttemptsException(登录失败次数过多)
-
public class SimpleAccountRealm extends AuthorizingRealm { //.......省略 protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException { UsernamePasswordToken upToken = (UsernamePasswordToken) token; SimpleAccount account = getUser(upToken.getUsername()); if (account != null) { if (account.isLocked()) { throw new LockedAccountException("Account [" + account + "] is locked."); } if (account.isCredentialsExpired()) { String msg = "The credentials for account [" + account + "] are expired"; throw new ExpiredCredentialsException(msg); } } return account; } protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principals) { String username = getUsername(principals); USERS_LOCK.readLock().lock(); try { return this.users.get(username); } finally { USERS_LOCK.readLock().unlock(); } } }
3)自定义 Realm
由于 Realm 相当于 Datasource 数据源,SecurityManager 进行安全认证需要通过 Realm 获取用户身份数据,所以可以自定义 Realm 获取用户身份的信息;
public class CustomerRealm extends AuthorizingRealm { // 授权 @Override protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principals) { System.out.println("===================="); return null; } // 认证 @Override protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException { String principal = (String) token.getPrincipal(); System.out.println("principal = " + principal); //根据身份信息使用jdbc mybatis查询相关数据库 if ("xiaochen".equalsIgnoreCase(principal)) { // 参数1:返回数据库中的用户名 参数2:返回数据库中的正确密码 参数3:提供当前的 realm 名字,this.getName() SimpleAuthenticationInfo simpleAuthenticationInfo = new SimpleAuthenticationInfo("wangwu", "123", this.getName()); return simpleAuthenticationInfo; } return null; } }
4)使用自定义 Realm 进行认证
public class TestCustomerRealm { public static void main(String[] args) { // 1.创建安全管理器 DefaultSecurityManager defaultSecurityManager = new DefaultSecurityManager(); // 2.给安全管理器设置 realm 【数据库中获取用户名和密码】 defaultSecurityManager.setRealm(new CustomerRealm()); // 3.SecurityUtils 设置安全管理器 SecurityUtils.setSecurityManager(defaultSecurityManager); // 4.获取用户登录的主体 Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject(); AuthenticationToken token = new UsernamePasswordToken("wangwu", "123"); try { subject.login(token); } catch (UnknownAccountException e) { System.out.println("用户名不正确"); e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IncorrectCredentialsException e) { System.out.println("用户密码不正确"); e.printStackTrace(); } } }
5) 使用 MD5 和 Salt
实际应用是将盐和散列后的值存在数据库中,自动realm从数据库取出盐和加密后的值由shiro完成密码校验。
A 自定义 MD5 + salt 的 Realm
public class CustomerMD5Realm extends AuthorizingRealm { /** * 一个主题可以有多个身份,参数是集合 principals;但是只有一个主身份; * @param principals * @return */ @Override protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principals) { // 获取身份信息 String principal = (String) principals.getPrimaryPrincipal(); System.out.println("身份信息 = " + principal); return null; } // 认证 @Override protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException { String principal = (String) token.getPrincipal(); System.out.println("principal = " + principal); //根据身份信息使用jdbc mybatis查询相关数据库 if ("wangwu".equalsIgnoreCase(principal)) { // 参数1:返回数据库中的用户名 参数2:返回数据库中的正确密码 参数3:注册时的随机盐 参数4:提供当前的 realm 名字,this.getName() SimpleAuthenticationInfo simpleAuthenticationInfo = new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(principal, "e4f9bf3e0c58f045e62c23c533fcf633", ByteSource.Util.bytes("X0*7ps"), this.getName()); return simpleAuthenticationInfo; } return null; } }
B 使用 MD5 + Salt 进行认证处理
public class TestCustomerMD5Authenticator { public static void main(String[] args) { // 1. 创建安全管理器 DefaultSecurityManager securityManager = new DefaultSecurityManager(); // 2. 给安全管理器设置 realm 【Realm 需要获取用户认证的数据源信息】 CustomerMD5Realm customerMD5Realm = new CustomerMD5Realm(); // 设置 realm 使用的 hash 凭证匹配器 HashedCredentialsMatcher credentialsMatcher = new HashedCredentialsMatcher(); credentialsMatcher.setHashAlgorithmName("md5"); // 设置使用的 Hash 算法 credentialsMatcher.setHashIterations(1024); // 需要散列多少次 customerMD5Realm.setCredentialsMatcher(credentialsMatcher); securityManager.setRealm(customerMD5Realm); // 3. SecurityUtils 设置安全管理器 SecurityUtils.setSecurityManager(securityManager); // 4. 获取关键对象 Subject 主体 Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject(); // 5. 创建令牌 UsernamePasswordToken token = new UsernamePasswordToken("wangwu", "123"); // 用户认证 try { System.out.println("认证状态: " + subject.isAuthenticated()); subject.login(token); System.out.println("认证状态: " + subject.isAuthenticated()); } catch (UnknownAccountException e) { e.printStackTrace(); System.out.println("认证失败: 用户名不存在~"); } catch (IncorrectCredentialsException e) { e.printStackTrace(); System.out.println("认证失败: 密码错误~"); } } }
注意:深入了解 Shiro 的认证流程,可以 debug 运行程序,查看源代码进行学习深究!



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号